IIT Guwahati has released the GATE ECE Syllabus 2026 on its official website. The GATE ECE Syllabus 2026 is divided into 3 major sections: General Aptitude, Engineering Mathematics, and Core subjects of Electronics & Communication.
- The General Aptitude has a weightage of 15%, including topics like verbal ability (including grammar, vocabulary, and reading comprehension), as well as quantitative, analytical, and spatial reasoning.
- Engineering Mathematics has 13% of the weightage, covering topics like linear algebra, calculus, differential equations, probability, and vector analysis, which create the foundation for solving circuit and system-related questions.
- The Core subjects of the GATE ECE Syllabus will have a weightage of 72%, with topics like Networks, Signals & Systems, Electronic Devices, Analog Circuits, Digital Circuits, Control Systems, Communications, and Electromagnetics.

Also Read
Key Summary
- The GATE ECE Syllabus PDF includes 3 sections: General Aptitude (GA), Engineering Mathematics, and Core ECE Subjects.
- General Aptitude includes topics like Verbal Ability, Grammar, Vocabulary, Reading Comprehension, Numerical Ability, and Logical Reasoning.
- Engineering Mathematics includes important topics like Linear Algebra, Calculus, Probability & Statistics, Complex Variables, and Differential Equations.
- Core ECE Subjects cover Networks, Electronic Devices, Analog Circuits, Digital Circuits, Signals & Systems, Control Systems, Communications, and Electromagnetics.
- As per the GATE ECE Weightage, 15% weightage is given to GA, Engineering Mathematics will have around 13%, and ~72% of Core ECE subjects.
- The GATE ECE 2026 will have a total of 65 questions for 100 marks, with a mix of MCQs, MSQs, and NATs.
- As per the previous year's analysis, Communications (~13%), Analog Circuits (~10%), and Digital Circuits (~11%) had the highest weightage, while GA and Mathematics remained scoring boosters.
- What is the GATE ECE Syllabus 2026?
1.1 GATE ECE Syllabus for General Aptitude 2026
1.2 GATE ECE Syllabus for Engineering Mathematics 2026
1.3 GATE ECE Syllabus for Networks, Signals & Systems
1.4 GATE ECE Syllabus for Electronic Devices
1.5 GATE ECE Syllabus for Analog Circuits
1.6 GATE ECE Syllabus for Digital Circuits
1.7 GATE ECE Syllabus for Control Systems
1.8 GATE ECE Syllabus for Communications
1.9 GATE ECE Syllabus for Electromagnetics (EMTL)
- GATE ECE Syllabus Weightage 2026
- GATE ECE Syllabus Books 2026
- GATE Electronics and Communication Engineering Important Topics
- Preparation Tips for GATE 2026 ECE Exam
- GATE ECE Syllabus 2026 FAQs
What is the GATE ECE Syllabus 2026?
The GATE ECE Syllabus 2026 has 3 major sections: General Aptitude with 15% weightage, Engineering Mathematics with around 13% weightage, and Core GATE ECE Syllabus subjects with the highest weightage of 72%.
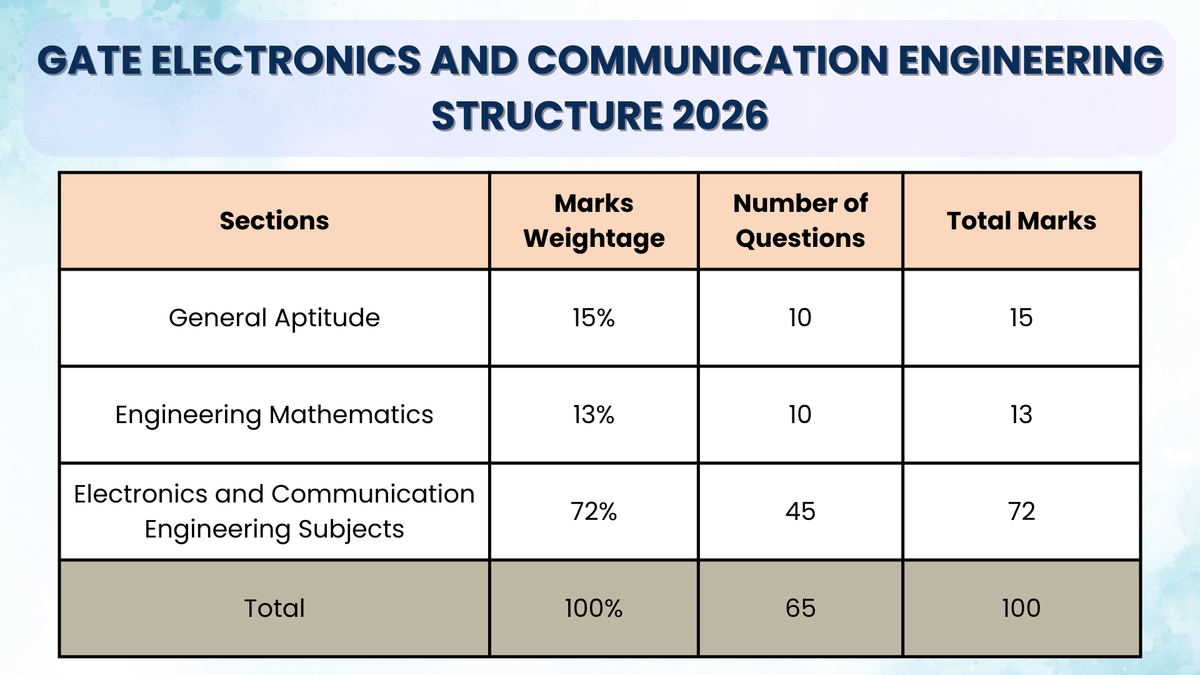
GATE ECE Syllabus for General Aptitude 2026
The General Aptitude section is common for all GATE Papers, which tests the analytical skills, reasoning ability, and communication skills, and this section is divided into 2 major parts:
- Verbal Ability: Grammar, vocabulary, reading comprehension, sentence completion, and verbal reasoning.
- Numerical Ability: Data interpretation, quantitative reasoning, percentages, ratios, exponents & logarithms, permutations & combinations, probability, and basic statistics.
GATE ECE Syllabus for Engineering Mathematics 2026
The Engineering Mathematics in the GATE ECE Syllabus will have a weightage of around 13% by testing the fundamental mathematical concepts required for electronics:
- Linear Algebra: Vector spaces, matrices, determinants, eigenvalues & eigenvectors, systems of linear equations.
- Calculus: Limits, continuity, mean value theorems, integrals, partial derivatives, maxima & minima, Taylor series, multiple integrals.
- Differential Equations: First- and higher-order ODEs, PDEs, boundary value and initial value problems.
- Vector Analysis: Gradient, divergence, curl, Gauss’s, Green’s, and Stokes’ theorems.
- Probability & Statistics: Random variables, distributions (Binomial, Poisson, Normal), mean, variance, standard deviation.
GATE ECE Syllabus for Networks, Signals & Systems
The Networks, Signals & Systems section of the GATE ECE Syllabus covers the basics of circuits, signal processing, and system analysis:
- Circuit Laws & Theorems: KCL, KVL, Thevenin, Norton, superposition.
- Analysis: Transient and steady-state analysis of AC/DC circuits.
- Signals & Systems: Fourier, Laplace, and Z-transforms, convolution, correlation, stability.
- Sampling Theorem and reconstruction of signals.
GATE ECE Syllabus for Electronic Devices
In the GATE ECE Syllabus 2026, Electronic Devices focuses on semiconductor physics and device modeling:
- Semiconductor Physics: Carrier transport, PN-junction diode characteristics.
- Devices: Zener diode, LED, photodiode, solar cell.
- Transistors: BJT, MOSFET, small-signal models, biasing.
- Device Models and applications.
GATE ECE Syllabus for Analog Circuits
The Analog Circuits topic of the GATE ECE Syllabus focuses on Analog design, amplifiers, and system applications:
- Amplifiers: BJT & MOSFET small-signal analysis, frequency response.
- Operational Amplifiers: Characteristics, applications, filters, oscillators.
- Feedback Circuits: Stability, gain, bandwidth trade-offs.
- Waveform Generators: Multivibrators, oscillators.
GATE ECE Syllabus for Digital Circuits
This topic covers the fundamentals of logic design and digital systems:
- Boolean Algebra & Number Systems.
- Logic Gates & Circuits: Combinational (adders, multiplexers, decoders) and Sequential (flip-flops, counters, registers).
- Memory & Data Conversion: RAM, ROM, ADC/DAC.
GATE ECE Syllabus for Control Systems
The Control systems of the GATE ECE Syllabus focus on system stability and control theory:
- Feedback Principles & Transfer Functions.
- Stability Analysis: Routh, Nyquist, Bode, Root-locus.
- Time & Frequency Response.
- Controllers: Compensators, PID controllers.
GATE ECE Syllabus for Communications
The Communication topic is one of the highest weightage sections in the GATE ECE Syllabus, with around 15-18% weightage by covering sub-topics like:
- Analog Modulation: AM, FM, PM.
- Digital Modulation: PCM, delta modulation, line coding.
- Random Processes & Noise: Power spectral density, autocorrelation.
- Information Theory: Entropy, channel capacity, coding theorems.
GATE ECE Syllabus for Electromagnetics (EMTL)
This topic of the GATE ECE Syllabus covers the electromagnetic theory and wave propagation:
- Maxwell’s Equations and boundary conditions.
- Transmission Lines: Impedance matching, Smith chart.
- Waveguides & Antennas: Radiation patterns, S-parameters.
- Wave Propagation in free space and media.
GATE ECE Syllabus Weightage 2026
The GATE ECE Syllabus Weightage 2026 shows that the Communications (12–13%), Digital Circuits (10–11%), and Analog Circuits (10%) will have the highest weightage, followed by Networks, Signals & Systems, and Electromagnetics with around 8-10%. The Control Systems and Electronic Devices have a moderate weightage of 7–8%.
As per the previous years’ analysis, a strong preparation in Communication, Digital, and Maths, along with the General Aptitude, can boost the chances of scoring more than 55 marks in the GATE ECE 2026 exam and can secure a good rank.
| Section | Topics Covered | Weightage (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| General Aptitude | Verbal aptitude, reading comprehension, quantitative aptitude, data interpretation, logical & spatial reasoning | 15% |
| Engineering Mathematics | Linear Algebra, Calculus, Differential Equations, Vector Analysis, Complex Analysis, Probability & Statistics | 13–16% |
| Networks, Signals & Systems | Circuit laws, theorems, phasors, transient/steady-state analysis, Fourier/Laplace transforms, sampling theorem, convolution | 8–10% |
| Electronic Devices | Semiconductors, PN junctions, Zener diodes, BJT, MOSFET, LEDs, photodiodes, solar cells | 7–8% |
| Analog Circuits | Diode applications, BJT & MOSFET amplifiers, biasing, frequency response, Op-amp applications | 10% |
| Digital Circuits | Logic gates, combinational/sequential circuits, flip-flops, counters, memory, data converters | 10–11% |
| Control Systems | Stability analysis (Routh, Nyquist, Bode, Root-locus), transient & steady-state response, PID controllers | 7% |
| Communications | Analog (AM, FM, PM) & Digital (PCM, delta modulation, line coding), information theory, channel capacity, noise analysis | 12–13% |
| Electromagnetics | Maxwell’s equations, transmission lines, waveguides, antennas, Smith chart, S-parameters | 9–10% |
GATE ECE Syllabus Books 2026
The recommended GATE ECE Books 2026 by toppers and experts suggest that the books play an important role in both strong fundamentals and problem-solving practice.
- The R.S. Agarwal and Hari Mohan Prasad are best for General Aptitude, while Mathematics is best approached with Grewal and Kreyszig.
- For Core subjects, classics like Oppenheim (Signals), Sedra & Smith (Analog), Morris Mano (Digital), Haykin (Communication), and Sadiku (Electromagnetics) are the most trustworthy.
- Control Systems provides multiple standard options like Kuo, Ogata, and Nagrath & Gopal, providing the candidates flexibility as per their preference.
| Subject | Recommended Books & Authors |
|---|---|
| General Aptitude | R.S. Agarwal (“Quantitative Aptitude”, “Logical Reasoning”), Hari Mohan Prasad (“Objective English”) |
| Engineering Mathematics | B.S. Grewal (“Higher Engineering Mathematics”), Erwin Kreyszig, R.K. Jain & S.R.K. Iyengar |
| Networks & Circuit Theory | Alexander Sadiku, Van Valkenburg, Hayt & Kemmerly, Chakraborty |
| Signals & Systems | Oppenheim & Willsky, Oppenheim & Schafer, Proakis, S.K. Mitra |
| Electronic Devices & Analog | Boylestad & Nashelsky (“Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory”), Sedra & Smith (“Microelectronic Circuits”) |
| Digital Circuits | Morris Mano (“Digital Logic and Computer Design”), Salivahanan, Toccii |
| Control Systems | Kuo (“Automatic Control Systems”), Ogata (“Modern Control Systems”), Nise, Nagrath & Gopal |
| Communications | Simon Haykin (“Analog & Digital Communication Systems”), Taub & Schilling, B.P. Lathi |
| Electromagnetics | Sadiku (“Elements of Electromagnetics”), Hayt, Balanis, Sadiku again for transmission lines/EM waves |

GATE Electronics and Communication Engineering Important Topics
Based on GATE Paper Analysis for previous years, the important topics in the core subjects of the GATE Syllabus for ECE 2026 include Networks, Signals, and Systems, Electronic Devices, Analog Circuits, etc. Subject-wise important topics are mentioned below for your reference.
| Subjects | Important Topics |
|---|---|
| Engineering mathematics |
|
| General Aptitude |
|
| Electronic Devices and Circuits |
|
| Control System |
|
| Analog Circuits |
|
| Digital Electronics |
|
| Electromagnet and Field Theory |
|
| Signal & Systems |
|
| Communications |
|
| Networks |
|
GATE Electronics and Communication Engineering Chapter-Wise Questions
Subject-wise questions asked over the years can give you insight on the importance of each subject. A table is presented below with the number of questions asked from all the subjects over the years.
| Subjects | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network Theory | 6 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 15 | 12 | 9 | 8 |
| Electric Devices | 12 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 11 | 15 | 12 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 3 | 7 | 9 | 9 |
| Analog Circuits | 10 | 10 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 12 | 9 | 11 | 7 | 14 | 8 | 10 | 14 |
| Digital Circuits | 11 | 7 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 5 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 9 |
| Signals and Systems | 10 | 12 | 6 | 10 | 6 | 10 | 5 | 12 | 9 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 8 | 11 | 7 |
| Control Systems | 8 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| Communications | 11 | 12 | 12 | 13 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Electromagnetics | 8 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 7 | 14 | 10 | 8 |
| Engineering Mathematics | 9 | 11 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 9 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 8 | 11 |
| General Aptitude | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
GATE Electronics and Communication Engineering Important Topics
Based on GATE Paper Analysis for previous years, the important topics in the core subjects of the GATE Syllabus for ECE 2025 include Networks, Signals, and Systems, Electronic Devices, Analog Circuits etc. Subject-wise important topics are mentioned below for your reference.
| Subjects | Important Topics |
|---|---|
| Engineering mathematics |
|
| General Aptitude |
|
| Electronic Devices and Circuits |
|
| Control System |
|
| Analog Circuits |
|
| Digital Electronics |
|
| Electromagnet and Field Theory |
|
| Signal & Systems |
|
| Communications |
|
| Networks |
|
GATE 2026 Electronics and Communication Engineering Exam Preparation Tips
What should be my revision strategy for GATE ECE?
Revision plays an important role in preparation so you must start your revision after completing each topic. You can start your revision from chapters like Circuit Theory, Control Theory and Signal Processing as these chapters are related to other chapters. Starting with these chapters can build the knowledge which you can apply when you study other chapters. Start with these chapters and then move towards complex subjects like Power Systems, Measurements, Machines etc.
What can be the subject sequence for ECE?
Determining the subject sequence can ease exam preparation. It can help you to complete the syllabus on time along with the revisions. A sequence of readings is suggested below.
| Category 1 Subject | Category 2 Subject | Category 3 Subject | Category 4 Subject |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engineering Mathematics | Control System | Communication | General Aptitude |
| Network Theory | Digital Circuits | Electromagnetics | - |
| Signals and Systems | Analog Circuits | - | - |
| EDC | - | - | - |
Should I practice PYQs and take tests?
Solving PYQs and taking tests not only gives you an idea of exam patterns but also enhances your speed and accuracy. After completing all the chapters in each subject you must solve PYQs and take online or offline tests. After the final revision, you must solve the entire question paper within a time limit. You can solve one to two papers per day till the exam day.
GATE ECE Syllabus 2026 FAQs
Ques. What is the rank of 70 marks in GATE ECE?
Ans. A score of 70 marks in GATE will place the candidate AIR between ~100 and 200, by offering admission into the top NITs, IIITs.
| Rank (AIR) | Possible Institutes |
|---|---|
| 50–100 | Multiple IITs, IISc, top NITs |
| 100–200 | Top NITs (Trichy, Warangal), IIITs, DTU, BITS etc. |
| 200–500 | NITs, IIITs, GFTIs |
| 500–1000 | NITs, state universities, mid-tier institutions |
Ques. Which branch GATE exam is easy?
Ans. As per the previous years’ analysis of GATE papers, it has been revealed that:
- Civil Engineering and specialized streams like Biotechnology, Chemistry, and Textiles are mostly rated as easy to moderate.
- Computer Science & IT (CSE), Mechanical (ME), and Electrical Engineering (EE) are generally considered moderate to difficult.
- The GATE Electronics & Communication (ECE) and Instrumentation (IN) are often rated as Moderate to Difficult.
| Branch | Relative Difficulty |
|---|---|
| Civil Engineering (CE) | Often Easy to Moderate |
| Biotechnology, Chemistry, Textiles | Frequently Easy to Moderate |
| CSE, EE, ECE, ME, IN | Mostly Moderate to Difficult |
Ques. Is the GATE exam 100 marks?
Ans. Yes, GATE is conducted for a total of 100 marks with 65 questions, 10 questions from General Aptitude for 15 marks, and 55 questions from Core ECE subjects with a total of 85 marks in 3 hours.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Maximum Marks | 100 |
| Total Questions | 65 questions |
| Sections | GA (15 marks) + Core Subject (85 marks) |
| Question Formats | MCQs (with negative marking), MSQs, NATs |
| Exam Duration | 3 hours (CBT) |
| Final GATE Score | Normalized to 1000, based on raw marks |
Ques: Which order should I follow for GATE 2026 ECE preparation?
Ans: You must start from mathematics, aptitude, network, EDC, Signal & Systems and then move on to other chapters. If you want to take two subjects at a time then the combination should be Aptitude & Mathematics, network theory & EDC, analog & signals, Digital & control systems and EMT & communication.
Ques: Can I complete the entire ECE syllabus in two months?
Ans: Completing the entire ECE syllabus in just two months is challenging. You need to make a good strategy for it and dedicate at least 6-8 hours per day to study. You can start with easy topics like Circuit Theory, Control Theory and Signal Processing and then move on to complex topics like Machines and Power Systems.







Comments