GATE 2024 EE Question Paper PDF is available here. IISc Banglore conducted GATE 2024 EE exam on February 11 in the Afternoon Session from 2:30 PM to 5:30 PM. Students have to answer 65 questions in GATE 2024 EE Question Paper carrying a total weightage of 100 marks. 10 questions are from the General Aptitude section and 55 questions are from Engineering Mathematics and Core Discipline.
GATE 2024 EE Question Paper with Answer Key PDF
| GATE 2024 EE Question Paper with Answer Key PDF | Download PDF | Check Solutions |

GATE 2024 EE Question Paper Solution
If ‘→’ denotes increasing order of intensity, then the meaning of the words [talk → shout → scream] is analogous to [please → _____ → pander]. Which one of the given options is appropriate to fill the blank?
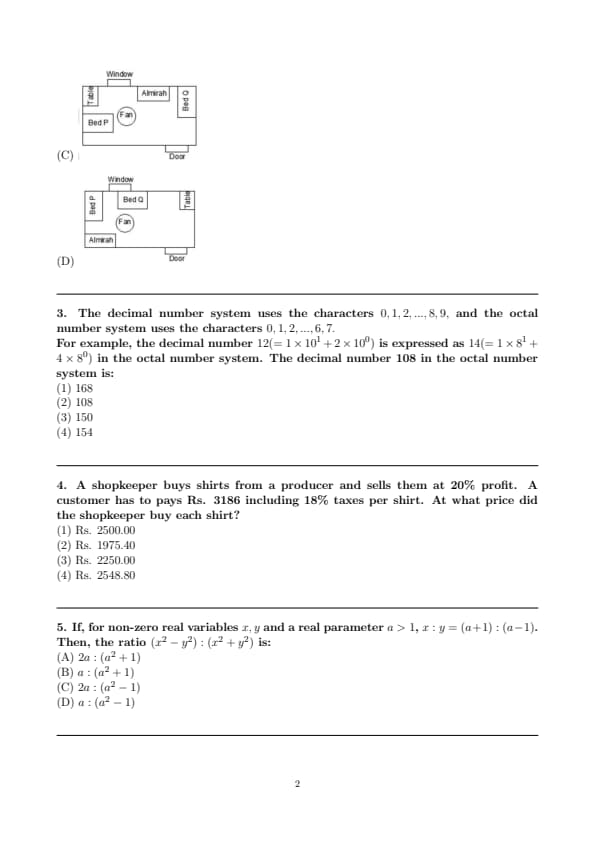
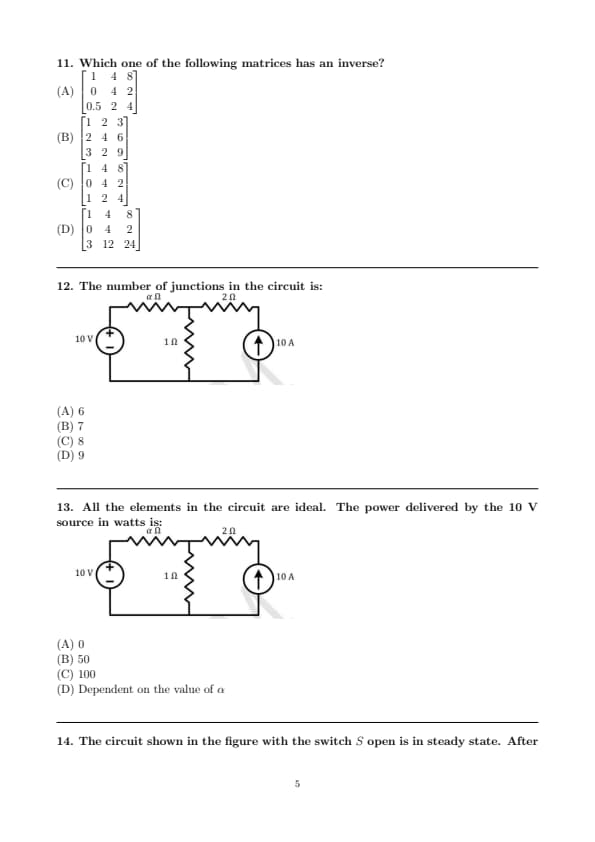
\(P\) and \(Q\) have been allotted a hostel room with two beds, a study table, and an almirah. \(P\) is an avid birdwatcher and wants to sit at the table and watch birds outside the window. \(Q\) prefers a bed close to the ceiling fan. Which one of the following arrangements suits them the most?
The decimal number system uses the characters \(0, 1, 2, ..., 8, 9,\) and the octal
number system uses the characters \(0, 1, 2, ..., 6, 7.\)
For example, the decimal number \(12 (= 1 \times 10^1 + 2 \times 10^0)\) is expressed as \(14 (= 1 \times 8^1 + 4 \times 8^0)\) in the octal number system. The decimal number 108 in the octal number system is:
A shopkeeper buys shirts from a producer and sells them at 20% profit. A customer has to pays Rs. 3186 including 18% taxes per shirt. At what price did the shopkeeper buy each shirt?
If, for non-zero real variables \(x, y\) and a real parameter \(a > 1\), \(x : y = (a+1) : (a-1)\). Then, the ratio \((x^2 - y^2) : (x^2 + y^2)\) is:
In the given text, the blanks are numbered (i)–(iv). Select the best match for all the blanks.
Following a row __ (i) __ the shopkeeper __ (ii) __ the price of a frying pan, the cook stood __ (iii) __ a row to withdraw cash __ (iv) __ the ATM booth.
In the following figure, CD = 5 cm, BE = 10 cm, AE = 12 cm, \(\angle DAB = \angle DCB\), and \(\angle DAE = \angle DBC = 90^\circ\). Points AFCD create a rhombus. The length of BF (in cm) is:

The chart below shows the data of the number of cars bought by Millennials and Gen X people in a country from the year 2010 to 2020 as well as the yearly fuel consumption of the country (in Million liters). Considering the data presented in the chart, which one of the following options is true?

The assembly shown below has three teethed circular objects (Pinions) and two teethed flat objects (Racks), which are perfectly mating with each other. Pinions can only rotate clockwise or anti-clockwise staying at its own center. Racks can translate towards the left (\(\leftarrow\)) or the right (\(\rightarrow\)) direction. If the object \(A\) (Rack) is translating towards the right (\(\rightarrow\)) direction, the correct statement among the following is:

A surveyor has to measure the horizontal distance from her position to a distant reference point \(C\). Using her position as the center, a 200 m horizontal line segment is drawn with the two endpoints \(A\) and \(B\). Points \(A\), \(B\), and \(C\) are not collinear. Each of the angles \(\angle CAB\) and \(\angle CBA\) are measured as \(87.8^\circ\). The distance (in m) of the reference point \(C\) from her position is nearest to:
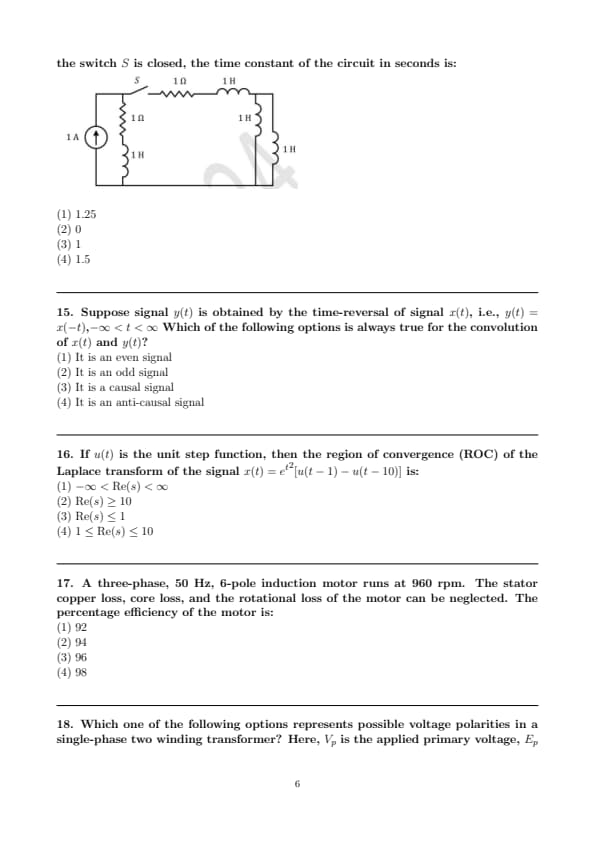
Which one of the following matrices has an inverse?
The number of junctions in the circuit is:

All the elements in the circuit are ideal. The power delivered by the 10 V source in watts is:

The circuit shown in the figure with the switch \( S \) open is in steady state. After the switch \( S \) is closed, the time constant of the circuit in seconds is:

Suppose signal \( y(t) \) is obtained by the time-reversal of signal \( x(t) \), i.e., \( y(t) = x(-t) \),\(-\infty < t < \infty\) Which of the following options is always true for the convolution of \( x(t) \) and \( y(t) \)?
If \( u(t) \) is the unit step function, then the region of convergence (ROC) of the Laplace transform of the signal \( x(t) = {e^t}^2 [ u(t-1) - u(t-10) ] \) is:
A three-phase, 50 Hz, 6-pole induction motor runs at 960 rpm. The stator copper loss, core loss, and the rotational loss of the motor can be neglected. The percentage efficiency of the motor is:
Which one of the following options represents possible voltage polarities in a single-phase two winding transformer? Here, \( V_p \) is the applied primary voltage, \( E_p \) is the induced primary voltage, \( V_s \) is the open circuit secondary voltage, and \( E_s \) is the induced secondary voltage.
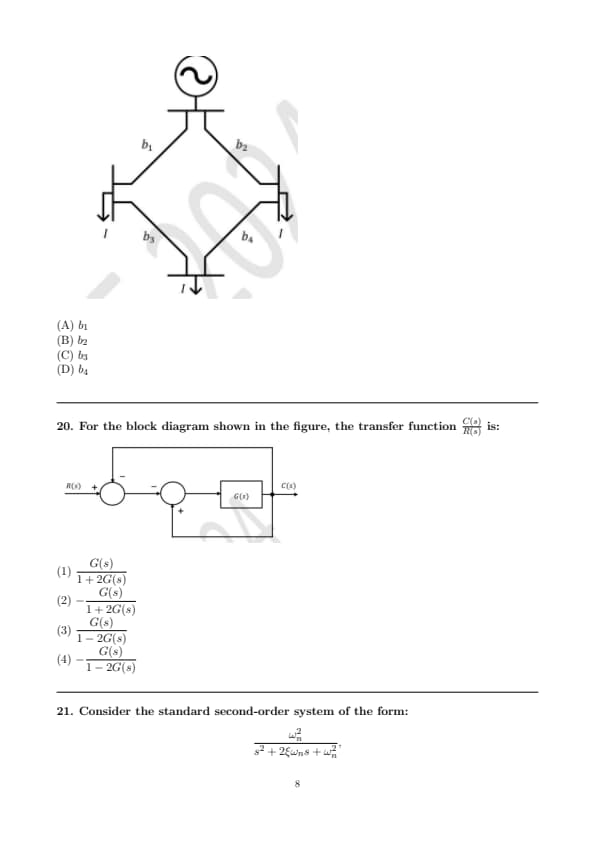
The figure shows the single-line diagram of a 4-bus power network. Branches \( b_1, b_2, b_3 \), and \( b_4 \) have impedances \( 4z, z, 2z \), and \( 4z \) per-unit (pu), respectively, where \( z = r + jx \) with \( r > 0 \) and \( x > 0 \). The current drawn from each load bus (marked as arrows) is equal to \( 1 \, pu \), where \( I \neq 0 \). If the network is to operate with minimum loss, the branch that should be opened is:

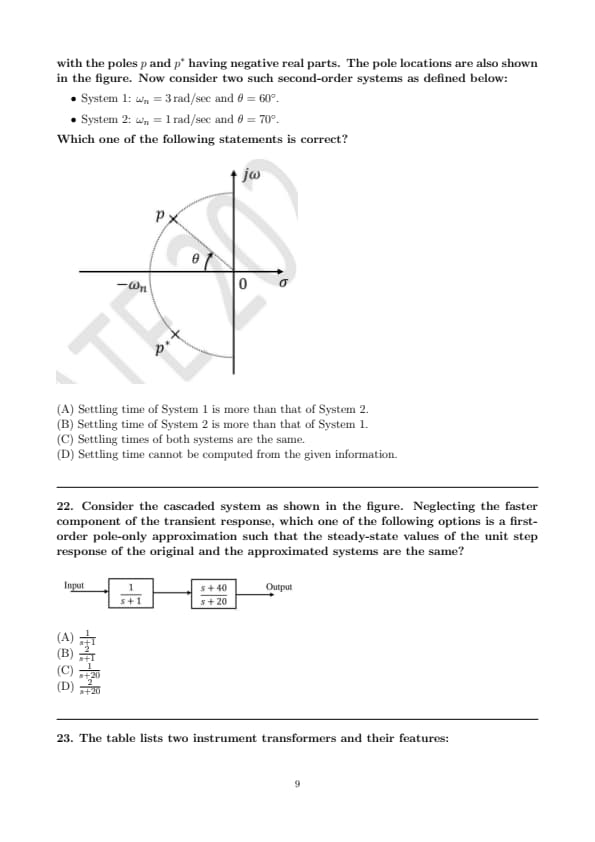
For the block diagram shown in the figure, the transfer function \( \frac{C(s)}{R(s)} \) is:

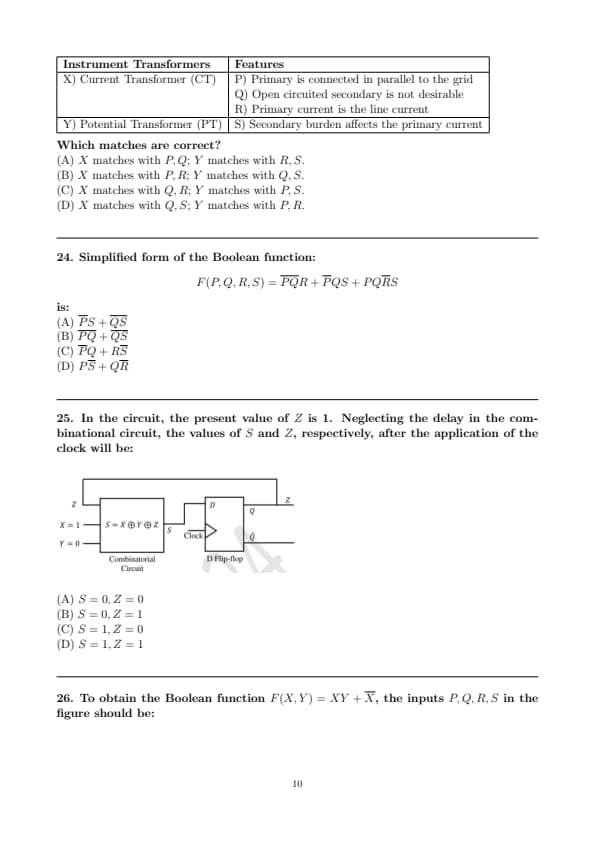
Consider the standard second-order system of the form: \[ \frac{\omega_n^2}{s^2 + 2\xi\omega_n s + \omega_n^2}, \]
with the poles \(p\) and \(p^*\) having negative real parts. The pole locations are also shown in the figure. Now consider two such second-order systems as defined below:
System 1: \( \omega_n = 3 \, rad/sec \) and \( \theta = 60^\circ \).
System 2: \( \omega_n = 1 \, rad/sec \) and \( \theta = 70^\circ \).
Which one of the following statements is correct?

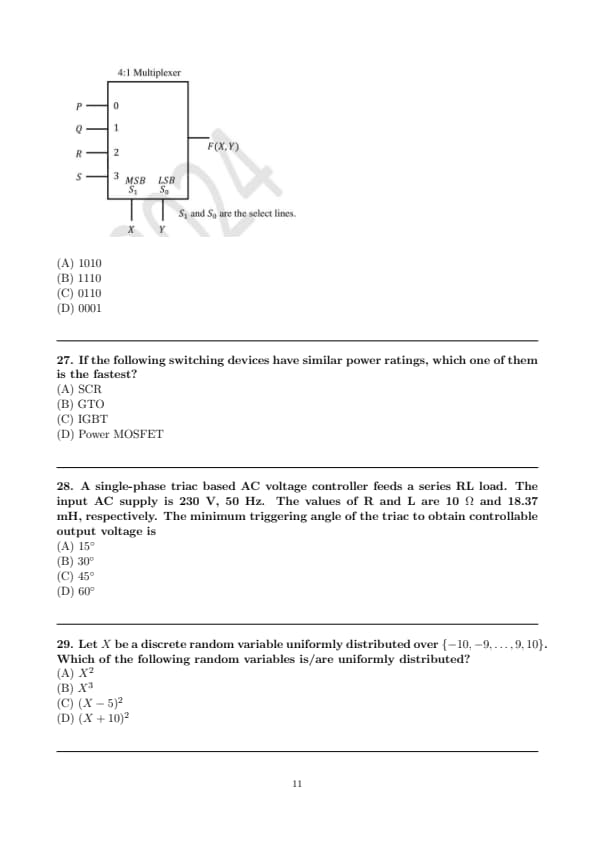
Consider the cascaded system as shown in the figure. Neglecting the faster component of the transient response, which one of the following options is a first-order pole-only approximation such that the steady-state values of the unit step response of the original and the approximated systems are the same?

The table lists two instrument transformers and their features:

Which matches are correct?
Simplified form of the Boolean function: \[ F(P, Q, R, S) = \overline{P}\overline{Q}R + \overline{P}QS + PQ\overline{R}S \]
is:
In the circuit, the present value of \( Z \) is 1. Neglecting the delay in the combinational circuit, the values of \( S \) and \( Z \), respectively, after the application of the clock will be:

To obtain the Boolean function \( F(X, Y) = XY + \overline{X} \), the inputs \( P, Q, R, S \) in the figure should be:

If the following switching devices have similar power ratings, which one of them is the fastest?
A single-phase triac based AC voltage controller feeds a series RL load. The input AC supply is 230 V, 50 Hz. The values of R and L are 10 \(\Omega\) and 18.37 mH, respectively. The minimum triggering angle of the triac to obtain controllable output voltage is
Let \( X \) be a discrete random variable uniformly distributed over \( \{-10, -9, \dots, 9, 10\} \). Which of the following random variables is/are uniformly distributed?
Which of the following complex functions is/are analytic on the complex plane?
Consider the complex function \( f(z) = \cos z + e^{z^2} \). The coefficient of \( z^5 \) in the Taylor series expansion of \( f(z) \) about the origin is _____ (rounded off to 1 decimal place).
The sum of the eigenvalues of the matrix  is _____ (rounded off to the nearest integer).
is _____ (rounded off to the nearest integer).
Let \( X(\omega) \) be the Fourier transform of the signal \( x(t) = e^{-4t} \cos(t), -\infty < t < \infty \). The value of the derivative of \( X(\omega) \) at \( \omega = 0 \) is _____ (rounded off to 1 decimal place).
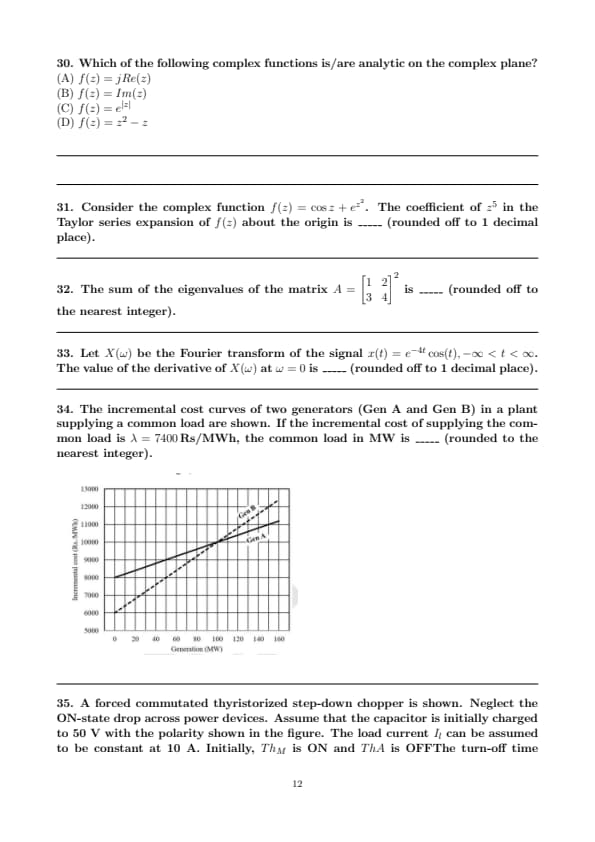
The incremental cost curves of two generators (\( Gen A \) and \( Gen B \)) in a plant supplying a common load are shown. If the incremental cost of supplying the common load is \( \lambda = 7400 \, Rs/MWh \), the common load in MW is _____ (rounded to the nearest integer).

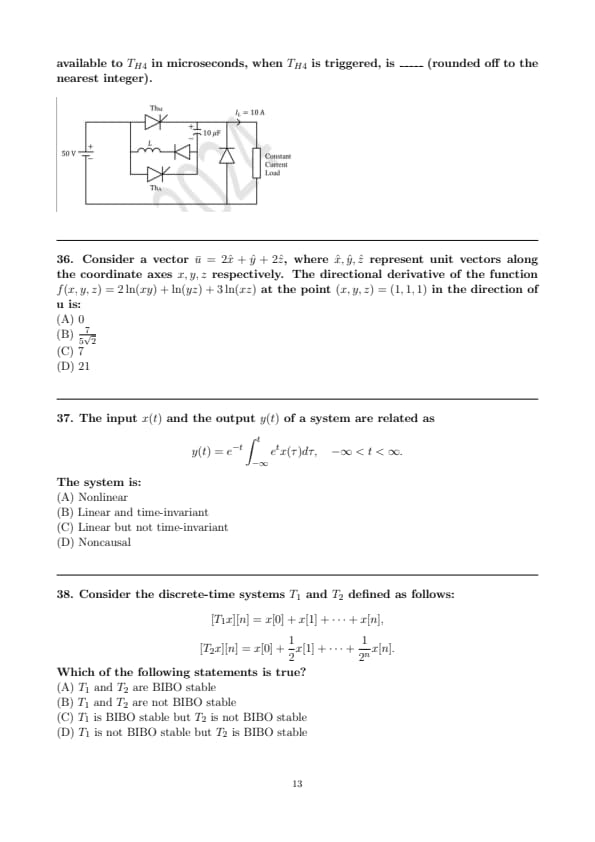
A forced commutated thyristorized step-down chopper is shown. Neglect the ON-state drop across power devices. Assume that the capacitor is initially charged to 50 V with the polarity shown in the figure. The load current \(I_l\) can be assumed to be constant at 10 A. Initially, \(Th_M\) is ON and \(ThA\) is OFFThe turn-off time available to \( T_{H4} \) in microseconds, when \( T_{H4} \) is triggered, is _____ (rounded off to the nearest integer).

Consider a vector \( \overline{u} = 2\hat{x} + \hat{y} + 2\hat{z} \), where \( \hat{x}, \hat{y}, \hat{z} \) represent unit vectors along the coordinate axes \( x, y, z \) respectively. The directional derivative of the function \( f(x, y, z) = 2 \ln(xy) + \ln(yz) + 3 \ln(xz) \) at the point \( (x, y, z) = (1, 1, 1) \) in the direction of \( \mathbf{u} \) is:
The input \( x(t) \) and the output \( y(t) \) of a system are related as \[ y(t) = e^{-t} \int_{-\infty}^t e^t x(\tau) d\tau, \quad -\infty < t < \infty. \]
The system is:
Consider the discrete-time systems \( T_1 \) and \( T_2 \) defined as follows: \[ [T_1x][n] = x[0] + x[1] + \dots + x[n], \] \[ [T_2x][n] = x[0] + \frac{1}{2}x[1] + \dots + \frac{1}{2^n}x[n]. \]
Which of the following statements is true?
If the Z-transform of a finite-duration discrete-time signal \( x[n] \) is \( X(z) \), then the Z-transform of the signal \( y[n] = x[2n] \) is:
A 3-phase, 11 kV, 10 MVA synchronous generator is connected to an inductive load of power factor \( \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \) via a lossless line with a per-phase inductive reactance of \( 5\Omega \). The per-phase synchronous reactance of the generator is \( 30\Omega \). If the generator is producing the rated current at the rated voltage, then the power factor at the terminal of the generator is:
For the three-bus lossless power network shown in the figure, the voltage magnitudes at all the buses are equal to 1 per unit (pu), and the differences of the voltage phase angles are very small. The line reactances are marked in the figure, where \(\alpha\), \(\beta\), \(\gamma\), and \(x\) are strictly positive. The bus injections \(P_1\) and \(P_2\) are in pu. If \(P_1 = mP_2\), where \(m > 0\) and the real power flow from bus 1 to bus 2 is 0 pu, then which one of the following options is correct?

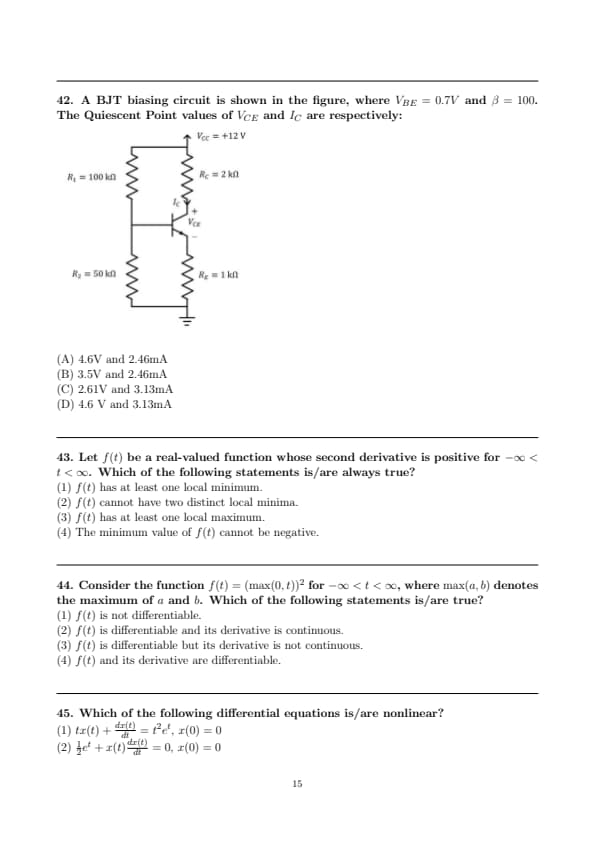
A BJT biasing circuit is shown in the figure, where \(V_{BE} = 0.7V\) and \(\beta = 100\). The Quiescent Point values of \(V_{CE}\) and \(I_{C}\) are respectively:

Let \( f(t) \) be a real-valued function whose second derivative is positive for \( -\infty < t < \infty \). Which of the following statements is/are always true?
Consider the function \( f(t) = (\max(0, t))^2 \) for \( -\infty < t < \infty \), where \( \max(a, b) \) denotes the maximum of \( a \) and \( b \). Which of the following statements is/are true?
Which of the following differential equations is/are nonlinear?
For a two-phase network, the phase voltages \( V_p \) and \( V_q \) are to be expressed in terms of sequence voltages \( V_\alpha \) and \( V_\beta \) as:

The possible option(s) for matrix \( S \) is/are:
Which of the following options is/are correct for the Automatic Generation Control (AGC) and Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) installed with synchronous generators?
Two passive two-port networks \( P \) and \( Q \) are connected as shown in the figure. The impedance matrix of network \( P \) is \( Z_P = \begin{bmatrix} 40 \, \Omega & 60 \, \Omega
80 \, \Omega & 100 \, \Omega \end{bmatrix} \). The admittance matrix of network \( Q \) is \( Y_Q = \begin{bmatrix} 5 \, S & -2.5 \, S
-2.5 \, S & 1 \, S \end{bmatrix} \). Let the ABCD matrix of the two-port network \( R \) in the figure be \( \begin{bmatrix} \alpha & \beta
\gamma & \delta \end{bmatrix} \). The value of \( \beta \) in \( \Omega \) is ______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places).

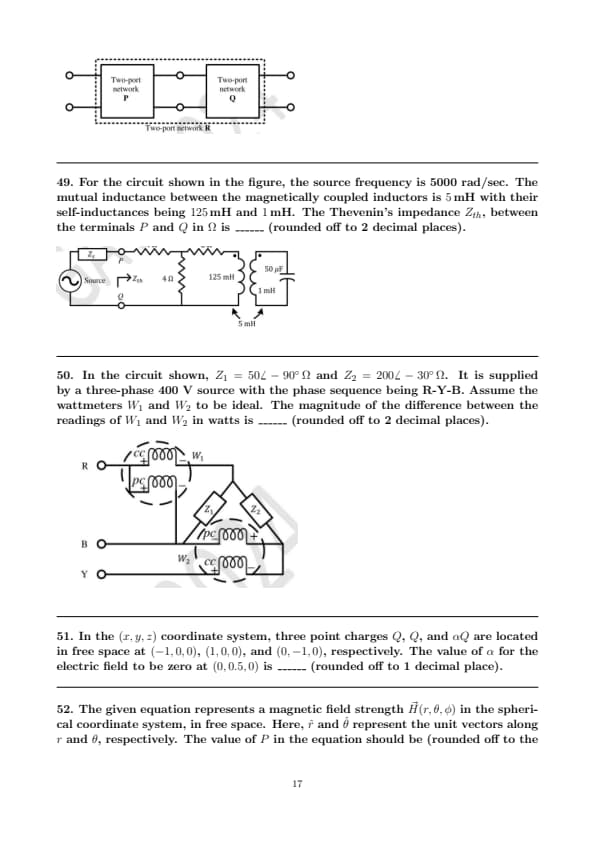
For the circuit shown in the figure, the source frequency is 5000 rad/sec. The mutual inductance between the magnetically coupled inductors is \( 5 \, mH \) with their self-inductances being \( 125 \, mH \) and \( 1 \, mH \). The Thevenin's impedance \( Z_{th} \), between the terminals \( P \) and \( Q \) in \( \Omega \) is ______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places).

In the circuit shown, \( Z_1 = 50 \angle -90^\circ \, \Omega \) and \( Z_2 = 200 \angle -30^\circ \, \Omega \). It is supplied by a three-phase 400 V source with the phase sequence being R-Y-B. Assume the wattmeters \( W_1 \) and \( W_2 \) to be ideal. The magnitude of the difference between the readings of \( W_1 \) and \( W_2 \) in watts is ______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places).

In the \( (x, y, z) \) coordinate system, three point charges \( Q \), \( Q \), and \( \alpha Q \) are located in free space at \( (-1, 0, 0) \), \( (1, 0, 0) \), and \( (0, -1, 0) \), respectively. The value of \( \alpha \) for the electric field to be zero at \( (0, 0.5, 0) \) is ______ (rounded off to 1 decimal place).
The given equation represents a magnetic field strength \( \vec{H}(r, \theta, \phi) \) in the spherical coordinate system, in free space. Here, \( \hat{r} \) and \( \hat{\theta} \) represent the unit vectors along \( r \) and \( \theta \), respectively. The value of \( P \) in the equation should be (rounded off to the nearest integer).
\[ \vec{H}(r, \theta, \phi) = \frac{1}{r^3} \big( \hat{r} P \cos \theta + \hat{\theta} \sin \theta \big) \]
If the energy of a continuous-time signal \( x(t) \) is \( E \) and the energy of the signal \( 2x(2t - 1) \) is \( cE \), then \( c \) is (rounded off to 1 decimal place).
A 3-phase star connected slip ring induction motor has the following parameters referred to the stator: \[ R_s = 3 \, \Omega, \, X_s = 2 \, \Omega, \, X_r' = 2 \, \Omega, \, R_r' = 2.5 \, \Omega \]
The per phase stator to rotor effective turns ratio is 3:1. The rotor winding is also star connected. The magnetizing reactance and core loss of the motor can be neglected. To have maximum torque at starting, the value of the extra resistance in ohms (referred to the rotor side) to be connected in series with each phase of the rotor winding is ______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places).
A 5 kW, 220 V DC shunt motor has \( 0.5 \, \Omega \) armature resistance including brushes. The motor draws a no-load current of \( 3 \, A \). The field current is constant at \( 1 \, A \). Assuming that the core and rotational losses are constant and independent of the load, the current (in amperes) drawn by the motor while delivering the rated load, for the best possible efficiency, is (rounded off to 2 decimal places).
The single line diagram of a lossless system is shown in the figure. The system is operating in steady-state at a stable equilibrium point with the power output of the generator being \( P_{max} \sin \delta \), where \( \delta \) is the load angle and the mechanical power input is \( 0.5 P_{max} \). A fault occurs on line 2 such that the power output of the generator is less than \( 0.5 P_{max} \) during the fault. After the fault is cleared by opening line 2, the power output of the generator is \( \frac{P_{max}}{\sqrt{2}} \sin \delta \). If the critical fault clearing angle is \( \pi/2 \) radians, the accelerating area on the power angle curve is ___ times \( P_{max} \) (rounded off to 2 decimal places).

Consider the closed-loop system shown in the figure with \[ G(s) = \frac{K(s^2 - 2s + 2)}{s^2 + 2s + 5}. \]
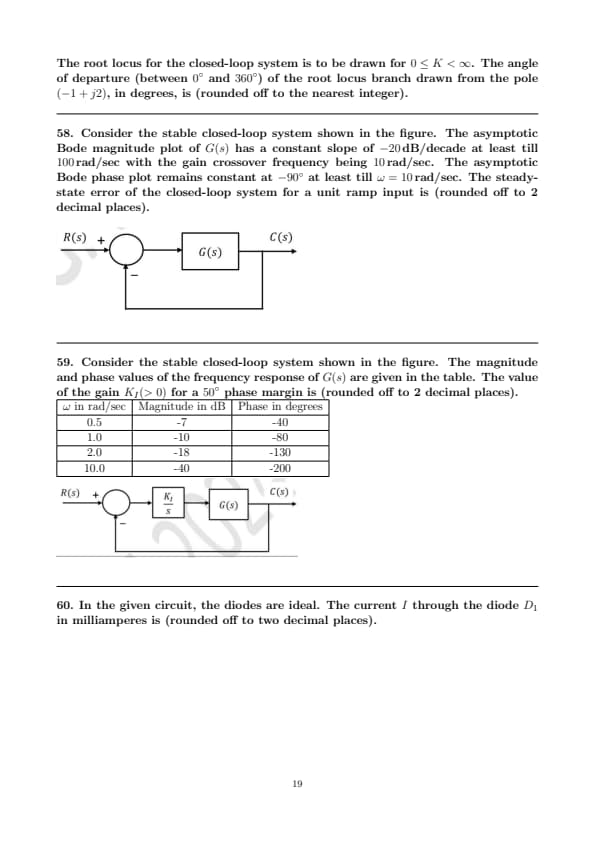
The root locus for the closed-loop system is to be drawn for \( 0 \leq K < \infty \). The angle of departure (between \( 0^\circ \) and \( 360^\circ \)) of the root locus branch drawn from the pole \( (-1 + j2) \), in degrees, is (rounded off to the nearest integer).
Consider the stable closed-loop system shown in the figure. The asymptotic Bode magnitude plot of \( G(s) \) has a constant slope of \( -20 \, dB/decade \) at least till \( 100 \, rad/sec \) with the gain crossover frequency being \( 10 \, rad/sec \). The asymptotic Bode phase plot remains constant at \( -90^\circ \) at least till \( \omega = 10 \, rad/sec \). The steady-state error of the closed-loop system for a unit ramp input is (rounded off to 2 decimal places).

Consider the stable closed-loop system shown in the figure. The magnitude and phase values of the frequency response of \( G(s) \) are given in the table. The value of the gain \( K_I (> 0) \) for a \( 50^\circ \) phase margin is (rounded off to 2 decimal places).


In the given circuit, the diodes are ideal. The current \( I \) through the diode \( D_1 \) in milliamperes is (rounded off to two decimal places).

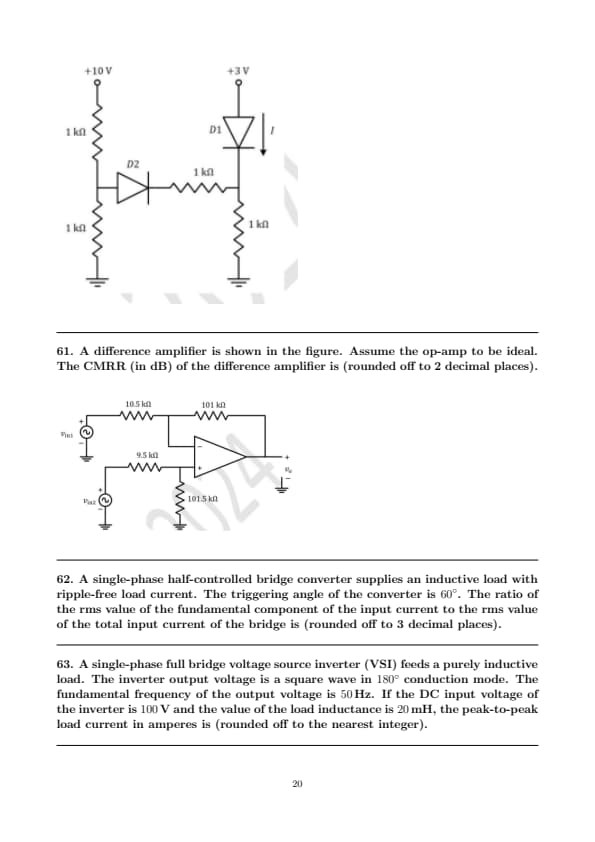
A difference amplifier is shown in the figure. Assume the op-amp to be ideal. The CMRR (in dB) of the difference amplifier is (rounded off to 2 decimal places).

A single-phase half-controlled bridge converter supplies an inductive load with ripple-free load current. The triggering angle of the converter is \( 60^\circ \). The ratio of the rms value of the fundamental component of the input current to the rms value of the total input current of the bridge is (rounded off to 3 decimal places).
A single-phase full bridge voltage source inverter (VSI) feeds a purely inductive load. The inverter output voltage is a square wave in \( 180^\circ \) conduction mode. The fundamental frequency of the output voltage is \( 50 \, Hz \). If the DC input voltage of the inverter is \( 100 \, V \) and the value of the load inductance is \( 20 \, mH \), the peak-to-peak load current in amperes is (rounded off to the nearest integer).
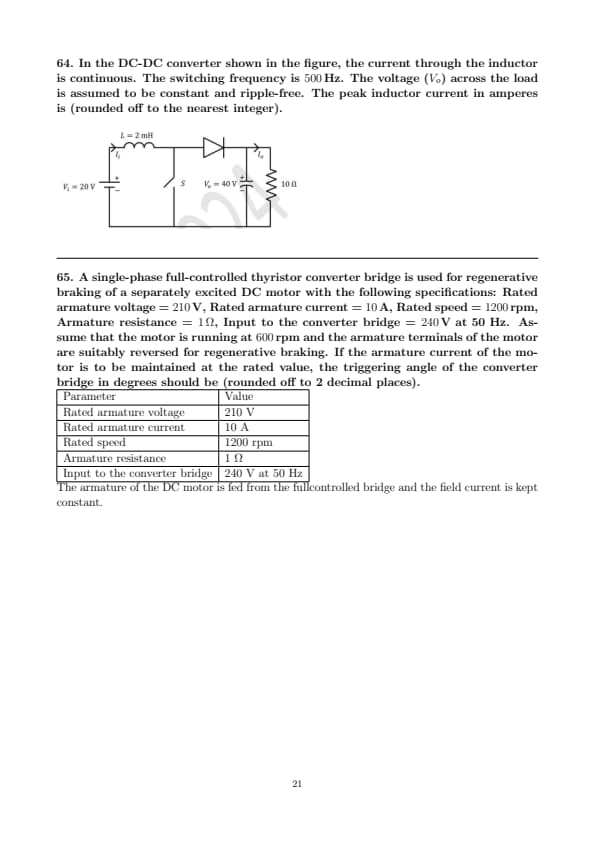
In the DC-DC converter shown in the figure, the current through the inductor is continuous. The switching frequency is \( 500 \, Hz \). The voltage (\( V_o \)) across the load is assumed to be constant and ripple-free. The peak inductor current in amperes is (rounded off to the nearest integer).

A single-phase full-controlled thyristor converter bridge is used for regenerative braking of a separately excited DC motor with the following specifications:
Rated armature voltage = \( 210 \, V \), Rated armature current = \( 10 \, A \), Rated speed = \( 1200 \, rpm \), Armature resistance = \( 1 \, \Omega \), Input to the converter bridge = \( 240 \, V at 50 Hz \). Assume that the motor is running at \( 600 \, rpm \) and the armature terminals of the motor are suitably reversed for regenerative braking. If the armature current of the motor is to be maintained at the rated value, the triggering angle of the converter bridge in degrees should be (rounded off to 2 decimal places).

The armature of the DC motor is fed from the fullcontrolled bridge and the field current is kept constant.


























Comments