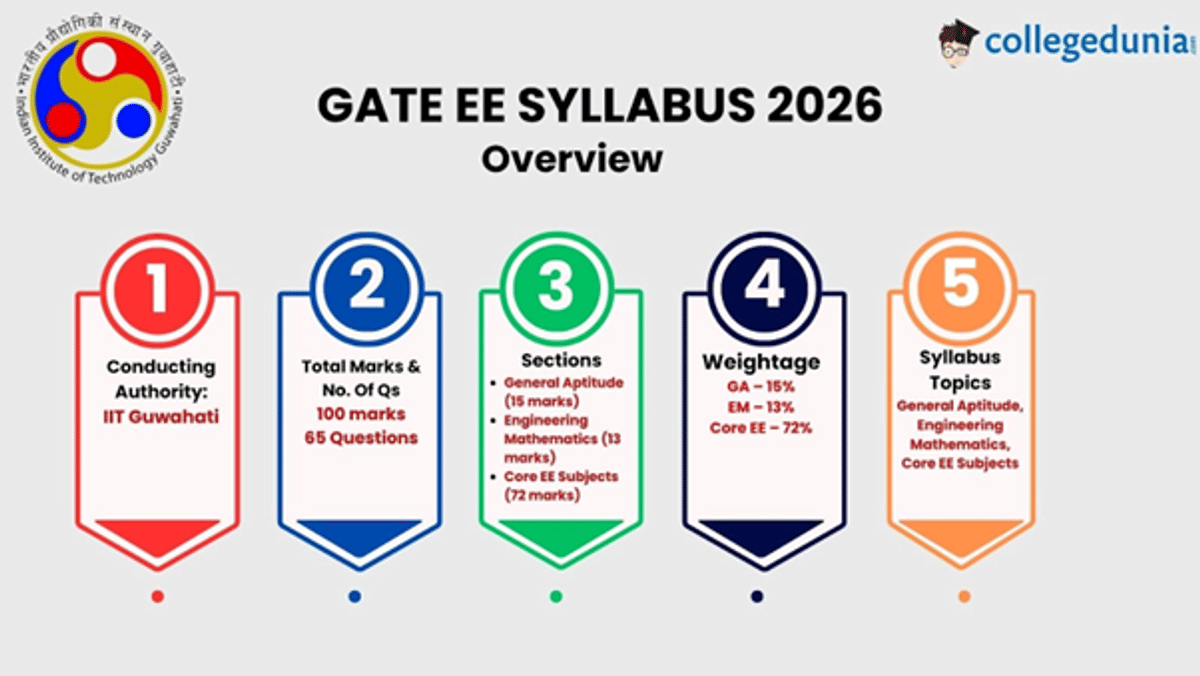
IIT Guwahati has released the GATE EE Syllabus 2026 on its official website. The GATE EE syllabus 2026 consists of 3 sections: General Aptitude, Core Subjects—Electrical Engineering, and Engineering Mathematics.
-
The GATE EE syllabus is further divided into 10 sections. In the GATE EE syllabus 2026, the maximum weightage will be given to the core subject syllabus, i.e., 72%.
- The General Aptitude & Engineering Mathematics syllabus will have a weightage of 15% and 13%, respectively.
- The GATE EE syllabus 2026 covers General Aptitude (15 marks), Engineering Mathematics (13 marks), and core EE subjects (72 marks).
- The Core topics include Electric Circuits, Electromagnetic Fields, Signals & Systems, Electrical Machines, Power Systems, Control Systems, Measurements, analogue & Digital Electronics, and Power Electronics.

Quick Links
Key Summary:
In this article, we discussed the GATE EE syllabus for 2026, including core subjects, weightage, important topics, books, and preparation tips.
- IIT Guwahati has released the GATE EE Syllabus 2026 on its official website.
- The GATE EE syllabus 2026 consists of 3 sections: General Aptitude, Core Subjects—Electrical Engineering, and Engineering Mathematics.
- The GATE Electrical Engineering syllabus is further divided into ten sections. In the GATE EE syllabus 2026, the maximum weightage will be given to the core subject syllabus, i.e., 72%.
- The General Aptitude & Engineering Mathematics syllabus will have a weightage of 15% and 13%, respectively.
- The GATE EE syllabus 2026 covers General Aptitude (15 marks), Engineering Mathematics (13 marks), and core EE subjects (72 marks).
- What is the GATE EE Syllabus 2026?
- GATE EE Syllabus 2026
- GATE EE Syllabus 2026 Weightage
- GATE EE Exam Pattern
- GATE Electrical Engineering Recommended Books
- GATE EE Previous Year Question Paper
- GATE Statistics and Toppers Tips
- What is a Good Score in the GATE EE Exam?
- GATE EE Exam Preparation Tips
- FAQs
What is the GATE EE Syllabus 2026?
The GATE EE syllabus 2026 consists of 3 sections: General Aptitude, Core Subjects—Electrical Engineering, and Engineering Mathematics.
- The GATE EE syllabus 2026 covers General Aptitude (15 marks), Engineering Mathematics (13 marks), and core EE subjects (72 marks).
- The Core topics include Electric Circuits, Electromagnetic Fields, Signals & Systems, Electrical Machines, Power Systems, Control Systems, Measurements, Analog & Digital Electronics, and Power Electronics.
GATE EE Syllabus 2026: Overview
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Paper Code | EE (Electrical Engineering) |
| Conducting Institute | IIT Guwahati |
| Exam Mode | Computer-Based Test (CBT) |
| Duration | 3 Hours |
| Total Marks | 100 |
| Total Questions | 65 |
| Sections |
|
| Question Types |
|
| Marking Scheme | +1 or +2 for correct answersNegative marking is applicable only for MCQs |
| Difficulty Level | Moderate to High |
| Key Topics |
|
| Official Website | GATE 2026 IIT Guwahati |
Ques. Which topics are included in engineering mathematics, and why are they important?
Ans. Engineering Mathematics in GATE EE includes Linear Algebra, Calculus, Differential Equations, Complex Variables, and Probability & Statistics.
| Topic | Relevance in GATE EE | Approx. Weightage |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Algebra | Fundamental for system modeling and Control Systems | 2–3 marks |
| Calculus | Used in Signals & Systems and Electromagnetic Fields | 2–3 marks |
| Differential Equations | Essential for transient and dynamic response analysis | 2–3 marks |
| Complex Variables | Helpful in network analysis and sinusoidal steady-state problems | 2 marks |
| Probability & Statistics | Applied in Measurements, Noise Analysis, and Reliability studies | 2–3 marks |
Ques. Which subjects generally have the highest weightage in the GATE EE core syllabus?
Ans. According to previous GATE trends, the highest-weightage subjects are given below:
| Subject | Approx. Weightage (Marks) |
|---|---|
| Electrical Machines | 8–12 marks |
| Power Systems | 8–12 marks |
| Control Systems | 8–10 marks |
| Electric Circuits | 6–8 marks |
| Power Electronics | 6–8 marks |
Ques. How difficult is the GATE EE Exam expected to be in 2026?
Ans. The difficulty level of GATE EE is generally moderate to high. The questions demand conceptual understanding, analytical thinking, and time management.
- Unlike university exams, GATE emphasizes multi-step numerical reasoning and problem-solving under time pressure.
- Students with consistent practice of previous papers and mock tests usually find the exam manageable.
GATE EE Syllabus 2026
The GATE EE syllabus 2026 consists of 3 sections: General Aptitude, Core Subjects—Electrical Engineering, and Engineering Mathematics.
The GATE Electrical Engineering syllabus is further divided into 10 sections. In the GATE EE syllabus 2026, the maximum weightage will be given to the core subject syllabus, i.e., 72%.
- Section 1: Engineering Mathematics
- Section 2: Electric Circuits
- Section 3: Electromagnetic Fields
- Section 4: Signals and Systems
- Section 5: Electrical Machines
- Section 6: Power Systems
- Section 7: Control Systems
- Section 8: Electrical and Electronic Measurements
- Section 9: Analog and Digital Electronics
- Section 10: Power Electronics
GATE EE Syllabus 2026 For Core EE Subjects
The Core topics include Electric Circuits, Electromagnetic Fields, Signals & Systems, Electrical Machines, Power Systems, Control Systems, Measurements, Analog & Digital Electronics, and Power Electronics.
The table below includes the section-wise topics for the GATE EE exam 2026:
| Section | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| Electric Circuits |
|
| Electromagnetic Fields |
|
| Signals and Systems |
|
| Electrical Machines |
|
| Power Systems |
|
| Control Systems |
|
| Electrical & Electronic Measurements |
|
| Analog & Digital Electronics |
|
| Power Electronics |
|
GATE EE Syllabus 2026 For Engineering Mathematics
The GATE EE Engineering Mathematics syllabus 2026 for exam preparation is given below for your reference:
| Topic | Key Concepts |
|---|---|
| Linear Algebra |
|
| Calculus |
|
| Differential Equations |
|
| Complex Variables |
|
| Probability & Statistics |
|
GATE EE Syllabus 2026 For General Aptitude
General Aptitude (GA) is a common section in all GATE papers and holds 15% of the total marks. It is the only section of the GATE exam that is shared by all 30 disciplines.
The GATE EE General Aptitude syllabus 2026 for exam preparation is given below for your reference:
| Topics | Syllabus |
|---|---|
| Verbal Aptitude |
|
| Quantitative Aptitude |
|
| Analytical Aptitude |
|
| Spatial Aptitude |
|
Ques. Which topics should be prioritised for scoring high in GATE EE 2026?
Ans. Based on the previous years’ trends, the high-weightage topics are:
- Electrical Machines (8–12 marks)
- Power Systems (8–10 marks)
- Control Systems (8–10 marks)
- Power Electronics (6–8 marks)
- Electric Circuits (6–8 marks)
Ques. Is the GATE EE syllabus revised for 2026?
Ans. As of now, the GATE EE for the 2026 syllabus remains the same as the previous year, 2025.
- It continues to be comprehensive, focusing on conceptual understanding and numerical application across core EE domains.
Ques. How many sections are there in the GATE EE syllabus 2026?
Ans. The GATE Electrical Engineering syllabus for 2026 consists of three main sections—General Aptitude, Engineering Mathematics, and Core Electrical Engineering Subjects.
- The core section is further divided into ten subjects, covering all major areas of electrical engineering.
Check More:
GATE EE Syllabus 2026 Weightage
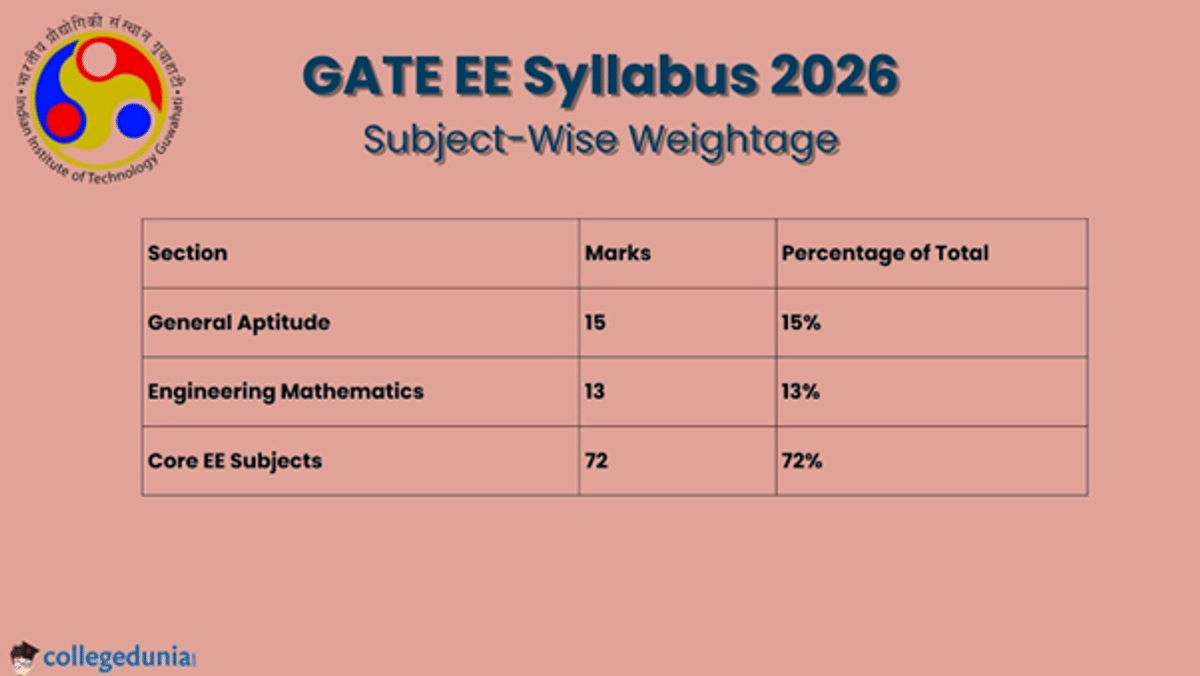
You must attentively examine the details and adjust their preparation plan according to the GATE exam syllabus for EE. The GATE EE syllabus weightage is shown in the table below.
GATE EE Syllabus Weightage 2026
The GATE EE subject-wise weightage is shown in the table below for your reference.
| Subjects | Marks Weightage |
|---|---|
| General Aptitude | 15 |
| Engineering Mathematics | 13 |
| Signals and Systems | 8 |
| Electromagnetic | 7 |
| Electrical Machines | 12 |
| Analog Circuits | 7 |
| Digital Circuits | 2 |
| Power Systems | 8 |
| Control Systems | 8 |
| Electric Circuits | 7 |
| Power Electronics | 11 |
| Electrical Measurements | 2 |
GATE EE Section-Wise Weightage 2026
Understanding the weightage of different sections in the GATE Electrical Engineering syllabus can significantly enhance your preparation strategy.
Below is a detailed table showcasing the section-wise weightage and the number of questions from each section in the last five years for the GATE exam syllabus for Electrical Engineering.
| Section | Weightage (%) | Number of Questions (Last 5 Years) |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Circuits | 10–12% | 8–10 |
| Electromagnetic Fields | 8–10% | 6–8 |
| Signals and Systems | 8–10% | 6–8 |
| Electrical Machines | 10–12% | 8–10 |
| Power Systems | 12–14% | 10–12 |
| Control Systems | 8–10% | 6–8 |
| Power Electronics | 10–12% | 8–10 |
| Electrical Measurements | 6–8% | 4–6 |
| Digital Electronics | 6–8% | 4–6 |
| General Aptitude | 15% | 10–12 |
GATE EE Exam Pattern
The GATE 2026 Electrical Engineering (EE) exam pattern outlines the structure, marking scheme, and distribution of questions.
The table below provides a detailed overview of the exam format and key components.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Exam Mode | Computer-Based Test (CBT) |
| Duration | 3 Hours |
| Total Marks | 100 |
| Total Questions | 65 |
| Sections | 1. General Aptitude (15 marks)2. Engineering Mathematics (13 marks)3. Core EE Subjects (72 marks) |
| Question Types | Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs), Multiple Select Questions (MSQs), Numerical Answer Type (NAT) |
| Marking Scheme | MCQs: +1 or +2 marks for correct, negative marking applicableMSQs/NATs: +1 or +2 marks, no negative marking |
| Difficulty Level | Moderate to High (focus on undergraduate EE concepts) |
| Weightage | GA: 15%, Engineering Mathematics: 13%, Core EE Subjects: 72% |
Ques. Is there negative marking in GATE EE 2026?
Ans. Yes, negative marking applies only to Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs). The details are given below in the table:
| Question Type | Marks per Question | Negative Marking (for Wrong Answer) |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) | 1 mark | –0.33 mark |
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) | 2 marks | –0.67 mark |
| Multiple Select Questions (MSQs) | 1 or 2 marks | No negative marking |
| Numerical Answer Type (NAT) | 1 or 2 marks | No negative marking |
Ques. How can knowing the weightage help in GATE preparation?
Ans. Understanding topic-wise weightage helps you prioritize subjects effectively.
- Focus more on high-weightage subjects (Machines, Power Systems, and Control Systems).
- Revise medium-weightage subjects (Power Electronics, Circuits) regularly.
- Strengthen low-weightage but easy areas (Measurements, Analog & Digital Electronics) for quick marks.
GATE Electrical Engineering Recommended Books
You can study the syllabus and questions for GATE EE from various online sources and books. Some of the most common and useful books are given below:
| Book Title | Author(s) |
|---|---|
| Electric Circuits | James W. Nilsson |
| Fundamentals of Electric Circuits | Alexander & Sadiku |
| Engineering Electromagnetics | William Hayt |
| Electromagnetic Waves | David K. Cheng |
| Signals and Systems | Alan V. Oppenheim |
| Linear Systems and Signals | B.P. Lathi |
| Electrical Machines | R.K. Rajput |
| Electrical Machinery | P.S. Bimbhra |
| Power System Engineering | N. V. N. Rao |
| Electrical Power Systems | C.L. Wadhwa |
| Control Systems Engineering | Norman S. Nise |
| Modern Control Engineering | Ogata |
| Power Electronics | Muhammad H. Rashid |
| Fundamentals of Power Electronics | Robert W. Erickson |
| Electrical Measurement and Measuring Instruments | A.K. Sawhney |
| Digital Design | M. Morris Mano |
| Fundamentals of Logic Design | Brown & Vranesic |
| Quantitative Aptitude | R.S. Aggarwal |
| Verbal and Non-Verbal Reasoning | R.S. Aggarwal |
GATE EE Previous Year Question Paper
Attempt the following previous year’s question papers for GATE EE to secure high scores in the first attempt. Also, Check GATE Preparation Tips
| Year | GATE EE Question Paper | GATE EE Answer Key |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | Download PDF | Download PDF |
| 2023 | Download PDF | Download PDF |
| 2021 | Download PDF | Download PDF |
| 2020 | Download PDF | Download PDF |
| 2019 | Download PDF | Download PDF |
| 2018 | Download PDF | Download PDF |
| 2017 | Download PDF | Download PDF |
Check:
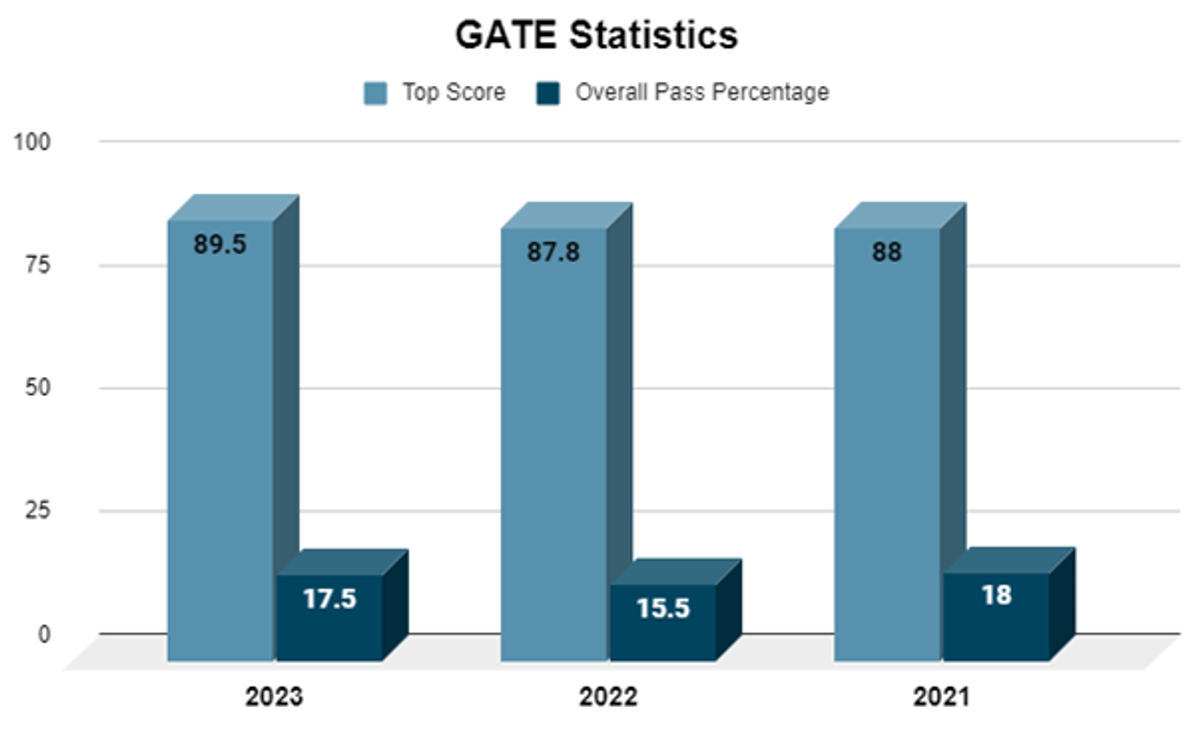
GATE Statistics and Toppers Tips
You must follow the GATE exam syllabus for EE to attain a good GATE score. The GATE statistics for Electrical Engineering for the last 3 years are as follows:
What is a Good Score in the GATE EE Exam?
If you are appearing for GATE 2026, you should aim to score 800+ in the GATE exam. Scoring an 800+ score in GATE is considered an exceptional score for a dream institute. Through an analysis, we get to know that 750+ is considered a very good score in the GATE exam.
You can follow the GATE Study Material for EE to score better. Students getting 750+ out of 1000 are expected to get some popular courses like
- Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
- Civil Engineering (CE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering (EE) at IITs.
Scoring 550+ can be a good score in the GATE syllabus EE, while a score above 400 can be taken as an average score in GATE 2024.
Check the Good Score in GATE 2024 for CSE, ECE, Mechanical, and EE here.
GATE EE Exam Preparation Tips
Some of the effective exam preparation tips for the GATE EE exam are given below in the table:
| Phase | Duration | Focus Areas | Preparation Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Syllabus Familiarization & Planning | 1–2 weeks | Understand the GATE EE syllabus, exam pattern, and topic weightage |
|
| Concept Building | 2–3 months | Engineering Mathematics, Electric Circuits, EM Fields, Signals & Systems |
|
| Core Subjects Mastery | 3–4 months | Electrical Machines, Power Systems, Control Systems, Power Electronics |
|
| Revision & Practice Tests | 1–2 months | All subjects |
|
| Final Revision & Strategy | Last 2–3 weeks | Weak areas, quick formula revision |
|
FAQs
Ques. How is the GATE EE 2026 syllabus structured?
Ans. The syllabus is divided into three main sections:
- General Aptitude (GA) – 15 marks
- Engineering Mathematics (EM)—13 marks
- Core Electrical Engineering Subjects – 72 marks
The core section is further subdivided into 10 subjects, covering the full breadth of electrical engineering from circuits to power electronics.
Ques. What is the weightage of each section in GATE EE 2026?
Ans. The weightage of each section in the GATE EE 2026 exam is given below in the table:
| Section | Marks | Percentage of Total |
|---|---|---|
| General Aptitude | 15 | 15% |
| Engineering Mathematics | 13 | 13% |
| Core EE Subjects | 72 | 72% |
Ques. Which subjects have the highest weightage in the core syllabus?
Ans. The highest weightage in the core EE syllabus of the GATE 2026 exam is given below:
| Subject | Approx. Weightage (Marks) |
|---|---|
| Electrical Machines | 8–12 |
| Power Systems | 8–10 |
| Control Systems | 8–10 |
| Electric Circuits | 6–8 |
| Power Electronics | 6–8 |
Ques. What topics are included in Engineering Mathematics for GATE EE?
Ans. The topics included in the engineering mathematics for the GATE EE 2026 exam are
| Topic | Key Concepts |
|---|---|
| Linear Algebra |
|
| Calculus |
|
| Differential Equations |
|
| Complex Variables |
|
| Probability & Statistics |
|
Ques. Does the GATE EE syllabus include general aptitude? What topics are tested?
Ans. The GATE EE syllabus for General Aptitude is given below for your reference:
| Section | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| Verbal Ability |
|
| Numerical Ability |
|
Ques. Where can I download the official GATE EE 2026 syllabus?
Ans. The official GATE EE 2026 syllabus PDF has been released by IIT Guwahati, the conducting institute for the 2026 exam.
- You can download it directly from the official portal: Website link
- It is advisable to refer only to the official document for the most accurate and updated topic list.







Comments