GATE 2024 Mining Engineering Question Paper PDF is available here. IISc Banglore conducted GATE 2024 Mining Engineering exam on February 4 in the Afternoon Session from 2:30 PM to 5:30 PM. Students have to answer 65 questions in GATE 2024 Mining Engineering Question Paper carrying a total weightage of 100 marks. 10 questions are from the General Aptitude section and 55 questions are from Engineering Mathematics and Core Discipline.
GATE 2024 Mining Engineering Question Paper with Solutions PDF
| GATE 2024 Mining Engineering Question Paper with Solutions PDF | Download | Check Solutions |
If `\(\rightarrow\)' denotes increasing order of intensity, then the meaning of the words
[drizzle \(\rightarrow\) rain \(\rightarrow\) downpour] is analogous to [............ \(\rightarrow\) quarrel \(\rightarrow\) feud].
Which one of the given options is appropriate to fill the blank?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the given analogy.
The sequence drizzle \(\rightarrow\) rain \(\rightarrow\) downpour represents an increasing order of intensity, where each word signifies a stronger form of rainfall than the previous one.
Step 2: Applying the same logic to the second set.
Similarly, in the sequence ............ \(\rightarrow\) quarrel \(\rightarrow\) feud, the missing word should represent a milder form of conflict that can gradually intensify into a quarrel and eventually become a feud.
Step 3: Evaluating the options.
(A) bicker: This refers to a petty or minor argument, which can escalate into a quarrel and later develop into a feud. Hence, it fits the increasing order of intensity.
(B) bog: This word refers to a swamp or to being stuck, and has no relation to conflict or argument.
(C) dither: This means to be indecisive or hesitant, not related to disputes or intensity of conflict.
(D) dodge: This means to avoid something and does not indicate any form of argument or conflict.
Step 4: Conclusion.
The word bicker correctly completes the analogy by representing the lowest level of conflict that can increase in intensity to a quarrel and then to a feud.
Quick Tip: In analogy questions based on intensity, always arrange the words from the weakest form to the strongest form of meaning.
Statements:
1. All heroes are winners.
2. All winners are lucky people.
Inferences:
I. All lucky people are heroes.
II. Some lucky people are heroes.
III. Some winners are heroes.
Which of the above inferences can be logically deduced from statements 1 and 2?
View Solution
Step 1: Represent the statements logically.
All heroes are winners (Heroes \(\subseteq\) Winners).
All winners are lucky people (Winners \(\subseteq\) Lucky).
Hence, Heroes \(\subseteq\) Winners \(\subseteq\) Lucky.
Step 2: Evaluate Inference I.
“All lucky people are heroes” means Lucky \(\subseteq\) Heroes, which is the reverse of the given logic. Hence, this inference does not follow.
Step 3: Evaluate Inference II.
Since heroes exist and all heroes are lucky people, it is logically valid that some lucky people are heroes. This inference follows.
Step 4: Evaluate Inference III.
All heroes are winners, so heroes fall within winners. Hence, some winners are heroes. This inference also follows.
Step 5: Conclusion.
Only Inferences II and III can be logically deduced.
Quick Tip: In syllogism questions, universal statements allow valid “some” conclusions but not reverse universal conclusions.
A student was supposed to multiply a positive real number \(p\) with another positive real number \(q\). Instead, the student divided \(p\) by \(q\). If the percentage error in the student’s answer is 80%, the value of \(q\) is
View Solution
Step 1: Identify correct and incorrect values.
Correct value \(= p \times q\).
Incorrect value \(= \dfrac{p}{q}\).
Step 2: Use percentage error formula.
\[ Percentage Error = \left| \frac{Incorrect - Correct}{Correct} \right| \times 100 \]
Step 3: Substitute the given values.
\[ 80 = \left| \frac{\frac{p}{q} - pq}{pq} \right| \times 100 \]
\[ 0.8 = \left| \frac{1 - q^2}{q^2} \right| \]
Step 4: Solve the equation.
\[ \frac{q^2 - 1}{q^2} = 0.8 \Rightarrow q^2 - 1 = 0.8q^2 \Rightarrow 0.2q^2 = 1 \Rightarrow q^2 = 5 \Rightarrow q = \sqrt{5} \]
Step 5: Conclusion.
The correct value of \(q\) is \(\sqrt{5}\).
Quick Tip: Always express percentage error equations in terms of ratios before substituting values.
If the sum of the first 20 consecutive positive odd numbers is divided by \(20^2\), the result is
View Solution
Step 1: Recall the formula for sum of odd numbers.
The sum of the first \(n\) odd numbers is \(n^2\).
Step 2: Apply the formula.
Sum of first 20 odd numbers \(= 20^2 = 400\).
Step 3: Divide by \(20^2\).
\[ \frac{400}{20^2} = \frac{400}{400} = 1 \]
Step 4: Conclusion.
The required result is 1.
Quick Tip: The sum of the first \(n\) odd numbers is always equal to \(n^2\).
The ratio of the number of girls to boys in class VIII is the same as the ratio of the number of boys to girls in class IX. The total number of students (boys and girls) in classes VIII and IX is 450 and 360, respectively. If the number of girls in classes VIII and IX is the same, then the number of girls in each class is
View Solution
Step 1: Assume the number of girls in each class.
Let the number of girls in each class be \(x\).
Step 2: Express boys in each class.
Total students in class VIII = 450, so boys in class VIII = \(450 - x\).
Total students in class IX = 360, so boys in class IX = \(360 - x\).
Step 3: Use the given ratio condition.
\[ \frac{Girls in VIII}{Boys in VIII} = \frac{Boys in IX}{Girls in IX} \]
\[ \frac{x}{450 - x} = \frac{360 - x}{x} \]
Step 4: Solve the equation.
\[ x^2 = (450 - x)(360 - x) \]
\[ x^2 = 162000 - 810x + x^2 \]
\[ 810x = 162000 \Rightarrow x = 200 \]
Step 5: Conclusion.
The number of girls in each class is 200.
Quick Tip: When ratios are reversed between two groups, equate them carefully using algebraic variables.
In the given text, the blanks are numbered (i)–(iv). Select the best match for all the blanks.
Yoko Roi stands ....... as an author for standing ....... as an honorary fellow, after she stood ...... her writings that stand ...... the freedom of speech.
View Solution
Step 1: Analyze each blank contextually.
The sentence describes resistance, support, and advocacy related to freedom of speech.
Step 2: Evaluate phrasal verb usage.
Stand out means to be prominent.
Stand down means to resign or step aside.
Stand by means to support.
Stand for means to represent or support an idea.
Step 3: Fit the words into the sentence.
The correct sequence is:
(i) out — stands out as an author
(ii) down — standing down as an honorary fellow
(iii) by — stood by her writings
(iv) for — writings stand for freedom of speech
Step 4: Conclusion.
Option (D) correctly completes the sentence with appropriate phrasal verbs.
Quick Tip: Understanding common phrasal verbs is essential for sentence completion questions.
Seven identical cylindrical chalk-sticks are fitted tightly in a cylindrical container. The figure shows the arrangement of the chalk-sticks inside the cylinder. The length of the container is equal to the length of the chalk-sticks. The ratio of the occupied space to the empty space of the container is
View Solution
Step 1: Understand the geometry of the arrangement.
There are 7 identical cylindrical chalk-sticks: one at the center and six surrounding it symmetrically. All chalk-sticks have the same radius \(r\) and the same height as the container.
Step 2: Determine the radius of the container.
The six outer chalk-sticks touch the central chalk-stick and the container wall. Hence, the radius of the container is equal to \(3r\).
Step 3: Calculate occupied volume.
Volume of one chalk-stick \(= \pi r^2 h\).
Volume of 7 chalk-sticks \(= 7\pi r^2 h\).
Step 4: Calculate total volume of the container.
Volume of container \(= \pi (3r)^2 h = 9\pi r^2 h\).
Step 5: Calculate empty space.
Empty space \(= 9\pi r^2 h - 7\pi r^2 h = 2\pi r^2 h\).
Step 6: Find the required ratio.
\[ Ratio = \frac{Occupied space}{Empty space} = \frac{7\pi r^2 h}{2\pi r^2 h} = \frac{7}{2} \]
Step 7: Conclusion.
The ratio of occupied space to empty space is \(\dfrac{7}{2}\).
Quick Tip: In packing problems, always determine the container dimensions from the extreme contact points of the objects.
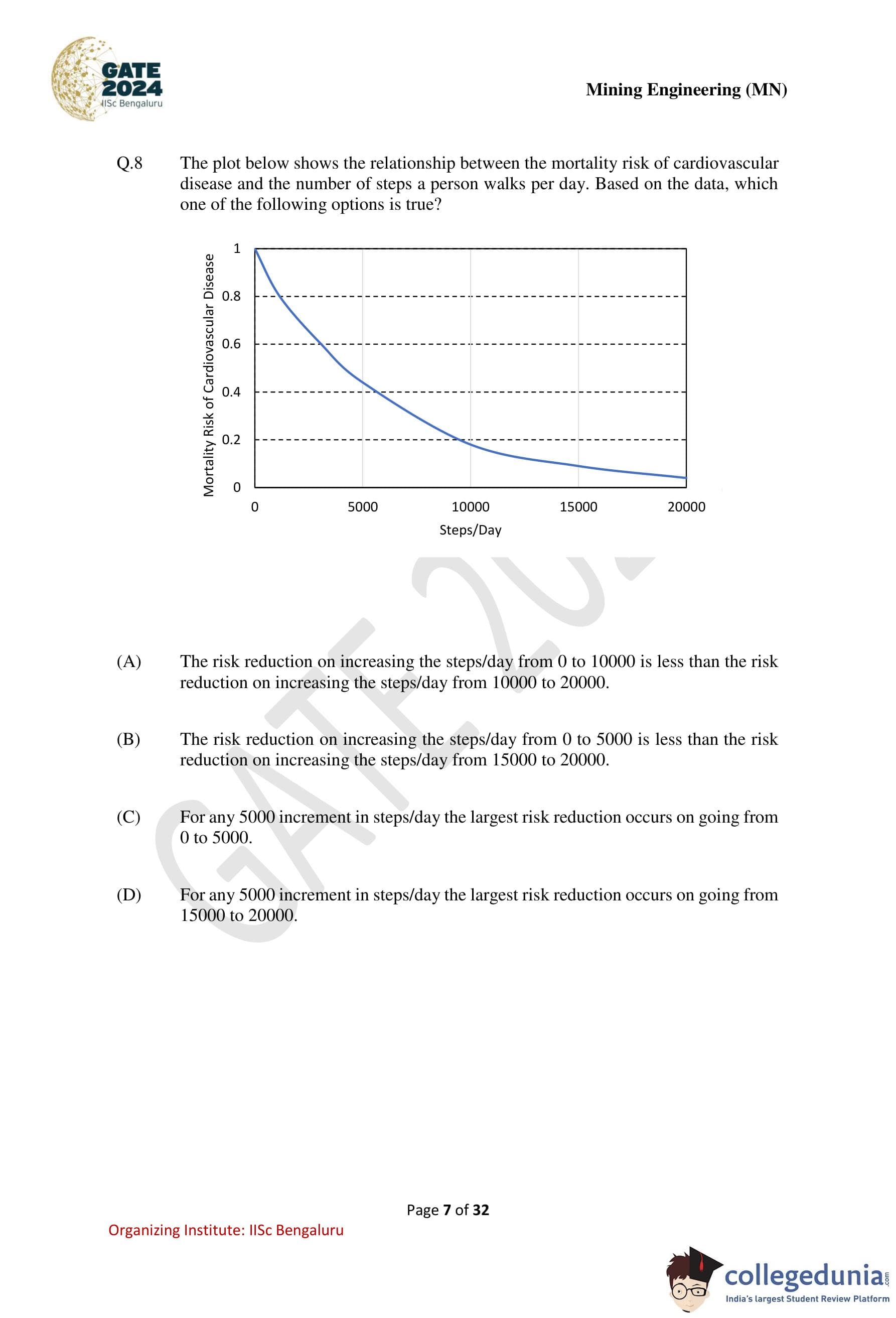
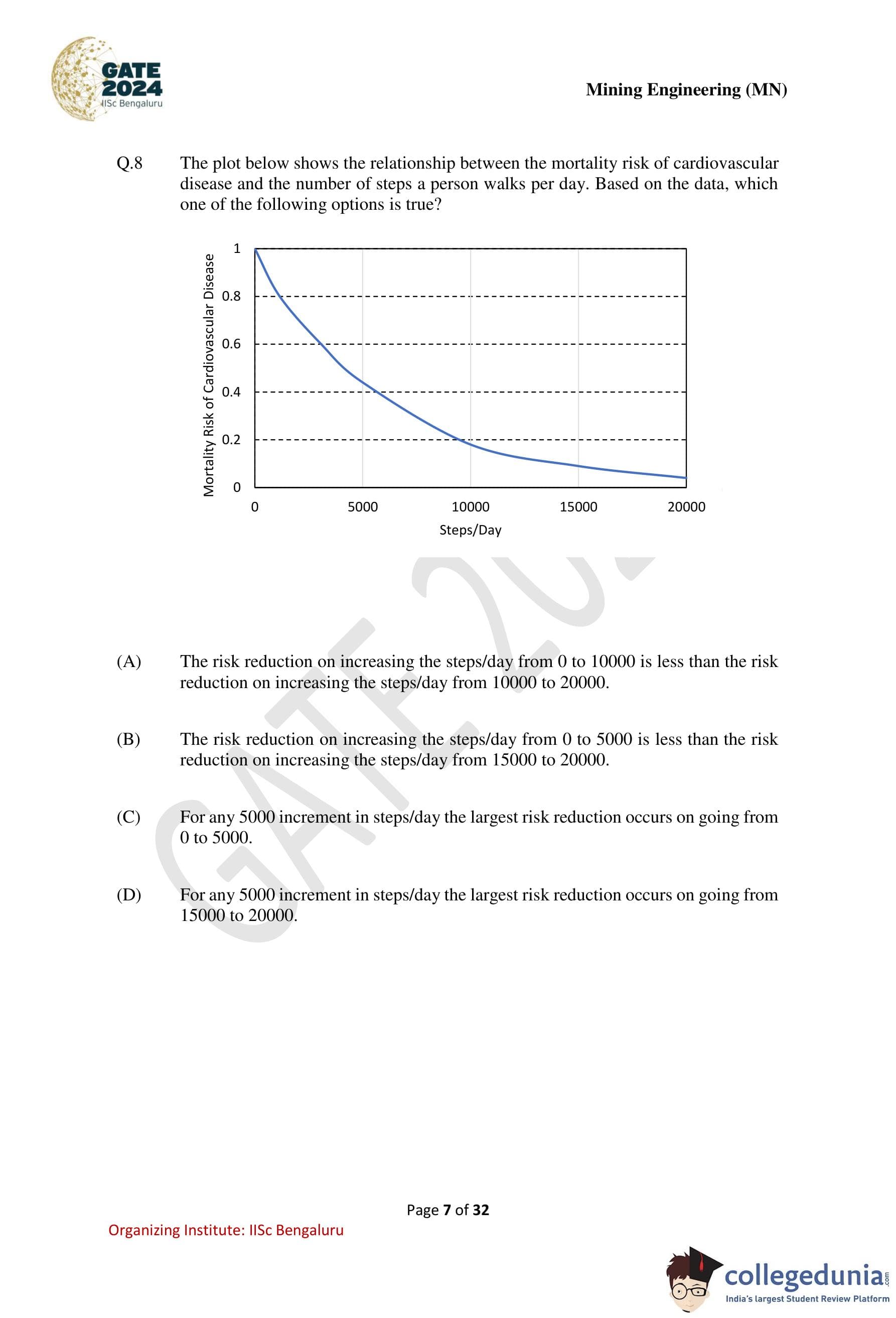
The plot shows the relationship between the mortality risk of cardiovascular disease and the number of steps a person walks per day. Based on the data, which one of the following options is true?
View Solution
Step 1: Observe the shape of the curve.
The graph shows a steep decline in mortality risk at lower step counts, followed by a gradual flattening as steps/day increase.
Step 2: Compare equal step increments.
From 0 to 5000 steps/day, the reduction in risk is the steepest.
From 5000 to 10000 and further intervals, the decrease becomes progressively smaller.
Step 3: Evaluate the options.
Option (C) correctly states that the maximum reduction for any 5000-step increment occurs between 0 and 5000 steps/day.
Step 4: Conclusion.
The largest marginal benefit in reducing mortality risk occurs at the lowest step range.
Quick Tip: For graph-based questions, compare slopes rather than absolute values to identify maximum changes.
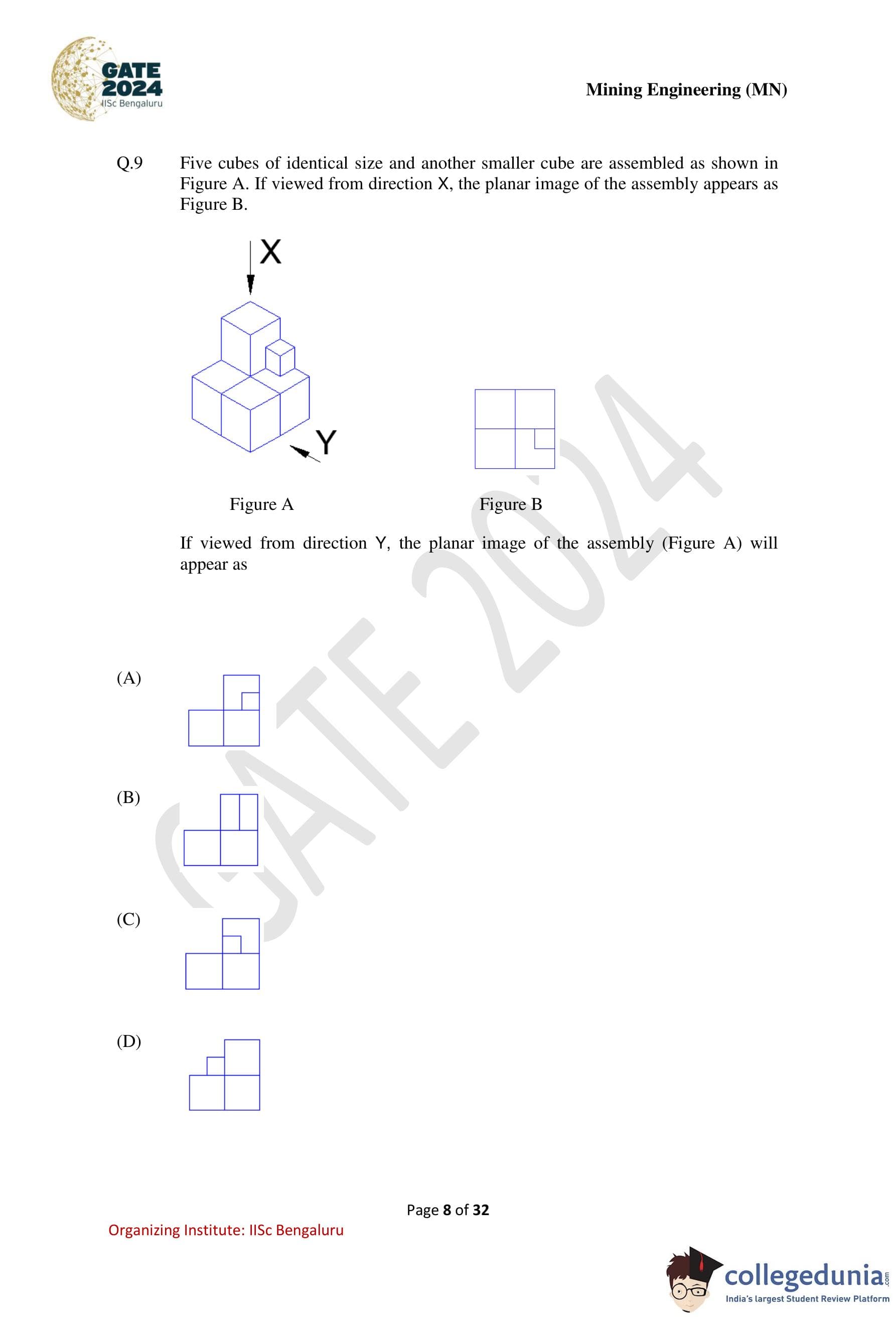
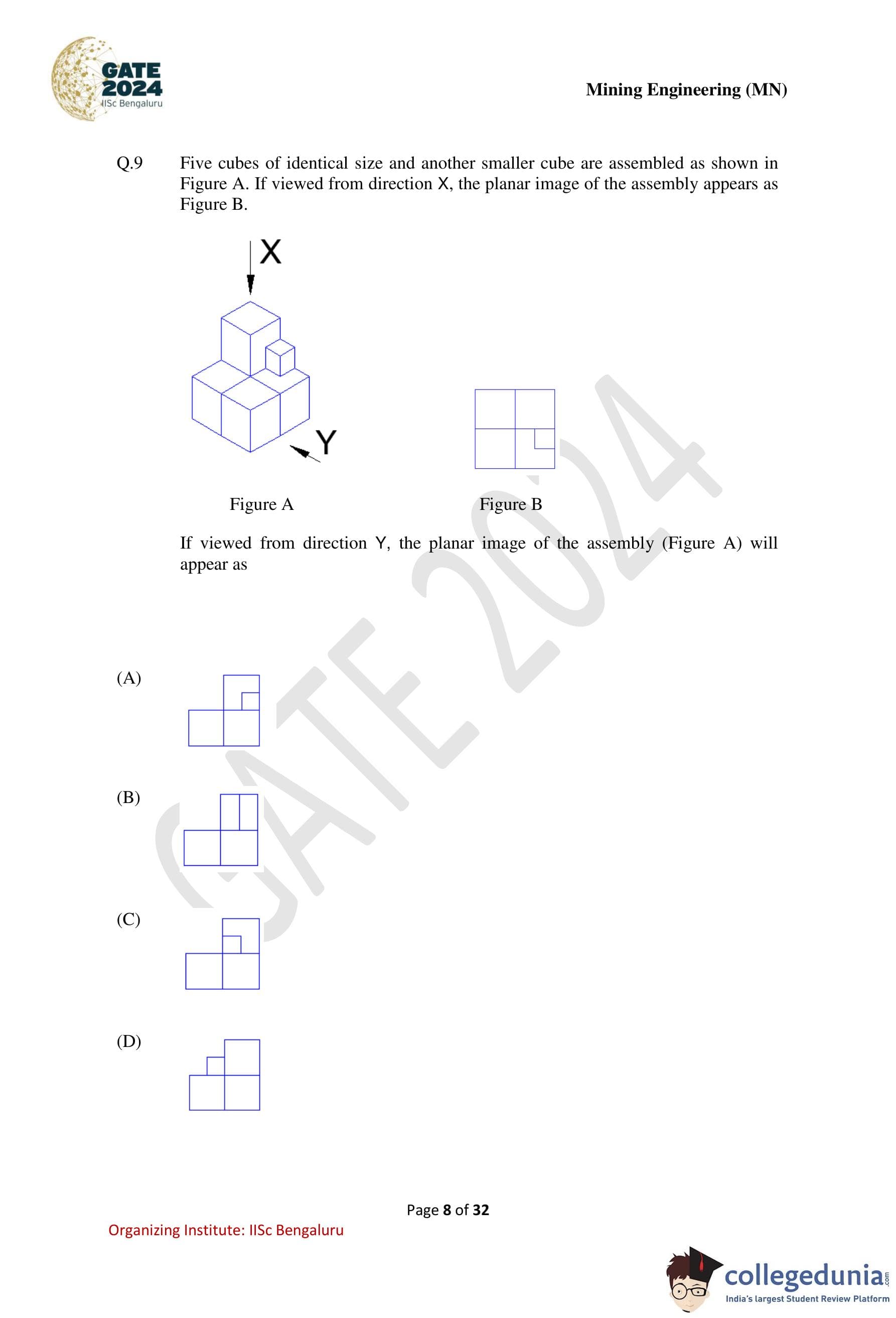
Five cubes of identical size and another smaller cube are assembled as shown in Figure A. If viewed from direction X, the planar image of the assembly appears as Figure B. If viewed from direction Y, the planar image of the assembly (Figure A) will appear as
View Solution
Step 1: Understand the given 3D arrangement.
The assembly consists of five identical cubes forming a stepped structure, along with one smaller cube placed on the upper right side of the structure. The directions X and Y indicate different viewing angles for obtaining planar (top/side) projections.
Step 2: Analyze the given planar image from direction X.
The planar image from direction X (Figure B) confirms the relative positions of the cubes when projected onto a plane. This helps in fixing the horizontal and vertical alignment of the cubes in the 3D structure.
Step 3: Determine the view from direction Y.
When viewed from direction Y, the depth information changes while the relative stacking and lateral positions of the cubes must be preserved according to the original assembly. The smaller cube appears offset on the upper right portion when projected in this direction.
Step 4: Compare with the given options.
Option (A) correctly shows:
– The base formed by the larger cubes,
– The stepped arrangement, and
– The correct placement of the smaller cube in the planar view from direction Y.
The other options either misplace the smaller cube or distort the relative positions of the larger cubes.
Step 5: Conclusion.
The correct planar image of the assembly when viewed from direction Y is shown in Option (A).
Quick Tip: For 3D visualization problems, first lock the relative positions using the given view, then mentally rotate the object to obtain the required projection.
Visualize a cube that is held with one of the four body diagonals aligned to the vertical axis. Rotate the cube about this axis such that its view remains unchanged. The magnitude of the minimum angle of rotation is
View Solution
Step 1: Understand the axis of rotation.
A cube has four body diagonals, each joining a pair of opposite vertices. When one body diagonal is aligned vertically, the cube is symmetric about this diagonal.
Step 2: Identify the rotational symmetry.
About a body diagonal, a cube exhibits three-fold rotational symmetry. This means the cube looks exactly the same after certain rotations about this diagonal.
Step 3: Determine the angle corresponding to three-fold symmetry.
Since a full rotation is \(360^\circ\) and the symmetry is of order 3, the cube matches its original orientation after rotations of:
\[ \frac{360^\circ}{3} = 120^\circ \]
Step 4: Check for smaller angles.
Any rotation smaller than \(120^\circ\) will not bring the cube back to an identical visual configuration. Hence, \(120^\circ\) is the minimum required angle.
Step 5: Conclusion.
The minimum angle of rotation about the body diagonal for which the cube appears unchanged is \(120^\circ\).
Quick Tip: A cube has 3-fold rotational symmetry about each body diagonal, 4-fold about face normals, and 2-fold about edge centers.
Exposure to loud impulsive noise may lead to
In a self-contained closed-circuit breathing apparatus,
A rectangular mine airway of 2.0 m width and 2.5 m height has a bend with deflection of \(\pi/4\) radian. If the radius of curvature of the bend is 4.0 m, the shock factor of the bend is (round off to three decimals)
In an underground coal mine, two fatalities and three serious bodily injuries occurred during the year 2022. The average daily employment is 1100 and annual working days is 300. The severity index as per DGMS guideline for the mine is
For a geared engine winding system, the man winding cage is placed at its normal position at pit top of the shaft. As per CMR 2017, the minimum space, in m, between the center of the hole of the detaching hook attached to the rope shackle and detaching bell plate is
The value of integral, \(I = \int_{0}^{\pi/4} 4 \cos x \sin^{3} x \, dx\) is
The value of \(\displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0} \left( \frac{n \sin 5x}{\sin 3x} \right)\) is
The spherical semivariogram model \(\gamma(h)\) is represented by the following expression, where \(h\) is the lag distance.
\[ \gamma(h) = \begin{cases} C_0, & for h = 0
C_0 + (C - C_0) \left[ 1.5 \frac{h}{a} - 0.5 \left( \frac{h}{a} \right)^3 \right], & for 0 < h \le a
C, & for h > a \end{cases} \]
The parameters \(C_0\), \(C\), and \(a\) are respectively known as
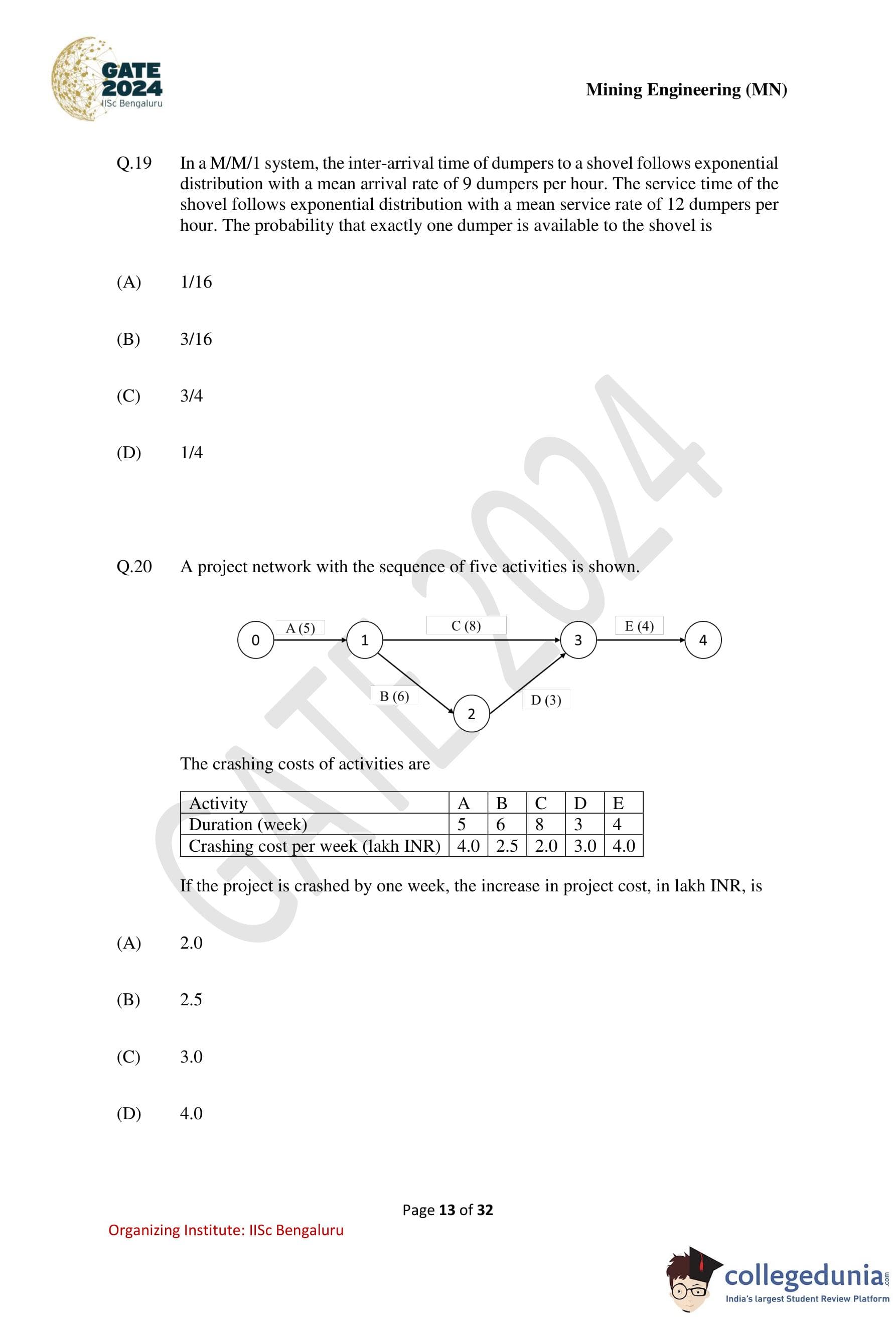
In an M/M/1 system, the inter-arrival time of dumpers to a shovel follows exponential distribution with a mean arrival rate of 9 dumpers per hour. The service time of the shovel follows exponential distribution with a mean service rate of 12 dumpers per hour. The probability that exactly one dumper is available at the shovel is
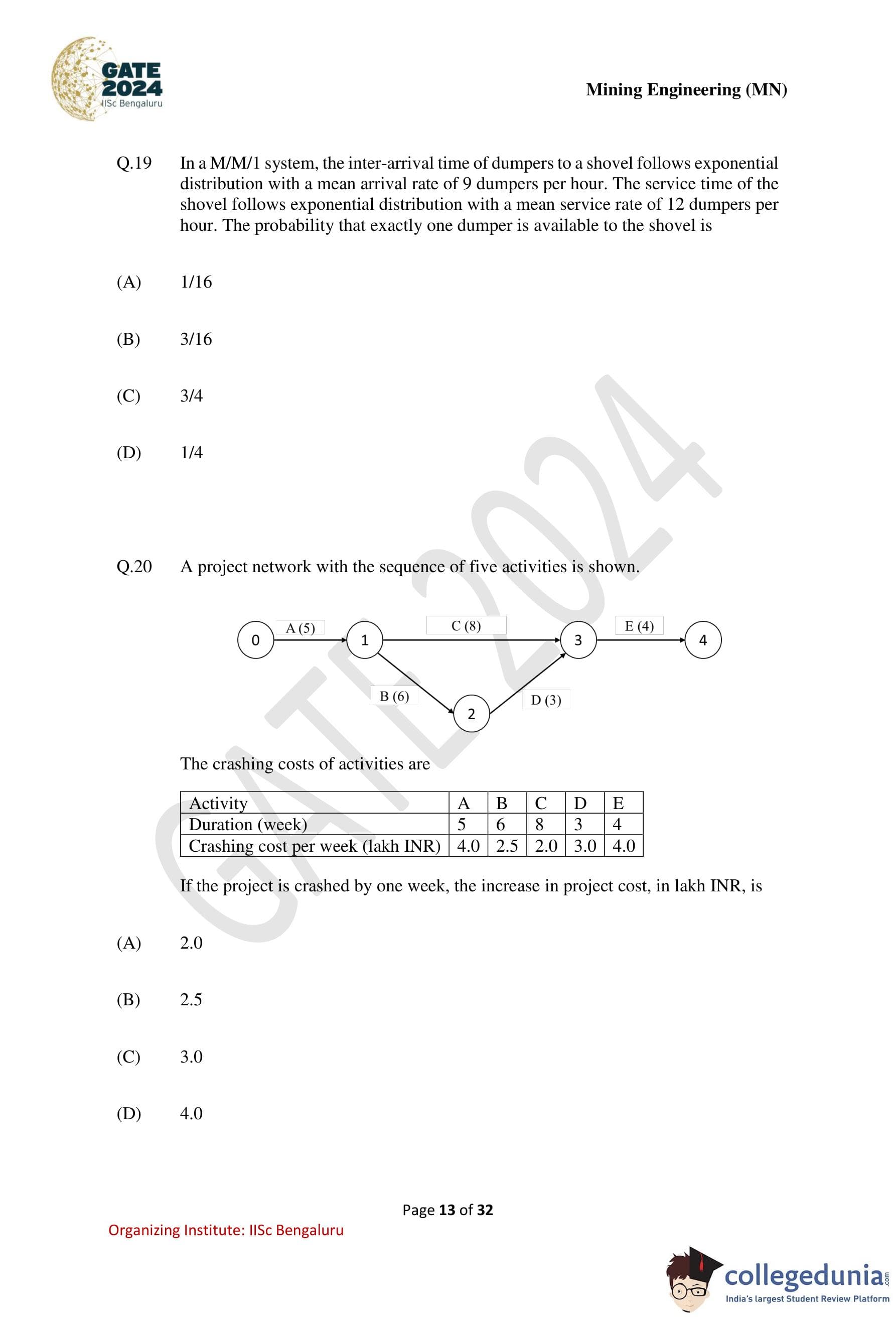
A project network with the sequence of five activities is shown.
The crashing costs of activities are given.If the project is crashed by one week, the increase in project cost, in lakh INR, is
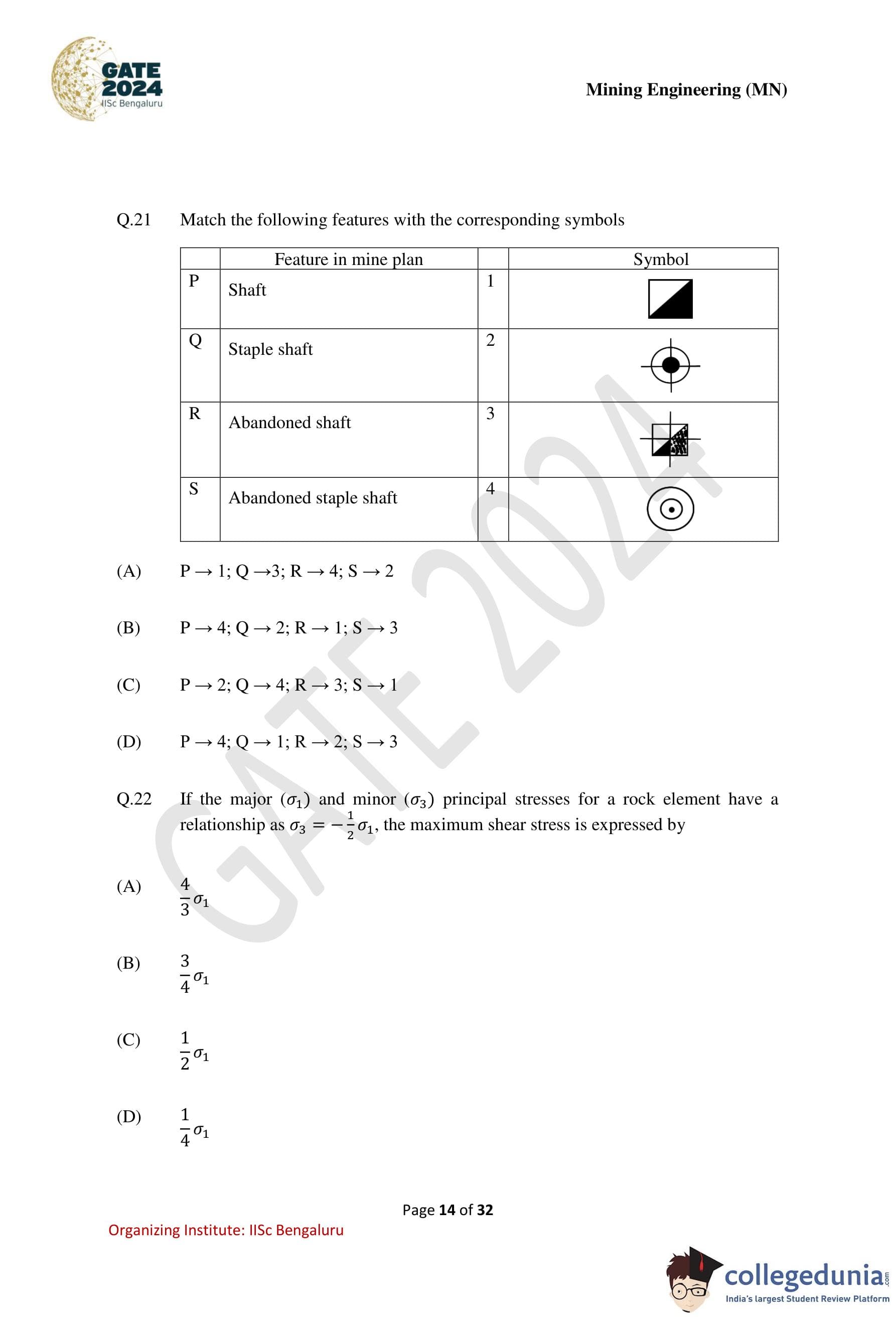
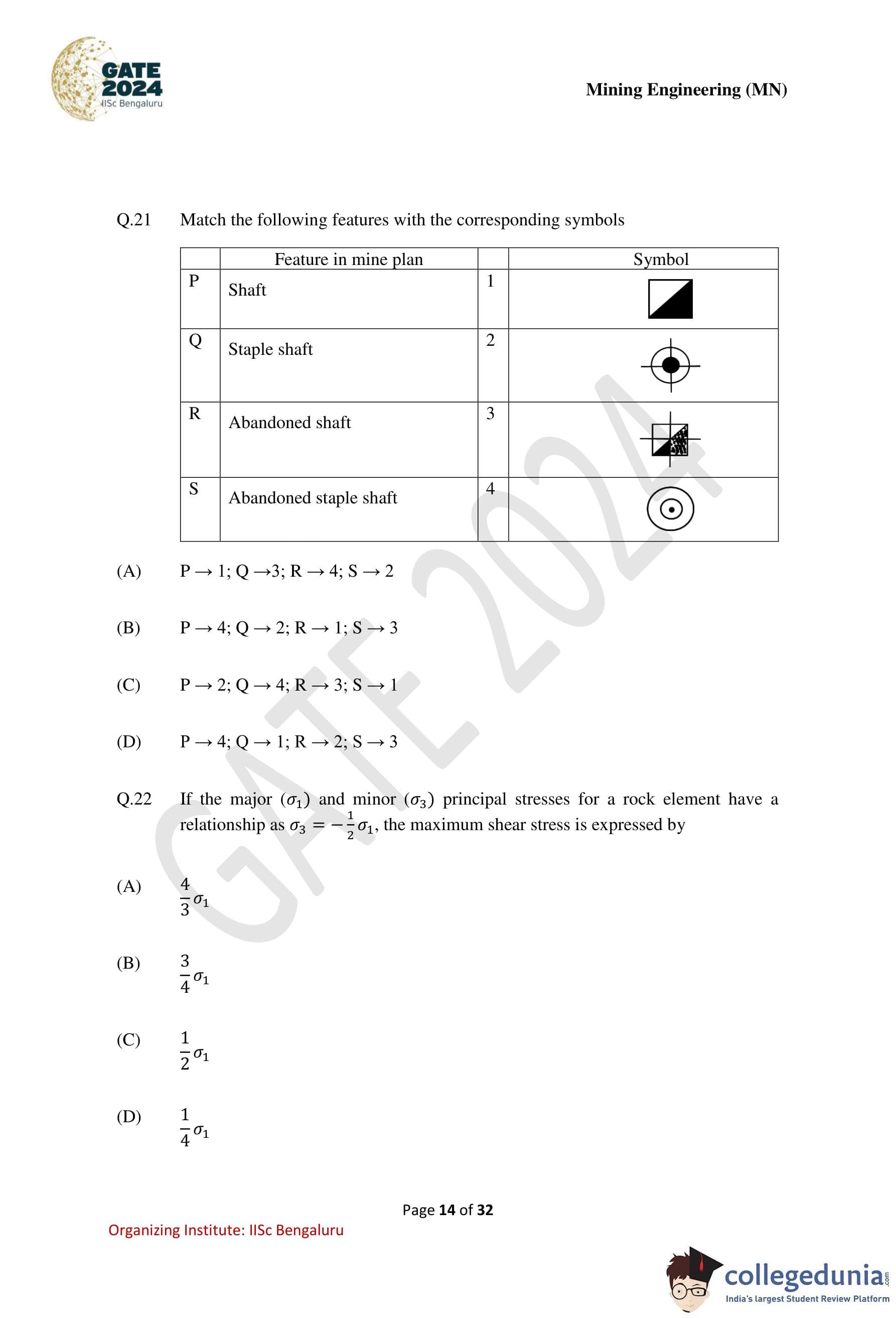
Match the following features with the corresponding symbols.
If the major \((\sigma_1)\) and minor \((\sigma_3)\) principal stresses for a rock element have a relationship as \(\sigma_3 = -\dfrac{1}{2}\sigma_1\), the maximum shear stress is expressed by
The ore that is NOT used for commercial extraction of metal is
The function of District Mineral Foundation established by state governments in India, is to
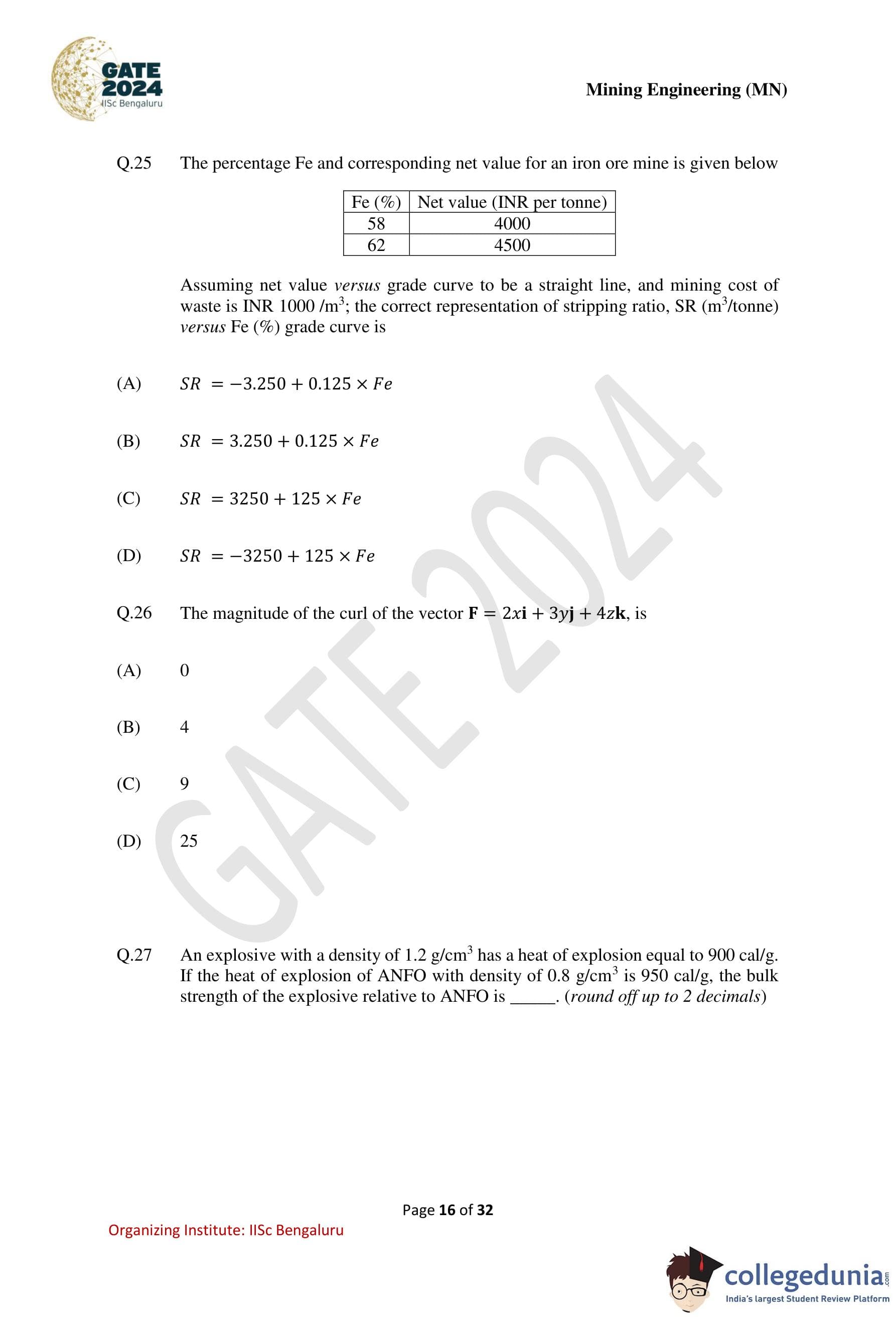
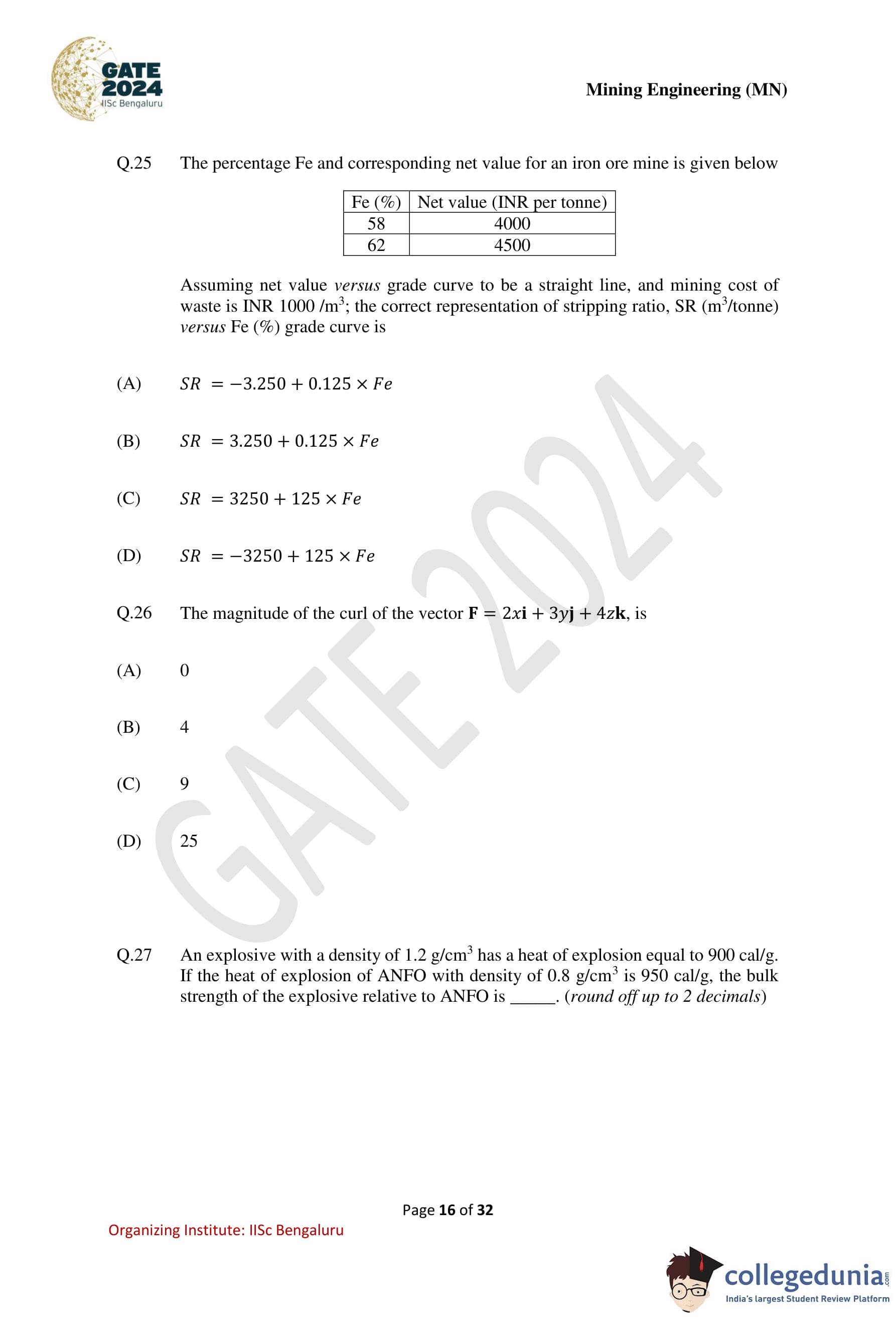
The percentage Fe and corresponding net value for an iron ore mine is given below.
Assuming net value versus grade curve to be a straight line, and mining cost of waste is INR 1000/m\(^3\), the correct representation of stripping ratio, SR (m\(^3\)/tonne) versus Fe (%) grade curve is
The magnitude of the curl of the vector \(\vec{F} = 2x\hat{i} + 3y\hat{j} + 4z\hat{k}\) is
An explosive with a density of 1.2 g/cm\(^3\) has a heat of explosion equal to 900 cal/g. If the heat of explosion of ANFO with density of 0.8 g/cm\(^3\) is 950 cal/g, the bulk explosive relative strength of the explosive relative to ANFO is .......... (round off up to 2 decimals).
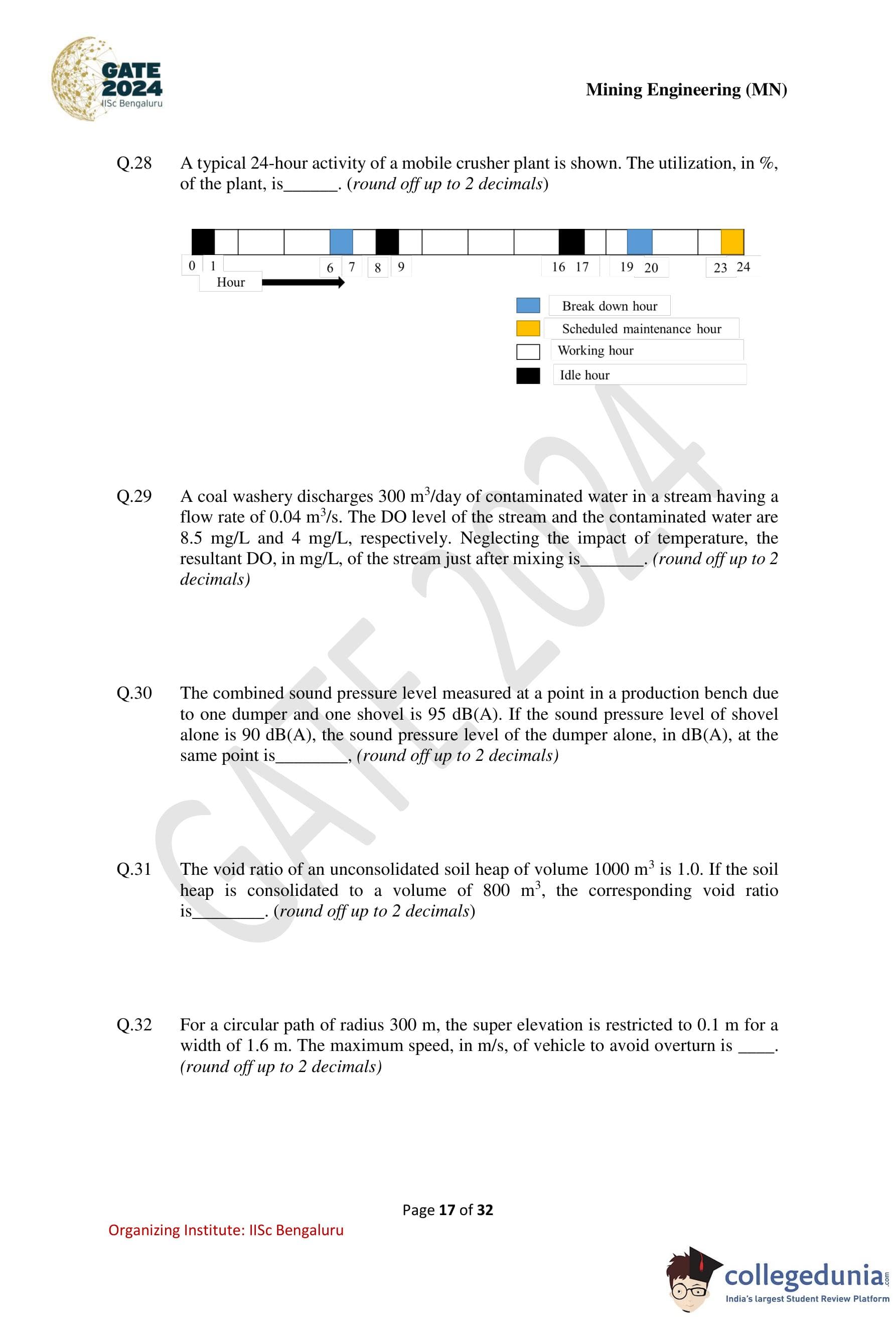
A typical 24-hour activity of a mobile crusher plant is shown. The utilization, in %, of the plant is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
A coal washery discharges 300 m\(^3\)/day of contaminated water in a stream having a flow rate of 0.04 m\(^3\)/s. The DO level of the stream and the contaminated water are 8.5 mg/L and 4 mg/L, respectively. Neglecting the impact of temperature, the resultant DO, in mg/L, of the stream just after mixing is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
The combined sound pressure level measured at a point in a production bench due to one dumper and one shovel is 95 dB(A). If the sound pressure level of shovel alone is 90 dB(A), the sound pressure level of the dumper alone, in dB(A), at the same point is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
The void ratio of an unconsolidated soil heap of volume 1000 m\(^3\) is 1.0. If the soil heap is consolidated to a volume of 800 m\(^3\), the corresponding void ratio is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
For a circular path of radius 300 m, the super elevation is restricted to 0.1 m for a width of 1.6 m. The maximum speed, in m/s, of vehicle to avoid overturn is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
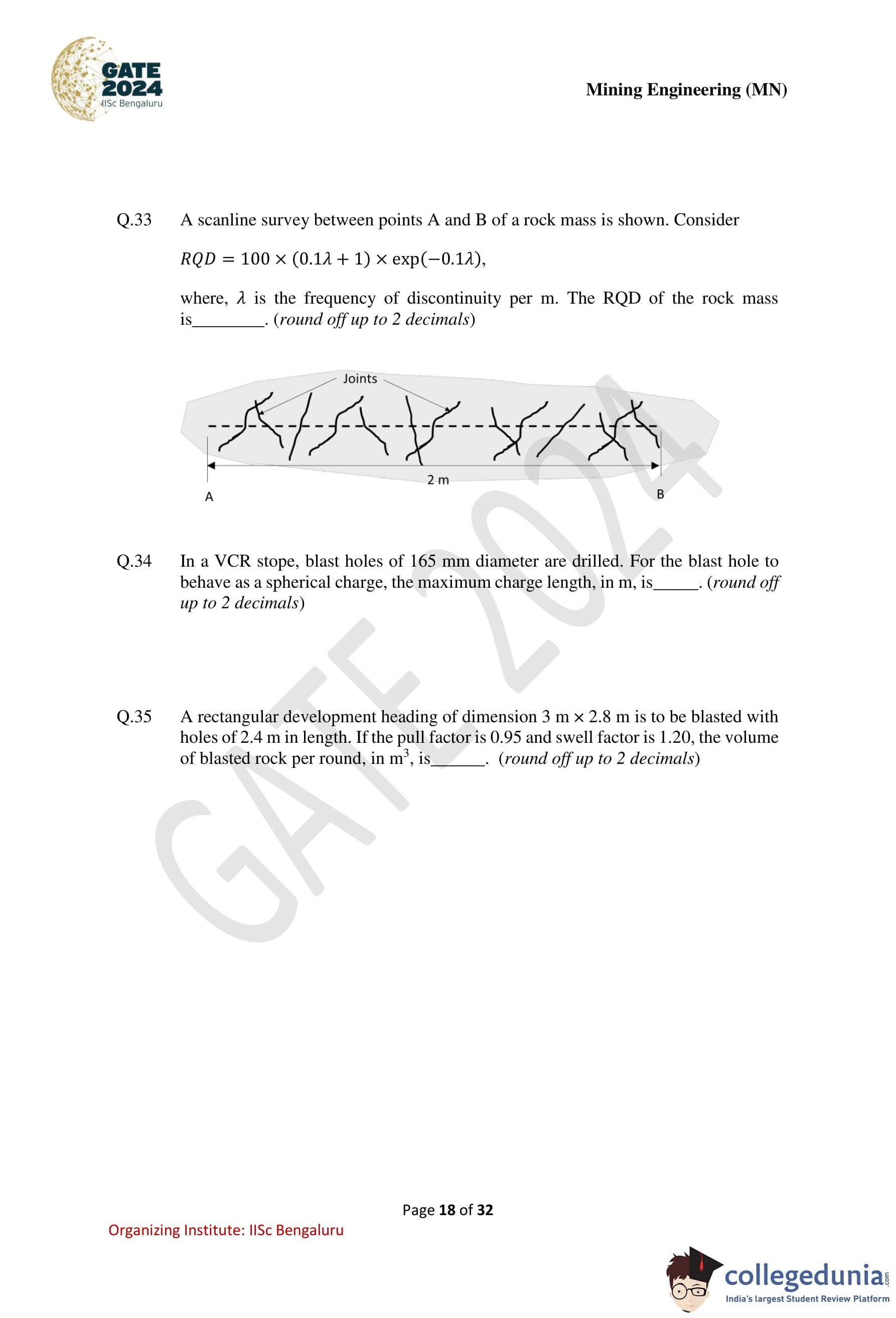
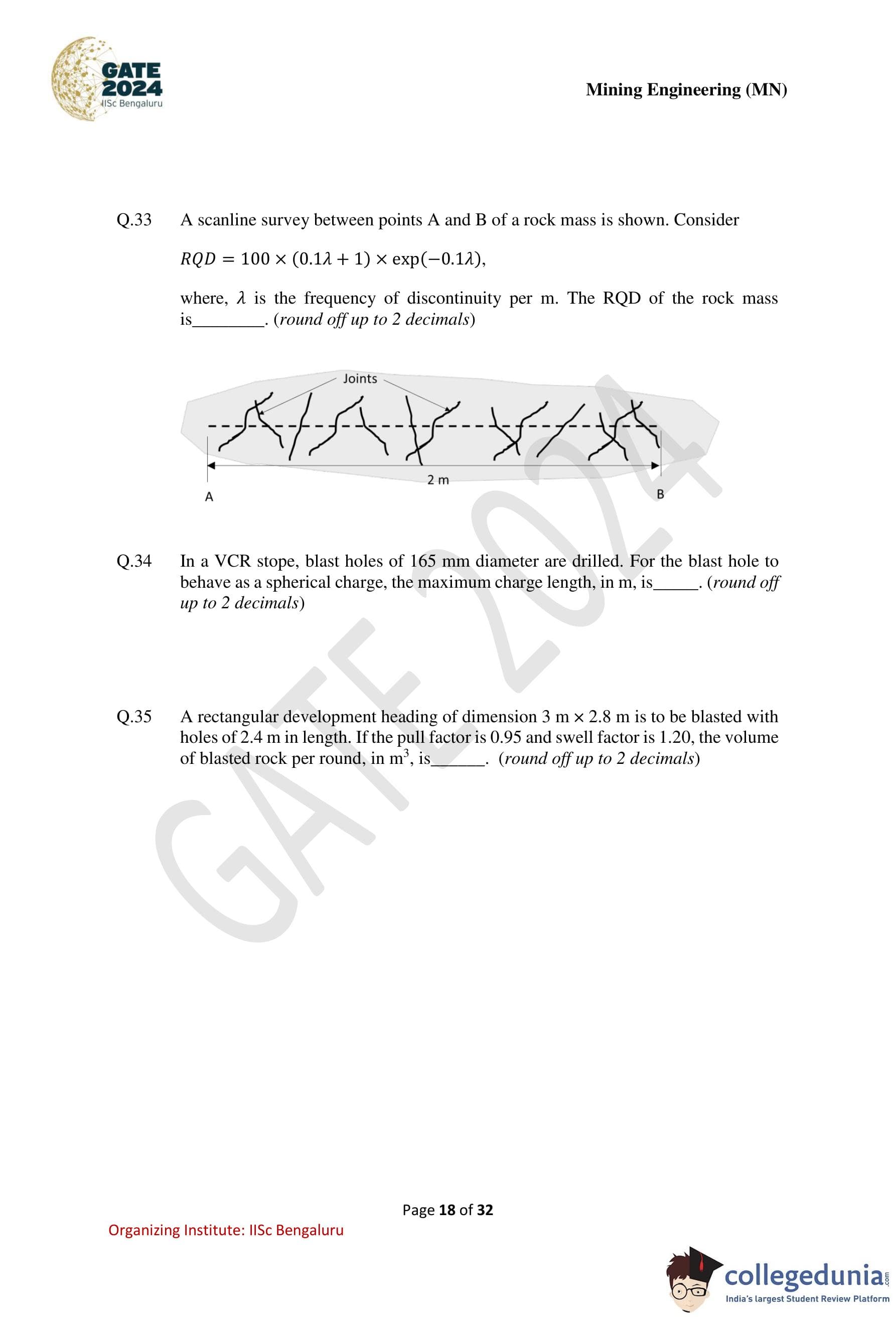
A scanline survey between points A and B of a rock mass is shown. Consider \(RQD = 100 \times (0.1\lambda + 1)\times \exp(-0.1\lambda)\),
where \(\lambda\) is the frequency of discontinuity per m. The RQD of the rock mass is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
In a VCR stope, blast holes of 165 mm diameter are drilled. For the blast hole to behave as a spherical charge, the maximum charge length, in m, is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
A rectangular development heading of dimension \(3\) m \(\times\) \(2.8\) m is to be blasted with holes of \(2.4\) m in length. If the pull factor is \(0.95\) and swell factor is \(1.20\), the volume of blasted rock per round, in m\(^3\), is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
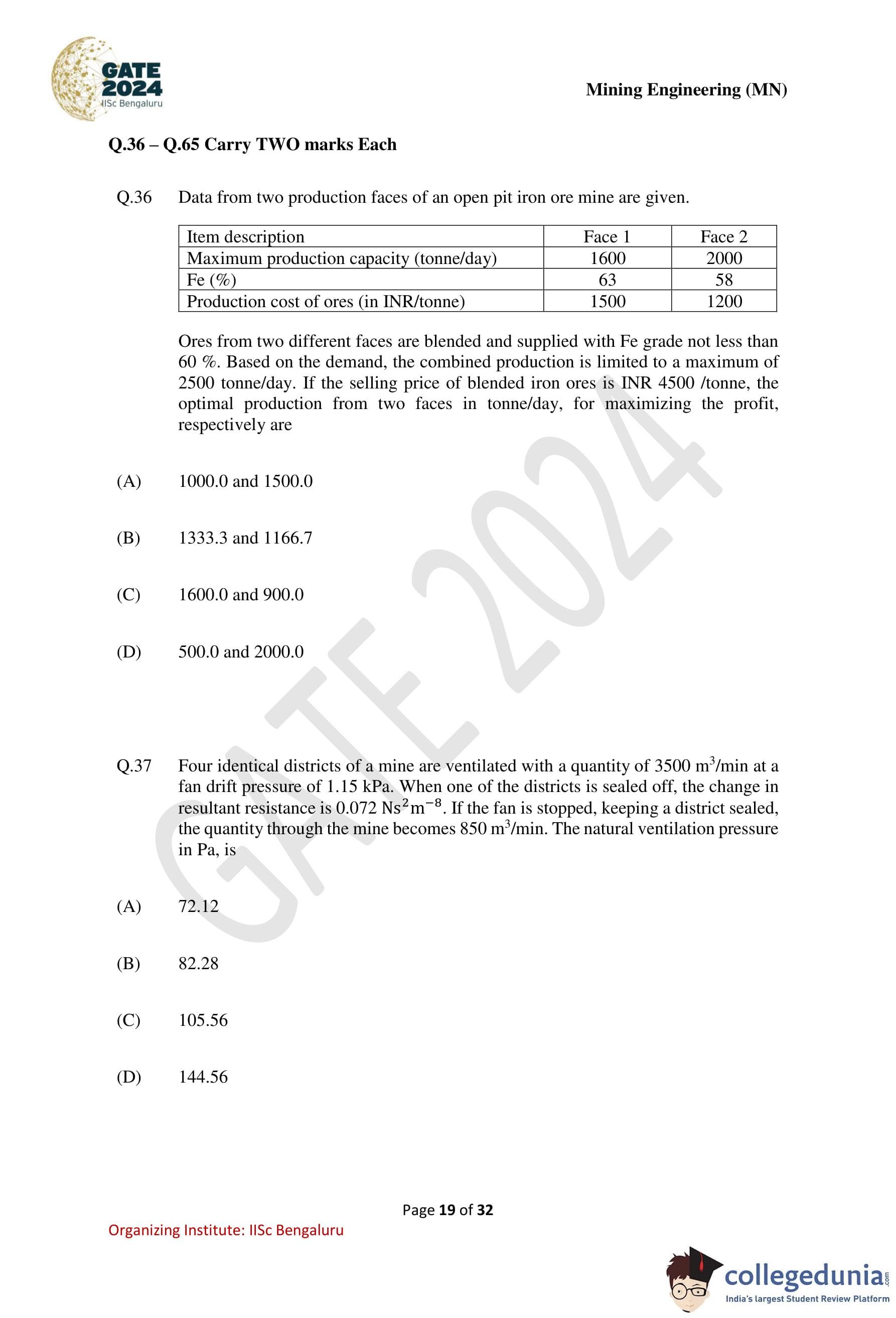
Data from two production faces of an open pit iron ore mine are given. Ores from two different faces are blended and supplied with Fe grade not less than 60%. Based on the demand, the combined production is limited to a maximum of 2500 tonne/day. If the selling price of blended iron ores is INR 4500/tonne, the optimum production from two faces in tonne/day, for maximizing the profit, respectively are
Four identical districts of a mine are ventilated with a quantity of 3500 m\(^3\)/min at a fan drift pressure of 1.15 kPa. When one of the districts is sealed off, the change in resultant resistance is 0.072 Ns\(^2\)m\(^{-8}\). If the fan is stopped, keeping a district sealed, the quantity through the mine becomes 850 m\(^3\)/min. The natural ventilation pressure, in Pa, is
Matrix \(A = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 4 & 3
5 & 2 & 1
6 & 4 & 3 \end{bmatrix}\), and \(B = A - A^T\), then \(B\) is
The roof convergence data for 30 days at a monitoring station in a coal mine gallery is given. The management decides on a Trigger Action Response Plan (TARP) if the following two premises occur simultaneously:
Premise 1: Rate of convergence exceeds 1.5 mm/day between two consecutive measurements.
Premise 2: Rate of cumulative increase in convergence exceeds 1.0 mm/day.
Identify the day on which TARP is enforced in that gallery.
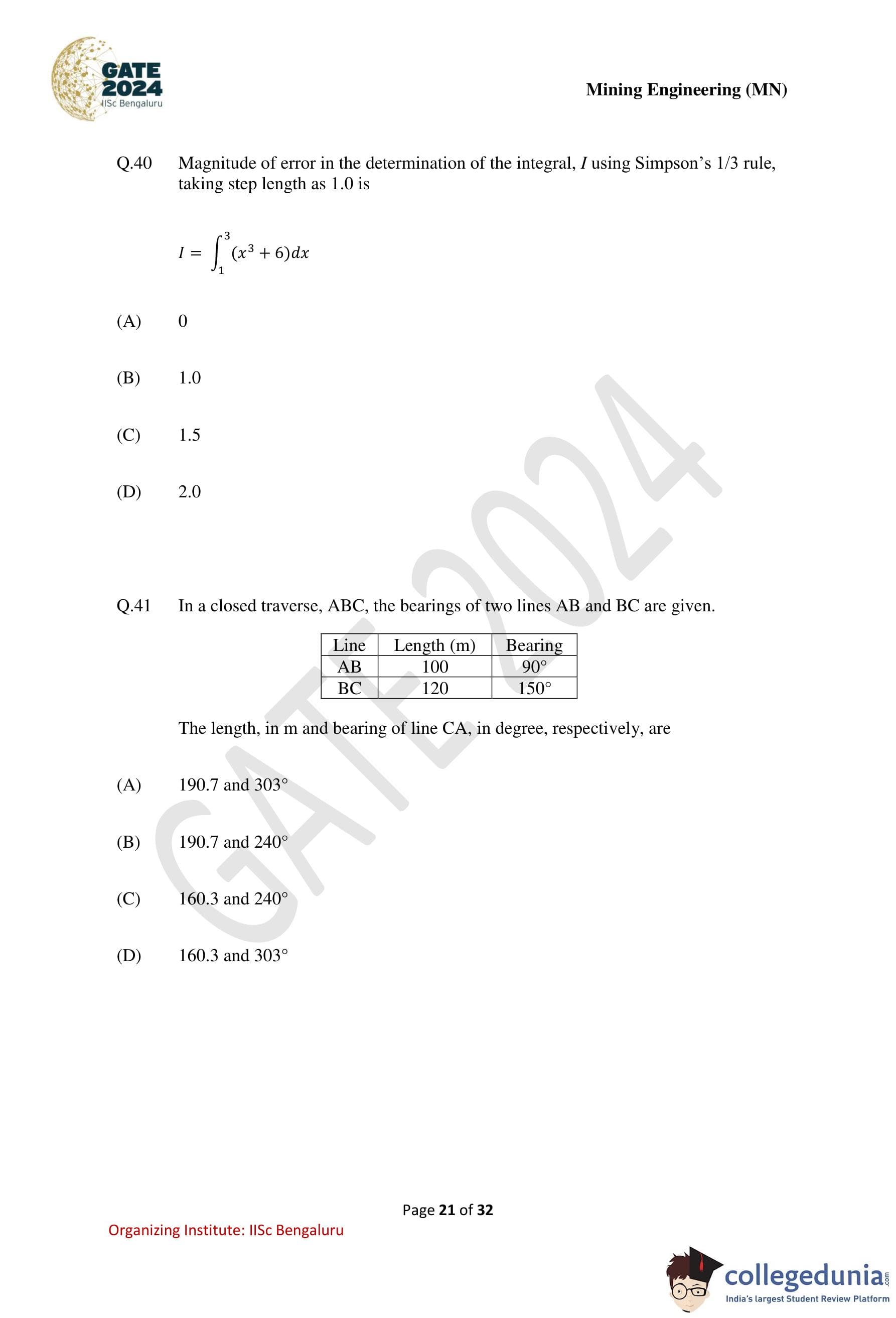
Magnitude of error in the determination of the integral, \(I\), using Simpson’s 1/3 rule, taking step length as 1.0 is
\[ I = \int_{1}^{3} (x^3 + 6)\,dx \]
In a closed traverse, ABC, the bearings of two lines AB and BC are given.
The length, in m, and bearing of line CA, in degree, respectively, are
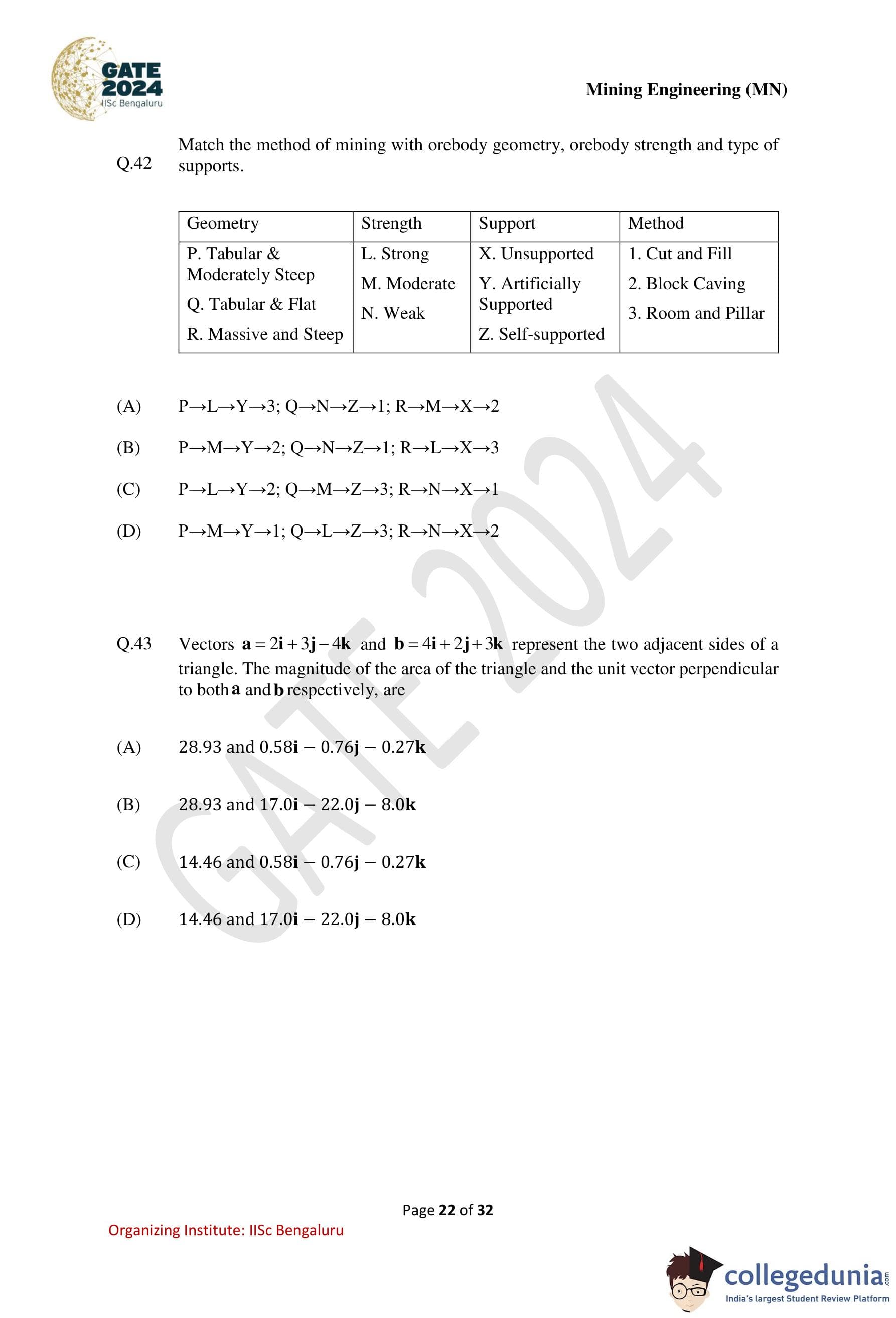
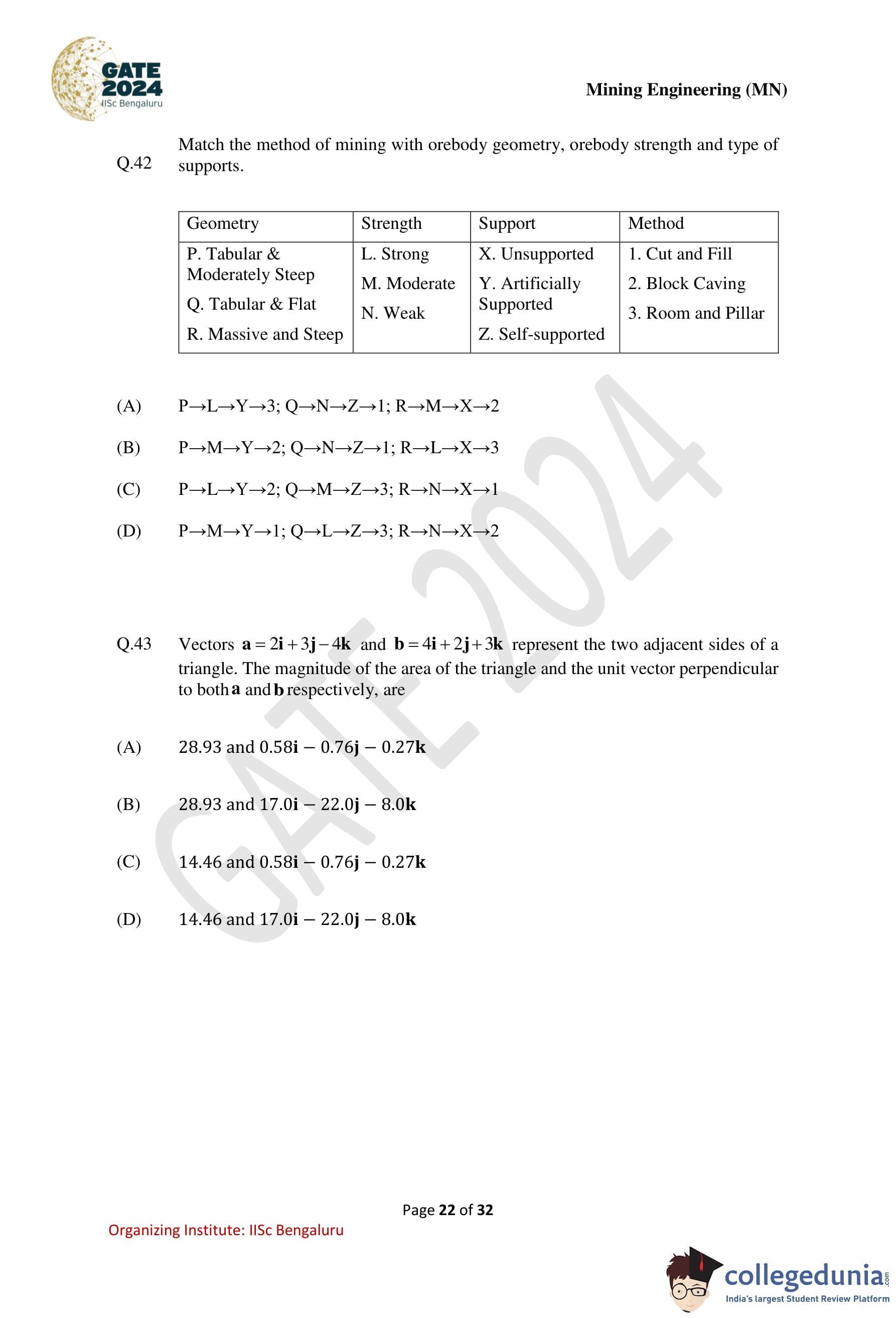
Match the method of mining with orebody geometry, orebody strength and type of supports.
Vectors \(\vec{a} = 2\hat{i} + 3\hat{j} - 4\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{b} = 4\hat{i} + 2\hat{j} + 3\hat{k}\) represent the two adjacent sides of a triangle. The magnitude of the area of the triangle and the unit vector perpendicular to both \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\) respectively, are
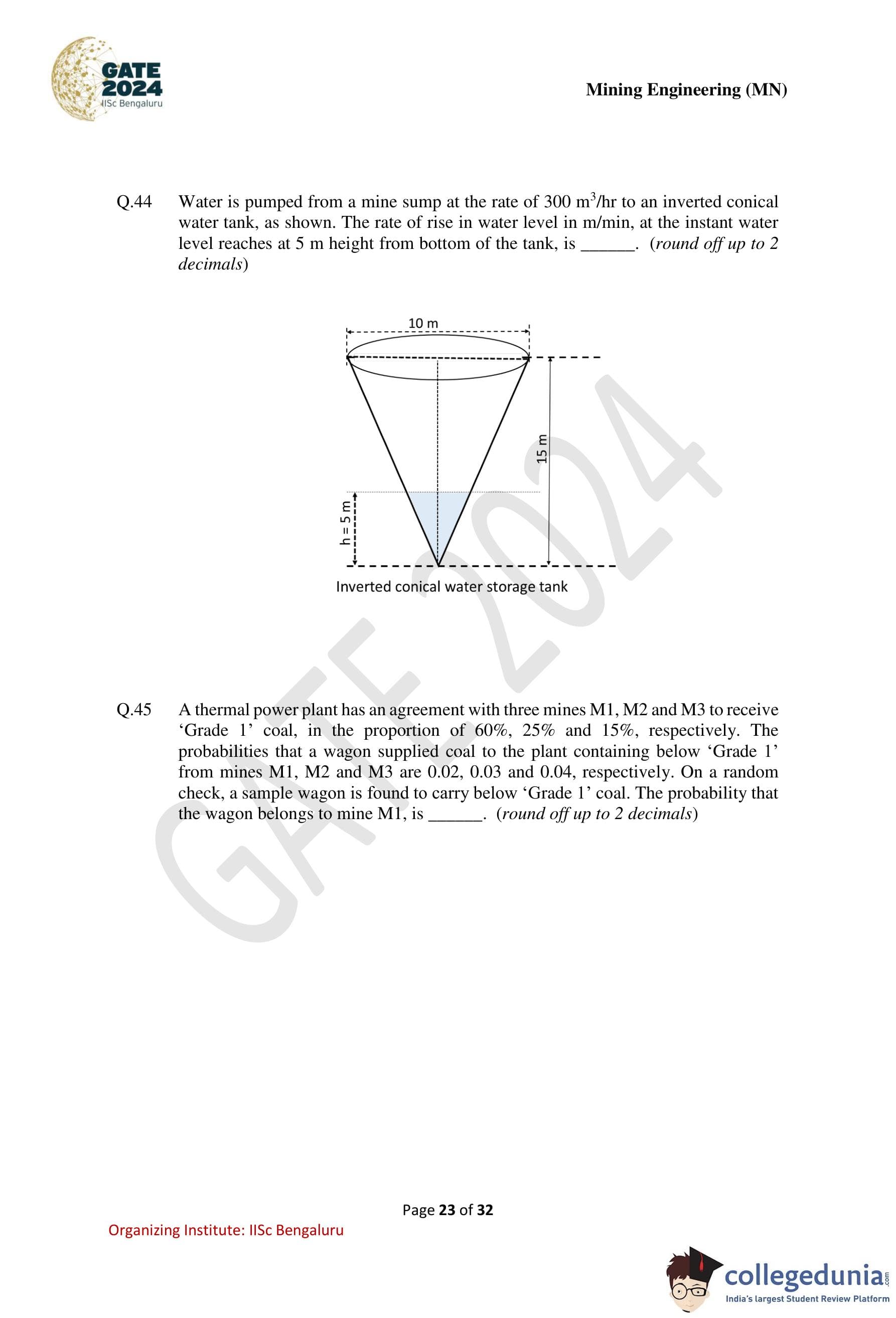
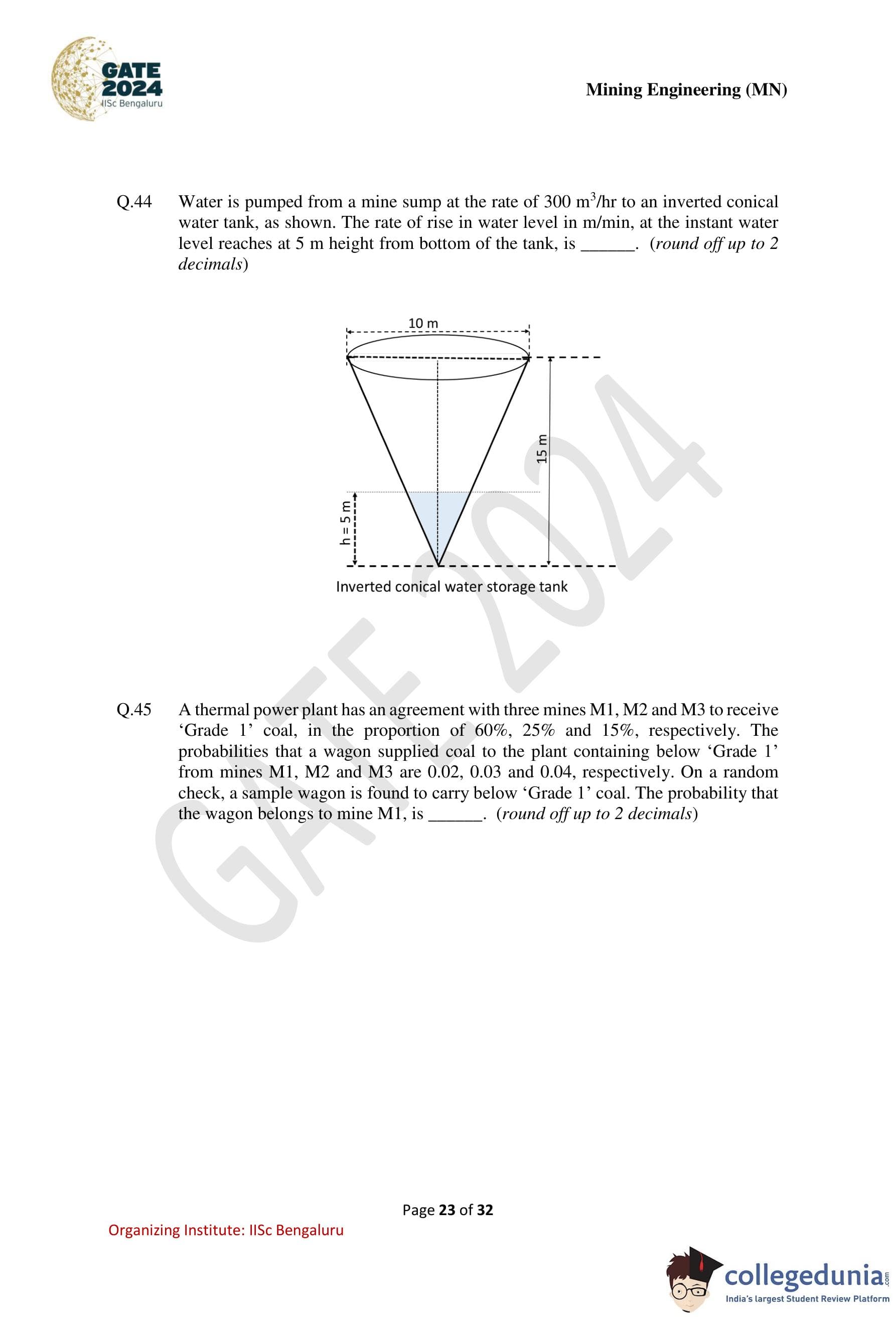
Water is pumped from a mine sump at the rate of \(300\) m\(^3\)/hr to an inverted conical water tank, as shown. The rate of rise in water level, in m/min, at the instant water level reaches at \(5\) m height from bottom of the tank is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
A thermal power plant has an agreement with three mines M1, M2 and M3 to receive `Grade 1' coal in the proportion of 60%, 25% and 15%, respectively. The probabilities that a wagon supplied coal to the plant containing below `Grade 1' coal from mines M1, M2 and M3 are 0.02, 0.03 and 0.04, respectively. On a random check, a sample wagon is found to carry below `Grade 1' coal. The probability that the wagon belongs to mine M1 is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
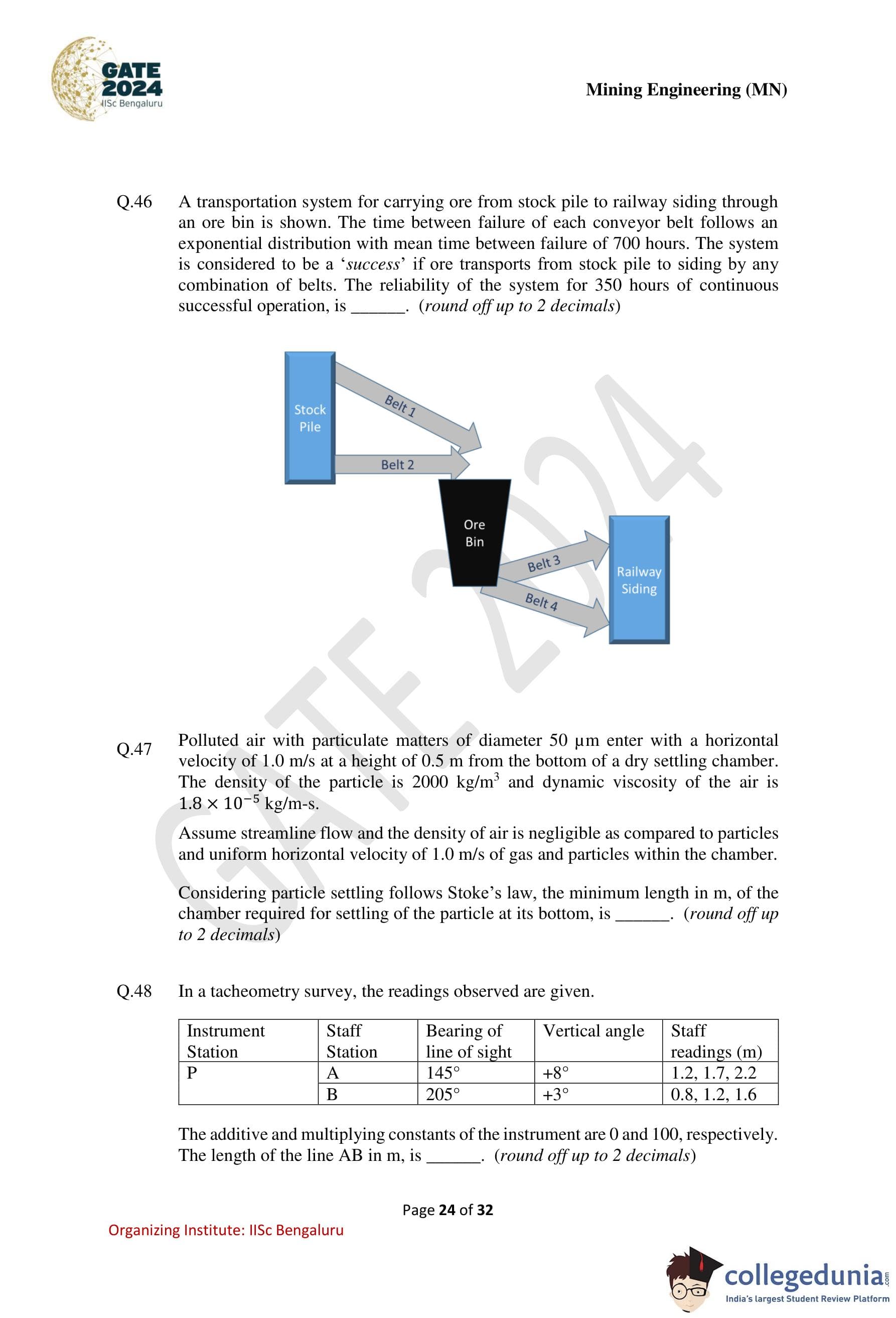
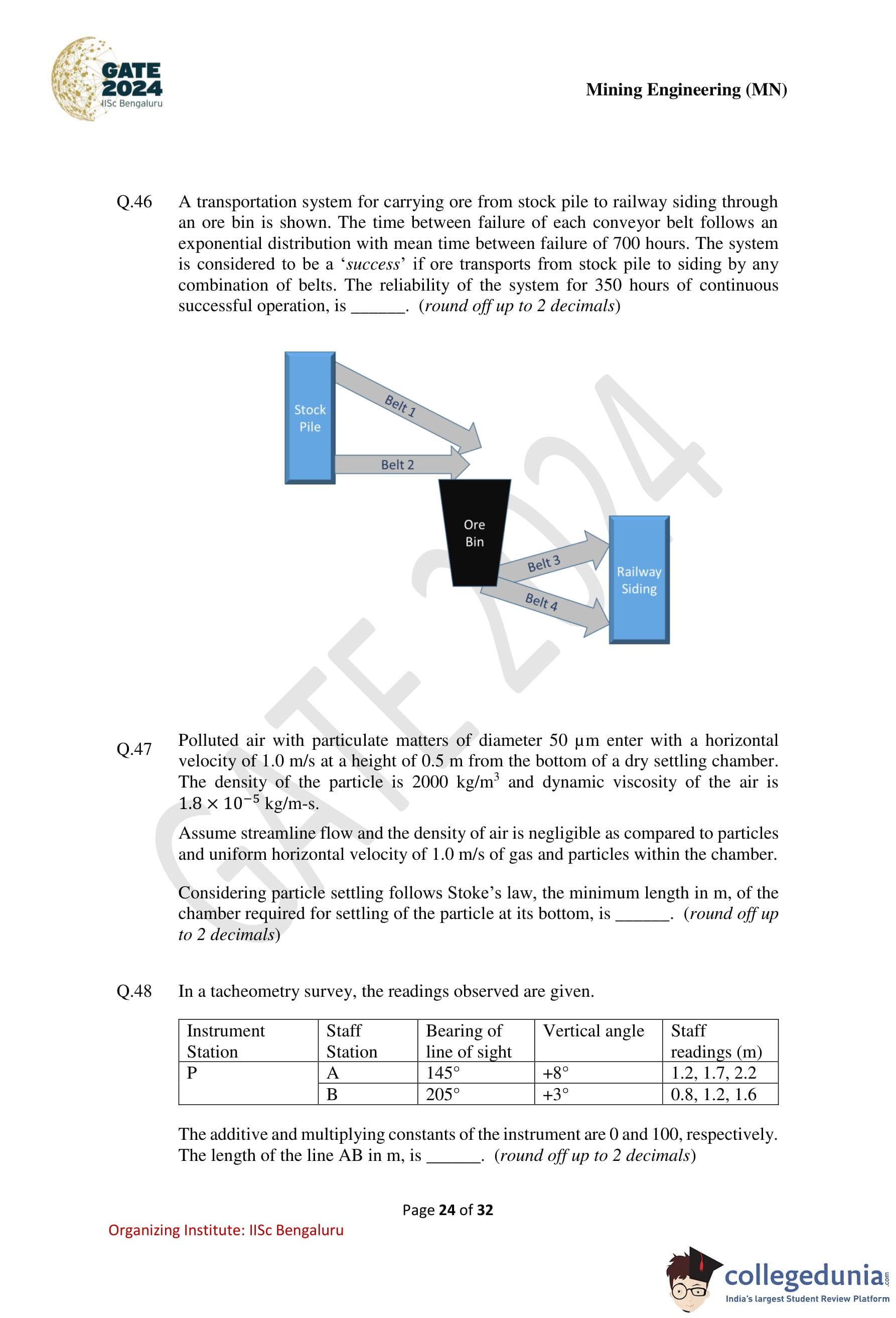
A transportation system for carrying ore from stock pile to railway siding through an ore bin is shown. The time between failure of each conveyor belt follows an exponential distribution with mean time between failure of 700 hours. The system is considered to be a `success' if ore transports from stock pile to siding by any combination of belts. The reliability of the system for 350 hours of continuous successful operation is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
Polluted air with particulate matters of diameter 50 \(\mu\)m enter with a horizontal velocity of 1.0 m/s at a height of 0.5 m from the bottom of a dry settling chamber. The density of the particle is 2000 kg/m\(^3\) and dynamic viscosity of the air is \(1.8 \times 10^{-5}\) kg/m-s. Assume streamline flow and that the density of air is negligible compared to particles. Considering particle settling follows Stoke’s law, the minimum length, in m, of the chamber required for settling of the particle at its bottom is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
In a tacheometry survey, the readings observed are given. The additive and multiplying constants of the instrument are 0 and 100, respectively. The length of the line AB, in m, is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
The data obtained from an air sample analysis of an old working in a coal mine are given.
O\(_2\) = 17.15%, CO\(_2\) = 3.40%, CH\(_4\) = 2.20%, N\(_2\) = 77.25%
Considering atmospheric air contains
O\(_2\) = 20.95%, CO\(_2\) = 0.03%, N\(_2\) = 79.02%,
the percentage of blackdamp in the old working is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
A rectangular face of 2.0 m \(\times\) 2.5 m dimension is blasted with 20 kg explosive in a 1000 m long drive. One kilogram of explosive produces 2200 cm\(^3\) of nitrous fumes. The face is ventilated with a duct located 10.0 m away from the face. To reduce the concentration of nitrous fumes to 5 ppm within a period of 5 minutes, the quantity of air, in m\(^3\)/s, to be circulated is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
Data for a centrifugal pump discharging water from a sump to the surface are given below:
\begin{tabular{ll
Head, m & : 180
Discharge rate, m\(^3\)/hr & : 320
Operating hours per day for 270 days in a year & : 14
Operating hours per day for remaining 95 days & : 20
Overall efficiency of the pumping system & : 0.70
Specific weight of mine water, kN/m\(^3\) & : 10.20
\end{tabular
The annual electrical power consumption, in GWh, due to pumping operation is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
The root of the function \(f(x)=x^3-2x^2+3x-1\) in the interval [0,1] using bisection method after two iterations is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
A Bord and Pillar panel is developed at a depth of 250 m in a flat coal seam. The extraction ratio of the pillar for a safety factor of 1.5 is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
A Mohr–Coulomb envelope between shear stress \(\tau\) and normal stress \(\sigma_n\) of a sandstone rock is given as \(\tau = 7.5 + 0.84\sigma_n\). The value of the shear stress, in MPa, at failure under triaxial test with confining pressure of 5.0 MPa is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
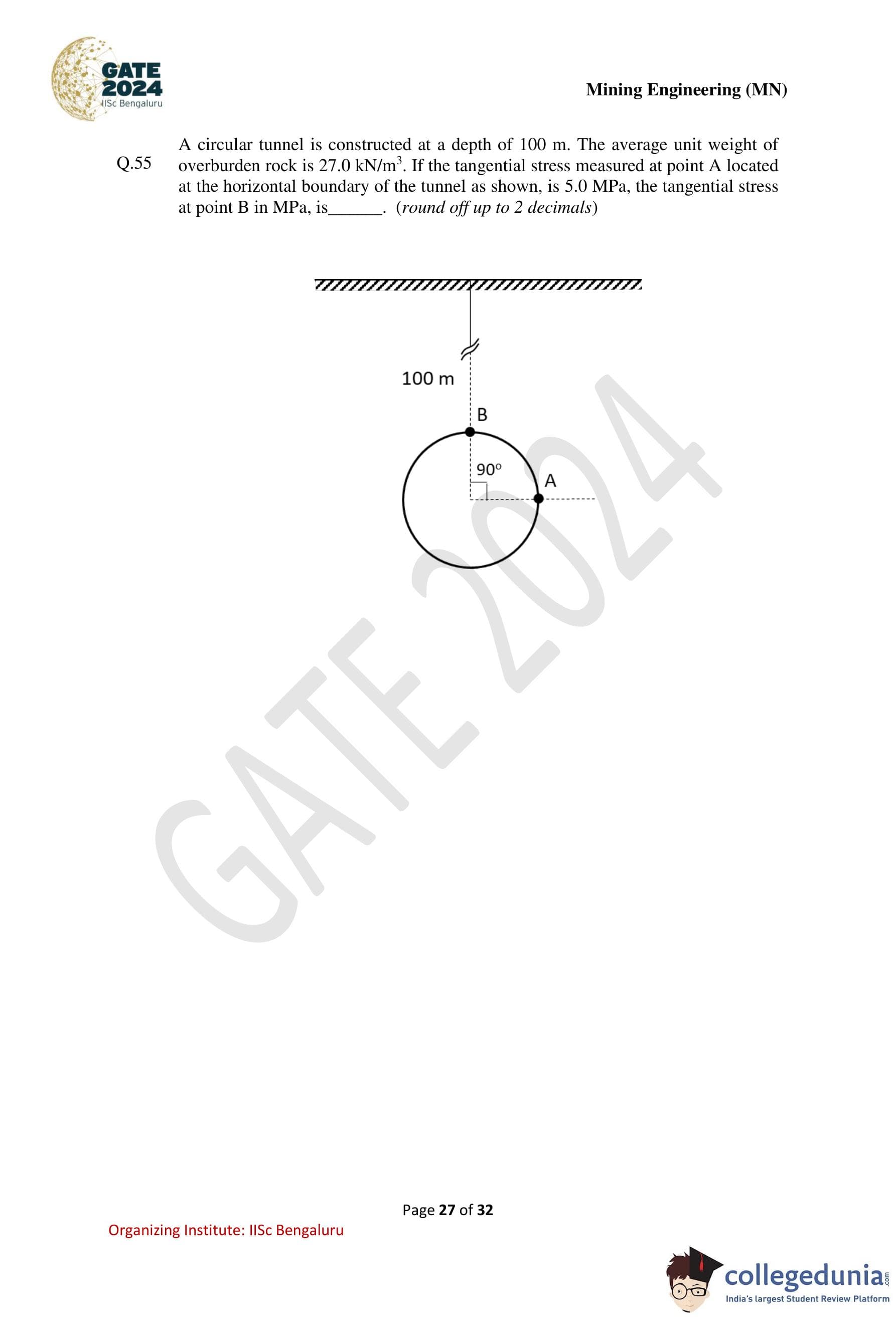
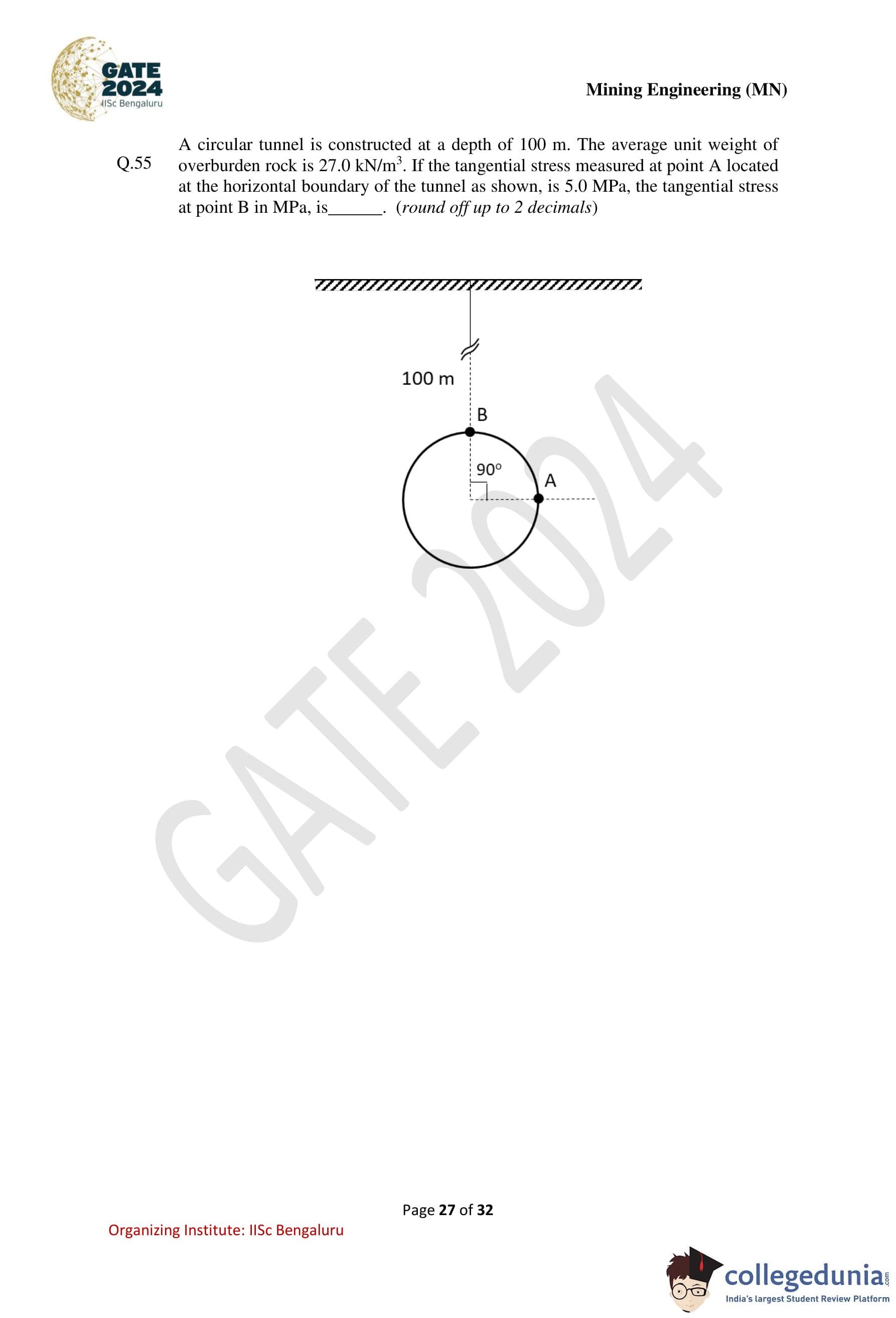
A circular tunnel is constructed at a depth of 100 m. The average unit weight of overburden rock is 27.0 kN/m\(^3\). If the tangential stress measured at point A located at the horizontal boundary of the tunnel is 5.0 MPa, the tangential stress at point B, in MPa, is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
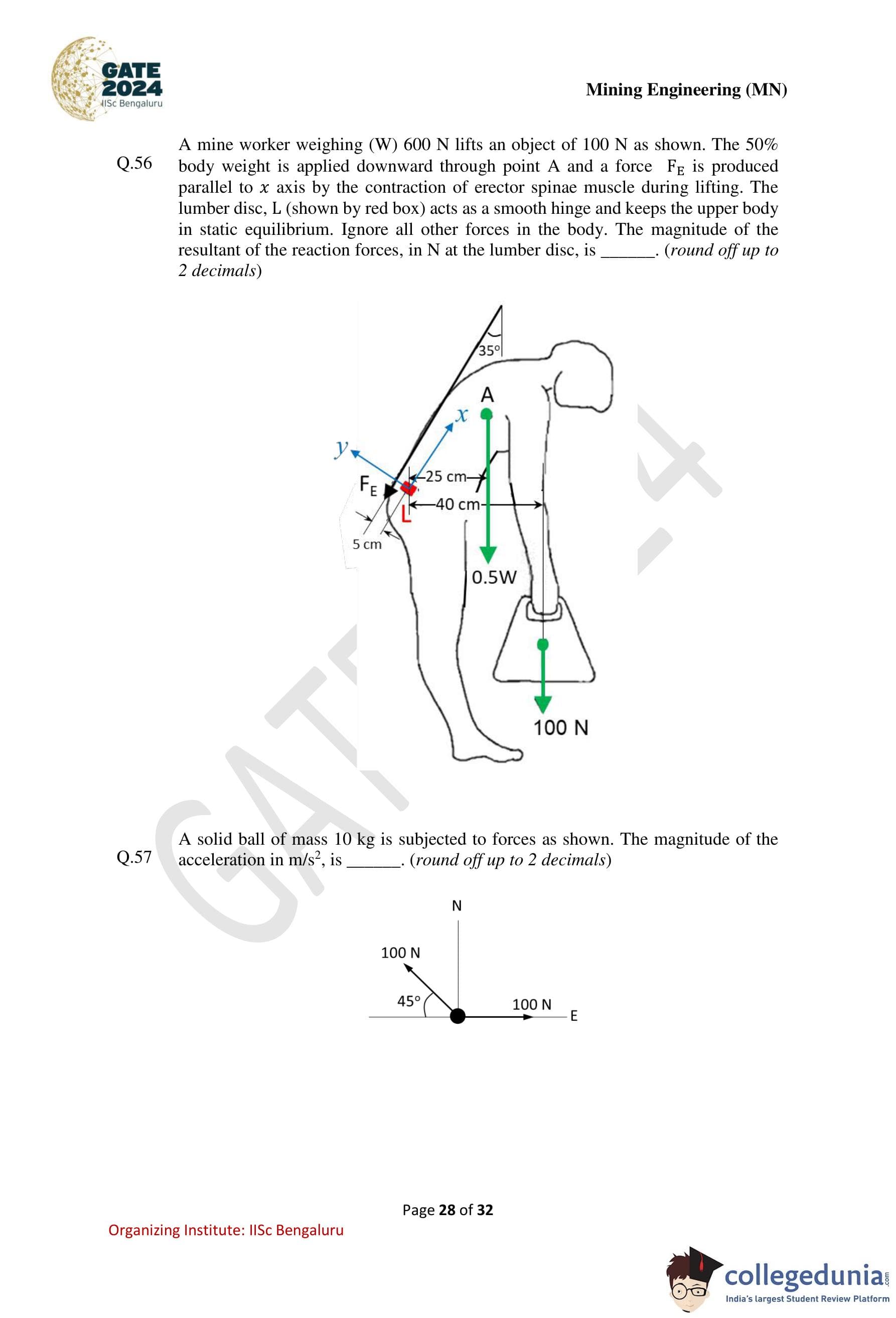
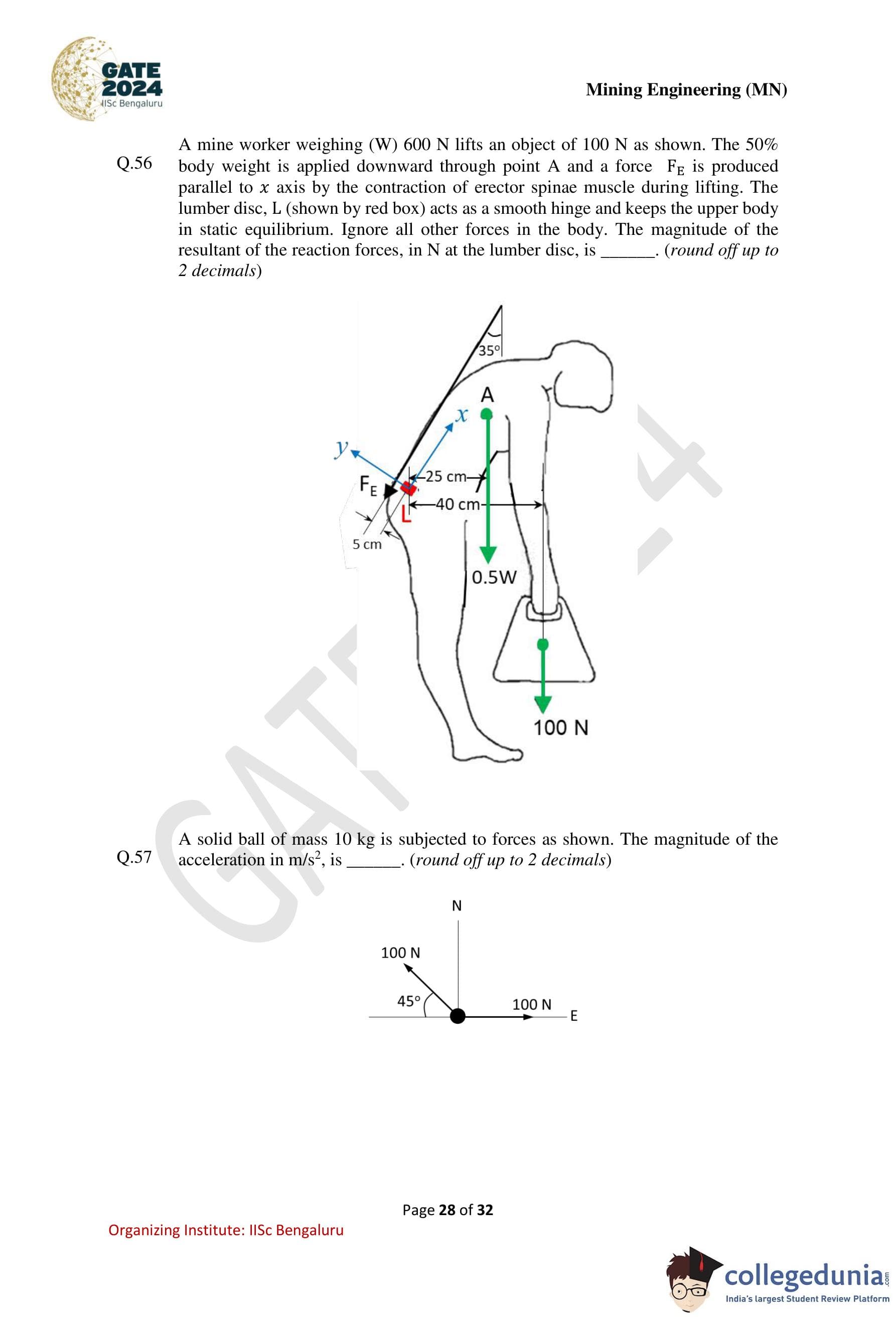
A mine worker weighing (\(W\)) 600 N lifts an object of 100 N as shown. The 50% body weight is applied downward through point A and a force \(F_E\) is produced parallel to x-axis by the contraction of erector spinae muscle during lifting. The lumber disc L (shown by red box) acts as a smooth hinge and keeps the upper body in static equilibrium. Ignore all other forces in the body. The magnitude of the resultant of the reaction forces, in N, at the lumber disc is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
A solid ball of mass 10 kg is subjected to forces as shown. The magnitude of the acceleration, in m/s\(^2\), is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
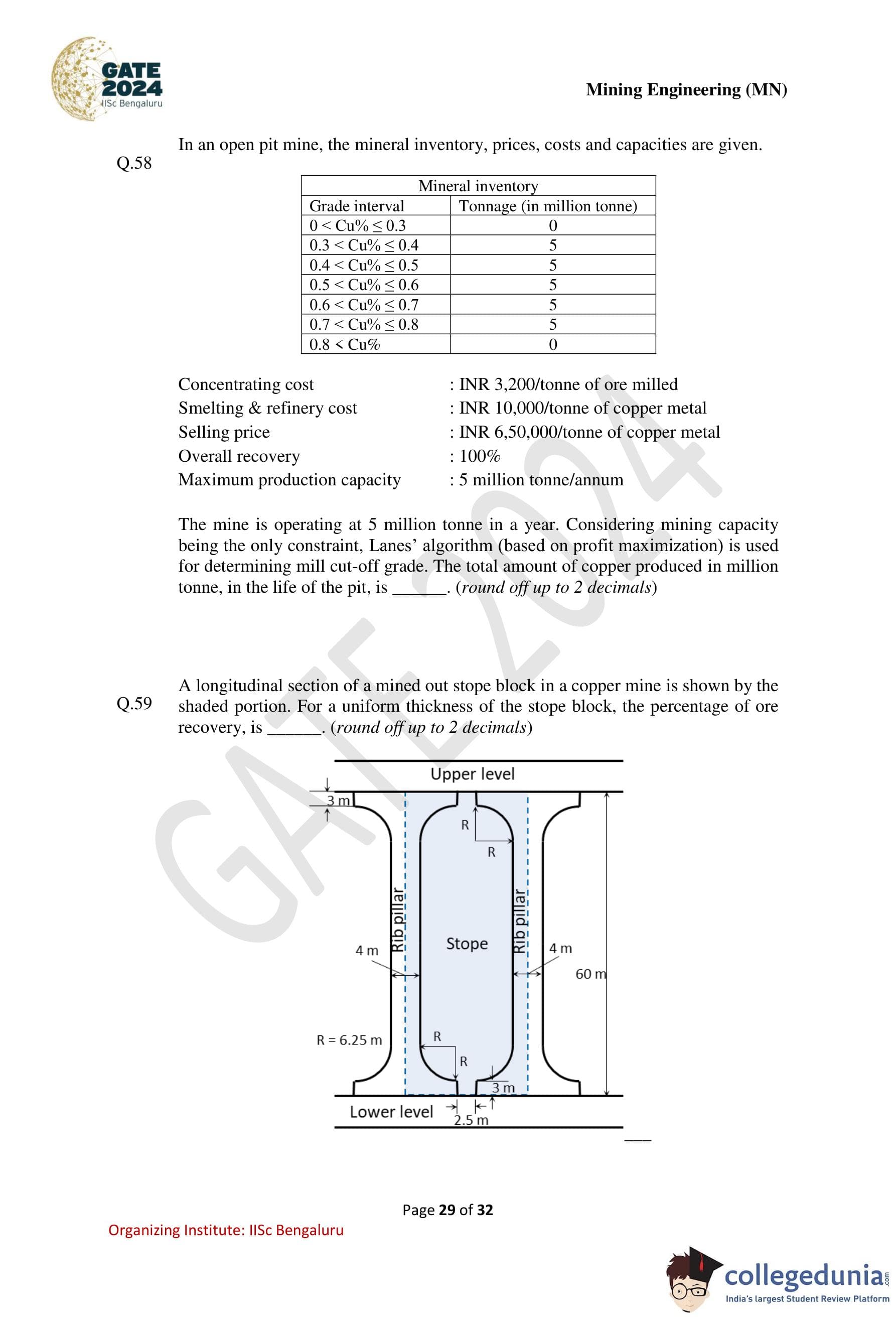
In an open pit mine, the mineral inventory, prices, costs and capacities are given below.
Additional information:
Concentrating cost = INR 3,200/tonne ore milled
Smelting \& refinery cost = INR 10,000/tonne of copper metal
Selling price = INR 6,50,000/tonne of copper metal
Overall recovery = 100%
Maximum production capacity = 5 million tonne/annum
The mine is operating at 5 million tonne in a year. Considering mining capacity being the only constraint, Lane’s algorithm (based on profit maximization) is used for determining mill cut-off grade. The total amount of copper produced, in million tonne, in the life of the pit is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
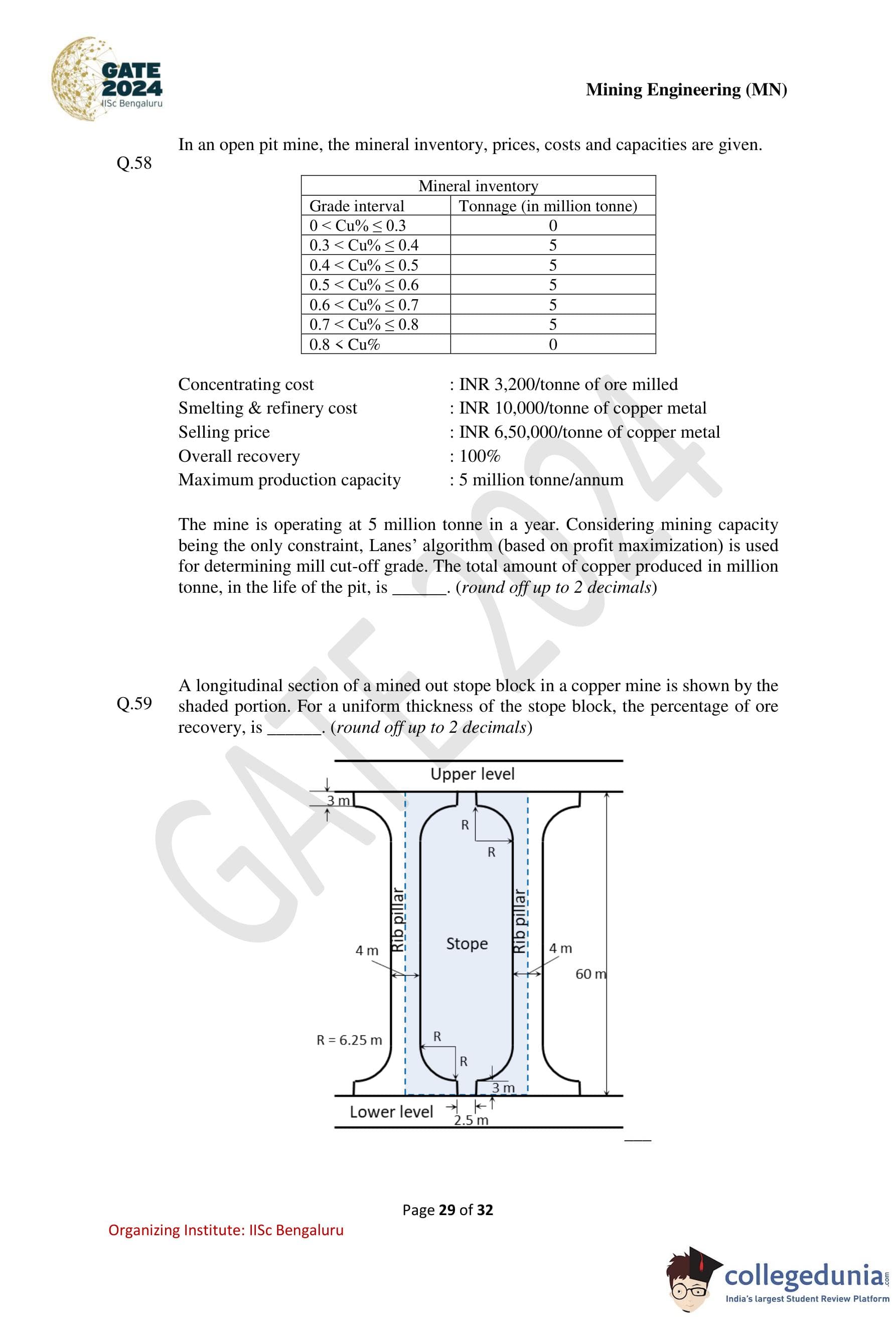
A longitudinal section of a mined out stope block in a copper mine is shown by the shaded portion. For a uniform thickness of the stope block, the percentage of ore recovery is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
The real rate of return from a mining project is 14%. If the inflation rate over the entire life of the mine is 5.5%, then the nominal rate of return in %, is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
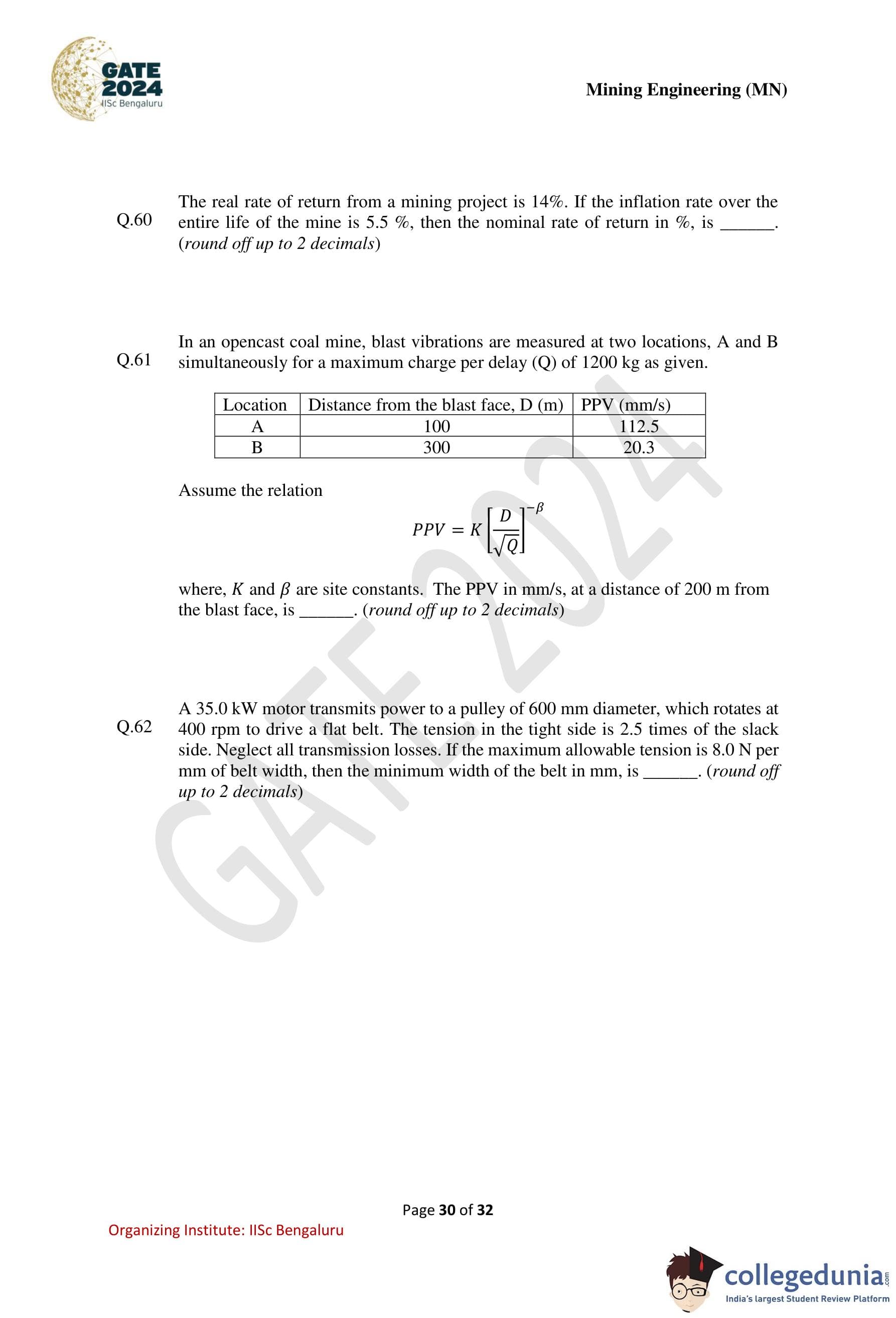
In an opencast coal mine, blast vibrations are measured at two locations A and B simultaneously for a maximum charge per delay (\(Q\)) of 1200 kg as given below.
Assume the relation
\[ PPV = K\left(\frac{D}{\sqrt{Q}}\right)^{-\beta} \]
where \(K\) and \(\beta\) are site constants.
The PPV, in mm/s, at a distance of 200 m from the blast face is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
A 35.0 kW motor transmits power to a pulley of 600 mm diameter, which rotates at 400 rpm to drive a flat belt. The tension in the tight side is 2.5 times of the slack side. Neglect all transmission losses. If the maximum allowable tension is 8.0 N per mm of belt width, then the minimum width of the belt, in mm, is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
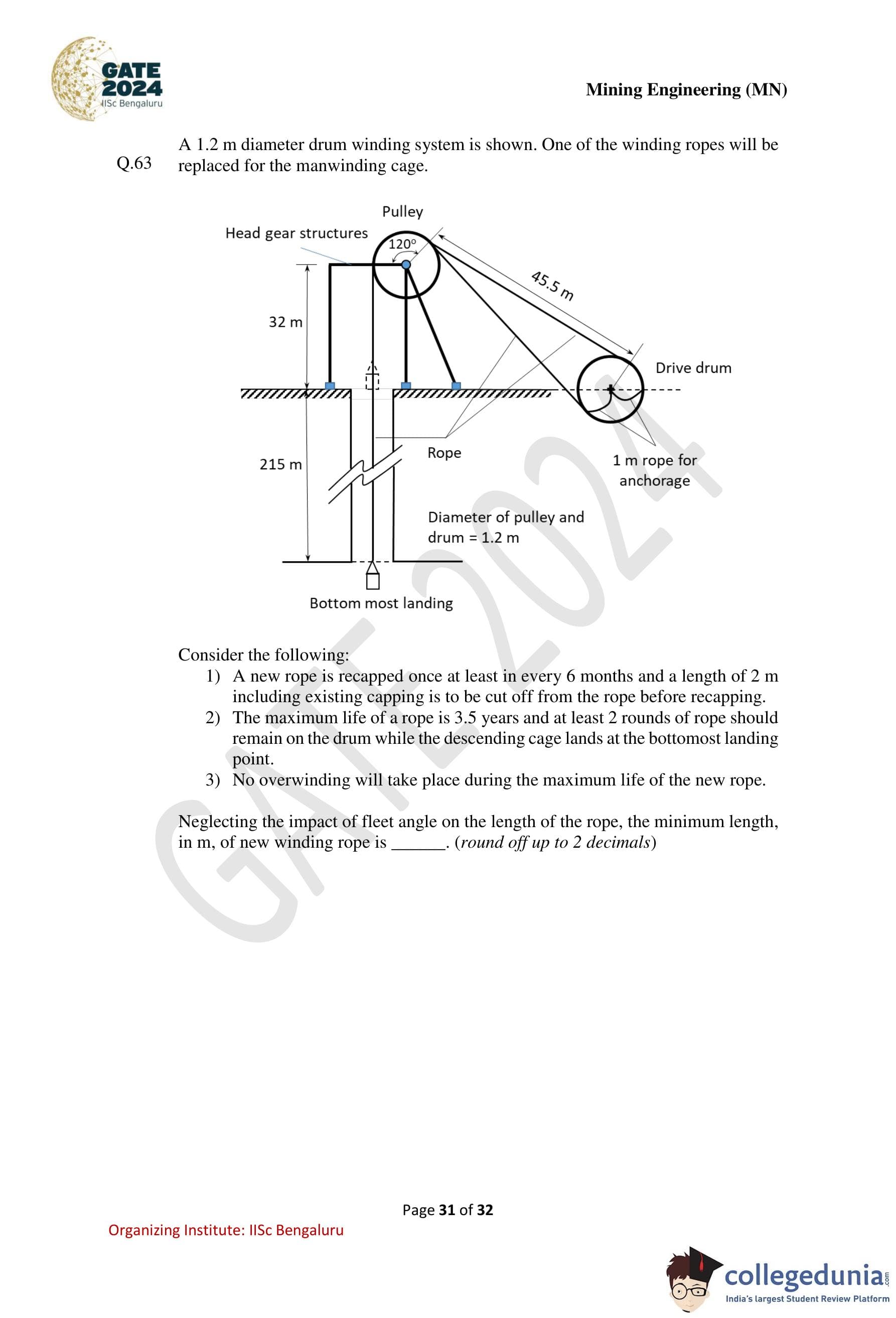
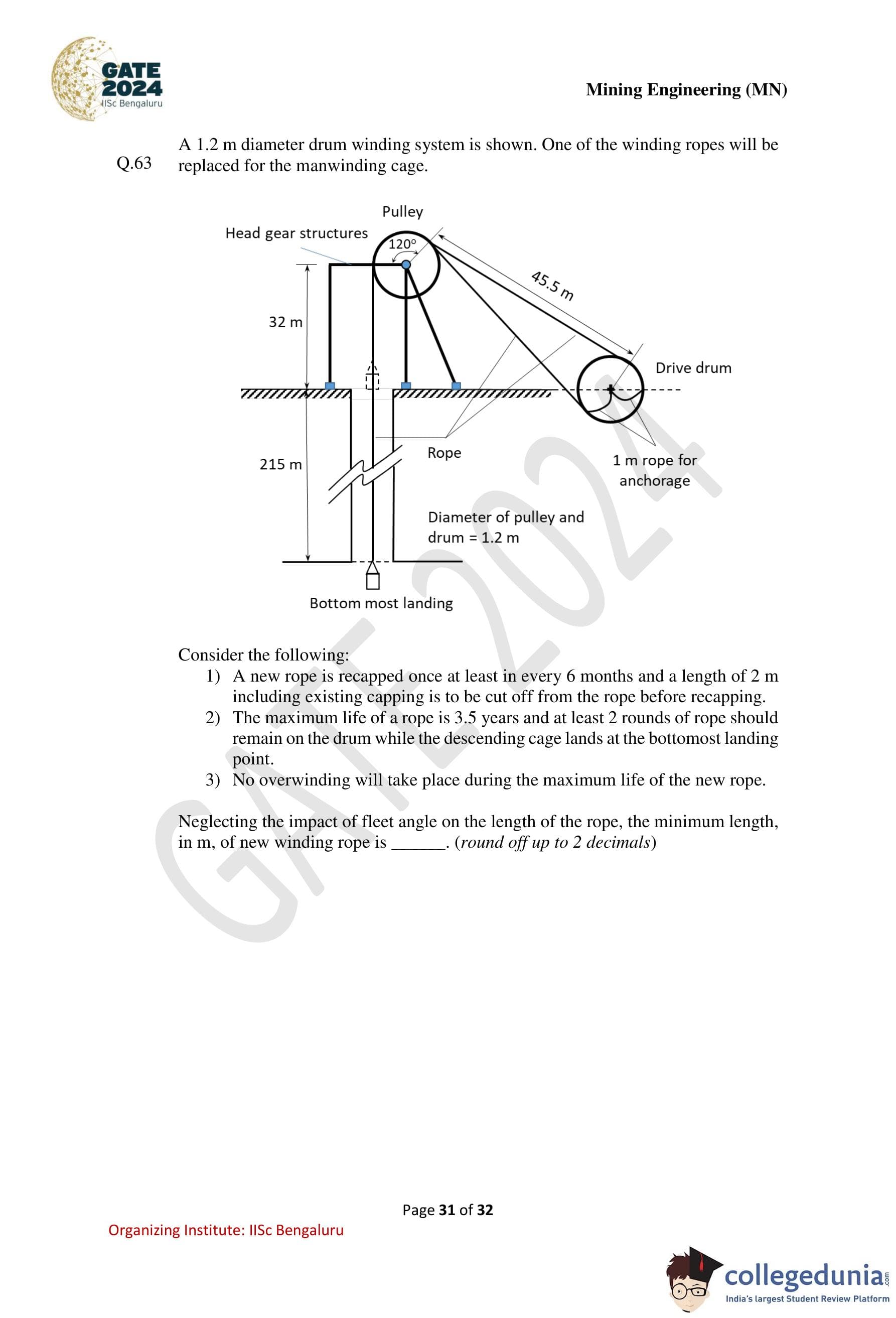
A 1.2 m diameter drum winding system is shown. One of the winding ropes will be replaced for the manwinding cage. The schematic arrangement of the head gear, pulley, drive drum and shaft is shown in the figure.
Consider the following:
1) A new rope is recapped once at least in every 6 months and a length of 2 m including existing capping is to be cut off from the rope before recapping.
2) The maximum life of a rope is 3.5 years and at least 2 rounds of rope should remain on the drum while the descending cage lands at the bottommost landing point.
3) No overwinding will take place during the maximum life of the new rope.
Neglecting the impact of fleet angle on the length of the rope, the minimum length, in m, of the new winding rope is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
For a continuous miner (CM) panel, the following data are given.
Data related to CM
Dimension of a working face : 5.0 m (width) \(\times\) 3.0 m (height)
Web depth, m : 0.6
Time for one web cut up to full height, min : 9
Data related to shuttle car
Bucket capacity of shuttle car, tonne : 10
Fill factor : 0.9
Number of cars : 2
Cycle time of each car including loading, travel and unloading, min : 6
Assume unit weight of coal is 1.4 tonne/m\(^3\) and its swell factor is 1.2.
Consider 6 working hours per shift.
The non-working time, in min, in working hours per shuttle car to dispatch all coal cut by the CM is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).
In a development coal face, 12 holes are drilled and charged with explosive. Holes are initiated with electric delay detonators connected in series. The length of a detonator lead wire is 1.5 m. The length of the blasting cable is 120 m.
Data are as given:
Resistance of each detonator : 1.48 \(\Omega\)
Resistance of lead wire : 0.04 \(\Omega\)/m
Resistance of one wire of the blasting cable : 0.009 \(\Omega\)/m
The total resistance of the circuit in \(\Omega\) is ............ (round off up to 2 decimals).

































Also Check:





Comments