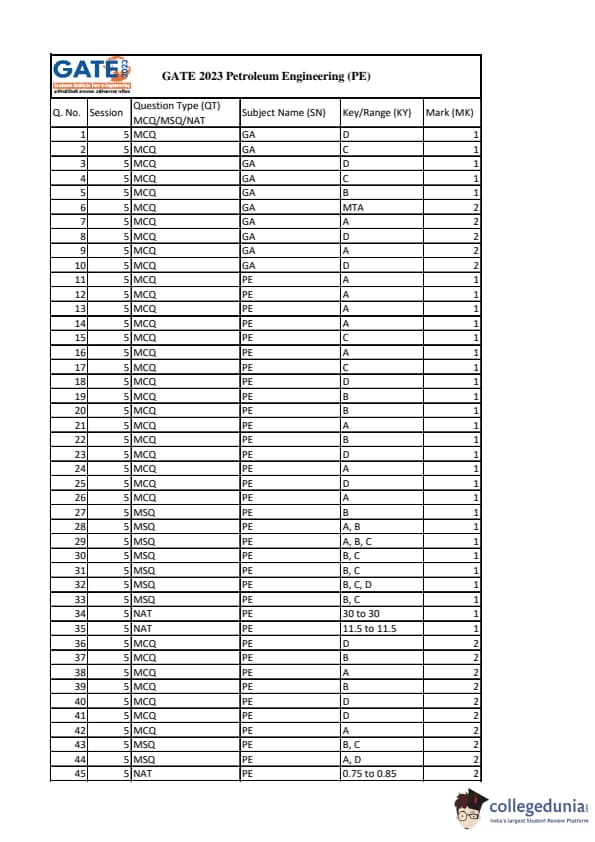
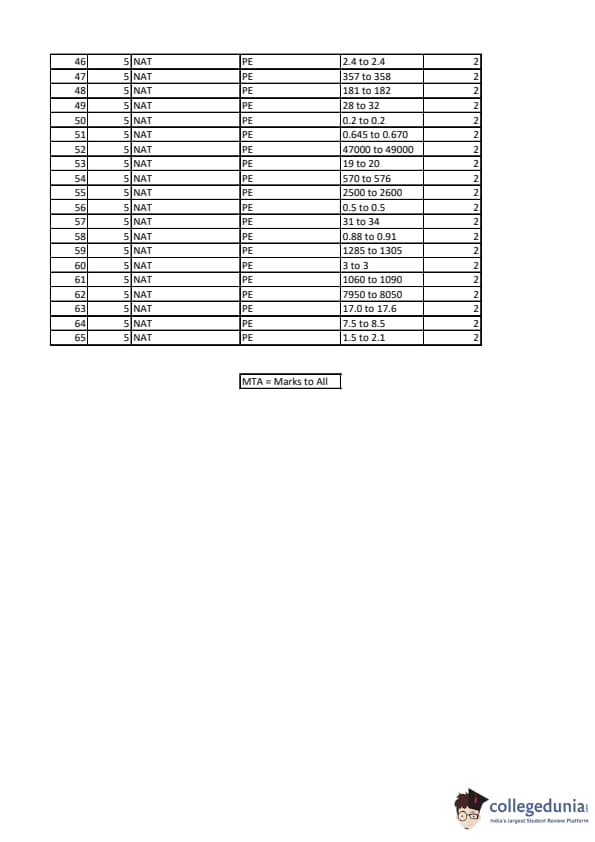
GATE 2023 Petroleum Engineering Question Paper PDF is available here for download. IIT Kanpur conducted GATE 2023 Petroleum Engineering exam on February 11, 2023 in the Forenoon Session from 09:30 AM to 12:30 PM. Students have to answer 65 questions in GATE 2023 Petroleum Engineering Question Paper carrying a total weightage of 100 marks. 10 questions are from the General Aptitude section and 55 questions are from Engineering Mathematics and Core Discipline.
GATE 2023 Petroleum Engineering (PE) Question Paper with Solutions PDF
| GATE 2023 Petroleum Engineering Question Paper with Solutions | Check Solutions |

The village was nestled in a green spot, ______ the ocean and the hills.
Disagree : Protest : : Agree : ______ (By word meaning)
A ‘frabjous’ number is defined as a 3 digit number with all digits odd, and no two adjacent digits being the same. For example, 137 is a frabjous number, while 133 is not. How many such frabjous numbers exist?
Which one among the following statements must be TRUE about the mean and the median of the scores of all candidates appearing for GATE 2023?
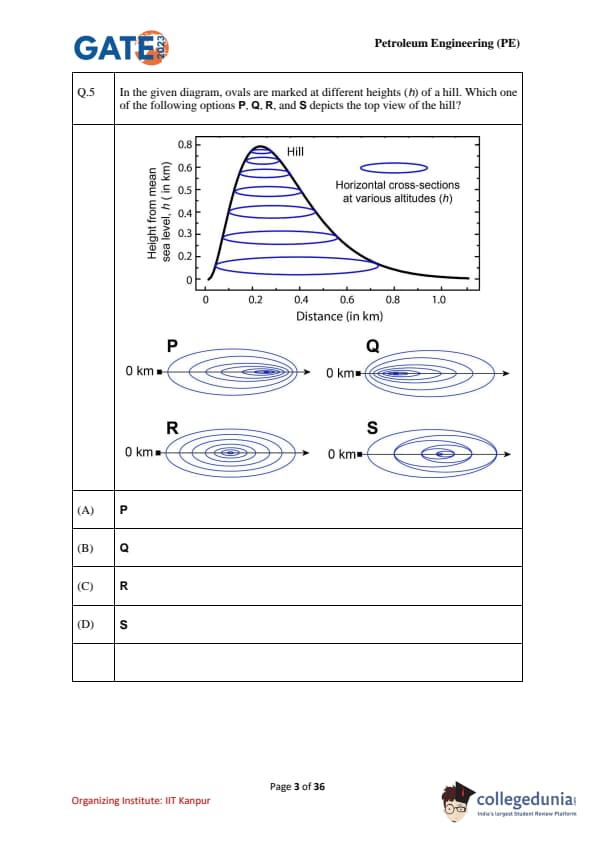
In the given diagram, ovals are marked at different heights (h) of a hill. Which one of the following options P, Q, R, and S depicts the top view of the hill?

Residency is a famous housing complex with many well-established individuals among its residents. A recent survey conducted among the residents of the complex revealed that all of those residents who are well established in their respective fields happen to be academicians. The survey also revealed that most of these academicians are authors of some best-selling books. Based only on the information provided above, which one of the following statements can be logically inferred with certainty?
Ankita has to climb 5 stairs starting at the ground, while respecting the following rules:
1. At any stage, Ankita can move either one or two stairs up.
2. At any stage, Ankita cannot move to a lower step.
Let \(F(N)\) denote the number of possible ways in which Ankita can reach the \(N^{th}\) stair. For example, \(F(1) = 1\), \(F(2) = 2\), \(F(3) = 3\). The value of \(F(5)\) is _______.
The information contained in DNA is used to synthesize proteins that are necessary for the functioning of life. DNA is composed of four nucleotides: Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G). The information contained in DNA can then be thought of as a sequence of these four nucleotides: A, T, C, and G. DNA has coding and non-coding regions. Coding regions—where the sequence of these nucleotides are read in groups of three to produce individual amino acids—constitute only about 2% of human DNA. For example, the triplet of nucleotides CCG codes for the amino acid glycine, while the triplet GGA codes for the amino acid proline. Multiple amino acids are then assembled to form a protein.
Based only on the information provided above, which of the following statements can be logically inferred with certainty?
(i) The majority of human DNA has no role in the synthesis of proteins.
(ii) The function of about 98% of human DNA is not understood.
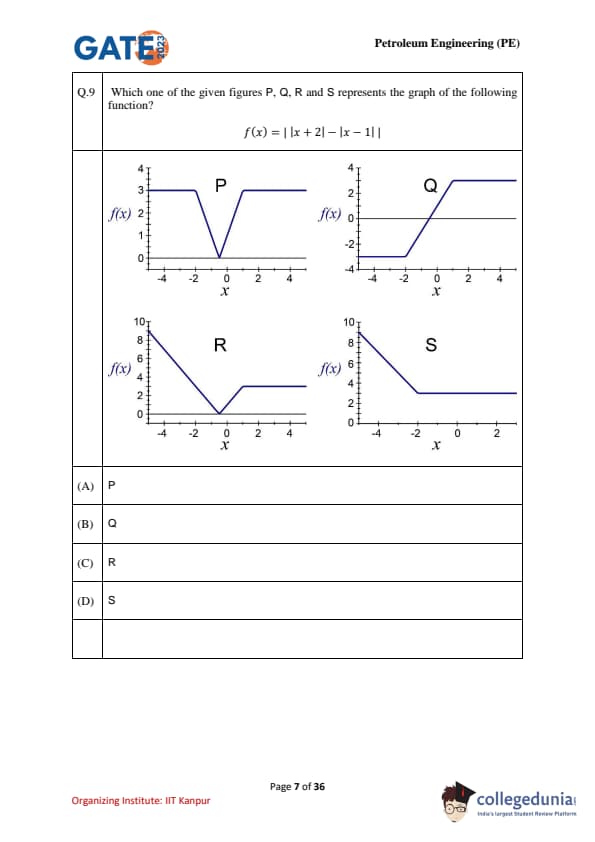
Which one of the given figures P, Q, R, and S represents the graph of the following function? \[ f(x) = |x + 2| - |x - 1| \]

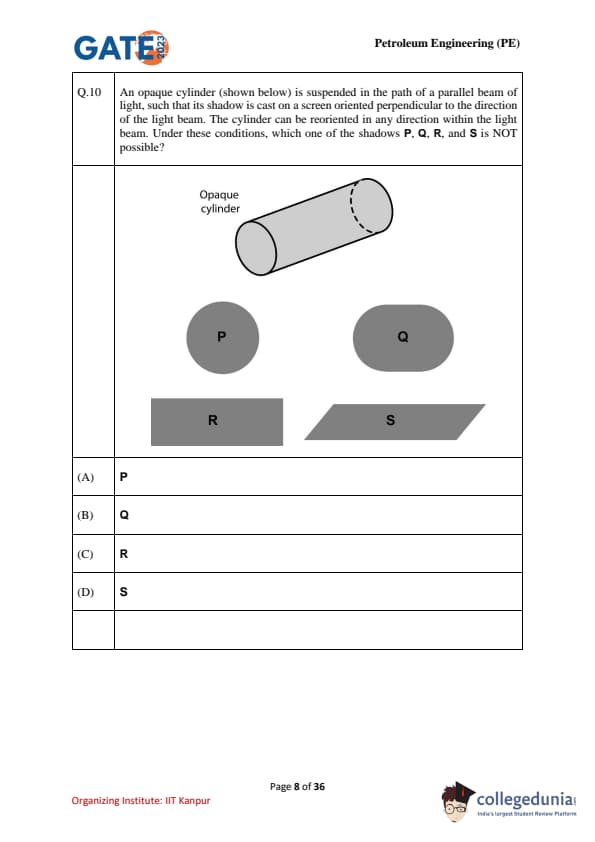
An opaque cylinder (shown below) is suspended in the path of a parallel beam of light, such that its shadow is cast on a screen oriented perpendicular to the direction of the light beam. The cylinder can be reoriented in any direction within the light beam. Under these conditions, which one of the shadows P, Q, R, and S is NOT possible?

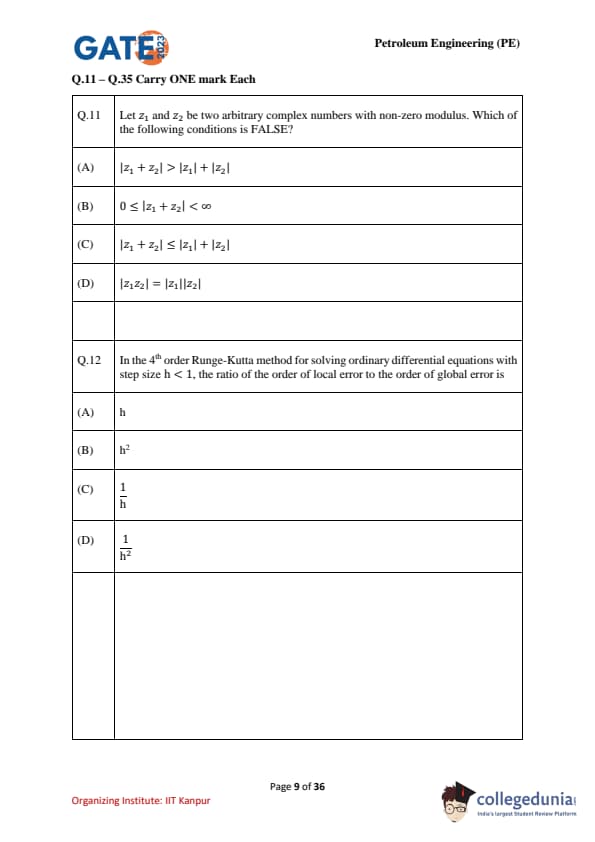
Let \(z_1\) and \(z_2\) be two arbitrary complex numbers with non-zero modulus. Which of the following conditions is FALSE?
In the 4th order Runge-Kutta method for solving ordinary differential equations with step size \(h < 1\), the ratio of the order of local error to the order of global error is
Which of the following instruments can measure contact angle of a liquid drop placed on a surface?
Which of the following is the primary role of proppants in hydraulic fracturing?
A mixture of a flammable gas and air can ignite ONLY if
Which of the following relations defines the coefficient of isothermal compressibility (\(C_g\)) for a gas?
Here, \(p\), \(T\), and \(v\) represent the pressure, temperature and volume of the gas, respectively.
Consider an ideal liquid–vapor mixture at equilibrium having liquid phase mole fraction \((x_i)\) and gas phase mole fraction \((y_i)\) of component \(i\). If at a given temperature, \(P_{v_i}\) is the vapor pressure of pure component \(i\) and \(P\) is the total pressure, then the equilibrium ratio \((k_i)\) is
In-situ combustion method for enhanced oil recovery is commonly used for
Which of the following is a sedimentary rock?
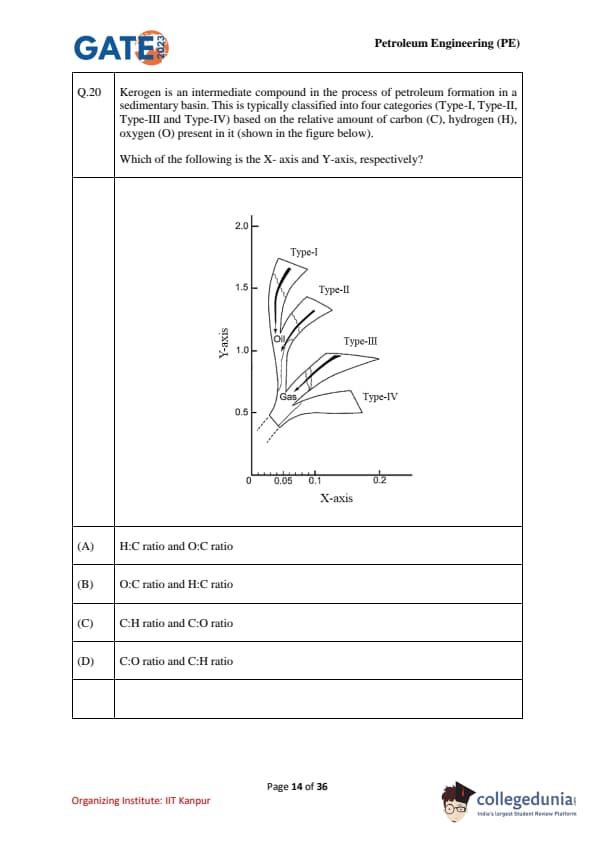
Kerogen is an intermediate compound in the process of petroleum formation in a sedimentary basin. This is typically classified into four categories (Type-I, Type-II, Type-III and Type-IV) based on the relative amount of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) present in it (shown in the figure below).
Which of the following is the X-axis and Y-axis, respectively?

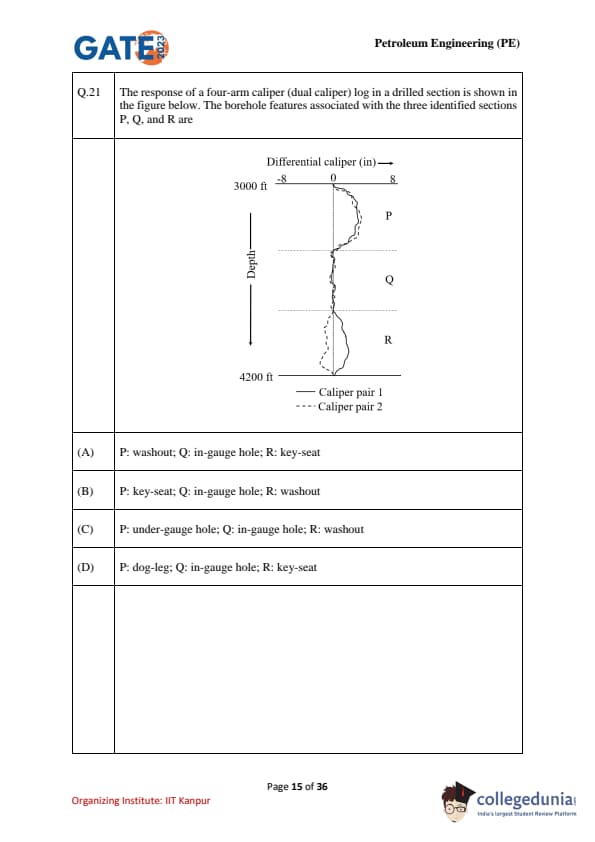
The response of a four-arm caliper (dual caliper) log in a drilled section is shown in the figure. The borehole features associated with the three identified sections P, Q, and R are:

Which of the following is necessary for the generation of electrokinetic potential across well-bore and permeable rock formation?
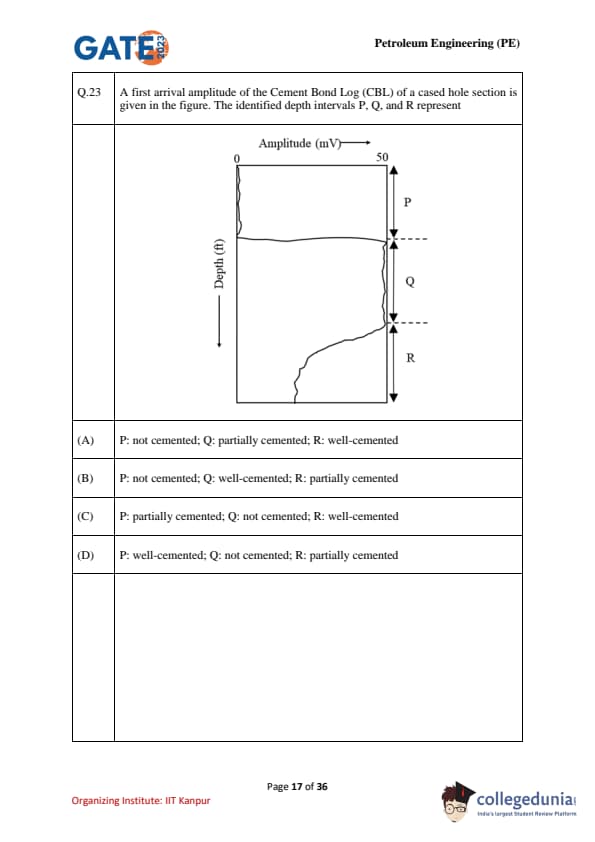
A first arrival amplitude of the Cement Bond Log (CBL) of a cased hole section is given in the figure. The identified depth intervals P, Q, and R represent

Contact angle measurements are often performed on smooth surfaces to gain information about the wettability of a surface. The interfacial tensions between solid-liquid, liquid-air, and air-solid are \(\gamma_{SL}\), \(\gamma_{LA}\), and \(\gamma_{AS}\), respectively. Which of the following expressions describes the contact angle, \(\Theta\)?

Which of the following offshore rigs has the HIGHEST water depth of operation?
Consider an immiscible liquid mixture of n-decane and water containing fully dissociated NaCl. The number of degrees of freedom for this system is
The mean free path of the gas molecule is \(10^{-6}\) mm, while the pore size of the rock is \(10^{-3}\) mm. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
Which of the following is/are the route(s) by which a toxic substance may enter a human body?
Select ALL the safety system(s) that is/are required in an offshore platform.
Polymer flooding enhances oil recovery from an oil reservoir by
Which is/are the thermodynamic inhibitor(s) for natural gas hydrate?
Which of the following hydrocarbon trap(s) is/are a result of sedimentary facies changes?
Which of the following option(s) is/are indication(s) of a well kick?
Let \(\mathbf{X}=\begin{bmatrix} x_{11}&x_{12}&x_{13}
x_{21}&x_{22}&x_{23}
x_{31}&x_{32}&x_{33}\end{bmatrix}\) be a \(3\times 3\) matrix. The determinant of \(\mathbf{X}\) is \(5\). The determinant of matrix \(\mathbf{Y}=\begin{bmatrix} x_{11}&x_{12}&x_{13}
2x_{21}&2x_{22}&2x_{23}
3x_{31}&3x_{32}&3x_{33}\end{bmatrix}\) is \underline{\hspace{1cm.
Consider a vector field \(\vec{V}=x^{3}\,\hat{\imath}+2y^{2}x\,\hat{\jmath}+0.5\,z\,\hat{k}\), where \(\hat{\imath}\), \(\hat{\jmath}\), and \(\hat{k}\) are the unit vectors in \(x\), \(y\), and \(z\) directions, respectively. The divergence of \(\vec{V}\) at the point \((1,2,1)\) is _____ (rounded to one decimal place).
The value of \(\displaystyle\int_{0}^{\pi}\!\!\int_{-1}^{1} r^{2}\sin^{2}\theta \, dr \, d\theta\) is
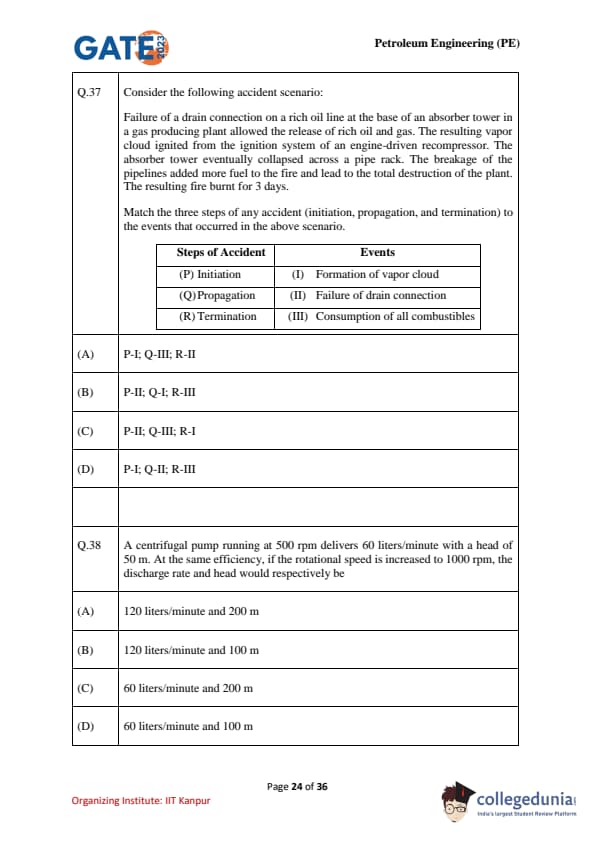
Consider the following accident scenario:
Failure of a drain connection on a rich oil line at the base of an absorber tower in a gas producing plant allowed the release of rich oil and gas. The resulting vapor cloud ignited from the ignition system of an engine-driven recompressor. The absorber tower eventually collapsed across a pipe rack. The breakage of the pipelines added more fuel to the fire and led to the total destruction of the plant. The resulting fire burnt for 3 days.
Match the three steps of any accident (initiation, propagation, and termination) to the events that occurred in the above scenario.

A centrifugal pump running at 500 rpm delivers 60 liters/minute with a head of 50 m. At the same efficiency, if the rotational speed is increased to 1000 rpm, the discharge rate and head would respectively be:
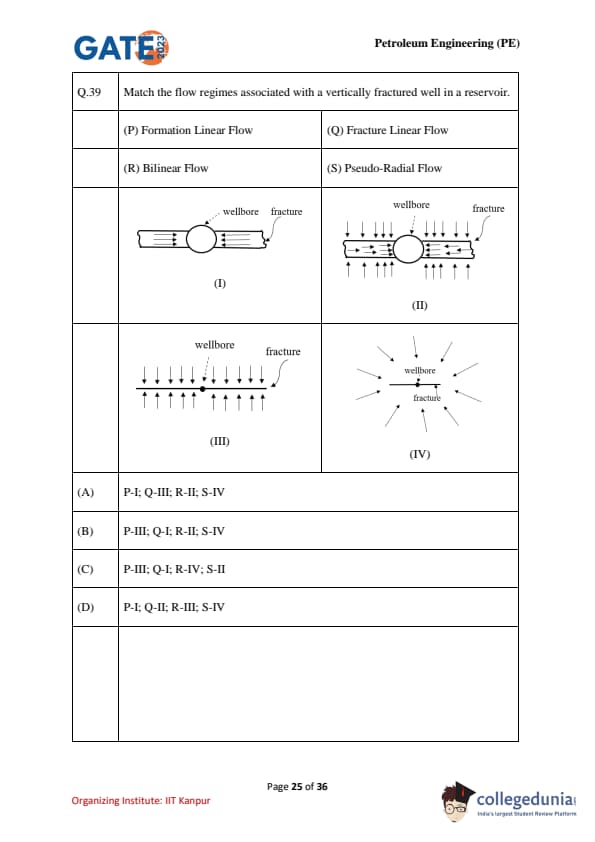
Match the flow regimes associated with a vertically fractured well in a reservoir.

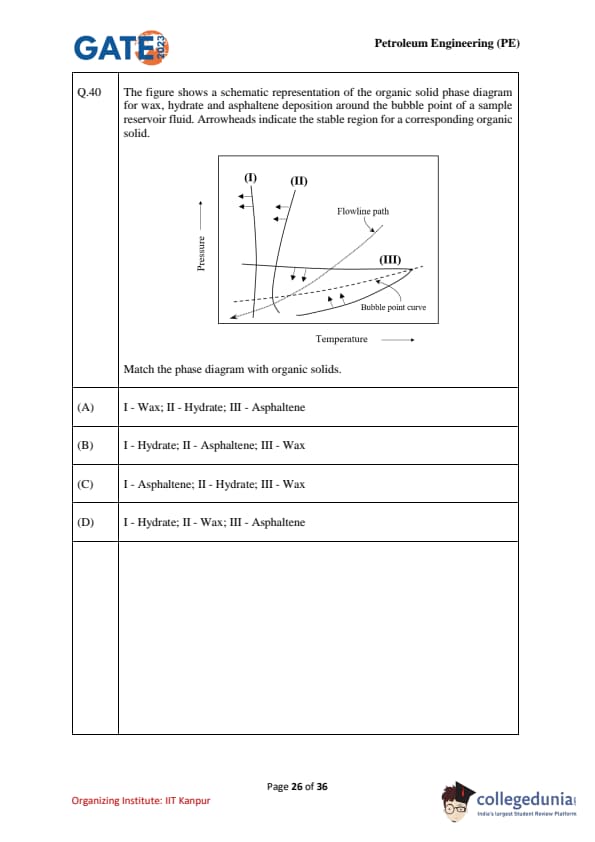
The figure shows a schematic representation of the organic solid phase diagram for wax, hydrate, and asphaltene deposition around the bubble point of a sample reservoir fluid. Arrowheads indicate the stable region for a corresponding organic solid. Match the phase diagram with organic solids.

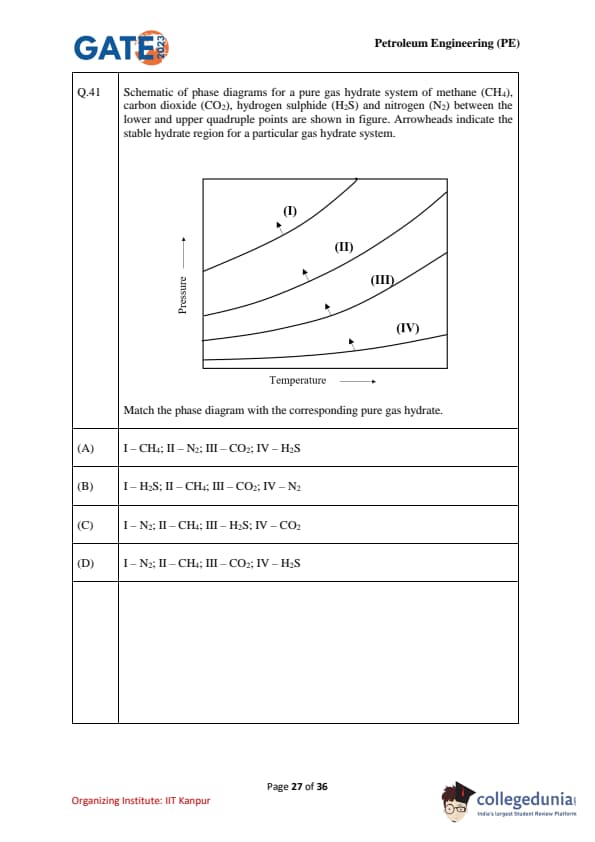
Schematic of phase diagrams for a pure gas hydrate system of methane (CH\(_4\)), carbon dioxide (CO\(_2\)), hydrogen sulphide (H\(_2\)S) and nitrogen (N\(_2\)) between the lower and upper quadruple points are shown in the figure. Arrowheads indicate the stable hydrate region for a particular gas hydrate system. Match the phase diagram with the corresponding pure gas hydrate.

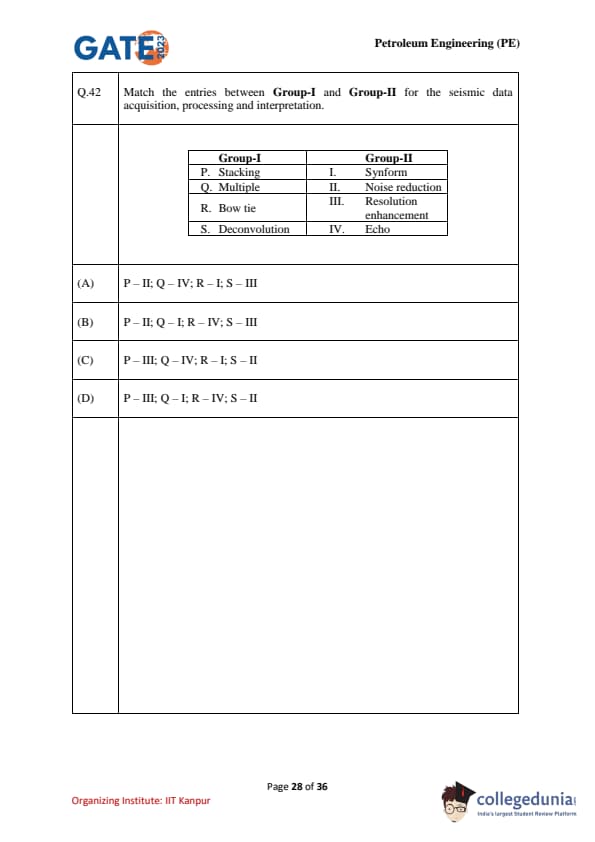
Match the entries between Group-I and Group-II for seismic data acquisition, processing and interpretation.

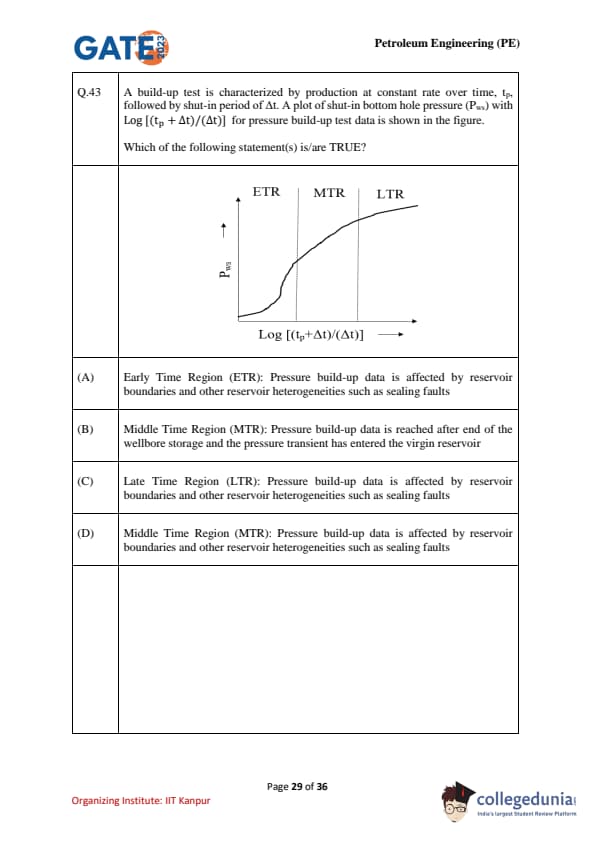
A build-up test is characterized by production at constant rate over time \(t_p\), followed by shut-in period of \(\Delta t\). A plot of shut-in bottom hole pressure (\(P_{ws}\)) with \(\log \left(\dfrac{t_p+\Delta t}{\Delta t}\right)\) for pressure build-up test data is shown in the figure. Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE?

Select the statement(s) that is/are TRUE.
Using Simpson’s one-third rule (with step size \(h=0.25\)), the area under the curve \(y=e^{-x^{3}}\), from \(x=0\) to \(x=1\) is _____ (rounded to two decimal places).
The directional derivative of \(f=x^{3}+4y^{2}+z^{2}\) at the point \(P(2,1,3)\) in the direction of the vector \(\vec{V}=3\hat{\imath}-4\hat{k}\) is _____ (rounded to one decimal place).
A switch-over event in a producing well occasionally results in a reportable oil leak. An analysis of the data shows that the chance of a reportable leak is 1 in 500 switch-over events. It is observed that 10 switch-over events occur every day.
If the occurrence of a reportable leak follows a Poisson distribution, the number of days in a year (of 365 days) with no reportable oil leaks from switch-over events is ________ (rounded to nearest integer).
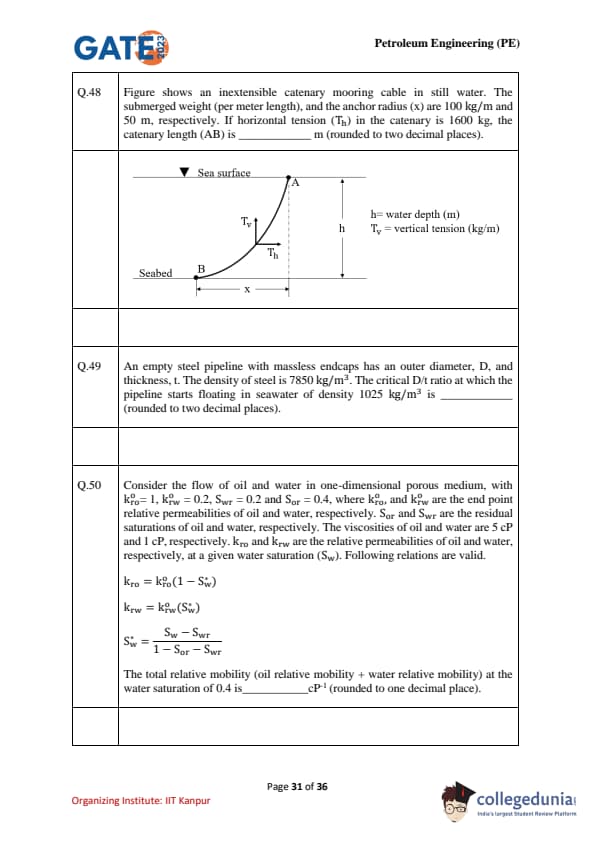
Figure shows an inextensible catenary mooring cable in still water. The submerged weight (per meter length), and the anchor radius are 100 kg/m and 50 m, respectively. If horizontal tension (\(T_h\)) in the catenary is 1600 kg, the catenary length (AB) is ________ m (rounded to two decimal places).

An empty steel pipeline with massless endcaps has an outer diameter, \(D\), and thickness, \(t\). The density of steel is \(7850\ \mathrm{kg/m^3}\). The critical \(D/t\) ratio at which the pipeline starts floating in seawater of density \(1025\ \mathrm{kg/m^3}\) is \underline{\hspace{1.5cm (rounded to two decimal places).
Consider 1D oil--water flow with \(k_{ro}^o=1,\ k_{rw}^o=0.2,\ S_{wr}=0.2,\ S_{or}=0.4\). Oil and water viscosities are \(5\) cP and \(1\) cP. With \[ k_{ro}=k_{ro}^o(1-S_w^*),\quad k_{rw}=k_{rw}^o(S_w^*),\quad S_w^*=\frac{S_w-S_{wr}}{1-S_{or}-S_{wr}}, \]
the total relative mobility at \(S_w=0.4\) is \hspace{1.5cm cP\(^{-1\) (rounded to one decimal place).
A binary mixture of n-butane (\(C_4H_{10}\)) and n-pentane (\(C_5H_{12}\)) is under thermodynamic equilibrium at 180°F and 95 psia. The vapor pressures of pure C4H10 and pure C5H12 at 180°F are 160 psia and 54 psia, respectively.
Assuming ideal solution behavior (i.e., Raoult's law and Dalton’s law are valid), the mole fraction of the n-butane in the gas phase is _______ (rounded to three decimal places).
A highly permeable reservoir with initial reservoir pressure of 3000 psi is under active water drive from a surrounding large aquifer. The final stabilized reservoir pressure is 2500 psi. Following data associated with the reservoir at 2500 psi are given.
Oil production rate = 30,000 STB/day
Water production rate = 0 STB/day
Oil formation volume factor, \(B_o = 1.5 \, bbl/STB\)
Gas formation volume factor, \(B_g = 0.00070 \, bbl/scf\)
Water formation volume factor, \(B_w = 1 \, bbl/STB\)
Producing Gas to Oil Ratio, GOR = 850 scf/STB
Gas solubility, \(R_s = 700 \, scf/STB\)
If the reservoir pressure and the reservoir production rates remain constant, the water influx rate is _________ bbl/day (rounded to nearest integer).
A volumetric undersaturated solution gas drive reservoir (without gas cap, no water influx, and with no initial gas saturation) has an initial water saturation of \(15%\) which remains unchanged during production. After the production of \(10%\) of the initial oil (measured at surface conditions), the oil formation volume factor \(B_o\) is reduced from its initial value of \(1.4~bbl/STB\) to \(1.2~bbl/STB\). The final gas saturation in percentage is \underline{\hspace{1.8cm (rounded to one decimal place).
After well completion, a discovery well in an oil reservoir is produced for a short period and then closed for pressure build-up test. The production history before shut-in is given below.

The Horner’s pseudo-producing time, \(t_{pH}\), is \underline{\hspace{1.2cm hr (rounded to nearest integer).
A compressional acoustic wave takes \(55~\mu s\) to travel \(0.3048~m\) through a rock formation having bulk modulus of \(37.5~GPa\) and shear modulus of \(31~GPa\). The bulk density of the rock is _____ kg/m\(^{3}\) (rounded to two decimal places).
A gamma ray log run across a sand–shale sequence recorded maximum and minimum values of \(70\) API and \(30\) API, respectively. A bed in this sequence has a gamma log value of \(50\) API. Assuming a linear relationship between shale index and shale volume, the volume fraction of shale in the bed is _____ (rounded to one decimal place).
The resistivity reading of a flushed zone across a permeable formation (drilled with water-based mud) is 20 \(\Omega\!\cdot\)m. Laboratory analysis shows that the resistivity of the core plug (100% saturated with a NaCl brine) from the same formation is 6 \(\Omega\!\cdot\)m. The resistivity of the NaCl brine is 0.6 \(\Omega\!\cdot\)m.
If the resistivity of the mud filtrate is 0.9 \(\Omega\!\cdot\)m and Archie's saturation exponent is 2, then the estimated residual hydrocarbon saturation (in percentage) in the flushed zone is _________ (rounded to two decimal places).
Consider a micellar displacement process in a homogeneous reservoir with a porosity of 30%. The volume of the microemulsion slug to be injected is 4% of the pore volume. The slug contains 4 vol% surfactant. The density of the rock and the surfactant is 2.7 g/cm\(^{3}\) and 1.1 g/cm\(^{3}\), respectively.
Assuming that the average surfactant adsorption is 0.25 mg/g of the reservoir rock, the fraction of the injected surfactant that will be adsorbed is __________ (rounded to two decimal places).
A kill mud of appropriate density is required to be injected in a well such that the shut-in pressure is \(6.8 \times 10^{6}\ \mathrm{Pa}\) at a depth of \(3500\ \mathrm{m}\). Here, the shut-in pressure is the quantity by which the bottom-hole pressure exceeds the hydrostatic pressure of the original mud at the given depth. The density of the original mud is \(1100\ \mathrm{kg/m^3}\). The density of the kill mud is \underline{\hspace{1.8cm kg/m\(^3\) (rounded to two decimal places).
A non-Newtonian drilling fluid (Bingham plastic) is between two flat parallel rectangular plates of area \(10\ \mathrm{cm^2}\) each, separated by \(1\ \mathrm{cm}\). A force of \(300\) dyne is required to initiate motion of the upper plate. A force of \(600\) dyne keeps the plate moving at a constant velocity of \(10\ \mathrm{cm/s}\). The constitutive law is \(\tau_{yx}=\mu_p \dot{\gamma}+\tau^o_{yx}\).
Find the Bingham plastic viscosity \(\mu_p\) in dyne\(\cdot\)s/cm\(^2\) (rounded to the nearest integer).

Crude oil having density and viscosity of \(850\ kg/m^3\) and \(2\times10^{-3}\ Pa\!\cdot\!s\), respectively, is flowing at an average velocity of \(0.35\ m/s\) through a horizontal capillary tube. The inside diameter and length of the capillary tube are \(2.5\times10^{-3}\ m\) and \(0.30\ m\), respectively. The Fanning friction factor is \(f=\dfrac{16}{\mathrm{Re}}\). The pressure drop across the capillary tube is \underline{\hspace{2cm Pa (rounded to one decimal place).
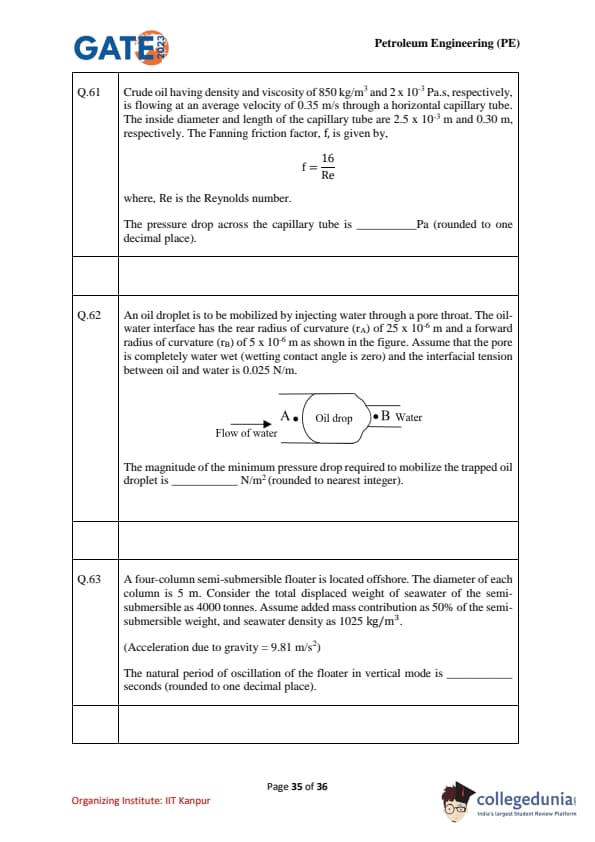
An oil droplet is to be mobilized by injecting water through a pore throat. The oil–water interface has the rear radius of curvature \(r_A=25\times10^{-6}\ m\) and the forward radius of curvature \(r_B=5\times10^{-6}\ m\). The pore is completely water-wet (contact angle \(=0^\circ\)) and interfacial tension is \(\sigma=0.025\ N/m\). The minimum pressure drop required to mobilize the trapped oil droplet is \underline{\hspace{2cm N/m\(^2\) (nearest integer).

A four–column semi–submersible floater is located offshore. The diameter of each column is \(5~m\). Consider the total displaced weight of seawater of the semi–submersible as \(4000~tonnes\). Assume added mass contribution as \(50%\) of the semi–submersible weight, and seawater density as \(1025~kg/m^3\). (Acceleration due to gravity \(=9.81~m/s^2\).) The natural period of oscillation of the floater in vertical mode is \underline{\hspace{1.4cm seconds (rounded to one decimal place).
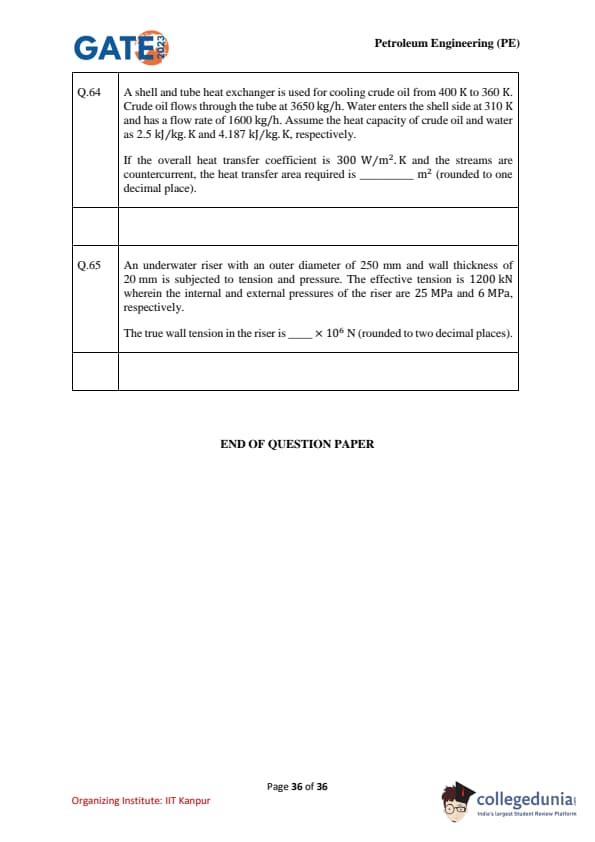
A shell-and-tube heat exchanger is used for cooling crude oil from \(400~K\) to \(360~K\). Crude oil flows through the tube at \(3650~kg/h\). Water enters the shell side at \(310~K\) and has a flow rate of \(1600~kg/h\). Assume \(c_{p,oil}=2.5~kJ/(kg.K)\), \(c_{p,w}=4.187~kJ/(kg.K)\), overall \(U=300~W/(m^2\!\cdot\!K)\), and countercurrent flow. The required heat–transfer area is \underline{\hspace{1.2cm m\(^2\) (rounded to one decimal place).
An underwater riser with an outer diameter of 250 mm and wall thickness of 20 mm is subjected to tension and pressure. The effective tension is \(1200\) kN wherein the internal and external pressures of the riser are \(25\) MPa and \(6\) MPa, respectively. The true wall tension in the riser is ____ \(\times 10^{6}\) N (rounded to two decimal places).















Also Check:
| Previous Year GATE Petroleum Engineering Question Papers | GATE 2023 Petroleum Engineering Paper Analysis |
| GATE Petroleum Engineering Exam Pattern | GATE Petroleum Engineering Syllabus |





Comments