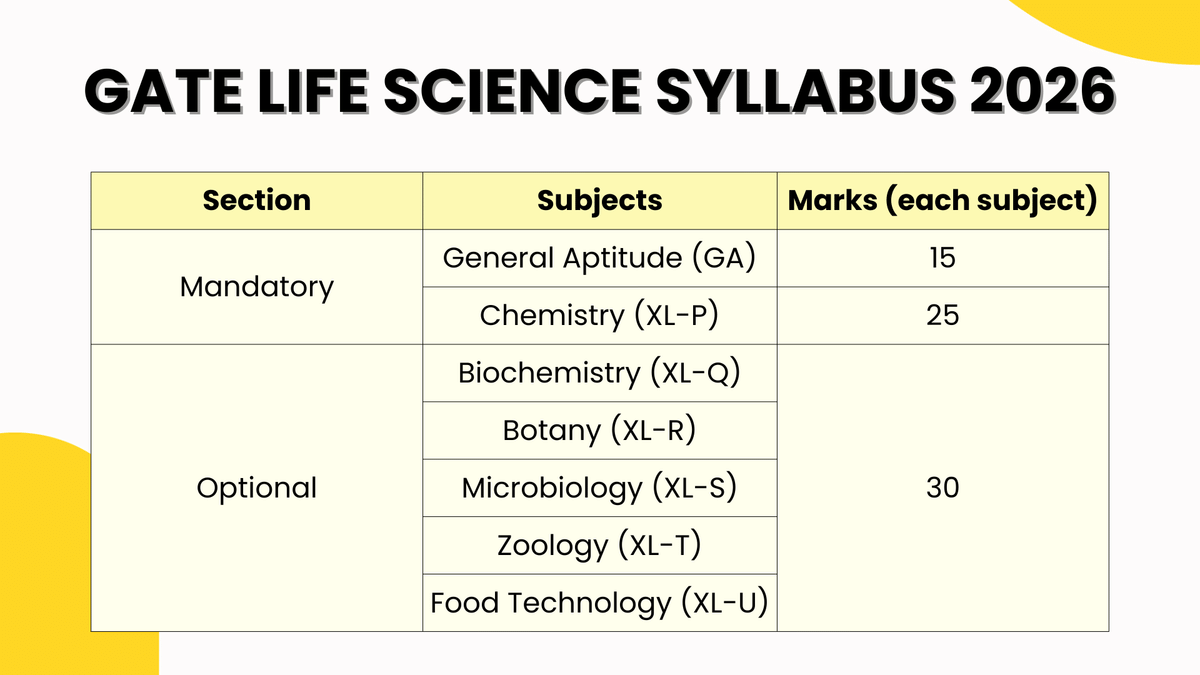
The IIT Guwahati has released the official GATE Life Science Syllabus 2026 on the official website. The GATE Life Science Syllabus 2026 is divided into 3 sections:
- Section 1: General Aptitude
- Section 2: Chemistry (XL-P)
- Section 3: Life Science subjects
The General Aptitude and Chemistry sections are mandatory, while other subjects, Biochemistry (XL-Q), Botany (XL-R), Microbiology (XL-S), Zoology (XL-T), and Food Technology (XL-U) are optional subjects; the candidates can choose any 2 as per their preference
The GATE Life Sciences 2026 paper will have 65 questions for 100 marks divided into General Aptitude (15 marks), Chemistry (25 marks), and two optional sections (30 marks each).

Also Read
Key Summary
- The GATE Life Sciences 2026 syllabus includes 3 main sections: General Aptitude (GA), Chemistry (XL-P), and Life Sciences Core Subjects.
- GA includes topics like Logical Reasoning, Numerical Ability, and Verbal Ability.
- Chemistry (XL-P) covers topics such as Physical Chemistry, Organic Chemistry, and Inorganic Chemistry, accounting for 25% of the weightage.
- Life Sciences Core Subjects include Biochemistry (XL-Q), Botany (XL-R), Microbiology (XL-S), Zoology (XL-T), and Food Technology (XL-U).
- Each subject contributes around 30 marks, with topics such as metabolism, molecular biology, plant physiology, microbial genetics, animal physiology, and food processing.
- A total of 100 questions, with GA contributing 15 marks, Chemistry 25 marks, and 60 marks from the chosen two core subjects.
- According to the analysis from the previous year, GA is moderate, with ~85% accuracy. Chemistry requires conceptual clarity for high scores, and Life Sciences Core Subjects carry a higher weightage, with recurring questions in Biochemistry, Microbiology, and Botany/Zoology.
- What are the subjects in GATE life science?
1.1 GATE Life Science Syllabus for General Aptitude (GA)
1.2 GATE Life Science Syllabus for Chemistry (Section P)
1.3 GATE Life Science Syllabus for Biochemistry (Section Q)
1.4 GATE Life Science Syllabus for Botany (Section R)
1.5 GATE Life Science Syllabus for Microbiology (Section S)
1.6 GATE Life Science Syllabus for Zoology (Section T)
1.7 GATE Life Science Syllabus for Food Technology (Section U)
- GATE Life Science Syllabus Section-wise Weightage 2026
- GATE Life Science Syllabus Books
3.1 GATE Life Science Syllabus Chemistry (XL-P) Books
3.2 GATE Life Science Syllabus Biochemistry (XL-Q) Books
3.3 GATE Life Science Syllabus Botany (XL-R) Books
3.4 GATE Life Science Syllabus Microbiology (XL-S) Books
3.5 GATE Life Science Syllabus Zoology (XL-T) Books
3.6 GATE Life Science Syllabus Food Technology (XL-U) Books
-
- GATE Life Science Chemistry Important Questions 2026
- GATE Life Science Question Paper
- GATE Life Science Syllabus FAQs
What are the subjects in GATE life science?
The GATE Life Science Syllabus has 3 sections: General Aptitude with 15 marks, Chemistry with 25 marks, and Optional Sections (Choose only 2 sections) with 30 marks each, making it a total of 100 marks.
GATE Life Science Syllabus for General Aptitude (GA)
The GATE General Aptitude section, common to all the papers of GATE, tests the candidate’s ability to think and word power. It is divided into two main parts:
- Verbal Ability: Includes grammar, word studies, fill-in-the-blank sentences, and verbal reasoning.
- Numerical Ability: Embedded with data and number interpretation, rough enumeration, and quantitative reasoning.
GATE Life Science Syllabus for Chemistry (Section P)
GATE Chemistry is one of the sections that is compulsory for the GATE Life Sciences exam. Important topics in this section include:
- Atomic Structure and Periodicity: Electron quantum numbers, electron configuration, and periodicity trends of elements.
- Bonding and Molecular Structure: Bonding theories include the covalent bond theory, the sigma and pi bond concept, the overlap of atomic orbitals, the electron-pair sharing concept, the dipole moment, the valency bond theory, the molecular orbital theory, the valence bond theory, hybridization, the hybrid orbital theory, and the spectroscopic method.
- Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics first and second, thermochemistry, and entropy.
- Equilibrium: Subtopic 2 – Phase rule, equilibrium constants, and Le Chatelier’s principle.
- Electrochemistry: Redox, conductance, and cell potentials.
- Reaction Kinetics: Kinetic control and mechanisms: rate laws and activation energy.
- Organic Chemistry: Strategies of reaction, types of functional groups, and stereochemistry.
GATE Life Science Syllabus for Biochemistry (Section Q)
Biochemistry of GATE Life Science Syllabus is one of the optional sections for GATE Life Sciences, focusing on molecular biology and biomolecules:
- Biomolecules: Organization and roles of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins as well as nucleic acid and acids.
- Enzymes: Instruction: Basic kinetic and regulatory principles; fundamental properties and methods of enzyme function.
- Metabolic Pathways: Fermentation, TCA cycle, light-dependent reactions of the chloroplast, and anabolic pathways.
- Molecular Biology: Total, DNA replication, the transcription process, the process of translation, and control of gene expression.
- Cell Signaling: Signalling pathways, receptors, and second messengers.
- Analytical Techniques: Chromatography Separation by moving through different media, electrophoresis is the relocation of charges, and spectroscopy is the separation of vibrations.
GATE Life Science Syllabus for Botany (Section R)
Botany covers plant biology, physiology, and genetics:
- Plant Systematics: Taxonomic, categorization, and evolutionary relationships.
- Plant Anatomy: Elements that refer to the structure of roots, stems, and leaves.
- Plant Physiology: Stomatal control of gas exchange, photosynthesis and respiration, plant growth hormones, and nitrogen metabolism.
- Genetics and Breeding: The principles of genetics, selective breeding, plant breeding, hereditary variation, and the technologies of plant genetic mapping, plant breeding, and genetic manipulation.
- Plant Pathology: Diseases, pathogens, and biotic stress.
- Ecology: Issues; Biology, Endangered species, Habitat, and wildlife.
GATE Life Science Syllabus for Microbiology (Section S)
Microbiology focuses on microorganisms and their applications:
- Microbial Taxonomy: Bacteria, viruses, fungi, and algae.
- Microbial Physiology: Fatty structure of microbes and how microbes work.
- Microbial Genetics: Transduction and transposition and conjugation, plasmids, and bacteriophages.
- Immunology: Innate response, specificity and sensitivity, and vaccinations.
- Industrial Microbiology: Bioproducts, fermentation, and microbial biotechnology.
- Environmental Microbiology: Bioremediation and wastewater treatment.
GATE Life Science Syllabus for Zoology (Section T)
Zoology focuses on animal biology, genetics, and physiology:
- Animal Diversity and Evolution: Classification, evolutionary relatedness, and phylogenetics.
- Comparative Anatomy and Physiology: Roles and organs in vertebrates and invertebrates.
- Developmental Biology: Spermatogenesis, oogenesis, and embryogenesis as well as organogenesis.
- Behavioral Ecology: Upgrade, survival, and habits of animals.
- Genetics and Evolutionary Biology: Genetics of man & domestic animals with special reference to domain and speciation.
GATE Life Science Syllabus for Food Technology (Section U)
Food Technology emphasizes food processing, safety, and quality:
- Food Chemistry and Nutrition: Macronutrients, micronutrients, and nutraceuticals.
- Food Microbiology: Spoilage microorganisms, foodborne pathogens, and probiotics.
- Food Processing Techniques: Thermal processing, drying, and packaging.
- Quality Control: Standards, quality assessment, and HACCP.
- Food Engineering: Mass transfer, heat transfer, and equipment in food processing.
GATE Life Science Syllabus Section-wise Weightage 2026
GATE Life Science Syllabus has 3 sections, with General Aptitude (15%), Chemistry (25%), making a total of compulsory 40% weightage of core subjects. The Other five subjects are Biochemistry, Botany, Microbiology, Zoology, and Food Technology, each carries 15% and candidates choose two subjects as per their preference.
| Section | Important Topics | Types of Questions | Approximate Weightage |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Aptitude (GA) | Verbal Ability, Numerical Ability, Reasoning, Data Interpretation | 1-mark MCQs and 2-mark MCQs | 15% |
| Chemistry (Section P) | Atomic Structure, Bonding, Thermodynamics, Electrochemistry, Organic Chemistry, Reaction Mechanisms, Stereochemistry | 1-mark MCQs, 2-mark MCQs, NATs | 25% |
| Biochemistry (Section Q) | Biomolecules, Enzymes, Metabolism, Molecular Biology, Cell Signaling, Analytical Techniques | 1-mark MCQs, 2-mark MCQs, NATs | 15% |
| Botany (Section R) | Plant Physiology, Plant Anatomy, Genetics and Breeding, Ecology, Plant Systematics | 1-mark MCQs, 2-mark MCQs, NATs | 15% |
| Microbiology (Section S) | Microbial Taxonomy, Physiology, Microbial Genetics, Immunology, Industrial and Environmental Microbiology | 1-mark MCQs, 2-mark MCQs, NATs | 15% |
| Zoology (Section T) | Animal Physiology, Comparative Anatomy, Developmental Biology, Genetics, Evolutionary Biology | 1-mark MCQs, 2-mark MCQs, NATs | 15% |
| Food Technology (Section U) | Food Chemistry, Food Microbiology, Processing, Quality Control, Food Engineering | 1-mark MCQs, 2-mark MCQs, NATs | 15% |
Also Read
GATE Life Science Syllabus Books
Here's a table with some of the most recommended books for GATE Life Sciences preparation, including key topics covered and approximate prices.
GATE Life Science Syllabus Chemistry (XL-P) Books
| Book Title | Author | Why Recommended / Data Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Chemistry | Ira N. Levine | Strong for numerical problem-solving; ~30–35% of XL-P questions are from physical chemistry. |
| Organic Chemistry | Clayden, Greeves, Warren & Wothers | Excellent for mechanisms and reaction pathways; organic contributes ~25–30% weightage in XL-P. |
| Principles of Inorganic Chemistry | Puri, Sharma & Kalia | Covers coordination chemistry & periodic trends; inorganic topics carry ~20% of XL-P marks. |

GATE Life Science Syllabus Biochemistry (XL-Q) Books
In the GATE Life Science Biochemistry, the Biochemistry by Voet & Voet and Principles & Techniques of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology by Wilson & Walker are considered the best because of their Comprehensive biomolecular coverage; ~40% of XL-Q questions and analytical methods like PCR, chromatography, spectroscopy
| Book Title | Author | Why Recommended / Data Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Biochemistry | Voet & Voet | Comprehensive biomolecular coverage; ~40% of XL-Q questions focus on metabolism & enzyme kinetics. |
| Principles & Techniques of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology | Wilson & Walker | Best for analytical methods like PCR, chromatography, spectroscopy — high recurrence in past PYQs. |

GATE Life Science Syllabus Botany (XL-R) Books
A Textbook of Botany, Vol-III by S.N. Pandey for Botany is good for plant anatomy and taxonomy, which covers 25% of Life Sciences marks.
Plant Physiology by Salisbury & Ross and Fundamentals of Ecology by Eugene Odum also cover 30% and 20% marks respectively of Life Sciences total marks.
| Book Title | Author | Why Recommended / Data Insights |
|---|---|---|
| A Textbook of Botany, Vol-III | S.N. Pandey | Good for plant anatomy & taxonomy; ~25% of XL-R marks from plant systematics & morphology. |
| Plant Physiology | Salisbury & Ross | High for photosynthesis, stress physiology; ~30% of Botany questions from physiology topics. |
| Fundamentals of Ecology | Eugene Odum | Ecology contributes ~20% of XL-R marks and overlaps with GA-style reasoning. |

GATE Life Science Syllabus Microbiology (XL-S) Books
To prepare well for Microbiology, there are 2 books named Microbiology by Prescott and Microbiology by Pelczar, Chan & Krieg, which cover the detailed microbial physiology & diversity by covering 35% of XL-S marks
| Book Title | Author | Why Recommended / Data Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Microbiology | Prescott | Detailed microbial physiology & diversity; ~35% of XL-S marks from cell structure & metabolism. |
| Microbiology | Pelczar, Chan & Krieg | Concise coverage for classification, culture methods; complements Prescott for short notes. |

GATE Life Science Syllabus Zoology (XL-T) Books
For GATE Life Science Zoology 2026, “Animal Biology (Instant Notes)’ by Jurd is ideal for quick revision, specifically in cell biology, genetics, and physiology, which together hold for about 40% of the section’s marks.
"Vertebrates: Comparative Anatomy, Function, and Evolution" by Kardong is important for mastering developmental biology and evolution topics that frequently appear and contribute around 20–25% of XL-T questions.
| Book Title | Author | Why Recommended / Data Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Animal Biology (Instant Notes) | Jurd | Great for quick revisions; cell biology, genetics & physiology together make ~40% of XL-T marks. |
| Vertebrates: Comparative Anatomy, Function, and Evolution | Kardong | Strong for developmental biology & evolution — common in 20–25% of XL-T questions. |

GATE Life Science Syllabus Food Technology (XL-U) Books
For GATE Life Science Food Technology (XL-U) 2026, "Processing and Food Engineering" by Garg & Chandra is important for understanding engineering principles with food processing and preservation contributing around 35% of the total marks.
"Fundamentals of Food Engineering" by D.G. Rao is excellent for studying operations, equipment, and numerical problem-solving.
"Food Chemistry" by Meyer & Fenema covers chemical and nutritional aspects, which holds around 25% of questions.
| Book Title | Author | Why Recommended / Data Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Processing and Food Engineering | Garg & Chandra | Focuses on engineering principles; food processing & preservation make ~35% of XL-U marks. |
| Fundamentals of Food Engineering | D.G. Rao | Clear explanation of operations & equipment; key for numerical problems. |
| Food Chemistry | Meyer & Fenema | Covers chemical & nutritional aspects; ~25% of XL-U questions from this area. |

GATE Life Science Syllabus Important Questions 2026
The GATE Life Science Syllabus 2026 shows that the General Aptitude consistently holds 15% of marks, with easy-scoring topics like numerical reasoning and data interpretation.
- Biochemistry (XL-Q) and Zoology (XL-T) are expected to dominate with ~25% and ~35% weightage, respectively, by focusing on analytical techniques, enzyme kinetics, animal physiology, and genetics.
- Food Technoology (XL-U) will also have a high proportion of Food Chemistry, ~40% of its sections.
- Microbiology (XL-S) will have more focus on microbial genetics and immunology (~30%), while Botany (XL-R) covers plant systematics and phylogeny (7–9%).
| Section | High-Weightage Topics | Common Question Types | Data Insights (Based on PYQs & Mocks) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Botany (XL-R) | Plant Systematics, Classification, Phylogeny | Concept-based MCQs, NATs | Plant Systematics appears in 7–9% of Botany questions each year; taxonomy definitions & phylogenetic tree interpretation are frequent. |
| Biochemistry (XL-Q) | Biomolecules, Enzymes, Chromatography, PCR, Spectroscopy | Problem-solving MCQs, Analytical NATs | Analytical techniques account for ~25% of the Biochemistry section; enzyme kinetics & chromatography principles repeat often. |
| Microbiology (XL-S) | Microbial Taxonomy, Culture Methods, Diagnostics, Genetics | Application-based MCQs, Experimental NATs | Microbial Genetics & Immunology form ~30% of Microbiology questions; scenario-based culture method problems are common. |
| Zoology (XL-T) | Developmental Biology, Animal Physiology, Genetics | Diagram interpretation MCQs, NATs | Animal Physiology & Genetics combined make up ~35% of Zoology questions in the last 5 years. |
| Food Technology (XL-U) | Food Chemistry, Processing, Quality Control | Calculation-based NATs, Theory MCQs | Food Chemistry topics contribute ~40% of the section; process control diagrams are frequent. |
| General Aptitude (GA) | Numerical Ability, Data Interpretation, Verbal Ability | 1-mark & 2-mark MCQs | GA consistently holds 15% of total marks; numerical reasoning and data interpretation dominate. |
GATE Life Science Chemistry Important Questions 2026
The important questions of the GATE Life Science Syllabus for the Chemistry section is expected to be heavily dominated by
- Organic Chemistry, contributing ~35–38% with frequent questions on reaction mechanisms, stereochemistry, and named reactions, appearing in nearly every paper.
- Physical Chemistry will have around 30% where thermodynamics and kinetics form over half the weightage, often as numerical NATs.
- Inorganic Chemistry will hold approximately 20–22%, with coordination compounds and bioinorganic chemistry being consistent PYQ.
- Spectroscopy & Analytical Techniques is expected to have 10–12%, with NMR and mass spectrometry data interpretation offering high scoring potential.
- General Chemistry will have around 5% mostly easy conceptual questions.
| Topic | High-Weightage Subtopics | Common Question Types | Data Insights (Based on PYQs & Mocks) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Chemistry | Reaction Mechanisms, Named Reactions (Aldol, Cannizzaro, Diels-Alder), Stereochemistry, Aromaticity, Functional Group Transformations | Mechanism-based MCQs, Stereochemistry NATs, Reaction Prediction | ~35–38% of Chemistry section; stereochemistry & reaction mechanism questions appear in almost every paper. |
| Physical Chemistry | Thermodynamics, Chemical Kinetics, Electrochemistry, Quantum Chemistry, Surface Chemistry | Numerical NATs, Graph-based MCQs | Contributes ~30% of Chemistry questions; thermodynamics & kinetics together make up over half of physical chemistry questions. |
| Inorganic Chemistry | Coordination Compounds, Crystal Field Theory, Bioinorganic Chemistry, Periodic Trends, Organometallics | Conceptual MCQs, Structure-based NATs | ~20–22% of Chemistry section; coordination compounds & bioinorganic chemistry are consistent repeat topics. |
| Spectroscopy & Analytical Techniques | UV-Vis, IR, NMR, Mass Spectrometry, Chromatography | Spectral data interpretation NATs, Matching-type MCQs | Around 10–12% weightage; NMR & mass spec data interpretation are frequent scoring areas. |
| General Chemistry & Interdisciplinary | Acid-Base Equilibria, Redox Reactions, Buffer Solutions, Colloids | Conceptual MCQs, Short Calculation NATs | Accounts for ~5% of section; often easy-scoring if fundamentals are clear. |
Also Read
GATE Life Science Question Paper
The GATE Life Science previous Years' Question Papers provide the trends of the GATE exam structure and difficulty level of the GATE exam.
By solving the PYQs from 2018 onwards, the candidates can identify recurring question formats that can help in building an efficient and effective preparation plan.
| Year | GATE XL Question Paper PDF |
|---|---|
| GATE Life Science Question Paper 2025 | Download PDF |
| GATE Life Science Question Paper 2024 | Download PDF |
| GATE Life Science Question Paper 2023 | Download PDF |
| GATE Life Science Question Paper 2022 | Download PDF |
| GATE Life Science Question Paper 2021 | Download PDF |
| GATE Life Science Question Paper 2020 | Download PDF |
| GATE Life Science Question Paper 2019 | Download PDF |
| GATE Life Science Question Paper 2018 | Download PDF |
GATE Life Science- Biochemistry (XL-Q) Important Topics Weightage
| Units | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organization of life, Biomolecules | 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 5 |
| Enzyme kinetics; Vitamins and Coenzymes; Metabolic pathways and their regulation: Photosynthesis | 3 | - | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| Biochemical separation techniques | 2 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| Cell biology and signal transduction: Hormones and neurotransmitters | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Molecular biology, Recombinant biotechnology | 4 | 2 | - | - | 2 | - |
| Immunology | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | - |
GATE Life Science- Botany (XL-R) Important Topics Weightage
| Units | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Systematics | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Plant Anatomy | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Morphogenesis & Development | 4 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Physiology And Biochemistry | 4 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 |
| Genetics | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| Plant Breeding And Genetic Modification | 3 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Economic Botany | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Plant Pathology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Ecology And Environment | - | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
GATE Life Science- Microbiology (XL-S) Important Topics Weightage
| Units | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Historical Perspective | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - |
| Methods In Microbiology | 2 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
| Microbial Taxonomy And Diversity | 3 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 |
| Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells: Structure And Function | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Microbial Growth | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 6 |
| Control Of Micro-Organisms | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
| Microbial Metabolism | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Microbial Diseases And Host Pathogen Interaction | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 |
| Chemotherapy/Antibiotics | 2 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| Microbial Genetics | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Microbial Ecology | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
GATE Life Science- Zoology (XL-T) Important Topics Weightage
| Units | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animal World | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Evolution | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Genetics | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| Biochemistry And Molecular Biology | 4 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| Cell Biology | 3 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Gene Expression In Eukaryotes | - | - | 1 | - | 2 | 1 |
| Animal Anatomy And Physiology | 2 | 6 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2 |
| Parasitology And Immunology | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Development Biology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| Ecology | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| Animal Behaviour | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - |
GATE Life Science- Food Technology (XL-U) Important Topics Weightage
| Units | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Chemistry and Nutrition | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 2 |
| Food Microbiology | 7 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 8 | 8 |
| Food Products Technology | 4 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 6 |
| Food Engineering | 3 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
GATE Life Science Questions
Here's an analysis based on the last 5 years of GATE Life Sciences (XL) papers, showing the frequently asked questions, types, and approximate number of questions from each section.
| Section | Frequently Asked Topics | Question Types | Average Number of Questions (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Aptitude (GA) | Numerical Ability, Reasoning, Grammar, Data Interpretation | 1-mark MCQs, 2-mark MCQs | 10 questions (5 of 1 mark, 5 of 2 marks) |
| Chemistry (Section P) | Atomic Structure, Bonding, Organic Reaction Mechanisms, Thermodynamics, Stereochemistry | 1-mark MCQs, 2-mark MCQs, NATs | 15 questions (8-10 of 1 mark, 5-7 of 2 marks) |
| Biochemistry (Section Q) | Biomolecules, Enzyme Kinetics, Metabolism, Molecular Biology | 1-mark MCQs, 2-mark MCQs, NATs | 10-12 questions (4-6 of 1 mark, 5-6 of 2 marks) |
| Botany (Section R) | Plant Physiology, Genetics, Plant Anatomy, Plant Pathology | 1-mark MCQs, 2-mark MCQs, NATs | 10-12 questions (5-6 of 1 mark, 4-6 of 2 marks) |
| Microbiology (Section S) | Microbial Physiology, Microbial Genetics, Immunology, Environmental Microbiology | 1-mark MCQs, 2-mark MCQs, NATs | 10-12 questions (5-6 of 1 mark, 4-6 of 2 marks) |
| Zoology (Section T) | Comparative Physiology, Developmental Biology, Animal Diversity, Genetics | 1-mark MCQs, 2-mark MCQs, NATs | 10-12 questions (5-6 of 1 mark, 4-6 of 2 marks) |
| Food Technology (Section U) | Food Processing, Food Chemistry, Food Microbiology, Quality Control | 1-mark MCQs, 2-mark MCQs, NATs | 10-12 questions (5-6 of 1 mark, 4-6 of 2 marks) |
Preparation Tips for GATE Life Science
You should fully grasp the syllabus at your institution in order to stand a better chance at passing your course. Toppers also stresses that starting with the syllabi of GATE Life Sciences is pleasant and unambiguous which needs to be understood first. What is more important, understanding the topic of each section lets you design your approach and concentrate on major-weight issues.
Create a Study Plan
Develop an effective timetable that has daily, weekly, and even monthly targets. Set more time on difficult lessons and frequently review previously taught lessons. The standard advice given by competitors is to dedicate 3 to 4 hours a day for a regular four to six months schedule.
Standard books and resources should be utilized
There is no need to run from one book to another in search of information just ensure you get quality books (Lehninger Biochemistry, Prescott’s Microbiology & Molecular Biology, Plant Physiology by Taiz and Zeiger). Preparation remains efficient if one or two well-recommended books for each topic are distinctly studied.
Solve Previous Year's Papers and Mock Tests
Solving previous years’ GATE question papers (of the previous 5-10 years) is essential. According to the toppers, it's better to write the mock tests on a weekly basis and review the mistakes committed while doing it. This also enables one to cope with questions and time during examination.
Focus on Important Topics
Concentrate on the subjects that carry high weight for that particular course; for instance, enzyme kinetics under the Biochemistry unit, plant physiology under the Botany unit, microbial physiology under the Microbiology unit, and comparative physiology under the Zoology unit. A must according to toppers since these areas are often covered in tests and the questions make up for a substantial number of marks.
Revise Regularly
Periodic review is required to help students retain the main ideas and solutions for problems in a subject area. According to the toppers, it is better to write brief notes for each topic and revise those notes on a weekly basis if there are tough subjects like Organic Chemistry and Genetics.
Build up the ability to solve quandaries
It is valuable to practice calculation and conceptual problems related to Numerical Answer Type (NAT) questions as it would prove to be quite tricky. The toppers have suggested that students should solve numerical problems on a daily basis especially, in chemistry and biochemistry to develop precision.
Strengthen General Aptitude
The General Aptitude section contributes to 15% of the total weightage of the exam, and most of the time, toppers also cover a maximum number of questions relating to this section to improve their respective ranks. Aptitude questions when taken in intervals assist in mastering speed and thus enhance general exam performance.
Seek Assistance from the Internet and Support from Others
For difficult topics attend online study groups, and forums, and follow the teachings of the coaching videos if needed. NPTEL and YouTube channels are other means that toppers resort to, to gain more understanding or clarification on difficult areas.
GATE Life Science Syllabus FAQs
Ques.Is GATE life science easy?
Ans. The GATE Life Science is not entirely easy, but it is scorable with proper preparation, subject focus, and practice. Strong basics and practicing PYQs are the key to scoring well in the GATE Life Science.
The questions in the GATE Life Science exam are mostly conceptual, analytical, and reasoning-based. As per the previous year's analysis, around 60–70% questions were directly from standard textbooks.
- Chemistry and Biochemistry: ~25–30% of questions are calculation or problem-based.
- Botany & Zoology: Around 40–50% questions are memory/concept-based.
- GA section: ~10 questions, high accuracy possible with practice.
Top scorers usually attempt 60–65 questions out of 65–70 and score 70–80% marks.
The candidates should focus on the high-scoring topics.
| Subject | Topics / Focus Areas | Ease Level | Weightage (%) | Notes / Tips |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Aptitude (GA) | Verbal Ability, Numerical Ability | Easy | 10–12% | High scoring if practiced regularly. Focus on vocabulary, reasoning, and basic arithmetic. |
| Chemistry (P) | Physical, Organic, Inorganic Chemistry | Moderate | 20–25% | Problem-solving heavy in Physical Chemistry; Organic Chemistry is memorization + reaction logic; Inorganic is mostly factual. |
| Biochemistry (Q) | Biomolecules, Enzymes, Metabolic Pathways, Molecular Biology | Moderate to Easy | 20–25% | Conceptual questions dominate; diagrams & pathways are important. Focus on TCA cycle, DNA/RNA processes. |
| Botany (R) | Plant Anatomy, Physiology, Genetics, Ecology, Pathology | Moderate | 15–20% | High factual content; diagrams & processes important. Ecology & physiology are scoring areas. |
| Microbiology (S) | Microbial Taxonomy, Physiology, Genetics, Immunology | Moderate | 15–20% | Microbial genetics and immunology are tricky; memorization + understanding needed. |
| Zoology (T) | Animal Diversity, Anatomy, Physiology, Genetics, and Developmental Biology | Moderate | 15–20% | Memorization-heavy; comparative anatomy & physiology can be scoring. |
| Food Technology (U) | Food Chemistry, Microbiology, Processing, Quality Control | Moderate | 15–20% | Industrial and applied focus; calculations and standards require attention. |
Ques. What is the scope of GATE life science?
Ans. The GATE Life Science opens doors to multiple opportunities across various sectors like academia, research, industry, and government.
Academic & Research Opportunities
- Postgraduate Admissions: A valid GATE Life Science score provides admission to M.Tech and Ph.D. programs in Life Sciences at premier institutions such as IITs, IISc, and NITs. These programs often offer financial assistance, including scholarships and stipends.
- Junior Research Fellowships (JRFs): Institutions like CSIR, DRDO, BARC, and many IITs offer JRF positions to GATE-qualified candidates, providing entry into advanced research projects, which can lead to further Ph.D. studies.
Government Jobs:
- PSUs: Many PSUs recruit Life Science graduates through GATE scores like, ONGC, BHEL, and IOCL (limited and competitive).
- Government Research Organizations: Research roles are often provided the institutes like ISRO, DRDO, and BARC.
Private Sector Careers
- Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Industries: Many companies in the private sector recruit candidates for professional roles in R&D, quality control, and regulatory roles in the biotech and pharma industries.
- Medical Writing and Clinical Research: Organizations in healthcare and pharmaceuticals provide opportunities in medical writing, clinical research.
Emerging Fields and Interdisciplinary Roles
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology: GATE XL-qualified candidates can pursue roles in data analysis, algorithm development, and systems biology.
- Environmental Science and Agricultural Innovation: The candidates with a GATE Life Science have an advantage to be an expert in sustainable agriculture, environmental monitoring, and conservation biology.
Also Read
GATE Life Sciences: Top Career Paths and Opportunities for Life Science GraduatesQues. What is the qualification for GATE Life Science?
Ans. The qualification Criteria for GATE Life Science is that the candidate should have a B.Sc. (Biology) or B. Tech (Biotechnology) backgrounds, as there is no age limit or minimum marks so anyone can apply for GATE Life Sciences.
| Criteria | Details |
|---|---|
| Educational Qualification | B.Sc. / B.E. / B.Tech / B.Pharm or equivalent in Biology, Biotechnology, Biochemistry, Microbiology, Zoology, Botany, Chemistry, Food Technology, or related subjects. Final-year students are also eligible. |
| Minimum Marks / Percentage | No minimum percentage required to appear in GATE. Admissions/scholarships may consider academic performance. |
| Age Limit | No age limit. Any candidate meeting the educational criteria can apply. |
| Number of Attempts | No restriction. Candidates can appear any number of times if eligible. |







Comments