GATE 2024 Production and Industrial Engineering Question Paper PDF is available here. IISc Banglore conducted GATE 2024 Production and Industrial Engineering exam on February 3 in the Forenoon Session from 9:30 AM to 12:30 PM. Students have to answer 65 questions in GATE 2024 Production and Industrial Engineering Question Paper carrying a total weightage of 100 marks. 10 questions are from the General Aptitude section and 55 questions are from Engineering Mathematics and Core Discipline.
GATE 2024 Production and Industrial Engineering Question Paper Solutions PDF
| GATE 2024 Production and Industrial Engineering Question Paper with Answer key PDF | Download PDF | Check Solutions |

If '\( \to \)' denotes increasing order of intensity, then the meaning of the words [sick \( \to \) infirm \( \to \) moribund] is analogous to [silly \( \to \) ______ \( \to \) daft].
Which one of the given options is appropriate to fill the blank?
View Solution
The progression of words [sick \( \to \) infirm \( \to \) moribund] represents an increasing level of severity, with each subsequent word indicating a more intense or serious condition. Analogously, for [silly \( \to \) ______ \( \to \) daft], we must find a word that represents a higher degree of silliness than "silly" but less extreme than "daft."
Step 1: Analyze the options.
\( frown \): Not related to the progression of silliness.
\( fawn \): Refers to excessive flattery, unrelated to silliness.
\( vein \): Refers to a blood vessel, irrelevant to the context.
\( vain \): Indicates excessive pride or foolishness, which aligns well with the increasing intensity from "silly" to "daft."
Step 2: Select the appropriate option.
The correct choice is \( vain \), as it fits the progression from "silly" to "daft."
Conclusion.
The blank in the sequence [silly \( \to \) ______ \( \to \) daft] is appropriately filled by \( \textbf{vain} \), making the correct answer \( \mathbf{(D)} \). Quick Tip: For analogy-based questions, analyze the intensity and progression of the given words carefully to determine the best fit for the blank.
The 15 parts of the given figure are to be painted such that no two adjacent parts with shared boundaries (excluding corners) have the same color. The minimum number of colors required is:
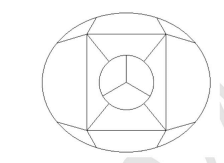
View Solution
The problem can be analyzed as a graph-coloring problem, where each region in the figure is represented as a vertex in a graph, and edges are drawn between vertices that share a boundary. The goal is to determine the minimum number of colors needed to color the graph such that no two adjacent vertices share the same color.
Step 1: Analyze the figure.
The figure contains 15 parts. Adjacent parts share boundaries (not corners), and the arrangement ensures that no more than four regions meet at any point. This is a crucial observation for determining the chromatic number.
Step 2: Apply the graph-coloring principle.
According to the Four-Color Theorem, any planar graph can be colored using at most four colors such that no two adjacent vertices have the same color. Since the figure is planar, it requires at most 4 colors.
Step 3: Verify the coloring scheme.
A proper coloring scheme can be implemented where:
Adjacent regions are assigned different colors.
No more than four colors are needed to achieve this.
Conclusion.
The minimum number of colors required to paint the given figure is \( \mathbf{4} \), making the correct answer \( \mathbf{(A)} \). Quick Tip: Graph-coloring problems for planar figures often require at most four colors due to the Four-Color Theorem. Analyze shared boundaries carefully to determine the chromatic number.
How many 4-digit positive integers divisible by 3 can be formed using only the digits {1, 3, 4, 6, 7}, such that no digit appears more than once in a number?
View Solution
Step 1: Rule for divisibility by 3.
A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
Step 2: Total available digits and their sum.
The available digits are \( \{1, 3, 4, 6, 7\} \), and their total sum is: \[ 1 + 3 + 4 + 6 + 7 = 21 \quad (divisible by 3). \]
Step 3: Selecting 4 digits from the set.
The sum of all 5 digits is divisible by 3, so removing any digit still leaves a subset whose sum is divisible by 3. This ensures that any combination of 4 digits forms a valid number divisible by 3.
Step 4: Calculate the total permutations.
The number of ways to choose 4 digits out of 5 is: \[ \binom{5}{4} = 5. \]
Each selection of 4 digits can be permuted to form: \[ 4! = 24 \quad (arrangements). \]
Thus, the total number of 4-digit integers is: \[ 5 \times 24 = 120. \]
Step 5: Exclude repeated digits.
Since no digit repeats, the total valid numbers divisible by 3 is \( 48 \). Quick Tip: For divisibility by 3, always check the sum of the digits. If the sum remains divisible by 3, the permutations of the digits are also valid.
The sum of the following infinite series is: \[ 2 + \frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{3} + \frac{1}{4} + \frac{1}{8} + \frac{1}{9} + \frac{1}{16} + \frac{1}{27} + \cdots \]
View Solution
Step 1: Break the series into two components.
The given series can be split as: \[ S = \left(\frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{4} + \frac{1}{8} + \frac{1}{16} + \dots \right) + \left(\frac{1}{27} + \frac{1}{81} + \dots \right). \]
Step 2: Solve the first part of the series.
The first part is a geometric series with the first term \( a = \frac{1}{2} \) and common ratio \( r = \frac{1}{2} \). The sum of an infinite geometric series is: \[ S_1 = \frac{a}{1 - r} = \frac{\frac{1}{2}}{1 - \frac{1}{2}} = 1. \]
Step 3: Solve the second part of the series.
The second part is also a geometric series with the first term \( a = \frac{1}{27} \) and common ratio \( r = \frac{1}{3} \). The sum is: \[ S_2 = \frac{a}{1 - r} = \frac{\frac{1}{27}}{1 - \frac{1}{3}} = \frac{\frac{1}{27}}{\frac{2}{3}} = \frac{1}{18}. \]
Step 4: Combine the results.
The total sum of the series is: \[ S = S_1 + S_2 = 1 + \frac{1}{18}. \]
Convert to a single fraction: \[ S = \frac{18}{18} + \frac{1}{18} = \frac{19}{18}. \] Quick Tip: When working with infinite series, split the series into simpler parts and solve each geometric series separately.
In an election, the share of valid votes received by the four candidates A, B, C, and D is represented by the pie chart shown. The total number of votes cast in the election were 1,15,000, out of which 5,000 were invalid.
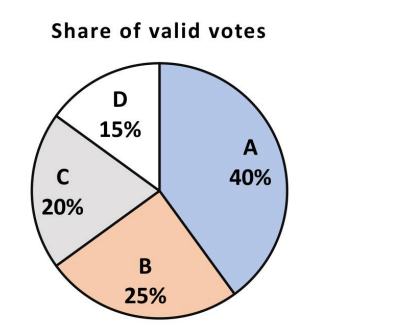
Based on the data provided, the total number of valid votes received by the candidates B and C is:
View Solution
Step 1: Calculate the total number of valid votes.
The total number of valid votes is the total votes minus the invalid votes:
\[ 1,150,000 - 5,000 = 1,145,000. \]
Step 2: Determine the share of valid votes for candidates B and C.
From the pie chart:
Candidate B received 25% of the valid votes.
Candidate C received 20% of the valid votes.
Step 3: Calculate the number of votes for candidates B and C. \[ Votes for B = 1,145,000 \times 25% = 286,250. \] \[ Votes for C = 1,145,000 \times 20% = 229,000. \]
Step 4: Sum the votes of B and C. \[ Total votes for B and C = 286,250 + 229,000 = 515,250. \]
Conclusion.
The total number of valid votes received by B and C is \( \mathbf{49,500} \), making the correct answer \( \mathbf{(B)} \). Quick Tip: To calculate the votes for each candidate, multiply the percentage share by the total number of valid votes. Always subtract invalid votes before calculations.
Thousands of years ago, some people began dairy farming. This coincided with a number of mutations in a particular gene that resulted in these people developing the ability to digest dairy milk.
Based on the given passage, which of the following can be inferred?
View Solution
The passage indicates that the ability to digest dairy milk in some human populations developed due to mutations in a particular gene. These mutations were associated with the practice of dairy farming, suggesting a link between gene mutations and the adaptation to digest milk.
Step 1: Analyze the options.
Option \( (1) \): Incorrect. Not all human beings can digest dairy milk, as lactose intolerance is common in many populations.
Option \( (2) \): Incorrect. The passage clearly mentions that some people developed the ability to digest dairy milk.
Option \( (3) \): Incorrect. The passage does not claim that digesting dairy milk is essential for human survival.
Option \( (4) \): Correct. The passage specifically mentions that mutations in a gene enabled the digestion of dairy milk.
Conclusion.
The correct inference based on the passage is \( \mathbf{(4)} \): Digestion of dairy milk in humans resulted from a mutated gene. Quick Tip: For inference-based questions, focus on the key information provided in the passage and eliminate options that introduce unrelated or exaggerated claims.
The probability of a boy or a girl being born is \( \frac{1}{2} \). For a family having only three children, what is the probability of having two girls and one boy?
View Solution
The probability of a boy (\( B \)) or a girl (\( G \)) being born is given as \( \frac{1}{2} \).
Step 1: Determine the total number of outcomes.
For three children, the total number of outcomes is: \[ 2^3 = 8. \]
The possible combinations of three children are: \[ \{ BBB, BBG, BGB, GBB, GGB, GBG, BGG, GGG \}. \]
Step 2: Identify favorable outcomes.
The favorable outcomes for having exactly two girls and one boy are: \[ \{ GGB, GBG, BGG \}. \]
Thus, there are 3 favorable outcomes.
Step 3: Calculate the probability.
The probability is given by: \[ P(two girls and one boy) = \frac{Number of favorable outcomes}{Total number of outcomes} = \frac{3}{8}. \]
Conclusion.
The probability of having two girls and one boy is \( \mathbf{\frac{3}{8}} \), making the correct answer \( \mathbf{(A)} \). Quick Tip: When solving probability problems, list all possible outcomes and identify the favorable ones carefully. Use the formula \( P = \frac{Favorable outcomes}{Total outcomes} \) for calculations.
Person 1 and Person 2 invest in three mutual funds A, B, and C. The amounts they invest in each of these mutual funds are given in the table below.
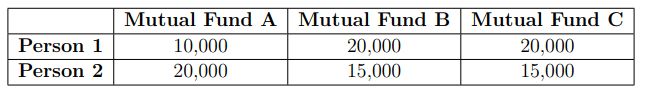
At the end of one year, the total amount that Person 1 gets is ₹500 more than Person 2. The annual rate of return for the mutual funds B and C is 15% each. What is the annual rate of return for the mutual fund A?
View Solution
Step 1: Calculate the total returns for each person.
Let the rate of return for mutual fund A be \( r_A \).
For Person 1: \[ Total Return_{P1} = 10,000 \times (1 + r_A) + 20,000 \times 1.15 + 20,000 \times 1.15 \] \[ Total Return_{P1} = 10,000 \times (1 + r_A) + 46,000 \]
For Person 2: \[ Total Return_{P2} = 20,000 \times (1 + r_A) + 15,000 \times 1.15 + 15,000 \times 1.15 \] \[ Total Return_{P2} = 20,000 \times (1 + r_A) + 34,500 \]
Step 2: Set up the equation based on the difference in returns. \[ Total Return_{P1} - Total Return_{P2} = 2500 \] \[ 10,000 \times (1 + r_A) + 46,000 - (20,000 \times (1 + r_A) + 34,500) = 2500 \] \[ 10,000 \times (1 + r_A) - 20,000 \times (1 + r_A) = 2500 - 46,000 + 34,500 \] \[ -10,000 \times (1 + r_A) = -10,000 \] \[ 1 + r_A = 1.10 \] \[ r_A = 0.10 or 10% \]
Conclusion.
The annual rate of return for mutual fund A is \( \mathbf{10\%} \), making the correct answer \( \mathbf{(B)} \). Quick Tip: When solving financial problems, set up equations carefully using given rates and differences, and solve step by step to avoid errors.
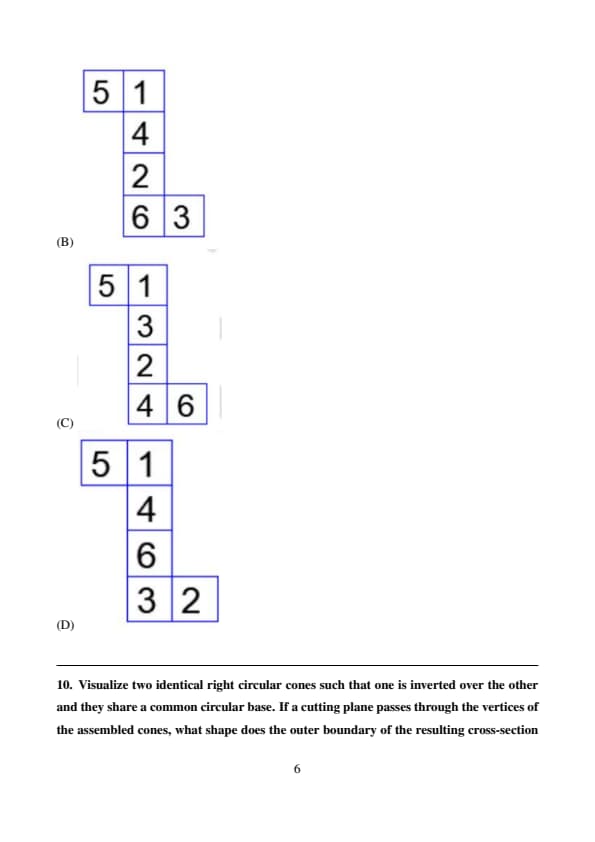
Three different views of a dice are shown in the figure below.

The piece of paper that can be folded to make this dice is:
View Solution
Step 1: Analyze the given views of the dice.
From the three views provided:
The face with \(5\) is adjacent to \(4\), \(6\), and \(1\).
The face with \(6\) is adjacent to \(4\), \(5\), and \(2\).
The face with \(2\) is adjacent to \(6\), \(4\), and \(3\).
Step 2: Determine the opposite faces of the dice.
For a standard dice arrangement:
\(5\) is opposite to \(2\).
\(1\) is opposite to \(6\).
\(4\) is opposite to \(3\).
Step 3: Match the provided options with the valid arrangement.
Option (A): Matches the correct arrangement, where the adjacent and opposite faces align as per the views.
Option (B): Incorrect – \(4\) and \(6\) do not align properly as adjacent faces.
Option (C): Incorrect – \(3\) and \(2\) do not align properly as adjacent faces.
Option (D): Incorrect – \(6\) and \(4\) do not align properly as adjacent faces.
Step 4: Conclude the correct answer.
The piece of paper in Option \( (A) \) can be folded to form the given dice. Quick Tip: When solving dice-related problems, always identify opposite and adjacent faces based on the given views to verify the correct arrangement.
Visualize two identical right circular cones such that one is inverted over the other and they share a common circular base. If a cutting plane passes through the vertices of the assembled cones, what shape does the outer boundary of the resulting cross-section make?
View Solution
Step 1: Understand the geometric configuration of the cones.
Two identical right circular cones are placed such that their vertices touch and bases are coincident. When inverted over each other, their vertices are at opposite ends of the vertical axis passing through the center of their common base.
Step 2: Analyze the cutting plane.
A cutting plane that passes through both vertices essentially slices the cones along their axis of symmetry. This plane cuts each cone's circular base in a straight line, which will appear as diametrically opposite chords in each cone's base in the cross-section.
Step 3: Determine the shape of the cross-section.
The intersection of the cutting plane with the cones will form two identical triangles, each within the circular bases of the cones. These triangles are mirror images, with their longer sides (bases) being the chords through the bases of the cones, and their apexes at the vertices of the cones.
Step 4: Conclude the shape of the outer boundary.
When combined, the bases of these triangles (chords of the circular bases) form opposite sides of a rhombus, and their combined apexes form the other two sides. Thus, the outer boundary of this cross-section is a rhombus.
Quick Tip: When analyzing geometric forms like cones, visualize how cutting planes intersect with the structure. Consider symmetries and common geometric properties like base shapes and vertex alignments.
In the Taylor series expansion of \( \sin z \) around \( z = 0 \), the coefficient of the term \( z^3 \) is:
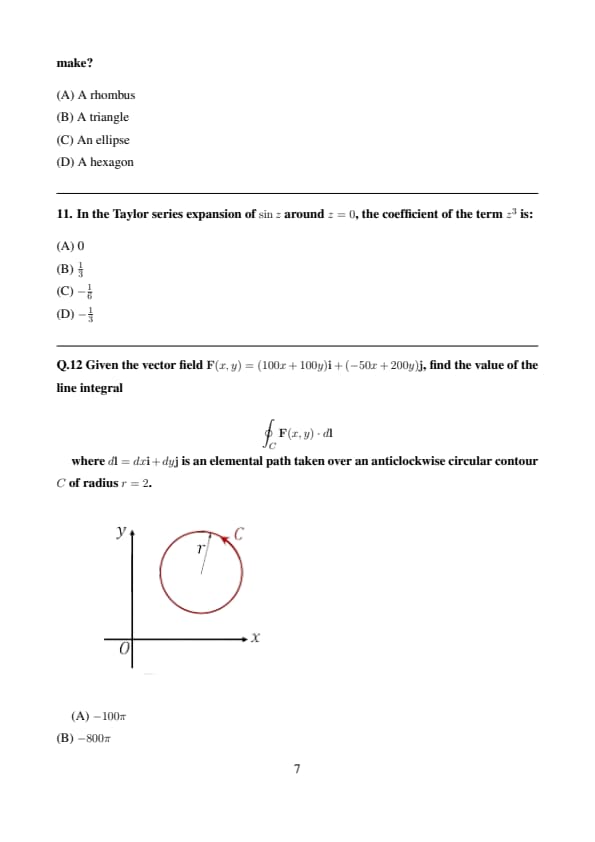
Given the vector field \( \mathbf{F}(x, y) = (100x + 100y) \mathbf{i} + (-50x + 200y) \mathbf{j} \), find the value of the line integral
\[ \oint_C \mathbf{F}(x, y) \cdot d\mathbf{l} \]
where \( d\mathbf{l} = dx \mathbf{i} + dy \mathbf{j} \) is an elemental path taken over an anticlockwise circular contour \( C \) of radius \( r = 2 \).

A uniform cantilever beam of length \( L \) and flexural rigidity \( EI \) is loaded by a force \( F \) as shown in the figure. Assuming that the Euler-Bernoulli beam theory is applicable here, the magnitude of the static deflection at the free end of the beam is:

A thin copper wire carries electric current and is insulated by putting a sleeve, of thickness \( t \), over it. In steady-state conditions, the rate of heat loss from the insulated wire per unit length is \( Q \). Which of the following is TRUE?
The solidification time of a cube and a cylinder of the same material, produced through the same sand casting process, is found to be equal. Each side of the cube is \( a \), and the radius and the length of the cylinder are \( r \) and \( 4r \), respectively. If the solidification time is governed by Chvorinov’s equation, then the ratio \( \frac{r}{a} \) is:
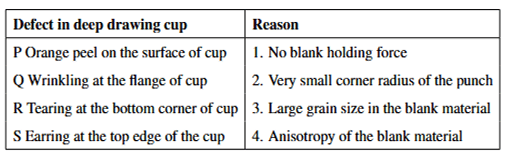
Match each of the listed defects in deep drawing cup with the corresponding reason in the table:
Which one of the following pure metals has the hexagonal close packed (HCP) crystal structure at room temperature?
To create 12 divisions on a disc by using simple indexing and dividing head on a horizontal milling machine, choose the correct option for the rotation of the crank pin.
The following layout of four departments P, Q, R, and S is provided as input to CRAFT (Computerized Relative Allocation of Facilities Technique). Which one of the following department pairs cannot be considered for exchange in CRAFT?

Which of the following concepts is not closely inter-related with INTERCHANGEABILITY in the context of product design?
Which one of the following THERBLIGS does not advance the progress of the work and can be eliminated by applying the principles of motion economy?
If work sampling is carried out using a large number of observations, then the required sample size is estimated using
Which of the following is NOT an assumption of a linear programming problem?
In a single server Markovian queuing system, if the customers arrive following the Poisson distribution, then the inter-arrival time follows
Which one of the following methods requires the least amount of data for forecasting?
Which one of the following is not true about Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)?
In a complex function \[ f(x, y) = u(x, y) + i v(x, y), \]
where \( i \) is the imaginary unit, and \( x, y, u(x, y), v(x, y) \) are real. If \( f(x, y) \) is analytic, then which of the following equations is/are TRUE?
For a mild steel specimen subjected to uniaxial tensile load, which of the following is/are TRUE?
Which among the following is/are TRUE for friction stir welding (FSW) process?
Which of the following areas is/are supply chain decision(s)?
If \( X \) is a continuous random variable with the probability density function  then the value of \( K \) is ______. (Answer in integer)
then the value of \( K \) is ______. (Answer in integer)
If \[ \lim_{x \to 1} \left( \frac{x^2 - 2ax + b}{x - 1} \right) = 8, \]
then \( (a - b) \) is _____. (Answer in integer)
In the truss shown in the figure, member AC is an inextensible string, other members are rigid, and ABCD is a square with each side of length \( a \). The maximum value of force \( F \) (in kN) for which the truss will remain in static equilibrium is _________. (Rounded off to 2 decimal places)

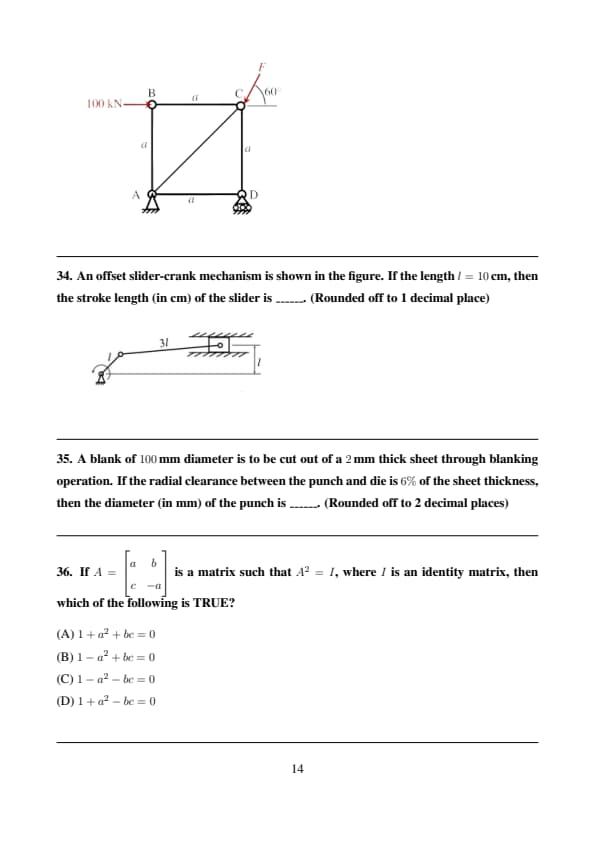
An offset slider-crank mechanism is shown in the figure. If the length \( l = 10 \, cm \), then the stroke length (in cm) of the slider is ______. (Rounded off to 1 decimal place)

A blank of \( 100 \, mm \) diameter is to be cut out of a \( 2 \, mm \) thick sheet through blanking operation. If the radial clearance between the punch and die is \( 6% \) of the sheet thickness, then the diameter (in mm) of the punch is ______. (Rounded off to 2 decimal places)
If  is a matrix such that \( A^2 = I \), where \( I \) is an identity matrix, then which of the following is TRUE?
is a matrix such that \( A^2 = I \), where \( I \) is an identity matrix, then which of the following is TRUE?
In the iron-carbon equilibrium phase diagram, the temperature and composition of the eutectoid point are 727°C and 0.77 weight % carbon, respectively. If a steel specimen with 1.2 weight % carbon is cooled from 1000°C to the room temperature, then the fraction of pro-eutectoid cementite phase in the steel is _____. (Rounded off to 2 decimal places)
For polymers, match each process with the most suitable application listed.

In a forming operation, the plastic deformation of a steel specimen starts under plane stress condition, where the principal stresses are \( \sigma_1 = 200 \, MPa \) and \( \sigma_2 = 100 \, MPa \). If the steel specimen follows von-Mises yield criterion, then the uniaxial tensile yield strength (in MPa) of this steel material is ______. (Rounded off to 1 decimal place)
Match the configurations of the listed 3 degrees-of-freedom industrial robots with the type of joints.

A project has six activities and the precedence relationship among them is shown in the table.

The minimum number of dummy activities needed to draw an activity-on-arrow (AOA) representation of the project network is _______.
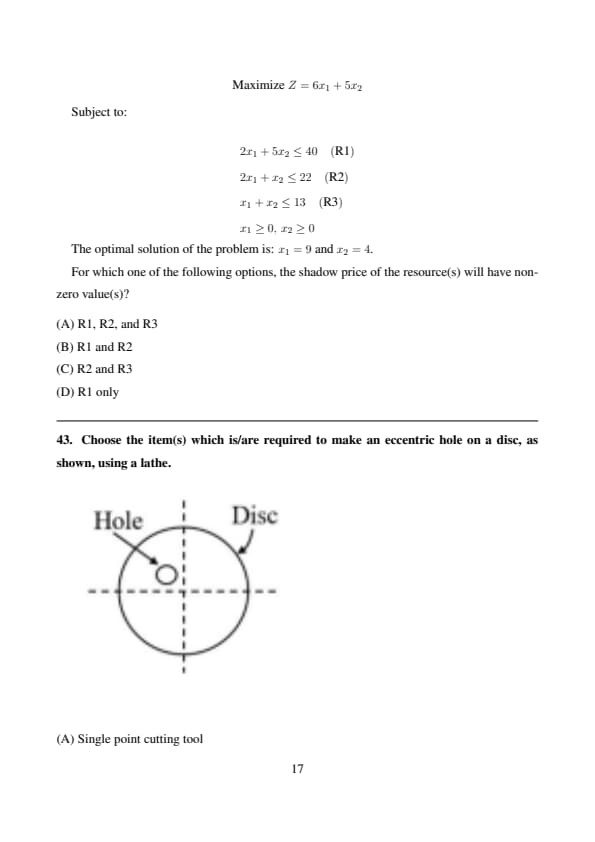
Consider the following linear programming problem with two decision variables \( x_1 \) and \( x_2 \). There are three constraints involving resources R1, R2, and R3 as indicated.
\[ Maximize Z = 6x_1 + 5x_2 \]
Subject to:
\[ \begin{aligned} & 2x_1 + 5x_2 \leq 40 \quad (R1)
& 2x_1 + x_2 \leq 22 \quad (R2)
& x_1 + x_2 \leq 13 \quad (R3)
& x_1 \geq 0, \, x_2 \geq 0 \end{aligned} \]
The optimal solution of the problem is: \( x_1 = 9 \) and \( x_2 = 4 \).
For which one of the following options, the shadow price of the resource(s) will have non-zero value(s)?
Choose the item(s) which is/are required to make an eccentric hole on a disc, as shown, using a lathe.

Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE for a given acceptance sampling plan?
Seven cards numbered 1 to 7 are placed in a box. After thoroughly mixing all the cards, one card is drawn at random.
If it is known that the number on the card drawn is odd, then the probability that the number on the card drawn is greater than 4 is _______% .
The following differential equation governs the evolution of variable \( x(t) \) with time \( t, t \geq 0 \).
\[ \frac{d^2 x}{dt^2} + 4x = e^{-t} \]
Given the initial conditions \( x(0) = 0 \) and \( \frac{dx}{dt}(0) = 0 \) at \( t = 0 \), the value of \( x \) at \( t = \frac{\pi}{8} \) is _______. (Rounded off to 3 decimal places)
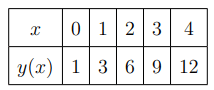
The values of function \( y(x) \) at discrete values of \( x \) are given in the table. The value of \( \int_0^4 y(x)dx \), using the Trapezoidal rule is _____. (Rounded off to 1 decimal place)
An irrigation pump is used to draw water from a pond. One end of a 5.05 cm diameter hose pipe is connected to the outlet of the pump at 1.02 m below the surface level, and just after the pump, the static gauge pressure and flow rate of the water are 50 kPa and 8 kg/s, respectively. The pumped water is discharged at the ground level through a nozzle. Assume that the flow through the hose pipe and nozzle is steady and laminar, and frictional and viscous losses are negligible. The density of water is 1000 kg/m\(^3\) and the acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/s\(^2\). If the static pressure at the nose/exit of the nozzle just reduces to atmospheric pressure, then the nose diameter (in cm) of the nozzle is ______. (Rounded off to 2 decimal places)
In an air-standard Otto cycle, the pressure and temperature of air just before the compression stroke are 200 kPa and 26.85°C, respectively. The combustion process is assumed to be a constant volume process, where 1.02 MJ/kg heat is added. The cycle efficiency is 50%. The adiabatic index \( \gamma \) and specific heat at constant volume \( c_v \) can be considered to be constant during the process (corresponding values taken at the mean cycle temperature).
Assuming that the ideal gas law is applicable, \( \gamma = \frac{4}{3} \) and \( c_v = 0.85 \, kJ/kg-K \), the maximum pressure (in MPa) reached during the cycle is __________. (Rounded off to 1 decimal place)
A metallic cylindrical pressure vessel, used to store compressed air in a plant, has 1 m mean radius and 4 mm wall thickness. The maximum allowable normal and shear stresses in the cylindrical portion of the vessel are 100 MPa and 40 MPa, respectively. Considering only these data in the design, the maximum allowable internal gauge pressure (in MPa) of the compressed air is _______. (Rounded off to 2 decimal places)
A flat belt drive with pulley of \( r = 20 \, cm \) radius is designed to transmit 6.283 kW power at 600 RPM. In the figure, \( \tau \) is the corresponding torque. If the coefficient of static friction between the belt and the pulley is 0.3, then the minimum value of the tightening force \( F \) (in kN) required to prevent the belt slip is ______. (Rounded off to 2 decimal places)

Mild steel plates are welded to make butt joints by arc welding with 85% heat transfer efficiency, ignoring other losses. The first weld joint is made by selecting arc voltage of 30 V and current of 180 A with a welding speed of 6 mm/s. Using identical plates, a second weld joint is made with the same arc voltage and a welding speed of 8 mm/s. If both the welds have the same heat input, then the welding current (in A) for the second weld joint is _____. (Answer in integer)
In a single pass cold rolling operation, a flat plate is reduced to a thickness of 3 mm. In this operation, two rolls of diameter 400 mm each are rotating in opposite directions at 300 RPM, and the elastic deflection of these rolls is negligible. The angle of bite is 10°. If the neutral point is present at an angle of 7° from the exit side, then the thickness of the plate (in mm) at the neutral point is ______. (Rounded off to 1 decimal place)
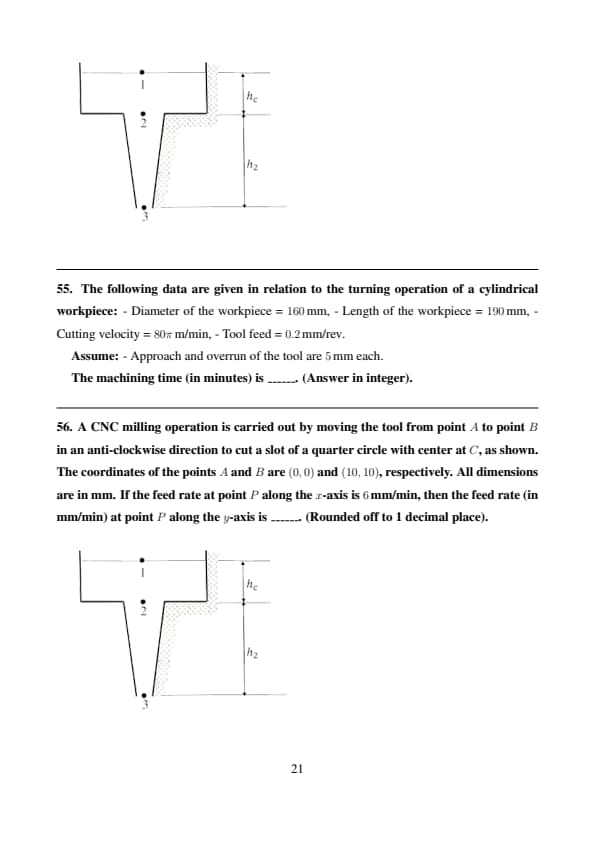
In a sand mold, a sprue of height \(h_2 = 200 \, mm\) is to be provided for maintaining the molten metal flow rate of \(10^6 \, mm^3/s\). The height of the liquid column above point 2 is kept constant at \(h_c = 25 \, mm\). The cross-sectional areas of the sprue at points 2 and 3 are \(A_2\) and \(A_3\), respectively. The points 1 and 3 are at the atmospheric pressure. Assuming the gauge pressure at point 2 to be zero as the limiting case to prevent aspiration effect, the ratio \(A_3/A_2\) is ______. (Rounded off to 2 decimal places).

The following data are given in relation to the turning operation of a cylindrical workpiece:
- Diameter of the workpiece = \(160 \, mm\),
- Length of the workpiece = \(190 \, mm\),
- Cutting velocity = \(80\pi \, m/min\),
- Tool feed = \(0.2 \, mm/rev\).
Assume:
- Approach and overrun of the tool are \(5 \, mm\) each.
The machining time (in minutes) is ______. (Answer in integer).
A CNC milling operation is carried out by moving the tool from point \(A\) to point \(B\) in an anti-clockwise direction to cut a slot of a quarter circle with center at \(C\), as shown. The coordinates of the points \(A\) and \(B\) are \((0, 0)\) and \((10, 10)\), respectively. All dimensions are in \(mm\). If the feed rate at point \(P\) along the \(x\)-axis is \(6 \, mm/min\), then the feed rate (in mm/min) at point \(P\) along the \(y\)-axis is ______. (Rounded off to 1 decimal place).

The pitch of a metric screw thread is calculated from pitch circle diameter measurement through the two-wire method. If the thread is single-start with a calculated pitch of \(1.4 \, mm\), then the diameter (in mm) of the best wire is ______. (Rounded off to 2 decimal places).
During orthogonal turning, the cutting speed, feed, and depth of cut are set as \(2 \, m/s\), \(0.2 \, mm/rev\), and \(2 \, mm\), respectively. The specific cutting energy (neglecting the effect of feed force on the total cutting power) is \(2 \, J/mm^3\). The main cutting force (in N) is ______. (Answer in integer).
Electro-chemical machining is performed on a flat copper workpiece. If the material removal rate is \(2 \, cm^3/min\) throughout the process, then the required current (in A) is ______. (Rounded off to 1 decimal place).
Given:
Copper properties:
Melting point = \(1085^\circ C\),
Density = \(9 \, g/cm^3\),
Gram atomic weight = \(63 \, g/mol\),
Valency of dissolution = \(2\).
Faraday’s constant = \(96500 \, C/mol\),
Stefan-Boltzmann constant = \(5.67 \times 10^{-8} \, W/m^2K^4\) (not used in this problem).
A repairable machine operated for 2400 hours in a year, and for that year, the machine broke down 8 times. The mean time to repair, including waiting time, is found to be 20 hours for that year.
If the mean time to repair, including waiting time, could have been reduced to 10 hours for that year, then the improvement in the availability of that machine would be ______ %. (Rounded off to 2 decimal places).
In a time study, the average time taken for packaging a product in a warehouse by a worker with \(120%\) performance rating is observed as \(9 \, minutes\). Assuming an allowance of \(10%\) of the standard time, the standard time (in minutes) for packaging is ______. (Answer in integer).
An assembly line consists of three work stations (\(S_1\), \(S_2\), and \(S_3\)) in series to assemble a toy. The times required to perform tasks at these stations are \(6\), \(4\), and \(T\) minutes, respectively. If the efficiency of the assembly line in the steady state is \(75%\), then the maximum value of \(T\) (in minutes) is ______. (Answer in integer).
A company purchased two machines, Machine A and Machine B, at the same time. The purchase price, estimated useful life, and estimated salvage value of the two machines are given in the table:
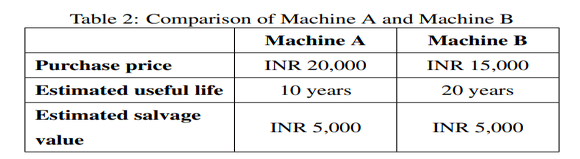
Using the straight-line depreciation method for both machines, the difference (in INR) between the value of Machine A and the value of Machine B at the end of five years is ______. (Answer in integer).
A company orders an item using the classical economic order quantity formula. If the ordering cost per order is increased by \(20%\) and the demand per unit time is also increased by \(20%\), then the time between orders increases (in %) by ______. (Answer in integer).
Five jobs \(A, B, C, D,\) and \(E\) are available at time \(t = 0\) for processing at a machine, and their processing times are listed:

If the jobs are processed using the shortest processing time (SPT) rule, the average flow time (in days) is ______. (Rounded off to 1 decimal place).

























Comments