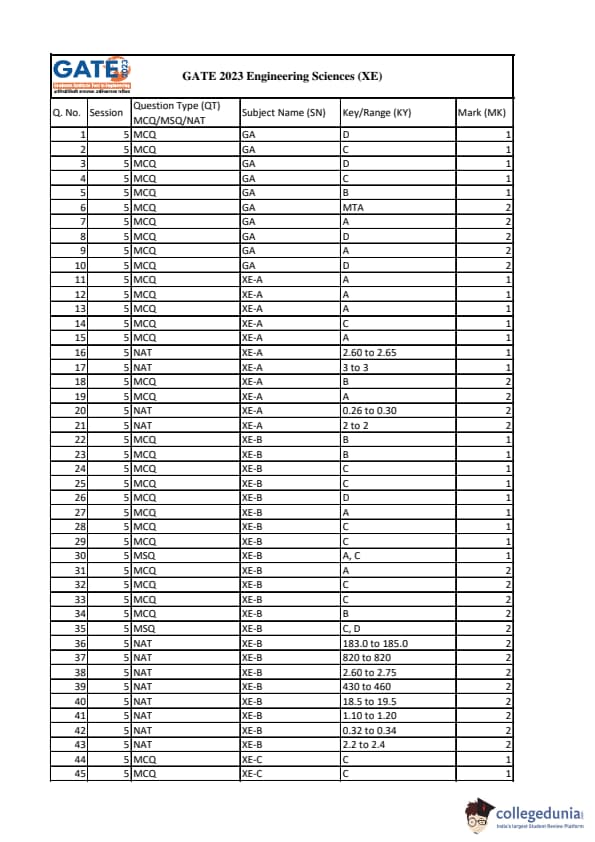
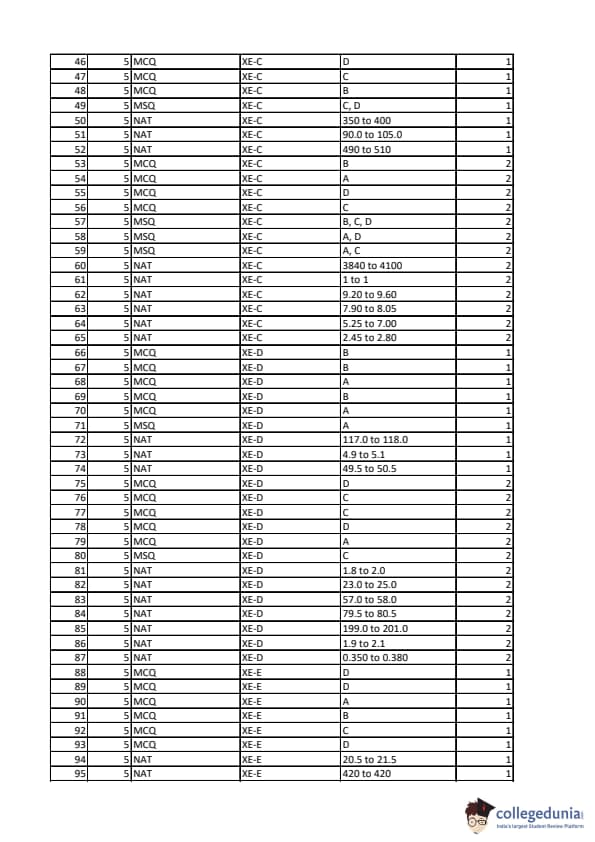
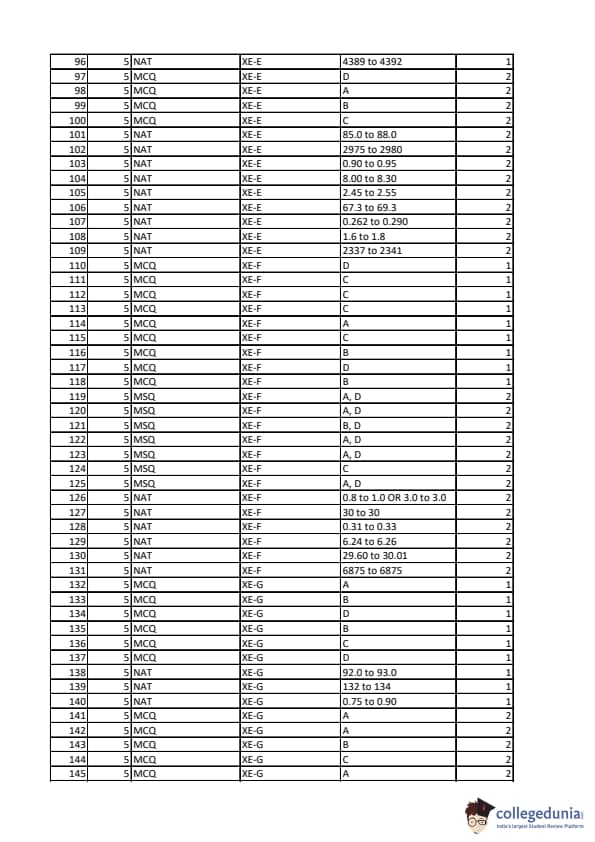
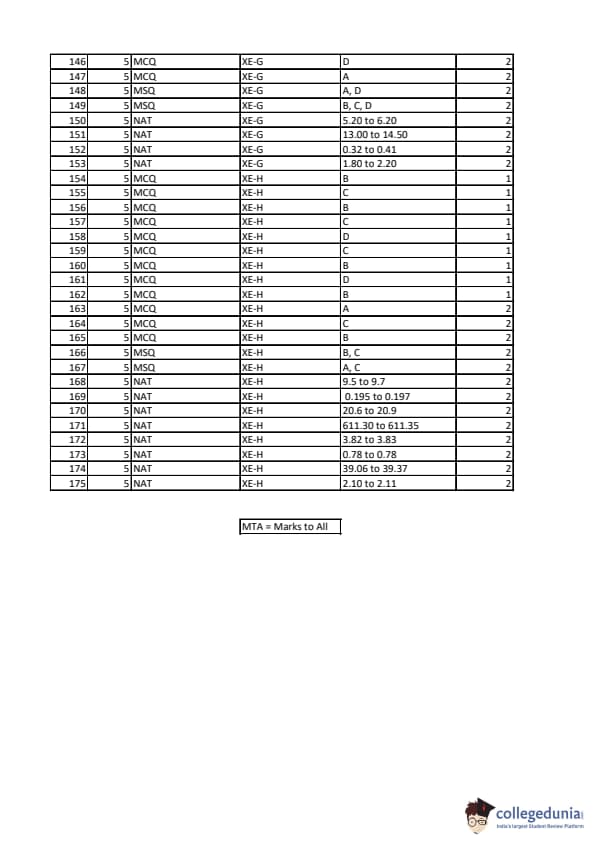
GATE 2023 Engineering Sciences Question Paper PDF is now available here for download. IIT Kanpur conducted GATE 2023 Engineering Sciences exam on February 11, 2023 in the Forenoon Session from 09:30 AM to 12:30 PM. Students have to answer 65 questions in GATE 2023 Engineering Sciences Question Paper carrying a total weightage of 100 marks. 10 questions are from the General Aptitude section and 55 questions are from Core Discipline.
GATE 2023 Engineering Sciences Question Paper with Solutions PDF
| GATE 2023 Engineering Sciences Question Paper with Solutions | Download | Check Solutions |

The village was nestled in a green spot, _____ the ocean and the hills.
Disagree : Protest :: Agree : ______ (By word meaning)
A ‘frabjous’ number is defined as a 3-digit number with all digits odd, and no two adjacent digits being the same. For example, 137 is a frabjous number, while 133 is not. How many such frabjous numbers exist?
Which one among the following statements must be TRUE about the mean and the median of the scores of all candidates appearing for GATE 2023?
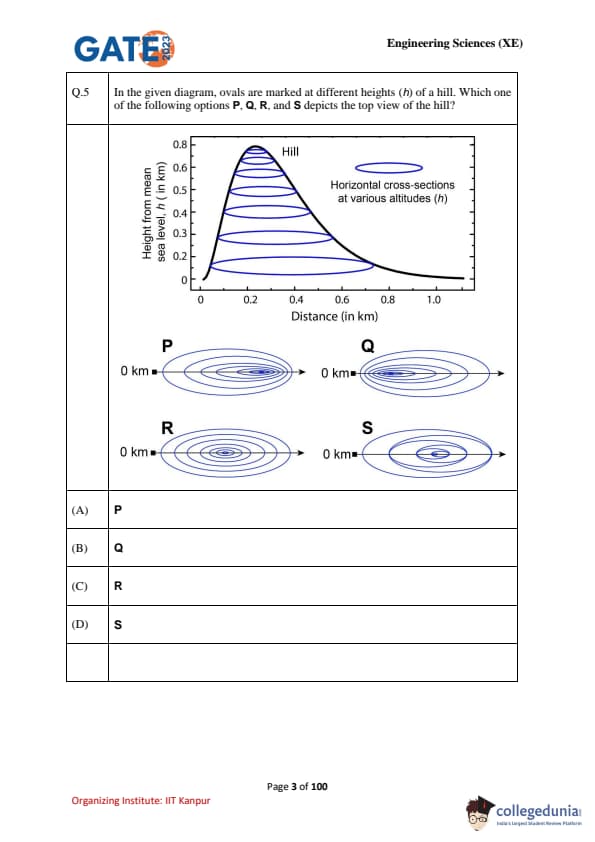
In the given diagram, ovals are marked at different heights (\(h\)) of a hill. Which one of the following options P, Q, R, and S depicts the top view of the hill?

Residency is a famous housing complex with many well-established individuals among its residents.
A survey revealed:
1. All residents who are well established in their respective fields are academicians.
2. Most of these academicians are authors of some best-selling books.
Based only on this information, which one of the following statements can be logically inferred with certainty?
Ankita has to climb 5 stairs starting at the ground, while respecting the following rules:
At any stage, Ankita can move either one or two stairs up.
At any stage, Ankita cannot move to a lower step.
Let \(F(N)\) denote the number of possible ways in which Ankita can reach the \(N^{th}\) stair. For example, \(F(1)=1\), \(F(2)=2\), \(F(3)=3\).
The value of \(F(5)\) is ______.
The information contained in DNA is used to synthesize proteins necessary for life. DNA is composed of four nucleotides: Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G). Coding regions—where nucleotide triplets code for amino acids—constitute only about 2% of human DNA.
Based only on the information above, which of the following statements can be inferred with certainty?
(i) The majority of human DNA has no role in the synthesis of proteins.
(ii) The function of about 98% of human DNA is not understood.
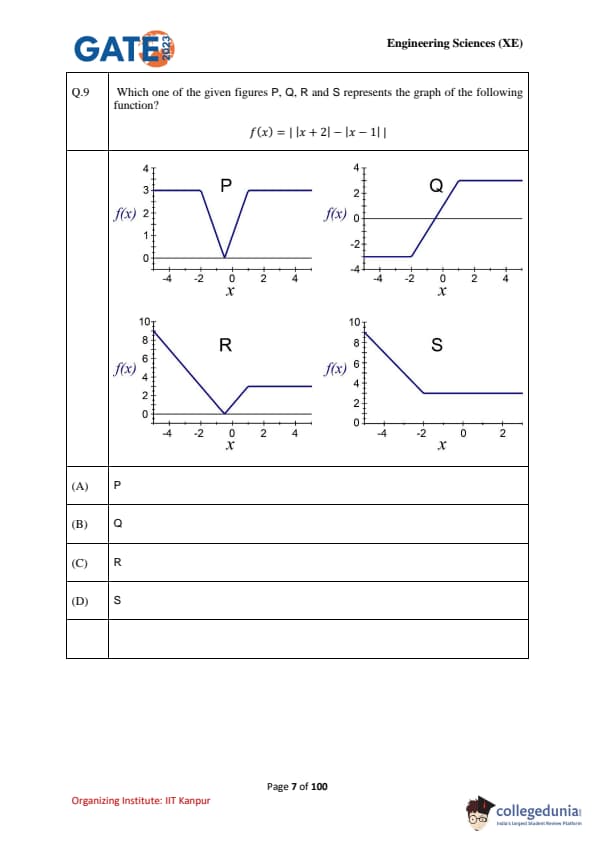
Which one of the given figures P, Q, R and S represents the graph of the following function? \[ f(x)=\left|\,|x+2|-|x-1|\,\right| \]

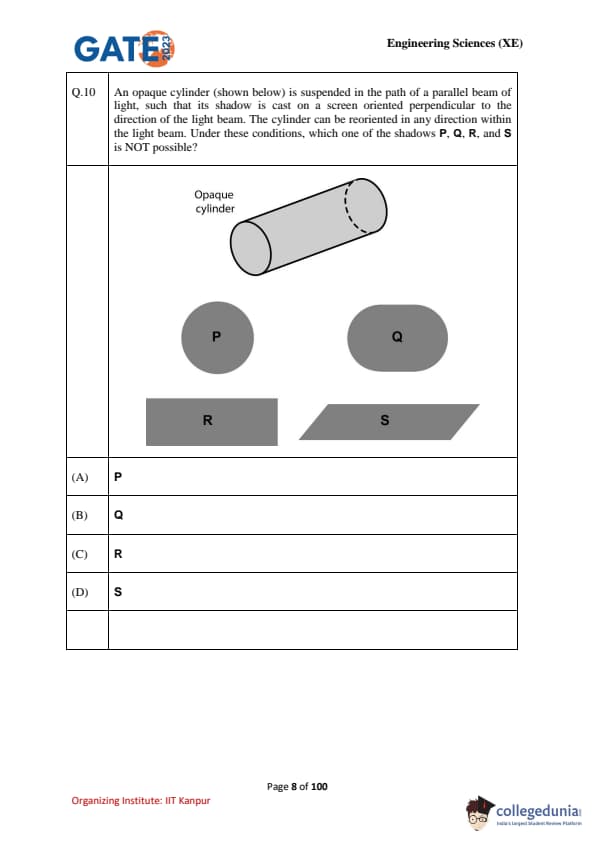
An opaque cylinder (shown below) is suspended in the path of a parallel beam of light, such that its shadow is cast on a screen oriented perpendicular to the direction of the light beam. The cylinder can be reoriented in any direction within the light beam. Under these conditions, which one of the shadows P, Q, R, and S is NOT possible?

Let \(A\) be a \(3 \times 3\) real matrix having eigenvalues \(1,2,3\). If \[ B = A^2 + 2A + I, \]
where \(I\) is the \(3 \times 3\) identity matrix, then the eigenvalues of \(B\) are:
Let \(f:\mathbb{R}^2 \to \mathbb{R}\) be defined by \[ f(x,y)= \begin{cases} \dfrac{xy}{|x|+y}, & y \neq -|x|,
[6pt] 0, & otherwise. \end{cases} \]
Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
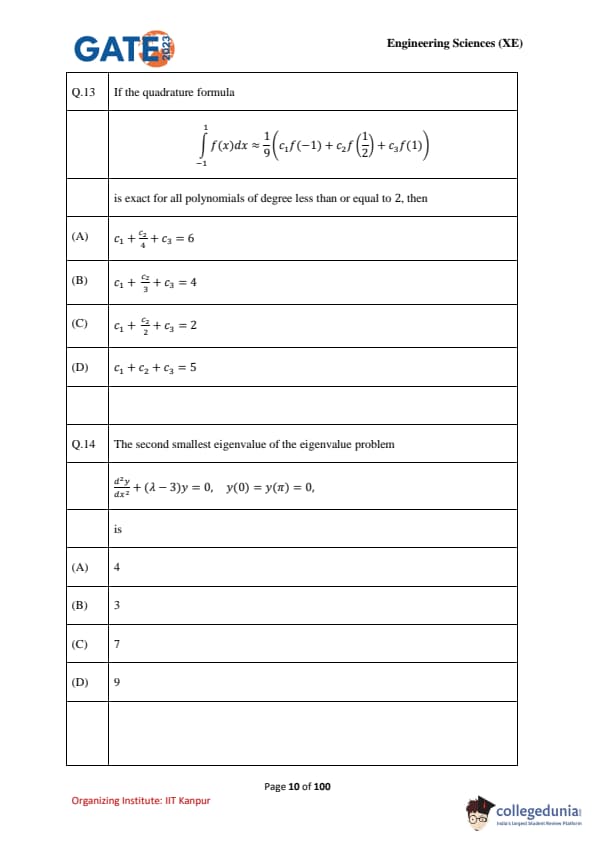
If the quadrature formula \[ \int_{-1}^{1} f(x)\,dx \;\approx\; \frac{1}{9}\Big(c_1 f(-1) + c_2 f\!\left(\tfrac{1}{2}\right) + c_3 f(1)\Big) \]
is exact for all polynomials of degree less than or equal to \(2\), then
The second smallest eigenvalue of the eigenvalue problem \[ \frac{d^2 y}{dx^2} + (\lambda - 3)\,y = 0,\qquad y(0)=y(\pi)=0, \]
is
Which one of the following functions is differentiable at \(z=0\) but NOT differentiable at any other point in the complex plane \(\mathbb{C}\)?
If the polynomial \[ P(x)=a_0+a_1x+a_2\,x(x-1)+a_3\,x(x-1)(x-2) \]
interpolates the points \((0,2)\), \((1,3)\), \((2,2)\), and \((3,5)\), then the value of \(P\!\left(\tfrac{5}{2}\right)\) is ______ (round off to 2 decimal places).
The value of \(m\) for which the vector field \[ \vec F(x,y)=\big(4x^{m}y^{2}-2xy^{m}\big)\,\mathbf{i}+\big(2x^{4}y-3x^{2}y^{2}\big)\,\mathbf{j} \]
is a conservative vector field, is __________ (in integer).
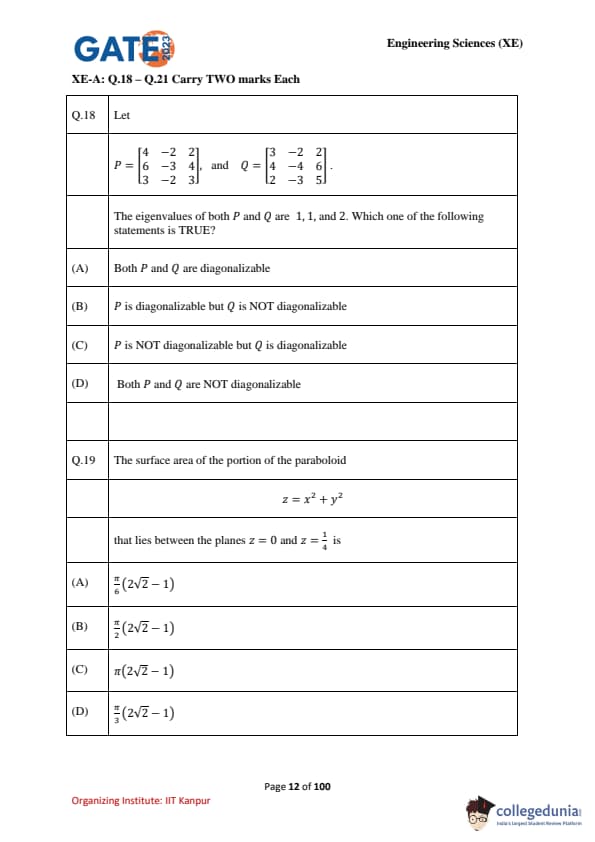
Let \[ P=\begin{bmatrix}4 & -2 & 2
6 & -3 & 4
3 & -2 & 3\end{bmatrix}, \qquad Q=\begin{bmatrix}3 & -2 & 2
4 & -4 & 6
2 & -3 & 5\end{bmatrix}. \]
The eigenvalues of both \(P\) and \(Q\) are \(1,1,2\). Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
The surface area of the portion of the paraboloid \[ z=x^2+y^2 \]
that lies between the planes \(z=0\) and \(z=\tfrac{1}{4}\) is
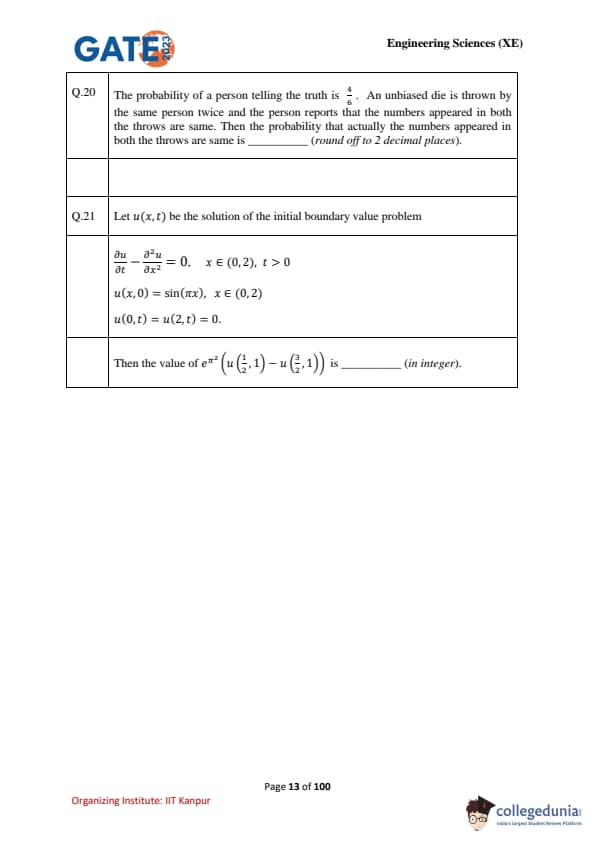
The probability of a person telling the truth is \(\dfrac{4}{6}\). An unbiased die is thrown by the same person twice and the person reports that the numbers appeared in both the throws are the same. Then the probability that actually the numbers appeared in both the throws are same is _______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places).
Let \(u(x,t)\) be the solution of the initial–boundary value problem \[ \frac{\partial u}{\partial t}-\frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial x^2}=0, x\in(0,2),\ t>0, \] \[ u(x,0)=\sin(\pi x), x\in(0,2),\qquad u(0,t)=u(2,t)=0. \]
Then the value of \(e^{\pi^2}\!\left(u\!\left(\tfrac{1}{2},1\right)-u\!\left(\tfrac{3}{2},1\right)\right)\) is ________ (in integer).
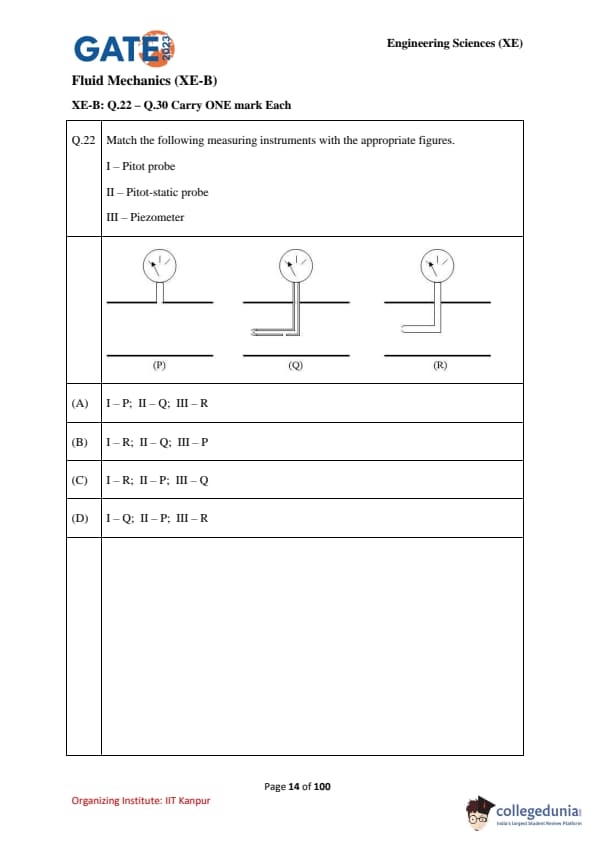
Match the following measuring instruments with the appropriate figures:
I – Pitot probe
II – Pitot-static probe
III – Piezometer

Figures: (P), (Q), (R)
Among the following non-dimensional numbers, which one characterizes periodicity present in a transient flow?
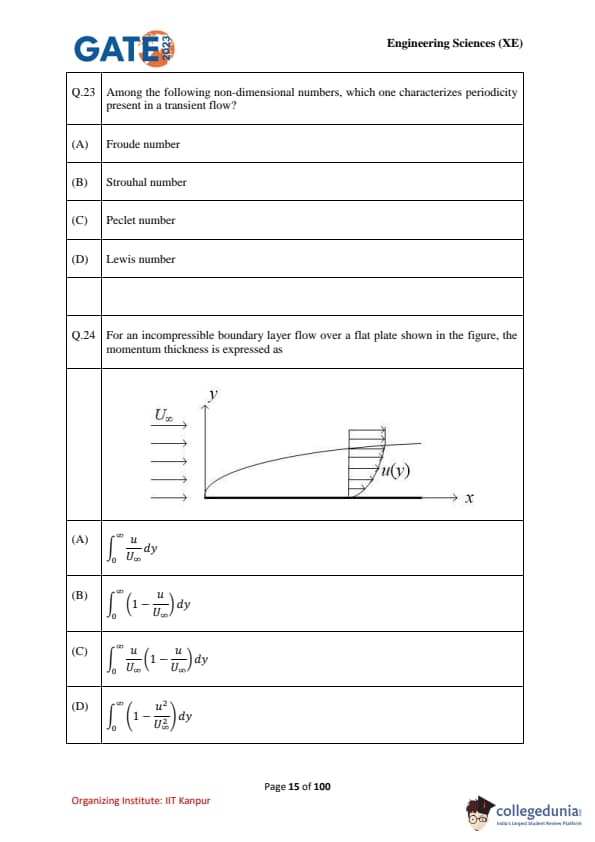
For an incompressible boundary layer flow over a flat plate (figure shown), the momentum thickness is expressed as

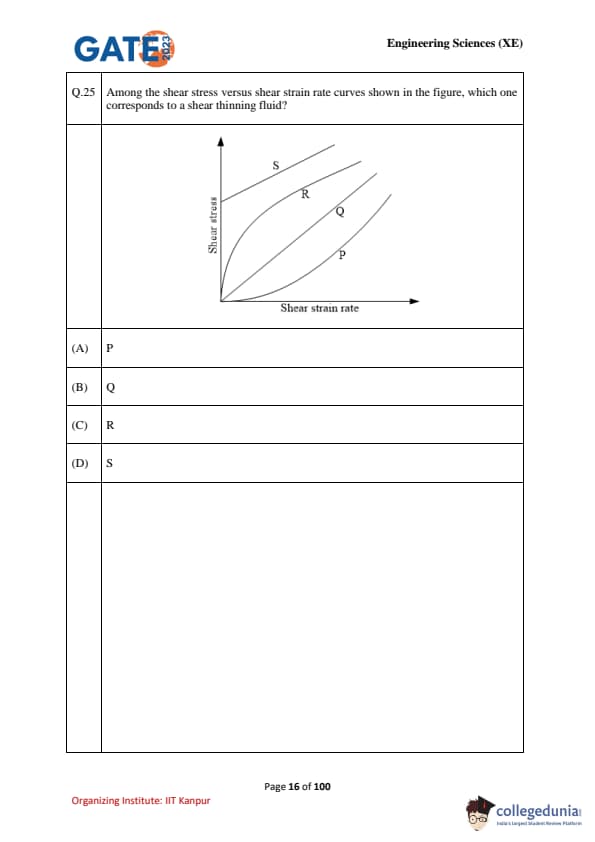
Among the shear stress versus shear strain rate curves shown in the figure, which one corresponds to a shear thinning fluid?

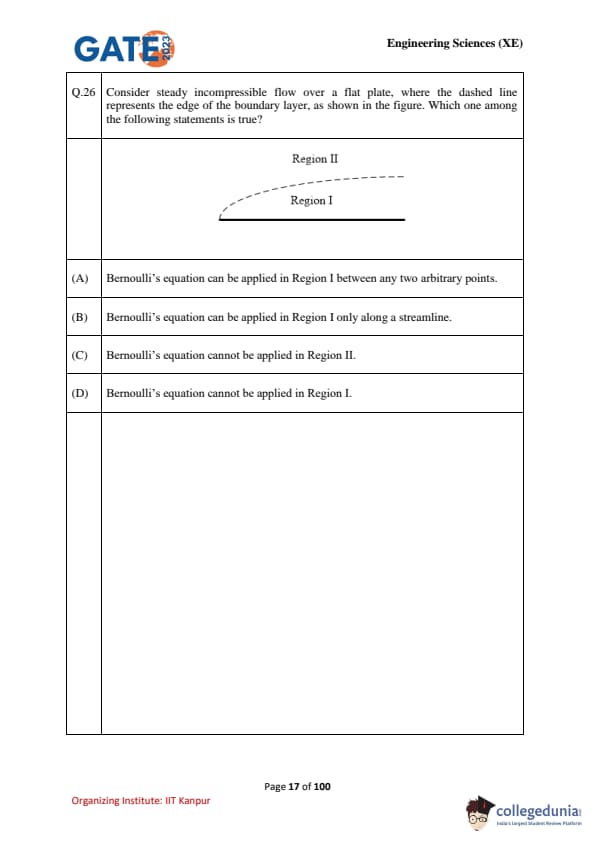
Consider steady incompressible flow over a flat plate, where the dashed line represents the edge of the boundary layer, as shown in the figure. Which one among the following statements is true?

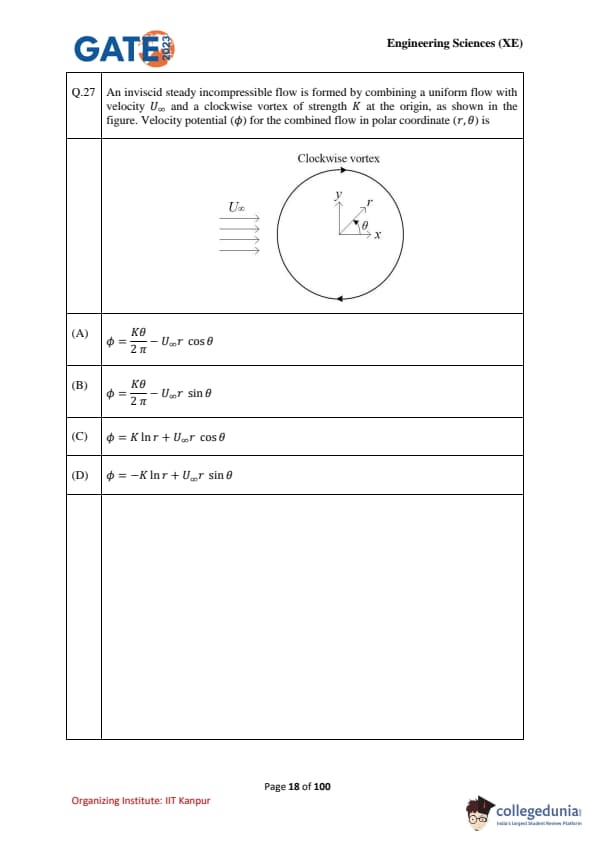
An inviscid steady incompressible flow is formed by combining a uniform flow with velocity \(U_\infty\) and a clockwise vortex of strength \(K\) at the origin, as shown in the figure. Velocity potential (\(\phi\)) for the combined flow in polar coordinates \((r,\theta)\) is

Which of the following statements are true?
(i) Conservation of mass for an unsteady incompressible flow can be represented as \(\nabla\!\cdot \vec V = 0\), where \(\vec V\) denotes velocity vector.
(ii) Circulation is defined as the line integral of vorticity about a closed curve.
(iii) For some fluids, shear stress can be a nonlinear function of the shear strain rate.
(iv) Integration of the Bernoulli’s equation along a streamline under steady-state leads to the Euler’s equation.
For a two-dimensional flow field given as \(\vec V = -x\,\hat{\imath} + y\,\hat{\jmath}\), a streamline passes through points \((2,1)\) and \((5,p)\). The value of \(p\) is
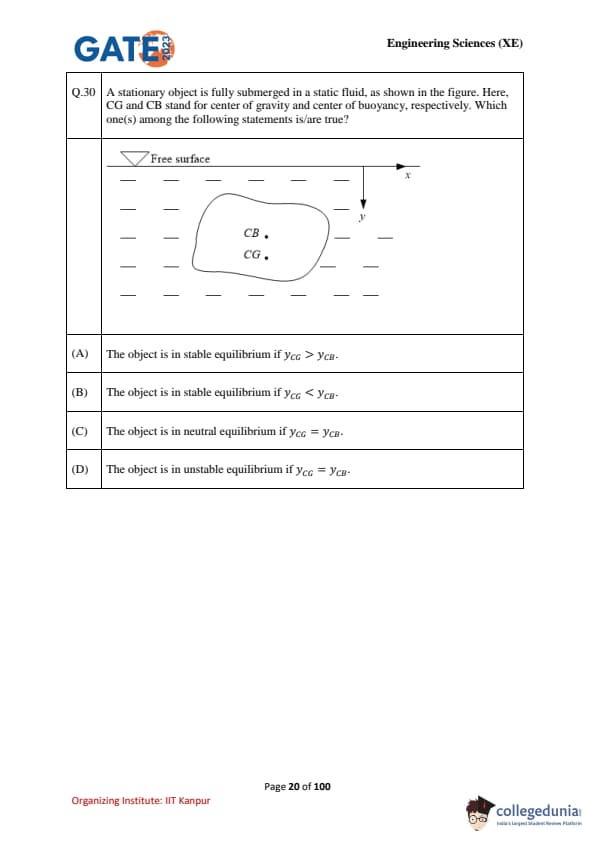
A stationary object is fully submerged in a static fluid, as shown in the figure. Here, CG and CB stand for the center of gravity and the center of buoyancy, respectively. Which one(s) among the following statements is/are true?
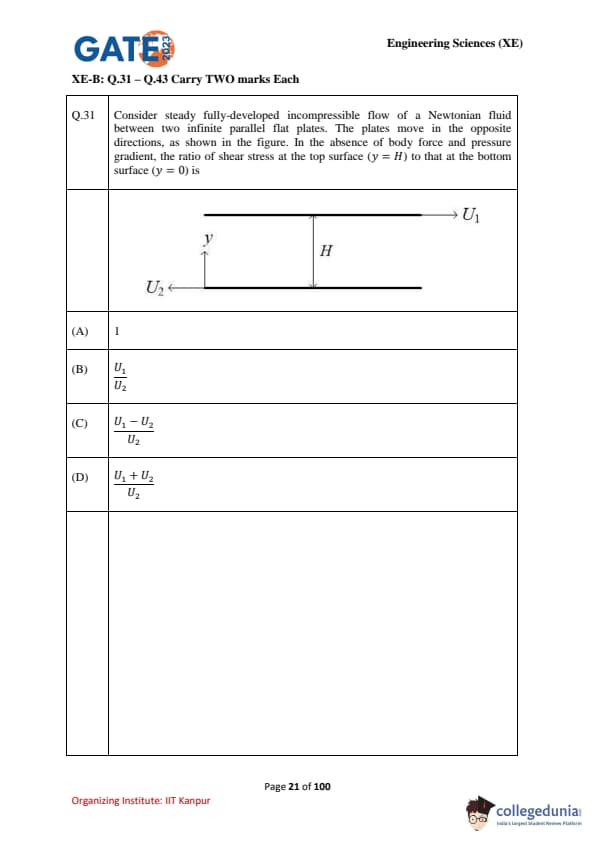
Consider steady fully-developed incompressible flow of a Newtonian fluid between two infinite parallel flat plates. The plates move in the opposite directions, as shown in the figure. In the absence of body force and pressure gradient, the ratio of shear stress at the top surface (\(y=H\)) to that at the bottom surface (\(y=0\)) is
A two-dimensional incompressible flow field is defined as \[ \vec V(x,y)=(Axy)\,\hat{\imath}+(By^2)\,\hat{\jmath}, \]
where \(A\) and \(B\) are constants. The dynamic viscosity is \(\mu\). In the absence of body force, which expression represents the pressure gradient at the location \((5,0)\) in the concerned flow field?
For a potential flow, the fluid velocity is given by \(\vec V(x,y)=u\,\hat{\imath}+v\,\hat{\jmath}\). The slope of the potential line at \((x,y)\) is
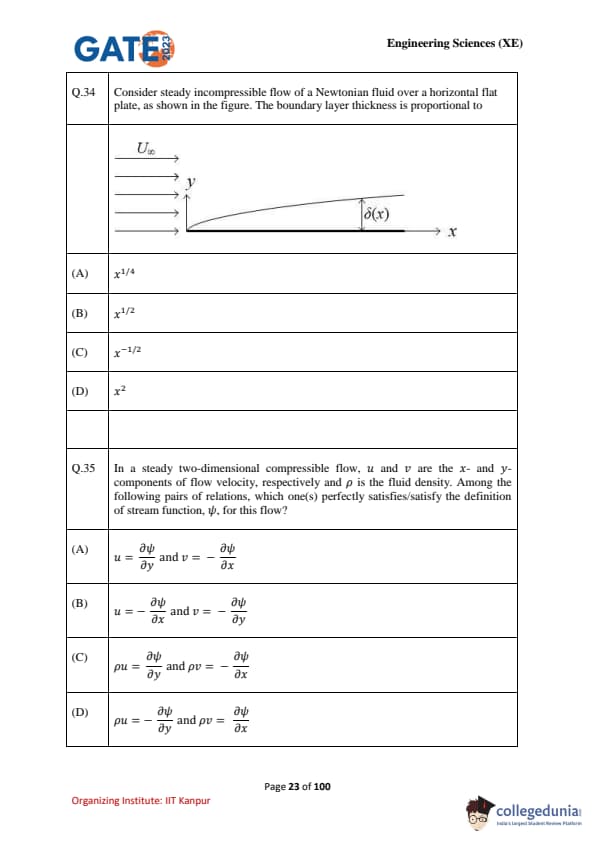
Consider steady incompressible flow of a Newtonian fluid over a horizontal flat plate, as shown in the figure. The boundary layer thickness is proportional to
In a steady two-dimensional compressible flow, \(u\) and \(v\) are the \(x\)- and \(y\)-components of velocity, and \(\rho\) is the fluid density. Among the following pairs of relations, which one(s) perfectly satisfies/satisfy the definition of stream function, \(\psi\), for this flow?
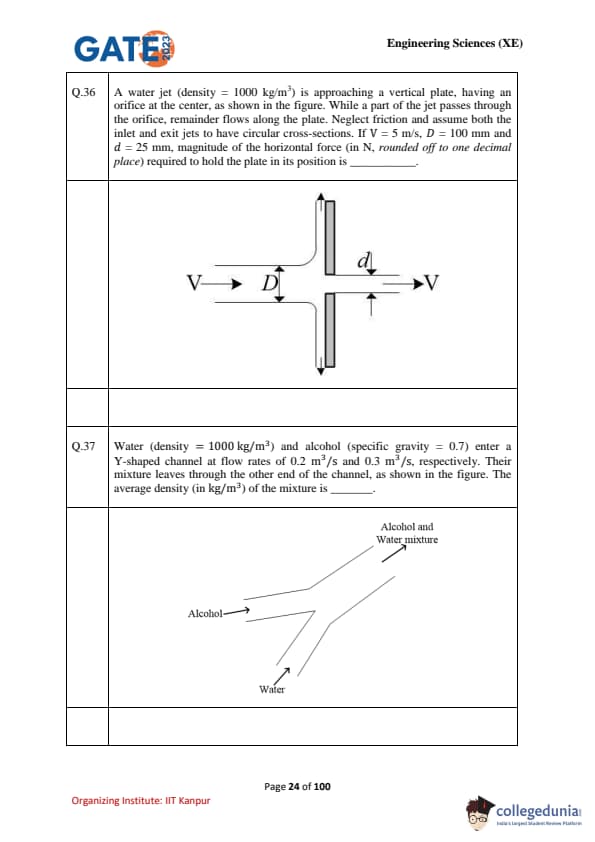
A water jet (density = 1000 kg/m\(^3\)) is approaching a vertical plate, having an orifice at the center, as shown in the figure. While a part of the jet passes through the orifice, remainder flows along the plate. Neglect friction and assume both the inlet and exit jets to have circular cross-sections. If \(V = 5\) m/s, \(D = 100\) mm and \(d = 25\) mm, magnitude of the horizontal force (in N, rounded off to one decimal place) required to hold the plate in its position is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\).
Water (density = 1000 kg/m\(^3\)) and alcohol (specific gravity = 0.7) enter a Y-shaped channel at flow rates of 0.2 m\(^3\)/s and 0.3 m\(^3\)/s, respectively. Their mixture leaves through the other end of the channel, as shown in the figure. The average density (in kg/m\(^3\)) of the mixture is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\).
The velocity and acceleration of a fluid particle are given as \(\vec{V} = (-\hat{i} + 2\hat{j})\) m/s and \(\vec{a} = (-2\hat{i} - 4\hat{j})\) m/s\(^2\), respectively. The magnitude of the component of acceleration (in m/s\(^2\), rounded off to two decimal places) of the fluid particle along the streamline is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\).
A hydraulic turbine with rotor diameter of 100 mm produces 200 W of power while rotating at 300 rpm. Another dynamically-similar turbine rotates at a speed of 1500 rpm. Consider both turbines to operate with the same fluid (identical density and viscosity), and neglect any gravitational effect. Then the power (in W, rounded off to nearest integer) produced by the second turbine is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\).
Water (density = 1000 kg/m\(^3\)) flows steadily with a flow rate of 0.05 m\(^3\)/s through a venturimeter having throat diameter of 100 mm. If the pipe diameter is 200 mm and losses are negligible, the pressure drop (in kPa, rounded off to one decimal place) between an upstream location in the pipe and the throat (both at the same elevation) is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\).
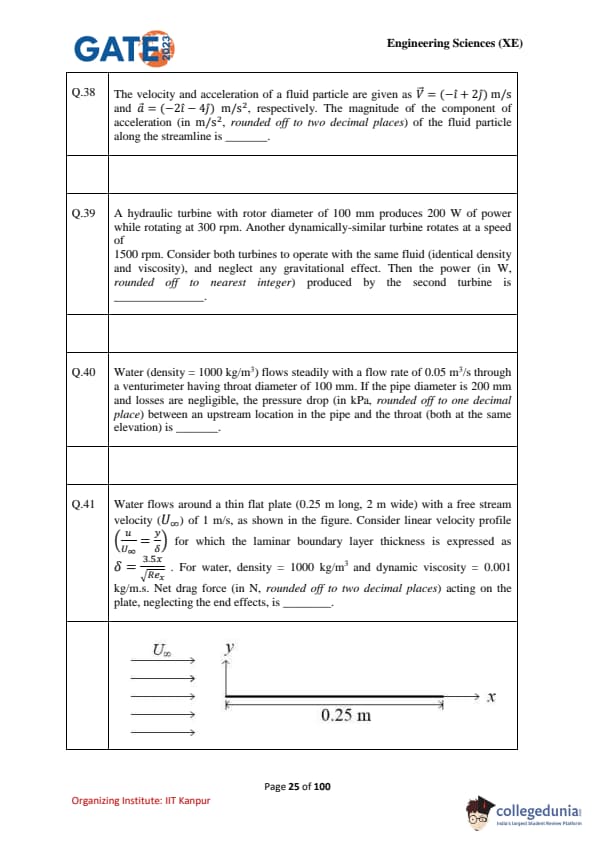
Water flows around a thin flat plate (0.25 m long, 2 m wide) with a free stream velocity (\(U_\infty\)) of 1 m/s, as shown in the figure. Consider linear velocity profile \(\left(\frac{u}{U_\infty} = \frac{y}{\delta}\right)\) for which the laminar boundary layer thickness is expressed as \(\delta = \frac{3.5x}{\sqrt{Re_x}}\). For water, density = 1000 kg/m\(^3\) and dynamic viscosity = 0.001 kg/m·s. Net drag force (in N, rounded off to two decimal places) acting on the plate, neglecting the end effects, is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\).
Axial velocity profile \(u(r)\) for an axisymmetric flow through a circular tube of radius \(R\) is given as, \[ \frac{u(r)}{U} = \left(1 - \frac{r}{R}\right)^{1/n} \]
where \(U\) is the centerline velocity. If \(V\) refers to the area-averaged velocity (volume flow rate per unit area), then the ratio \(V/U\) for \(n = 1\) (rounded off to two decimal places) is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\).
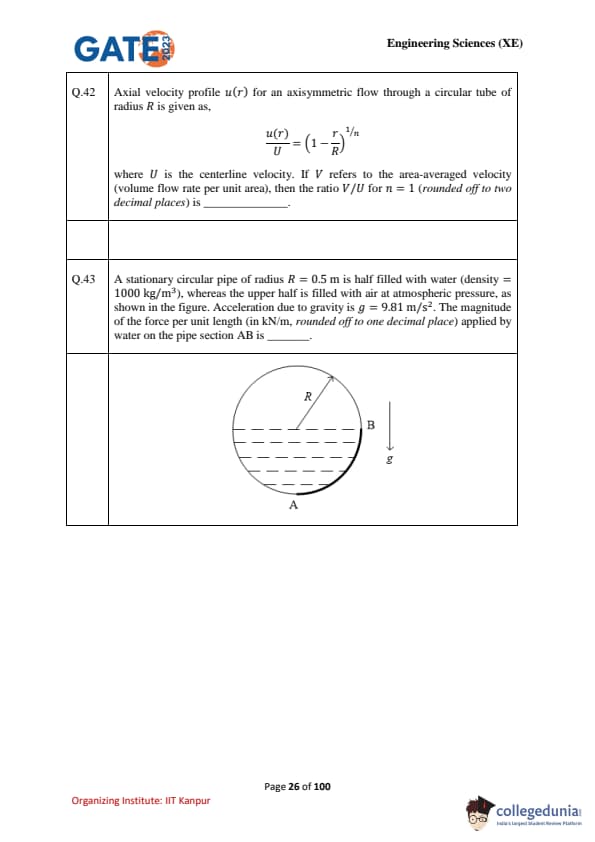
A stationary circular pipe of radius \(R = 0.5\) m is half filled with water (density = 1000 kg/m\(^3\)), whereas the upper half is filled with air at atmospheric pressure, as shown in the figure. Acceleration due to gravity is \(g = 9.81\) m/s\(^2\). The magnitude of the force per unit length (in kN/m, rounded off to one decimal place) applied by water on the pipe section AB is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\).
In age-hardening of an aluminium alloy, the purpose of solution treatment followed by quenching is to
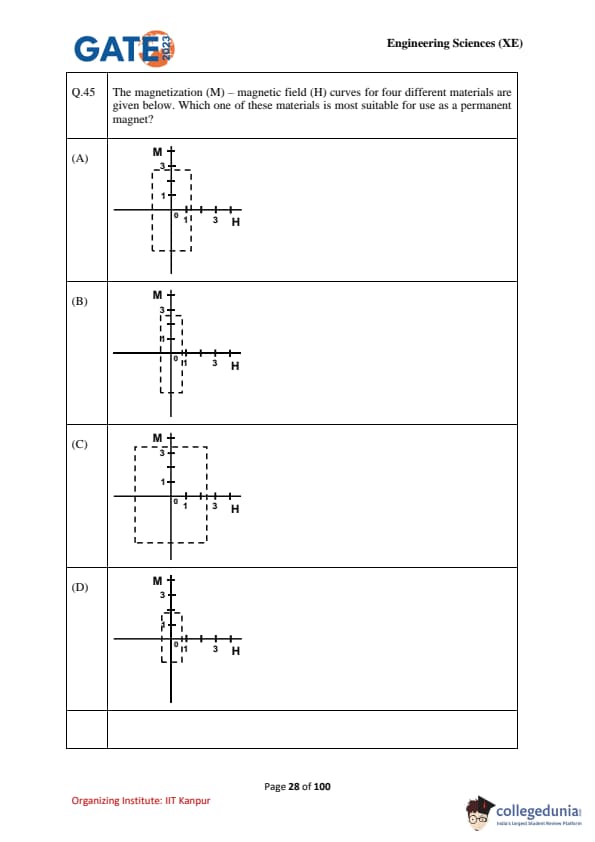
The magnetization (M) – magnetic field (H) curves for four different materials are given below. Which one of these materials is most suitable for use as a permanent magnet?
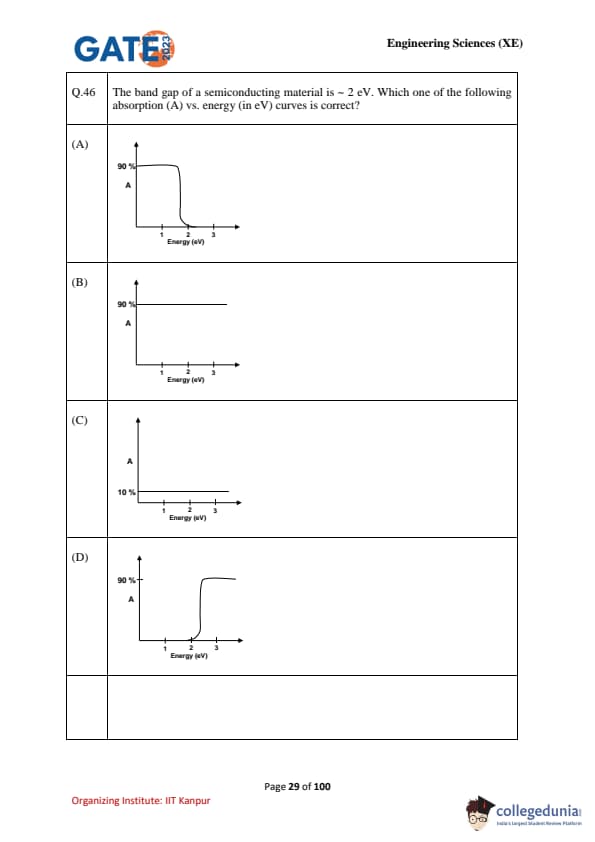
The band gap of a semiconducting material is \(\sim 2\) eV. Which one of the following absorption (A) vs. energy (in eV) curves is correct?
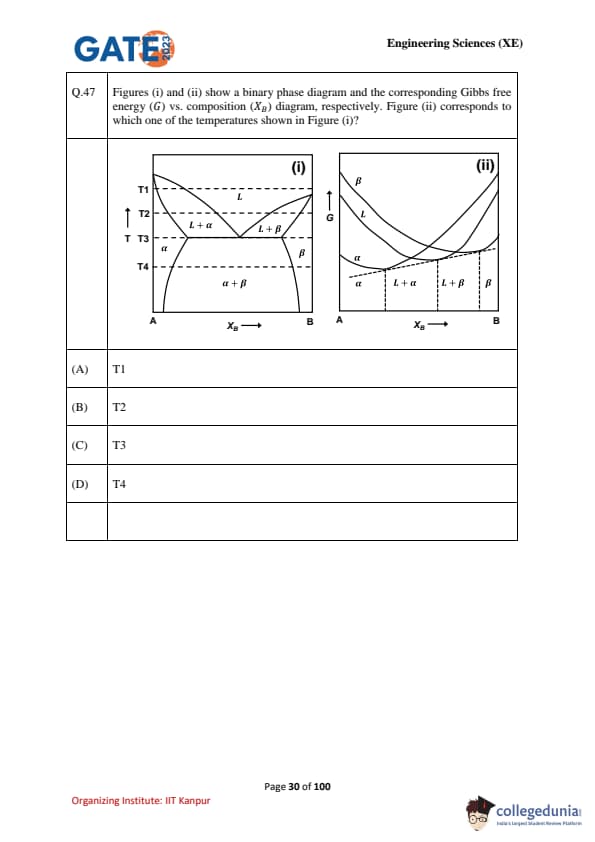
Figures (i) and (ii) show a binary phase diagram and the corresponding Gibbs free energy (G) vs. composition (\(X_B\)) diagram, respectively. Figure (ii) corresponds to which one of the temperatures shown in Figure (i)?
Aliovalent doping of \(MgCl_2\) in \(NaCl\) leads to the formation of defects. Which one of the following is the correct defect reaction?
A screw dislocation in a FCC crystal has Burgers vector of \(\frac{a}{2}[110]\), where \(a\) is the lattice constant. The possible slip plane(s) is/are:
The tensile true stress (\(\sigma\)) – true strain (\(\varepsilon\)) curve follows the Hollomon equation: \[ \sigma = 500 \, \varepsilon^{0.15} \ MPa \]
At the maximum load, the work-hardening rate \(\left(\frac{d\sigma}{d\varepsilon}\right)\) is (in MPa):
A metal has a certain vacancy fraction at a temperature of 600 K. On increasing the temperature to 900 K, the vacancy fraction increases by a factor of \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\).
Given: \(R = 8.31 \ J mol^{-1}K^{-1}\), \(Q = 68 \ kJ mol^{-1}\)
In a semiconductor, the ratio of electronic mobility to hole mobility is 10. The density of electrons and holes are \(10^{15}\) m\(^{-3}\) and \(10^{16}\) m\(^{-3}\), respectively. If the conductivity is \(1.6 \ \Omega^{-1}\) m\(^{-1}\), then the mobility of holes is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \ (m^2 V^{-1} s^{-1})\).
Given: \(q = 1.6 \times 10^{-19}\) C
A student performed X-ray diffraction experiment on a FCC polycrystalline pure metal. The following \(\sin^2 \theta\) values were calculated from the diffraction peaks:
\[ \sin^2 \theta = 0.136,\; 0.185,\; 0.504,\; 0.544 \]
However, the student was negligent and missed noting one of the peaks. Which one of the following Miller indices corresponds to the missing peak?
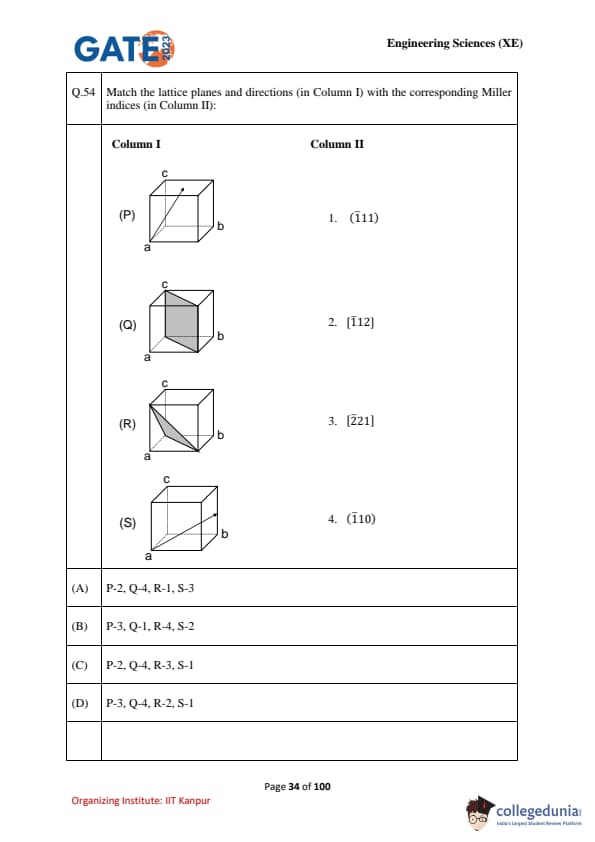
Match the lattice planes and directions (in Column I) with the corresponding Miller indices (in Column II):
Match the hardness test (in Column I) with its indenter type (in Column II):
\begin{tabular{|c|c|
Column I & Column II
(P) Brinell & 1. Diamond pyramidal
(Q) Rockwell & 2. Diamond cone
(R) Vickers & 3. Tungsten carbide sphere
& 4. Steel sphere
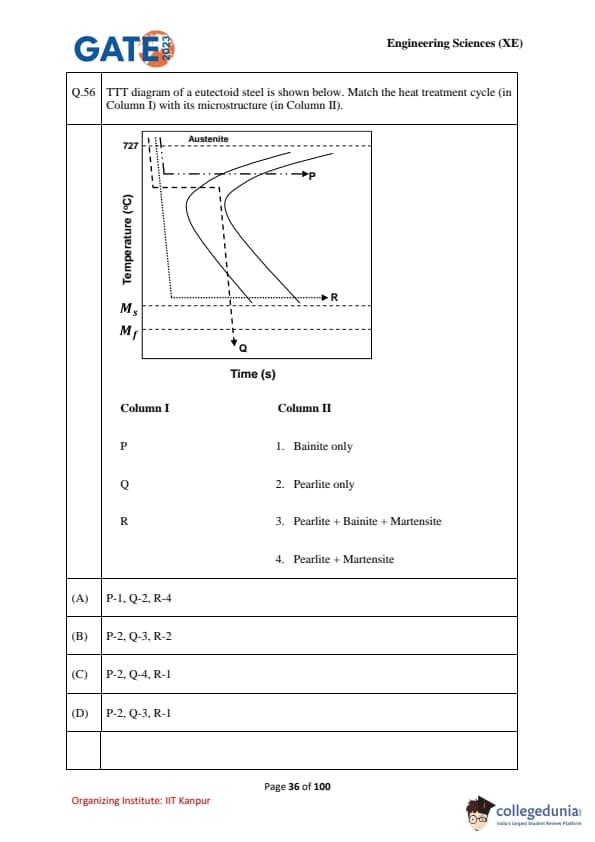
TTT diagram of a eutectoid steel is shown below. Match the heat treatment cycle (in Column I) with its microstructure (in Column II).
\begin{tabular{|c|c|
Column I & Column II
P & 1. Bainite only
Q & 2. Pearlite only
R & 3. Pearlite + Bainite + Martensite
& 4. Pearlite + Martensite
Which of the following statement(s) is/are true for an optical microscope?
Among the 14 Bravais lattices, there is no base-centred cubic unit cell. Which of the following statement(s) is/are true?
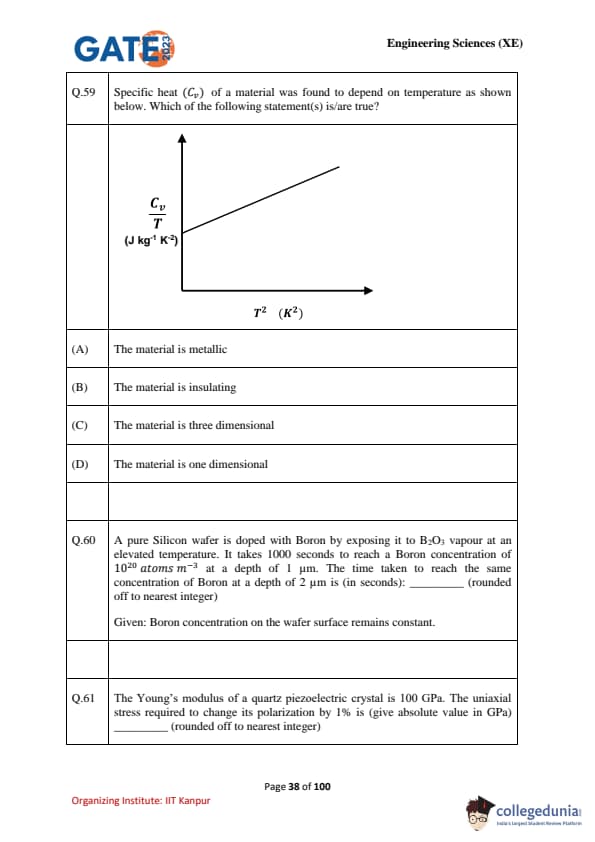
Specific heat (\(C_v\)) of a material was found to depend on temperature as shown below. Which of the following statement(s) is/are true?
A pure Silicon wafer is doped with Boron by exposing it to \(B_2O_3\) vapour at an elevated temperature. It takes 1000 seconds to reach a Boron concentration of \(10^{20}\) atoms \(m^{-3}\) at a depth of \(1 \, \mu m\). The time taken to reach the same concentration of Boron at a depth of \(2 \, \mu m\) is (in seconds): ................ (rounded off to nearest integer).
The Young’s modulus of a quartz piezoelectric crystal is 100 GPa. The uniaxial stress required to change its polarization by 1% is (give absolute value in GPa) .............. (rounded off to nearest integer).
A one-dimensional nanowire has a linear electron density of \(10^8 \, electrons \, cm^{-1}\). The Fermi energy of the system is (in eV) ............ (rounded off to two decimal places).
Given: \[ \frac{\hbar^2}{2m} = 0.24 \, (eV)^2 \, s^2 \, kg^{-1} \]
where \(m\) is the electron mass.
Two moles of a monoatomic ideal gas at 10 atm and 300 K is expanded isothermally and reversibly to a pressure of 2 atm. The absolute value of work done by the system is (in kJ) .......... (rounded off to two decimal places).
An electrochemical cell consists of pure Zn electrode (anode) and a hydrogen electrode (cathode) in a dilute Zn\(^{+2}\) solution. The overall reaction is: \[ Zn(s) + 2H^+ \rightarrow H_2 + Zn^{+2} \]
If the overall cell potential is +0.690 V, then the value of \(\ln \left( \frac{[Zn^{+2}]}{[H^+]^2} \right)\) is ........... (rounded off to two decimal places).
Given: Pressure of hydrogen gas = 1 atm; Temperature = 298 K; \[ \frac{RT}{F} = 0.0256 \, V \]
Standard reduction potentials: \[ Zn^{+2} + 2e^- \rightarrow Zn (E^0 = -0.762 \, V) \] \[ 2H^+ + 2e^- \rightarrow H_2 (E^0 = 0 \, V) \]
In a Raman spectroscopy experiment done at 300 K, a Raman line is observed at \(200 \, cm^{-1} \, (\sim 25 \, meV)\). The ratio of the intensity of the Stokes line to that of the Anti-Stokes line is ............ (rounded off to two decimal places).
Given: Boltzmann constant, \(k = 8.62 \times 10^{-5} \, eV K^{-1}\)
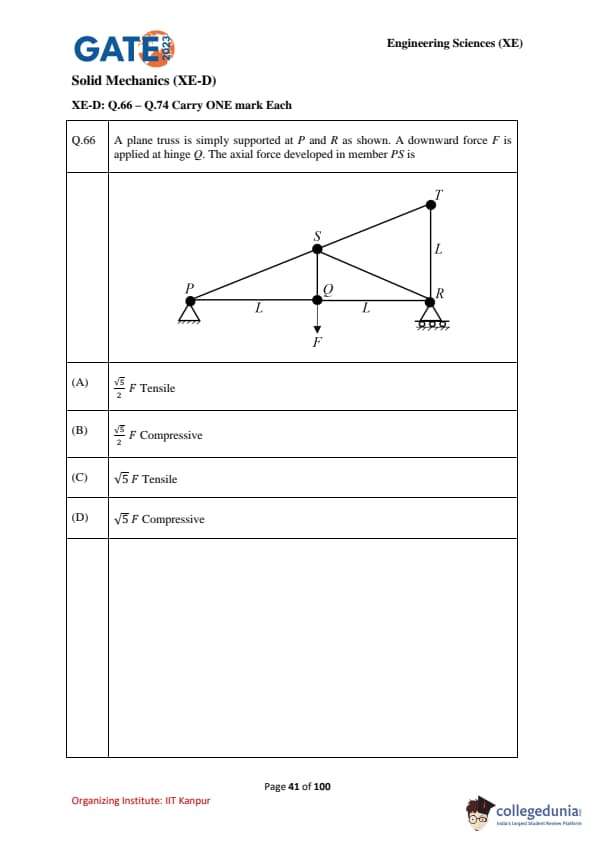
A plane truss is simply supported at \(P\) and \(R\) as shown. A downward force \(F\) is applied at hinge \(Q\). The axial force developed in member \(PS\) is:
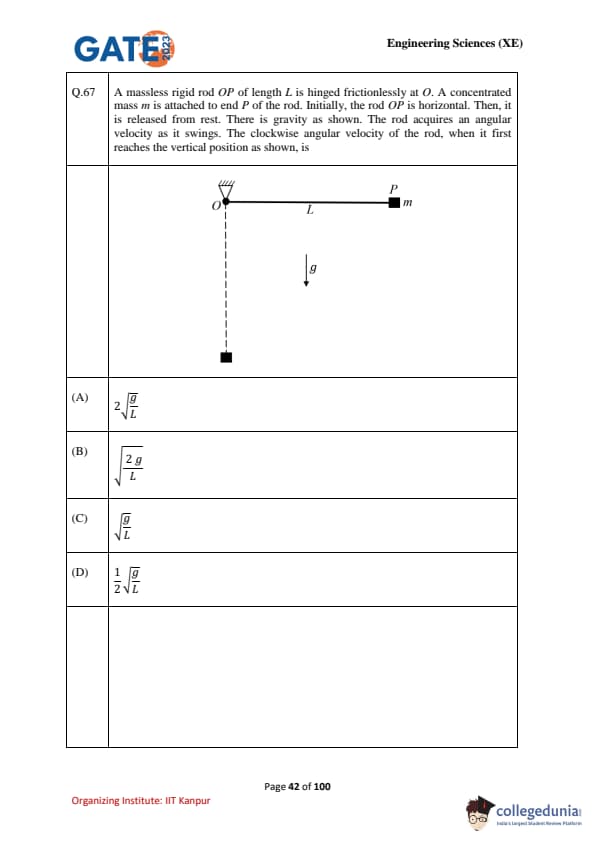
A massless rigid rod \(OP\) of length \(L\) is hinged frictionlessly at \(O\). A concentrated mass \(m\) is attached to end \(P\) of the rod. Initially, the rod \(OP\) is horizontal. Then, it is released from rest. There is gravity as shown. The rod acquires an angular velocity as it swings. The clockwise angular velocity of the rod, when it first reaches the vertical position as shown, is:
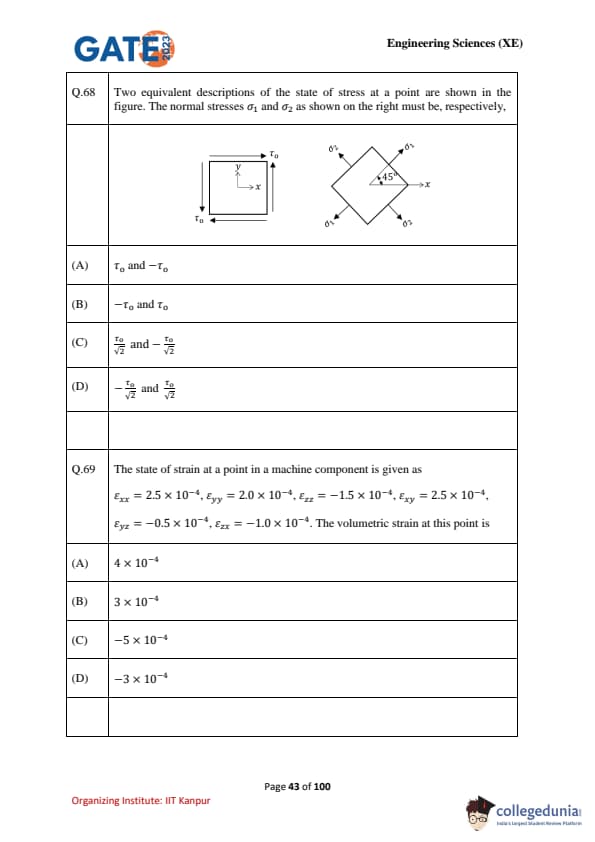
Two equivalent descriptions of the state of stress at a point are shown in the figure. The normal stresses \(\sigma_1\) and \(\sigma_2\) as shown on the right must be, respectively,
The state of strain at a point in a machine component is given as \[ \varepsilon_{xx} = 2.5 \times 10^{-4}, \varepsilon_{yy} = 2.0 \times 10^{-4}, \varepsilon_{zz} = -1.5 \times 10^{-4}, \] \[ \varepsilon_{xy} = 2.5 \times 10^{-4}, \varepsilon_{yz} = -0.5 \times 10^{-4}, \varepsilon_{zx} = -1.0 \times 10^{-4}. \]
The volumetric strain at this point is .............
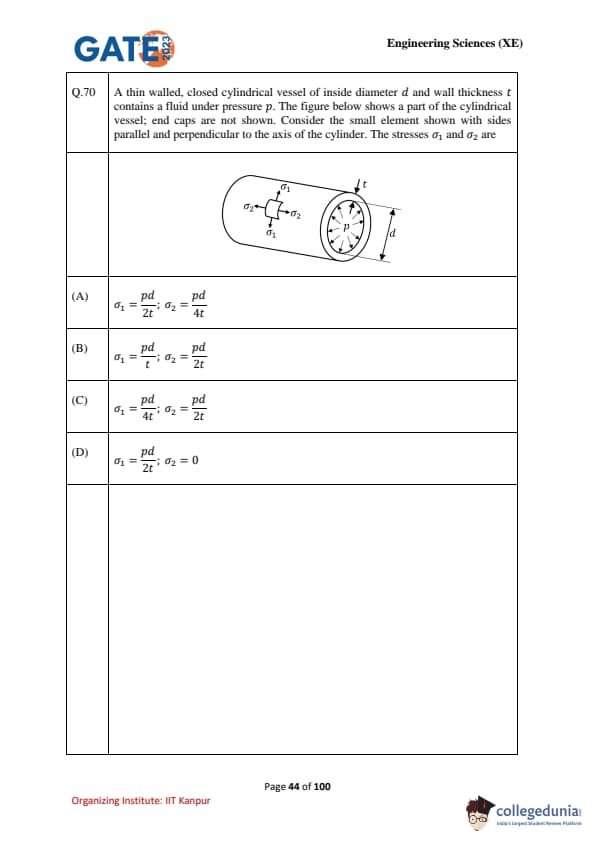
A thin-walled, closed cylindrical vessel of inside diameter \(d\) and wall thickness \(t\) contains a fluid under pressure \(p\). The figure shows a part of the cylindrical vessel; end caps are not shown. Consider the small element with sides parallel and perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder. The stresses \(\sigma_1\) and \(\sigma_2\) are:
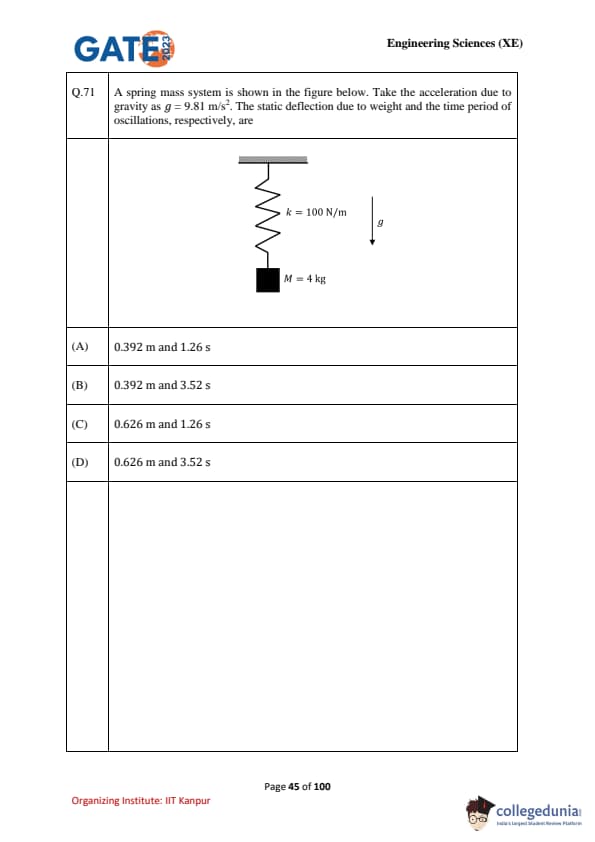
A spring–mass system is shown in the figure below. Take the acceleration due to gravity as \(g = 9.81 \, m/s^2\). The static deflection due to weight and the time period of oscillations, respectively, are:
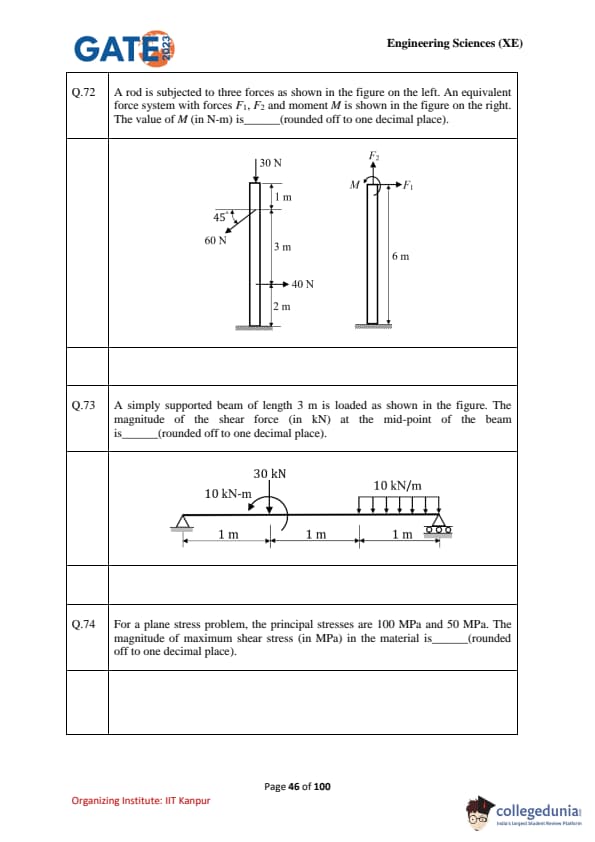
A rod is subjected to three forces as shown in the figure on the left. An equivalent force system with forces \(F_1\), \(F_2\) and moment \(M\) is shown in the figure on the right. The value of \(M\) (in N·m) is ................ (rounded off to one decimal place).
A simply supported beam of length 3 m is loaded as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the shear force (in kN) at the mid-point of the beam is ............ (rounded off to one decimal place).
For a plane stress problem, the principal stresses are 100 MPa and 50 MPa. The magnitude of maximum shear stress (in MPa) in the material is ............... (rounded off to one decimal place).
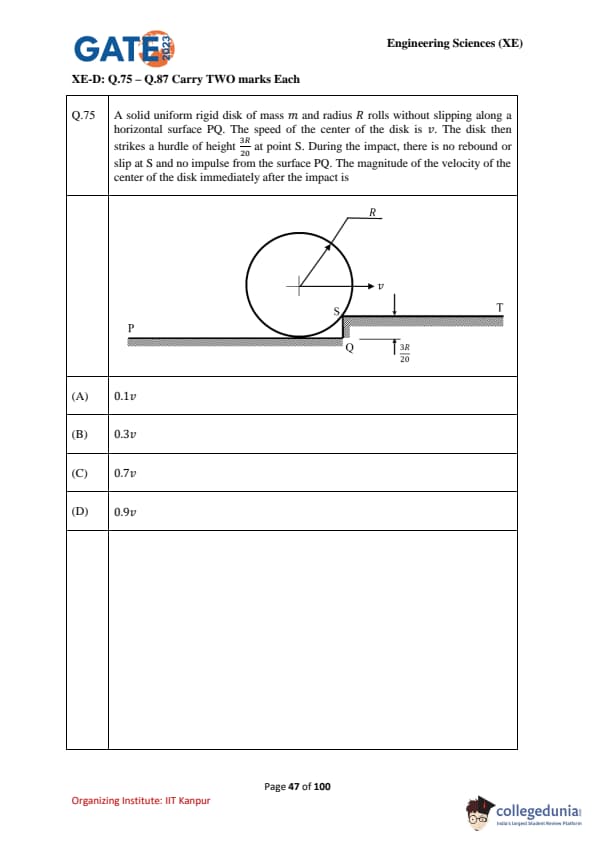
A solid uniform rigid disk of mass \(m\) and radius \(R\) rolls without slipping along a horizontal surface \(PQ\). The speed of the center of the disk is \(v\). The disk then strikes a hurdle of height \(\tfrac{3R}{20}\) at point \(S\). During the impact, there is no rebound or slip at \(S\) and no impulse from the surface \(PQ\). The magnitude of the velocity of the center of the disk immediately after the impact is:
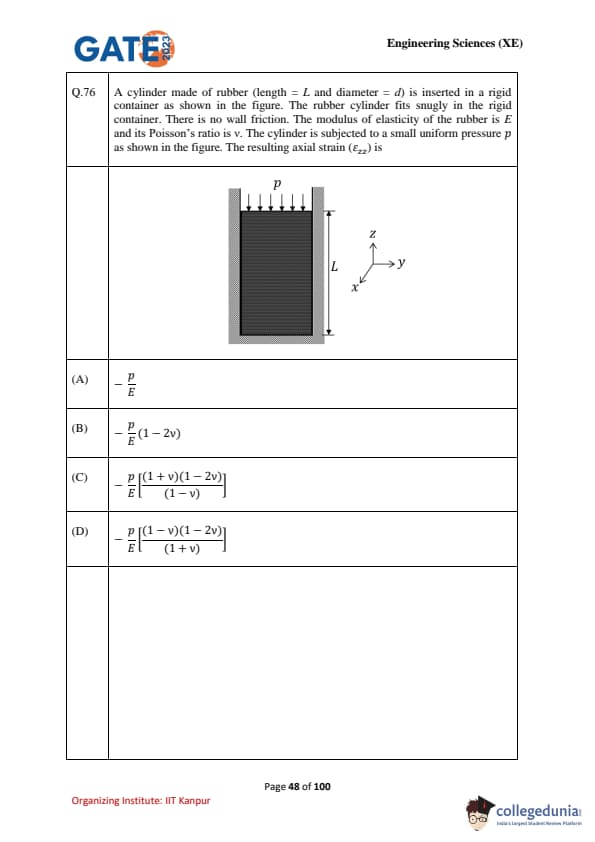
A cylinder made of rubber (length \(= L\) and diameter \(= d\)) is inserted in a rigid container as shown in the figure. The rubber cylinder fits snugly in the rigid container. There is no wall friction. The modulus of elasticity of the rubber is \(E\) and its Poisson’s ratio is \(\nu\). The cylinder is subjected to a small uniform pressure \(p\) as shown in the figure. The resulting axial strain (\(\varepsilon_{zz}\)) is:
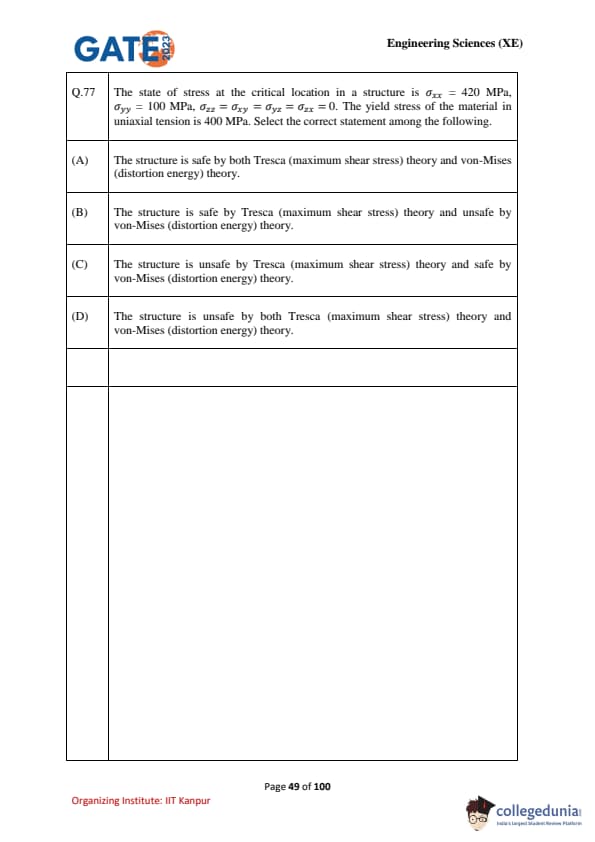
The state of stress at the critical location in a structure is \[ \sigma_{xx} = 420 \, MPa, \sigma_{yy} = 100 \, MPa, \sigma_{zz} = 0, \tau_{xy} = \tau_{yz} = \tau_{zx} = 0 \]
The yield stress of the material in uniaxial tension is \(400 \, MPa\). Select the correct statement among the following:
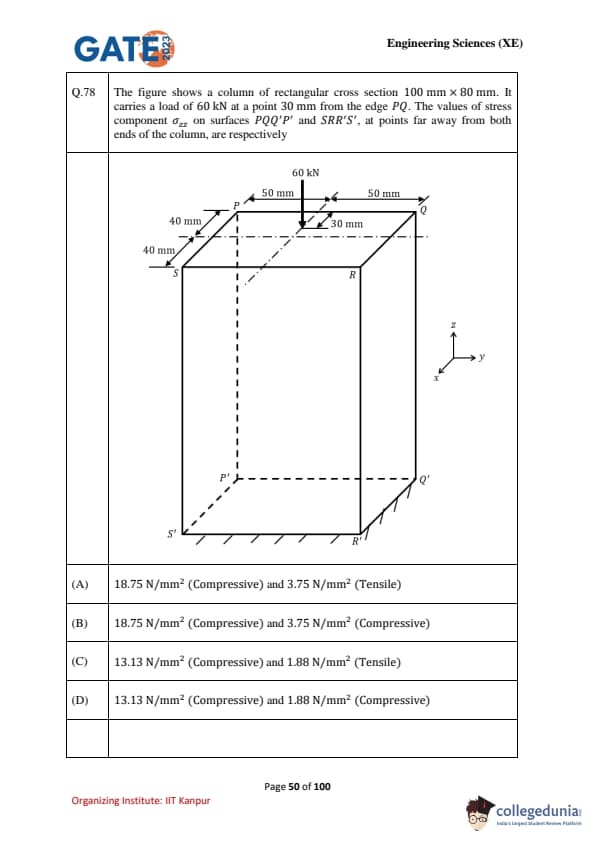
The figure shows a column of rectangular cross section \(100 \, mm \times 80 \, mm\). It carries a load of \(60 \, kN\) at a point \(30 \, mm\) from the edge \(PQ\). The values of stress component \(\sigma_{zz}\) on surfaces \(PQQ'P'\) and \(SRR'S'\), at points far away from both ends of the column, are respectively:
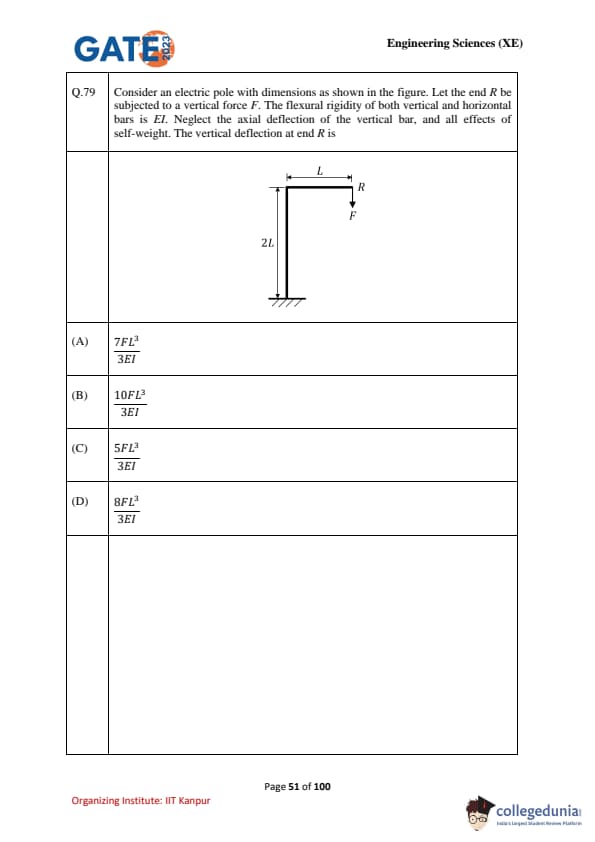
Consider an electric pole with dimensions as shown in the figure. Let the end \(R\) be subjected to a vertical force \(F\). The flexural rigidity of both vertical and horizontal bars is \(EI\). Neglect the axial deflection of the vertical bar, and all effects of self-weight. The vertical deflection at end \(R\) is:
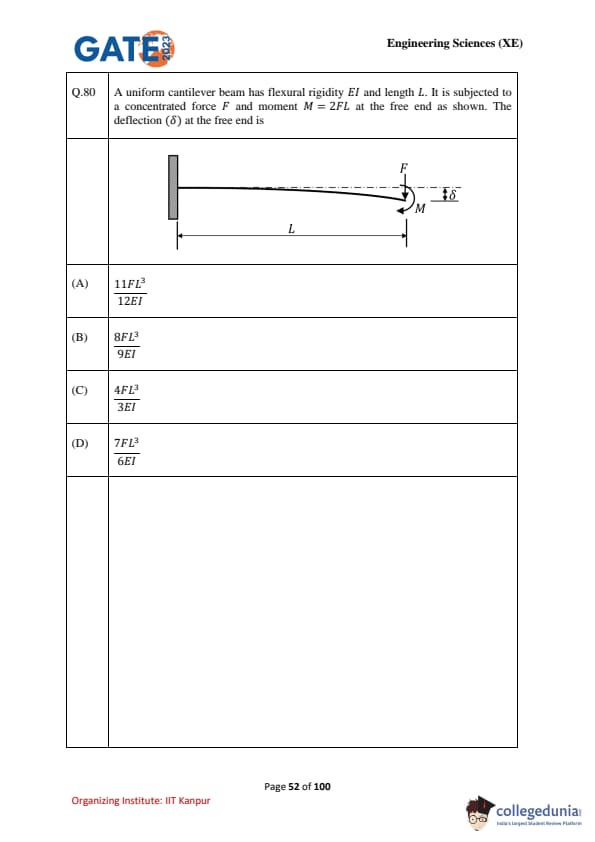
A uniform cantilever beam has flexural rigidity \(EI\) and length \(L\). It is subjected to a concentrated force \(F\) and moment \(M = 2FL\) at the free end as shown. The deflection \((\delta)\) at the free end is:
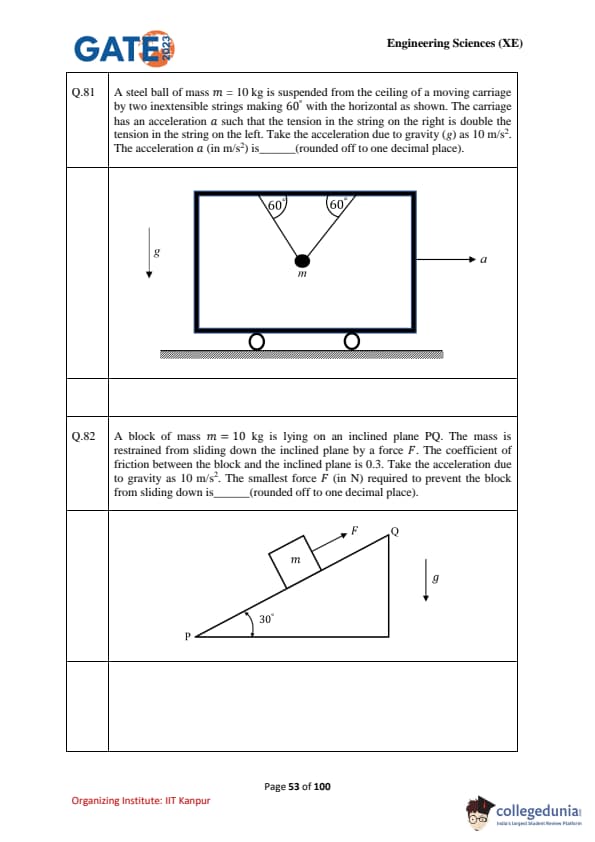
A steel ball of mass \(m = 10 \, kg\) is suspended from the ceiling of a moving carriage by two inextensible strings making \(60^\circ\) with the horizontal as shown. The carriage has an acceleration \(a\) such that the tension in the string on the right is double the tension in the string on the left. Take \(g = 10 \, m/s^2\). The acceleration \(a\) (in \(m/s^2\)) is ............. (rounded off to one decimal place).
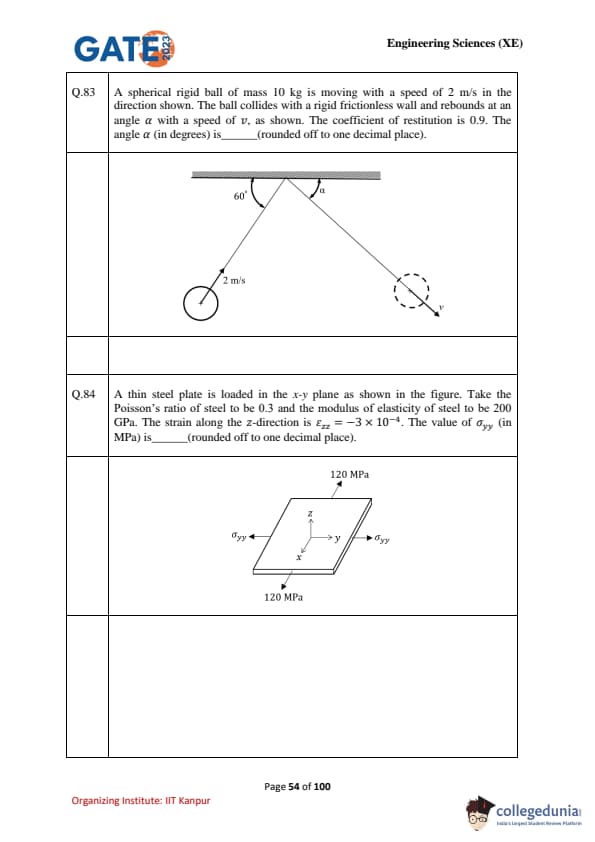
A block of mass \(m = 10 \, kg\) is lying on an inclined plane \(PQ\) at \(30^\circ\). The mass is restrained from sliding down by a force \(F\) applied up the plane. The coefficient of friction is \(\mu = 0.3\). Take \(g = 10 \, m/s^2\). The smallest force \(F\) (in N) required to prevent the block from sliding down is ............ (rounded off to one decimal place).
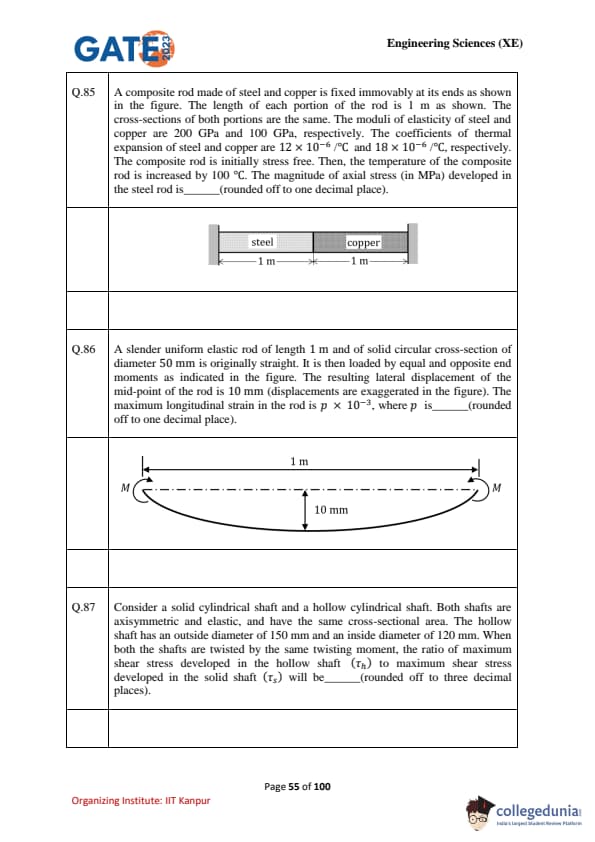
A spherical rigid ball of mass \(10 \, kg\) is moving with a speed of \(2 \, m/s\) in the direction shown. The ball collides with a rigid frictionless wall and rebounds at an angle \(\alpha\) with a speed \(v\), as shown. The coefficient of restitution is \(0.9\). The angle \(\alpha\) (in degrees) is ........... (rounded off to one decimal place).
A thin steel plate is loaded in the \(x\)-\(y\) plane as shown in the figure. Take Poisson’s ratio \(\nu = 0.3\) and modulus of elasticity \(E = 200 \, GPa\). The strain along \(z\)-direction is \(\varepsilon_{zz} = -3 \times 10^{-4}\). The value of \(\sigma_{yy}\) (in MPa) is .......... (rounded off to one decimal place).
A composite rod made of steel and copper is fixed immovably at its ends. Each portion has length \(1 \, m\). Cross-sectional areas are the same. \(E_{steel} = 200 \, GPa\), \(E_{copper} = 100 \, GPa\). \(\alpha_{steel} = 12 \times 10^{-6}/^\circ C\), \(\alpha_{copper} = 18 \times 10^{-6}/^\circ C\). The temperature is increased by \(100^\circ C\). Find axial stress (in MPa) in the steel rod.
A slender elastic rod of length \(1 \, m\), circular cross-section \(d = 50 \, mm\), is subjected to equal and opposite end moments \(M\). The midpoint lateral deflection is \(10 \, mm\). Find maximum longitudinal strain in the rod, expressed as \(p \times 10^{-3}\).
A solid shaft and a hollow shaft have the same cross-sectional area. The hollow shaft: \(D_o = 150 \, mm\), \(D_i = 120 \, mm\). Both are subjected to same torque. Find ratio \(\dfrac{\tau_h}{\tau_s}\).
A: The number of properties required to fix the state of a system is given by the “state postulate”.
R: The state of a simple compressible system is completely specified by two independent, intensive properties.
About the statements A and R applied to a single-phase system,
Which of the following is an extensive property of a system?
A tank of volume \(V\) contains a homogeneous mixture of two ideal gases, A and B, at temperature \(T\) and pressure \(P\). The mixture contains \(n_A\) moles of gas A and \(n_B\) moles of gas B. If \(P_A\) and \(P_B\) are the partial pressures of gas A and B, respectively, then:
If an ideal air-standard Otto cycle and an ideal air-standard Diesel cycle operate on the same compression ratio, then the relation between thermal efficiencies (\(\eta_{th}\)) of the cycles is:
The following statements are given:
(i) The third law of thermodynamics deals with the entropy of a substance at the absolute zero temperature.
(ii) Entropy of any non-crystalline structure is zero at absolute zero temperature.
(iii) At the absolute zero temperature, the crystal structure has maximum degree of order.
(iv) The thermal energy of the substance at absolute zero temperature is maximum.
The correct option describing these statements is:
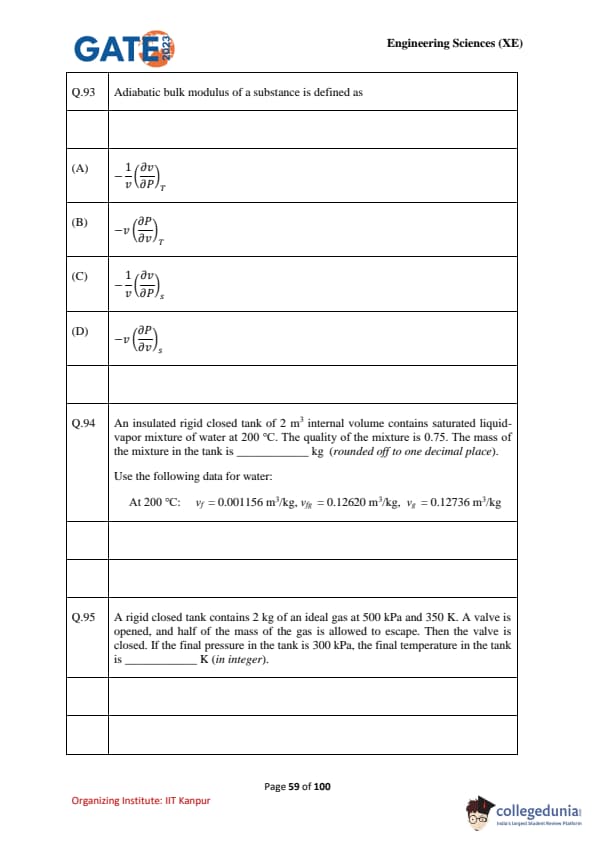
Adiabatic bulk modulus of a substance is defined as:
An insulated rigid closed tank of \(2 \, m^3\) contains saturated liquid-vapor mixture of water at \(200^\circ C\). Quality of mixture = \(0.75\). Find mass of mixture.
Data at \(200^\circ C\): \(v_f = 0.001156 \, m^3/kg\), \(v_{fg} = 0.12620 \, m^3/kg\), \(v_g = 0.12736 \, m^3/kg\).
A rigid tank contains \(2 \, kg\) of an ideal gas at \(500 \, kPa\) and \(350 \, K\). A valve is opened and half of the gas is released. Then valve is closed. Final pressure = \(300 \, kPa\). Find final temperature \(T_2\) (in K).
Air at 400 K and 200 kPa is heated at constant pressure to 600 K. Assuming internal energy is a function of temperature only, the magnitude of change in internal energy during this process is __________ kJ/kmol (rounded off to one decimal place).
Molar specific heat of air at constant volume: \[ \bar{c}_v = a + bT + cT^2 \]
where \(a = 19.686 \, kJ/kmol-K\), \(b = 0.002 \, kJ/kmol-K^2\), \(c = 0.5 \times 10^{-5} \, kJ/kmol-K^3\).
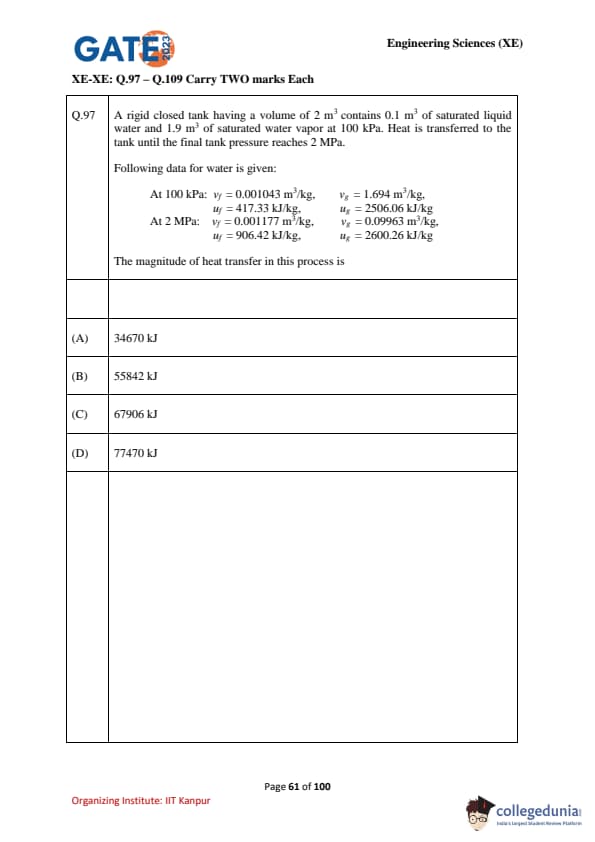
A rigid closed tank of volume \(2 \, m^3\) contains \(0.1 \, m^3\) of saturated liquid water and \(1.9 \, m^3\) of saturated water vapor at \(100 \, kPa\). Heat is transferred until the final pressure reaches \(2 \, MPa\). Find the magnitude of heat transfer.
% Data
At \(100 \, kPa\): \(v_f = 0.001043 \, m^3/kg\), \(v_g = 1.694 \, m^3/kg\), \(u_f = 417.33 \, kJ/kg\), \(u_g = 2506.06 \, kJ/kg\)
At \(2 \, MPa\): \(v_f = 0.001177 \, m^3/kg\), \(v_g = 0.09963 \, m^3/kg\), \(u_f = 906.42 \, kJ/kg\), \(u_g = 2600.26 \, kJ/kg\)
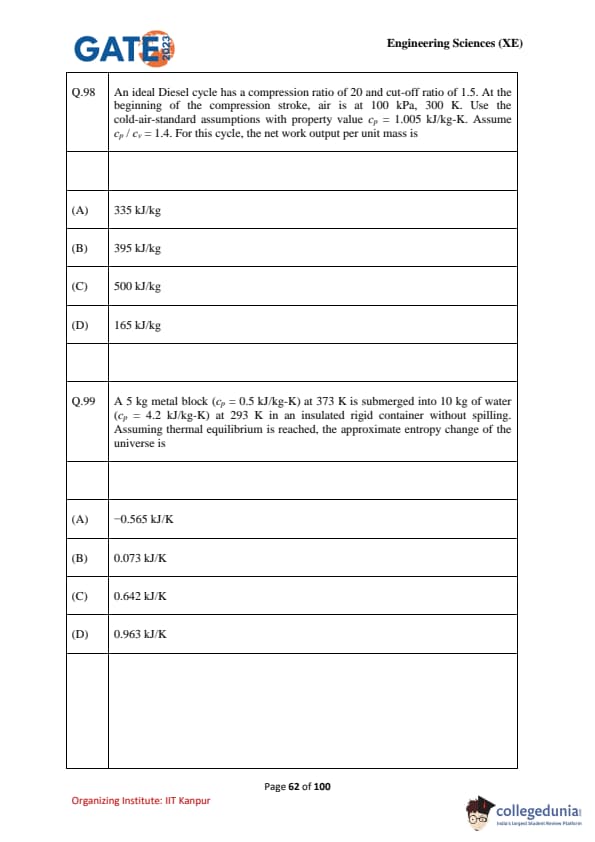
An ideal Diesel cycle has compression ratio \(r = 20\) and cut-off ratio \(r_c = 1.5\). At the beginning of compression, \(P_1 = 100 \, kPa\), \(T_1 = 300 \, K\). Use cold-air-standard assumptions with \(c_p = 1.005 \, kJ/kgK\), \(\gamma = 1.4\). Find the net work output per unit mass.
A \(5 \, kg\) metal block (\(c_p = 0.5 \, kJ/kgK\)) at \(373 \, K\) is placed in \(10 \, kg\) of water (\(c_p = 4.2 \, kJ/kgK\)) at \(293 \, K\) inside an insulated rigid container. Find entropy change of universe.
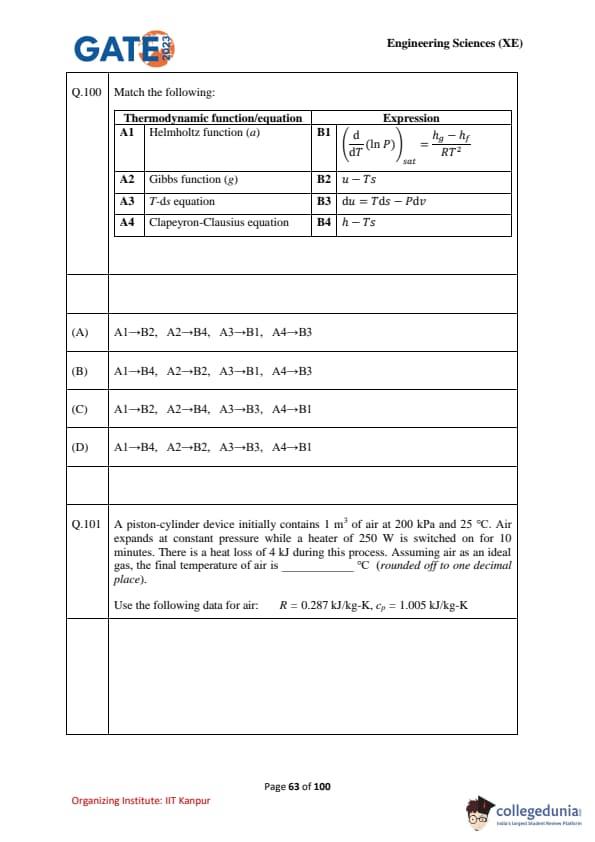
Match the following thermodynamic functions/equations with their expressions:
\[ \begin{array}{|c|c|} \textbf{Thermodynamic Function/Equation} & \textbf{Expression}
A1: \, Helmholtz function (a) & B1: \, \left(\frac{d}{dT} \ln P \right)_{sat} = \frac{h_g - h_f}{RT^2}
A2: \, Gibbs function (g) & B2: \, u - Ts
A3: \, Tds \, equation & B3: \, du = Tds - Pdv
A4: \, Clapeyron–Clausius equation & B4: \, h - Ts
\end{array} \]
A piston–cylinder device initially contains \(1 \, m^3\) of air at \(200 \, kPa\) and \(25^\circ C\). Air expands at constant pressure while a heater of \(250 \, W\) is switched on for 10 minutes. There is a heat loss of \(4 \, kJ\). Assuming air as an ideal gas, the final temperature of air is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\) \(^\circ C\) (rounded off to one decimal place).
Given: \(R = 0.287 \, kJ/kgK\), \(c_p = 1.005 \, kJ/kgK\).
Steam at 2 MPa and 300\(^\circ\)C steadily enters a nozzle of inlet diameter 20 cm. Steam leaves with a velocity of 300 m/s. The mass flow rate of steam through the nozzle is 10 kg/s. Assume no work interaction and no change in potential energy. If the heat loss from the nozzle per kg of steam is 3 kJ, the exit enthalpy per kg of steam is \(\_\_\_\_\_\) kJ (rounded off to nearest integer).
Given: At 2 MPa and 300\(^\circ\)C, \(v = 0.12551 \, m^3/kg, \, h = 3024.2 \, kJ/kg\)
A rigid tank of 2 \(m^3\) internal volume contains 5 kg of water as a saturated liquid–vapor mixture at 400 kPa. Half of the mass of the saturated liquid in the tank is drained-off while maintaining constant pressure of 400 kPa. The final quality of the mixture remaining in the tank is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\) (rounded off to two decimal places).
Given: At 400 kPa: \(v_f = 0.001084 \, m^3/kg\), \(v_{fg} = 0.46138 \, m^3/kg\), \(v_g = 0.46246 \, m^3/kg\).
Consider a spark ignition engine which operates on an ideal air-standard Otto cycle. It uses a fuel which produces 44 MJ/kg of heat in the engine. If the engine requires 40 mg of fuel to produce 1 kJ of work output, then the compression ratio of the Otto cycle is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\) (rounded off to two decimal places).
For the entire cycle, use \(\dfrac{c_p}{c_v} = 1.4\).
A refrigerator operates on an ideal vapor compression cycle between the pressure limits of 140 kPa and 800 kPa. The working fluid is refrigerant R-134a. The refrigerant enters the compressor as saturated vapor at 140 kPa and exits at 800 kPa. It leaves the condenser as a saturated liquid at 800 kPa. The coefficient of performance (COP) of the refrigerator is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\) (rounded off to two decimal places).
Given property data for R-134a:
At 140 kPa: \(h_f = 27.06 \, kJ/kg, \, h_g = 239.19 \, kJ/kg\)
At 800 kPa: \(h_f = 95.48 \, kJ/kg, \, h_g = 267.34 \, kJ/kg\)
At 800 kPa and 60\(^\circ\)C: \(h = 296.82 \, kJ/kg\)
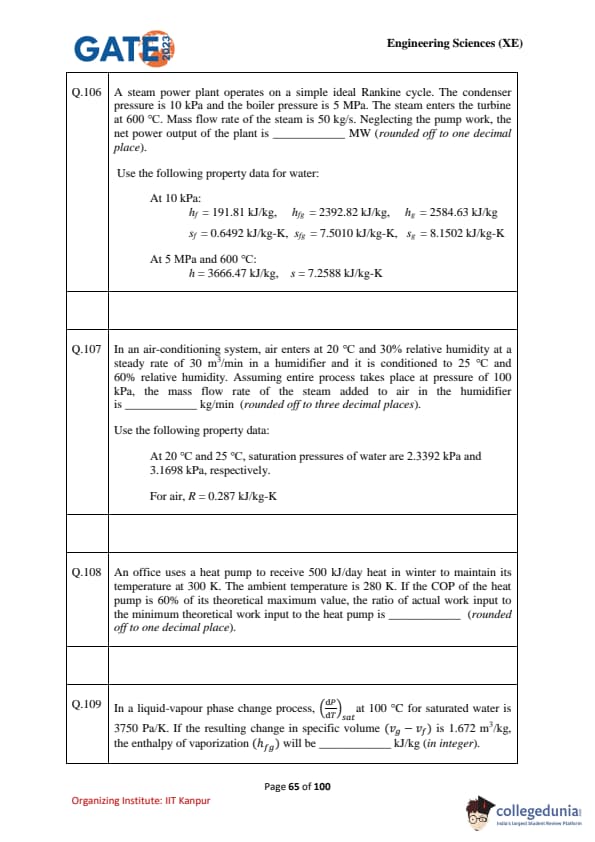
A steam power plant operates on a simple ideal Rankine cycle. The condenser pressure is 10 kPa and the boiler pressure is 5 MPa. The steam enters the turbine at 600\(^\circ\)C. Mass flow rate of the steam is 50 kg/s. Neglecting the pump work, the net power output of the plant is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\) MW (rounded off to one decimal place).
In an air-conditioning system, air enters at 20\(^\circ\)C and 30% relative humidity at a steady rate of 30 m\(^3\)/min in a humidifier and it is conditioned to 25\(^\circ\)C and 60% relative humidity. Assuming entire process takes place at pressure of 100 kPa, the mass flow rate of steam added to air in the humidifier is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\) kg/min (rounded off to three decimal places).
An office uses a heat pump to receive 500 kJ/day heat in winter to maintain its temperature at 300 K. The ambient temperature is 280 K. If the COP of the heat pump is 60% of its theoretical maximum value, the ratio of actual work input to the minimum theoretical work input to the heat pump is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\) (rounded off to one decimal place).
In a liquid-vapour phase change process, \(\left(\dfrac{dP}{dT}\right)_{sat}\) at 100\(^\circ\)C for saturated water is 3750 Pa/K. If the resulting change in specific volume (\(v_g - v_f\)) is 1.672 m\(^3\)/kg, the enthalpy of vaporization (\(h_{fg}\)) will be \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\) kJ/kg (in integer).
Which one of the monomers given is used in the synthesis of cellulose?
A copper wire upon loading instantaneously increases in length to \(l\), and then continues to elongate gradually. Upon unloading, the wire retracts to length \(l\). According to the Maxwell model, which one of the options given correctly relates the total strain \(E\), the applied stress \(S\), the modulus \(G\), the material’s resistance to flow \(\eta\), and the elapsed time \(t\) between loading and unloading?
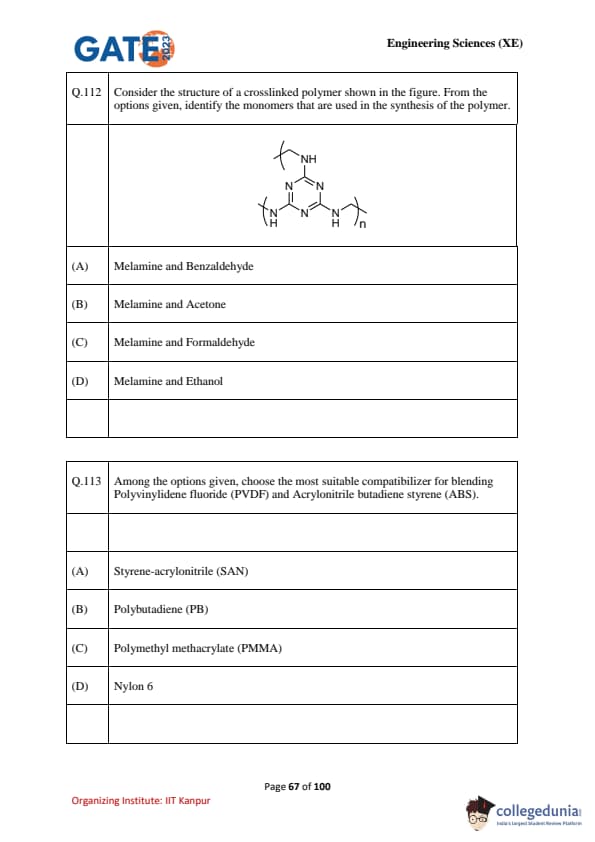
Consider the structure of a crosslinked polymer shown in the figure. From the options given, identify the monomers that are used in the synthesis of the polymer.
Among the options given, choose the most suitable compatibilizer for blending Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS).
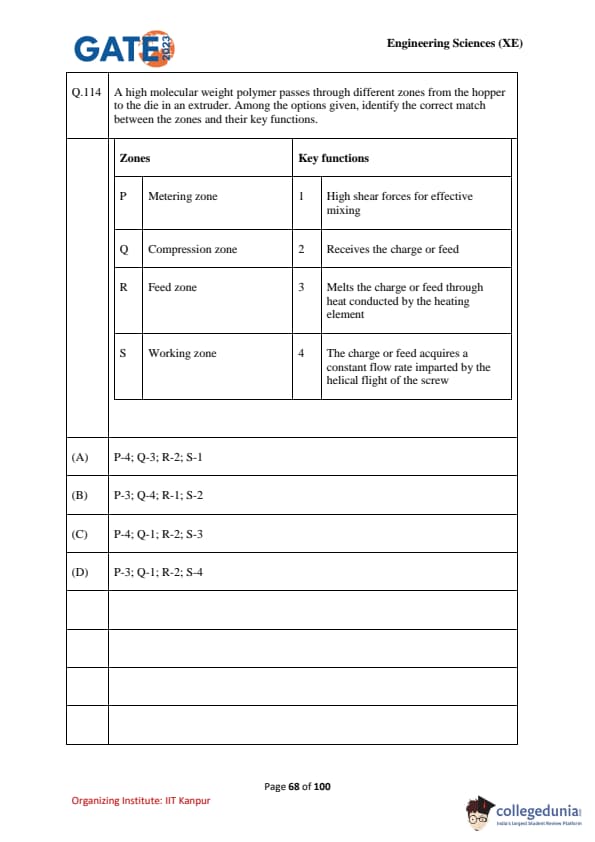
A high molecular weight polymer passes through different zones from the hopper to the die in an extruder. Among the options given, identify the correct match between the zones and their key functions.
\begin{tabular{p{0.45\linewidthp{0.45\linewidth
Zones & Key functions
P Metering zone & 1 High shear forces for effective mixing
Q Compression zone & 2 Receives the charge or feed
R Feed zone & 3 Melts the charge or feed through heat conducted by the heating element
S Working zone & 4 The charge or feed acquires a constant flow rate imparted by the helical flight of the screw
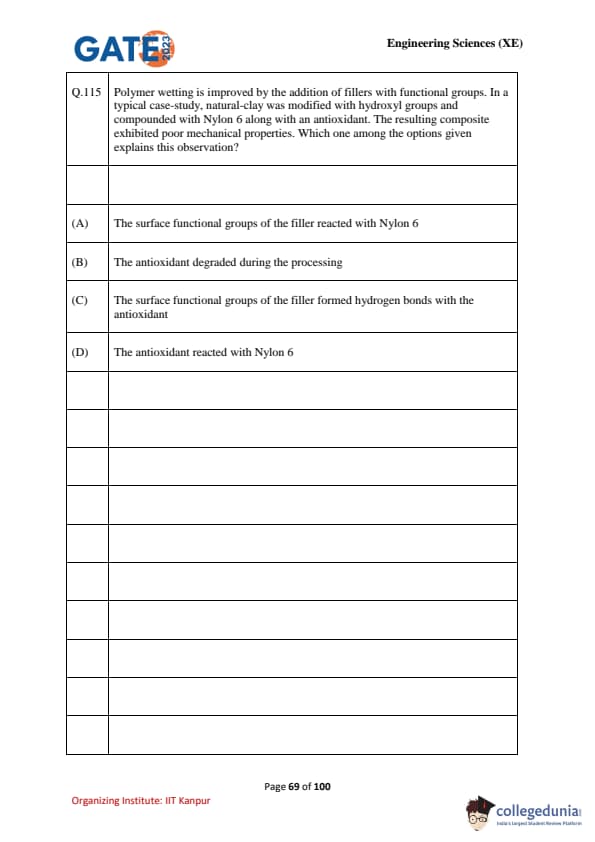
Polymer wetting is improved by the addition of fillers with functional groups. In a typical case-study, natural-clay was modified with hydroxyl groups and compounded with Nylon 6 along with an antioxidant. The resulting composite exhibited poor mechanical properties. Which one among the options given explains this observation?
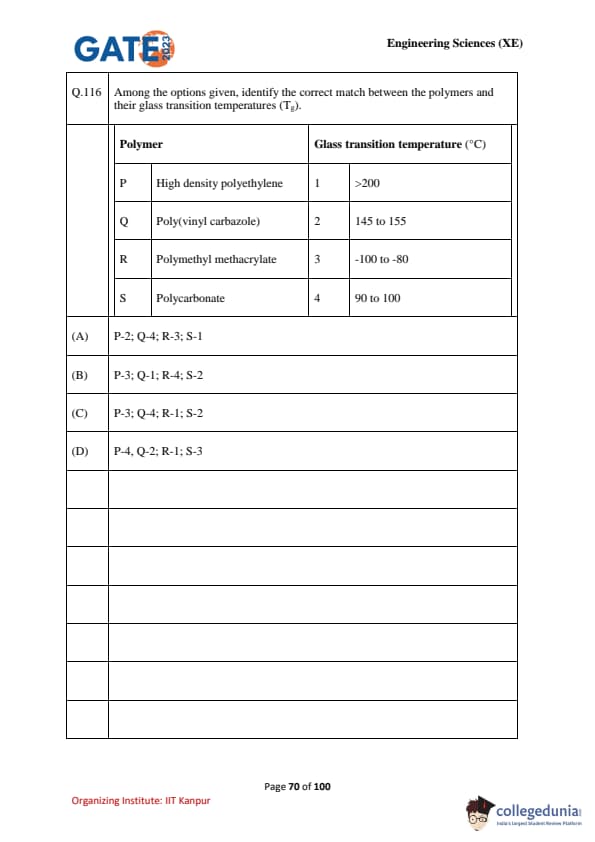
Among the options given, identify the correct match between the polymers and their glass transition temperatures (\(T_g\)).
\begin{tabular{p{0.45\linewidthp{0.45\linewidth
Polymer & Glass transition temperature (\(T_g\))
P High density polyethylene & 1 \(>\)200 °C
Q Poly(vinyl carbazole) & 2 145–155 °C
R Polymethyl methacrylate & 3 –100 to –80 °C
S Polycarbonate & 4 90–100 °C
What is the correct order of decreasing crystallinity of the given polymers?
\begin{tabular{p{0.45\linewidthp{0.45\linewidth
P Atactic–Polypropylene &
Q Syndiotactic–Polystyrene &
R Nylon 6 &
S Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) &
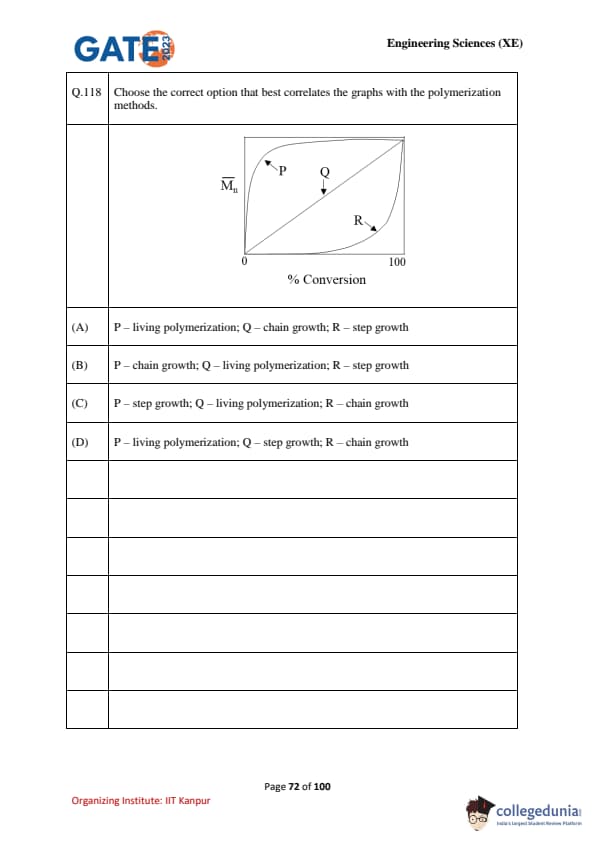
Choose the correct option that best correlates the graphs with the polymerization methods.
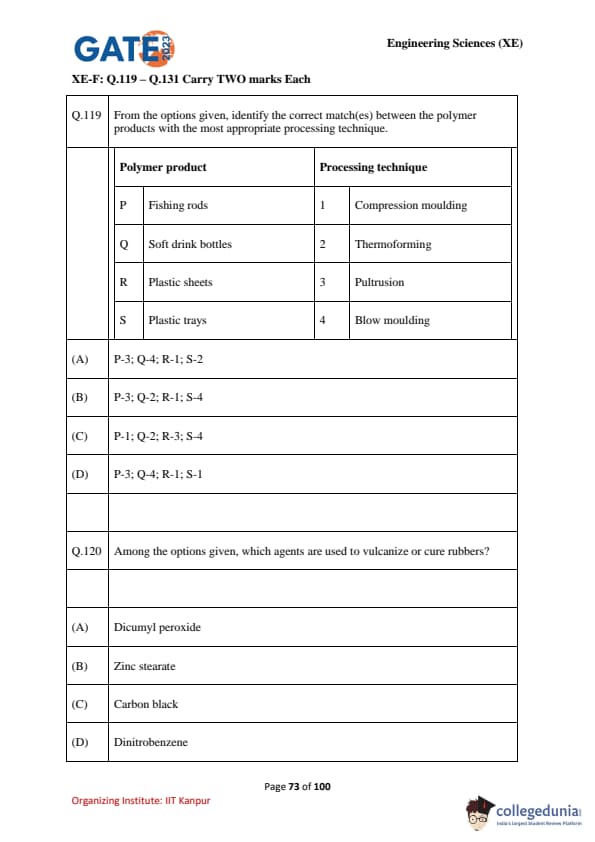
From the options given, identify the correct match(es) between the polymer products with the most appropriate processing technique.
\begin{tabular{p{0.45\linewidthp{0.45\linewidth
Polymer product & Processing technique
P Fishing rods & 1 Compression moulding
Q Soft drink bottles & 2 Thermoforming
R Plastic sheets & 3 Pultrusion
S Plastic trays & 4 Blow moulding
Among the options given, which agents are used to vulcanize or cure rubbers?
Lipase is a natural enzyme, which cleaves carboxylic ester bonds. Among the options given, identify the polymer(s) degraded by lipase.
Among the options given, identify the correct pair(s) of catalyst and co-catalyst that form a Ziegler–Natta catalyst.
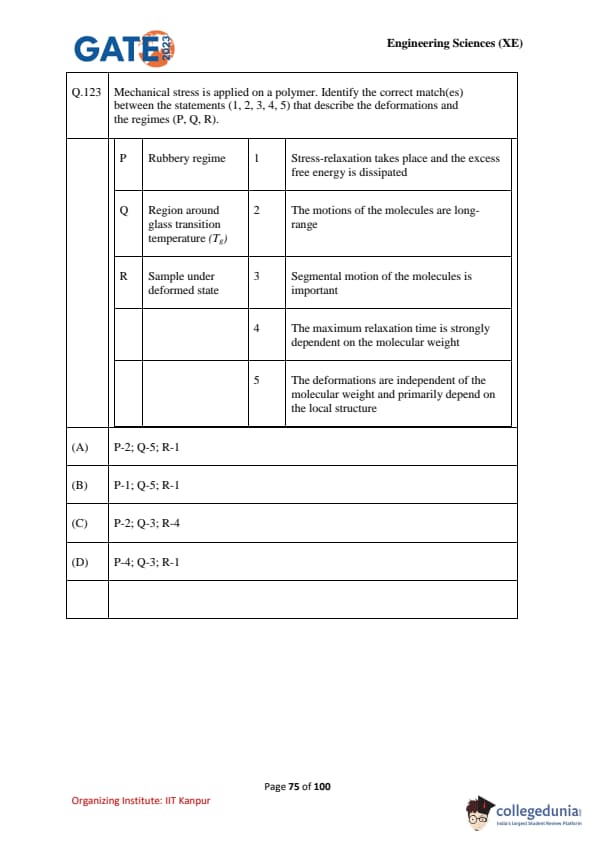
Mechanical stress is applied on a polymer. Identify the correct match(es) between the statements (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) that describe the deformations and the regimes (P, Q, R).
\begin{tabular{p{0.45\linewidthp{0.45\linewidth
Regime & Statement
P Rubbery regime & 1 Stress-relaxation takes place and the excess free energy is dissipated
Q Region around glass transition temperature (\(T_g\)) & 2 The motions of the molecules are long-range
R Sample under deformed state & 3 Segmental motion of the molecules is important
& 4 The maximum relaxation time is strongly dependent on the molecular weight
& 5 The deformations are independent of the molecular weight and primarily depend on the local structure
Stress versus elongation profiles for different polymeric materials are shown in the figure. Choose the combination that best describes these profiles.
Among the options given, which method(s) is/are used for the synthesis of atactic polystyrene?
A nylon sample of 0.03 m\(^2\) cross-sectional area is subjected to a creep load of 10 kN. The load is removed after a duration of 60 s. Young’s modulus and the viscosity for nylon are 1 GPa and 300 Giga Poise. The compliance of the specimen is ______ \(\times 10^{-9}\) m\(^2\)/N.
PVDF was quenched in one case and slowly cooled at 10\(^\circ\)C/min in another case. The crystallinity of slowly cooled PVDF = 60%. The heat of fusion of the quenched PVDF = 0.54 \(\Delta H_m\) (where \(\Delta H_m\) = heat of fusion of slowly cooled PVDF). Heat of fusion of 100% crystalline PVDF = 100 J/g. Find crystallinity of quenched PVDF.
Density = 0.9 g/cc, melt volume = 10 cc, residence time = 100 s. Find extruder output in kg/h.
Polymer 0.2 g in 100 mL benzene. Relative viscosity = 1.5. Mark–Houwink: \([\eta] = K M^a\) with \(a=0.5\), \(K=0.001\). Find molecular weight.
Glass-fiber composite: 40% glass fibers (\(E_f = 69\) GPa), 60% polyester resin (\(E_m=3.4\) GPa). Find modulus of elasticity of composite in longitudinal direction.
The molar mass distribution of a polymer is given as:
\begin{tabular{|c|c|
Number of molecules & Molar mass (g/mol)
100 & 7500
50 & 5000
The resulting weight average molecular weight of the polymer is ................ g/mol. (Answer in integer)
Choose the correct group of fat-soluble vitamins.
The synthesis of thyroxine T4 in the human body requires .............
Which among the followings is NOT an essential amino acid?
The time required for stipulated destruction of a microbial population at a given temperature is ______.
Which among the following statements is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Calculate the efficiency in percent (rounded off to 1 decimal place) of an oil expeller which yields 37 kg oil containing 5% solid impurities from 100 kg mustard seeds. The oil content of the mustard seed is 38%.
Orange juice is packaged aseptically and stored under ambient conditions. The degradation of vitamin C in the juice occurs during storage following first-order reaction kinetics. The degradation rate constant is \(5.2 \times 10^{-3}\) day\(^{-1}\). The half-life of vitamin C in days is ............. (in integer).
The weight of 10 kg dried cauliflower containing 5% moisture (wet basis) after rehydration is 60 kg. If the fresh cauliflower contained 87% moisture (wet basis), calculate the coefficient of rehydration (rounded off to 2 decimal places).
Match the industrial product in Column I with the fermentative organism in Column II.
\begin{tabular{|c|c|
Column I (Product) & Column II (Organism)
P. Vinegar & 1. Enterobacter aerogenes
Q. Citric acid & 2. Saccharomyces cerevisiae
R. Ethanol & 3. Acetobacter aceti
S. L-Lysine & 4. Aspergillus niger
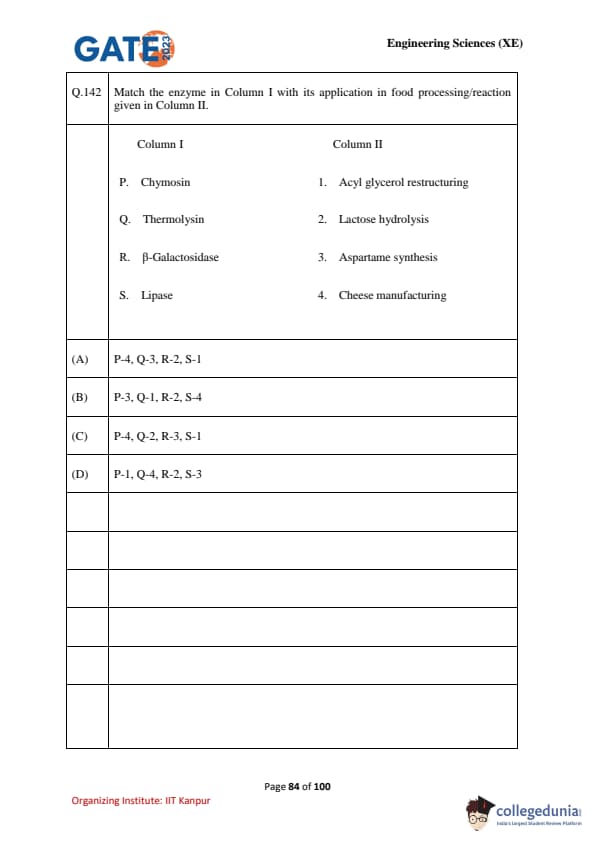
Match the enzyme in Column I with its application in food processing/reaction given in Column II.
\begin{tabular{|c|l|c|l|
Column I & Enzyme & Column II & Application
P & Chymosin & 1 & Acyl glycerol restructuring
Q & Thermolysin & 2 & Lactose hydrolysis
R & \(\beta\)-Galactosidase & 3 & Aspartame synthesis
S & Lipase & 4 & Cheese manufacturing
Identify the Gram +ve bacteria responsible for causing food borne diseases among the following.
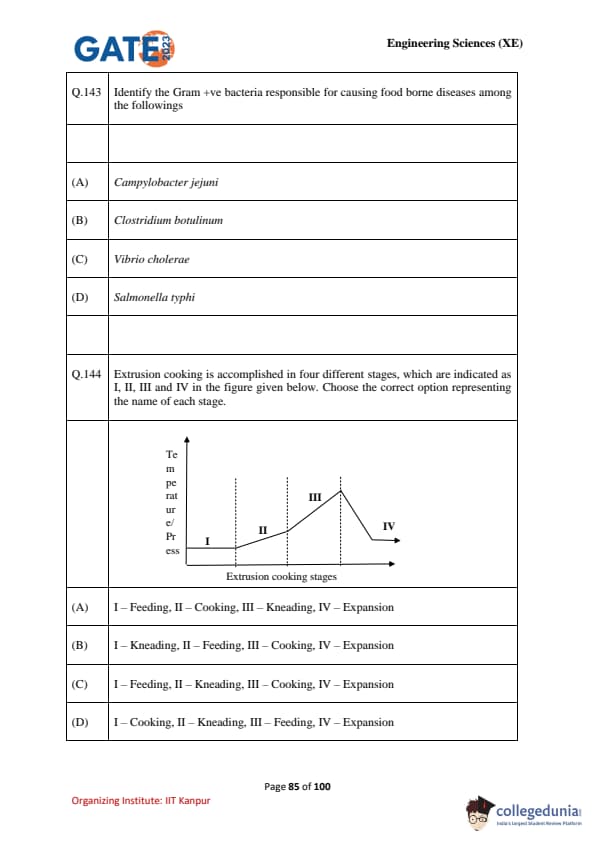
Extrusion cooking is accomplished in four different stages (I, II, III, IV). Identify the correct order from the given options.
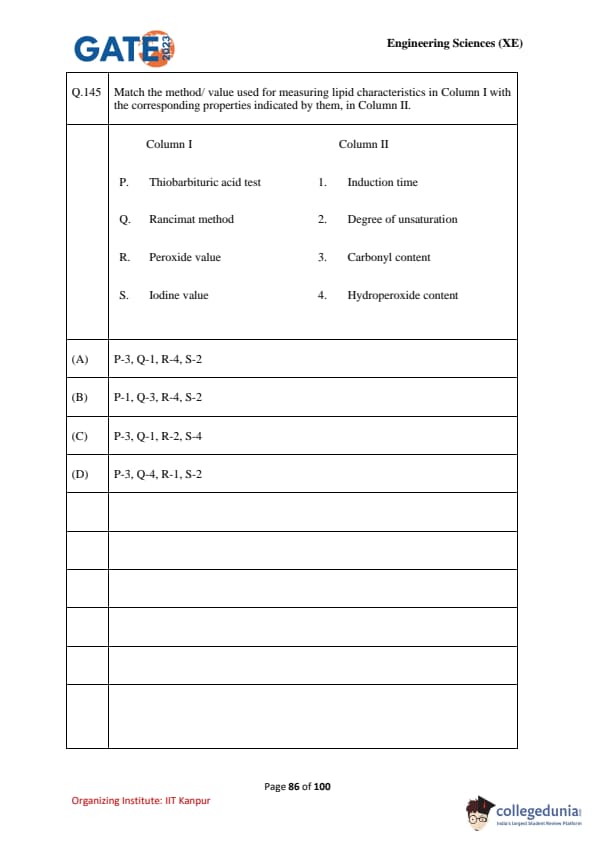
Match the method/value used for measuring lipid characteristics in Column I with the corresponding properties indicated by them, in Column II.
\begin{tabular{|c|l|c|l|
Column I & Method/Value & Column II & Property
P & Thiobarbituric acid test & 1 & Induction time
Q & Rancimat method & 2 & Degree of unsaturation
R & Peroxide value & 3 & Carbonyl content
S & Iodine value & 4 & Hydroperoxide content
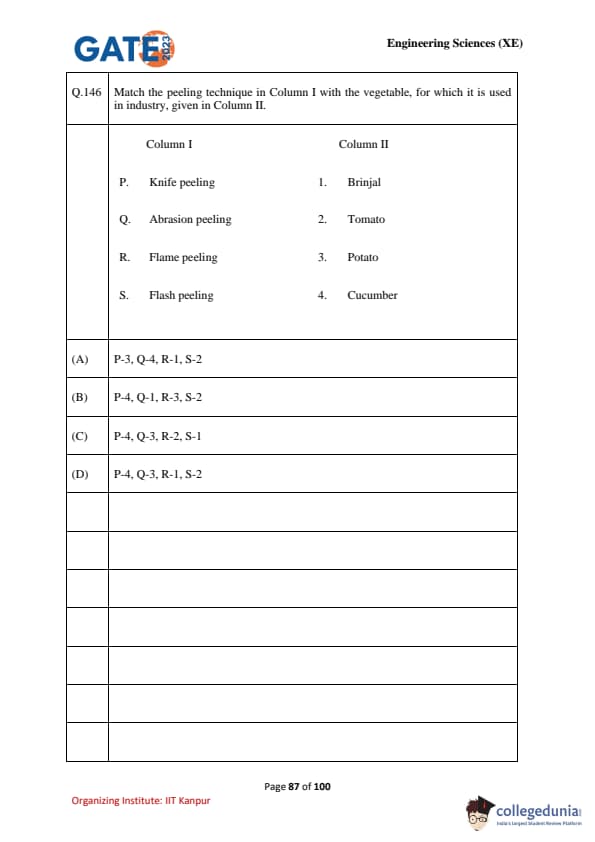
Match the peeling technique in Column I with the vegetable, for which it is used in industry, given in Column II.
\begin{tabular{|c|l|c|l|
Column I & Peeling Technique & Column II & Vegetable
P & Knife peeling & 1 & Brinjal
Q & Abrasion peeling & 2 & Tomato
R & Flame peeling & 3 & Potato
S & Flash peeling & 4 & Cucumber
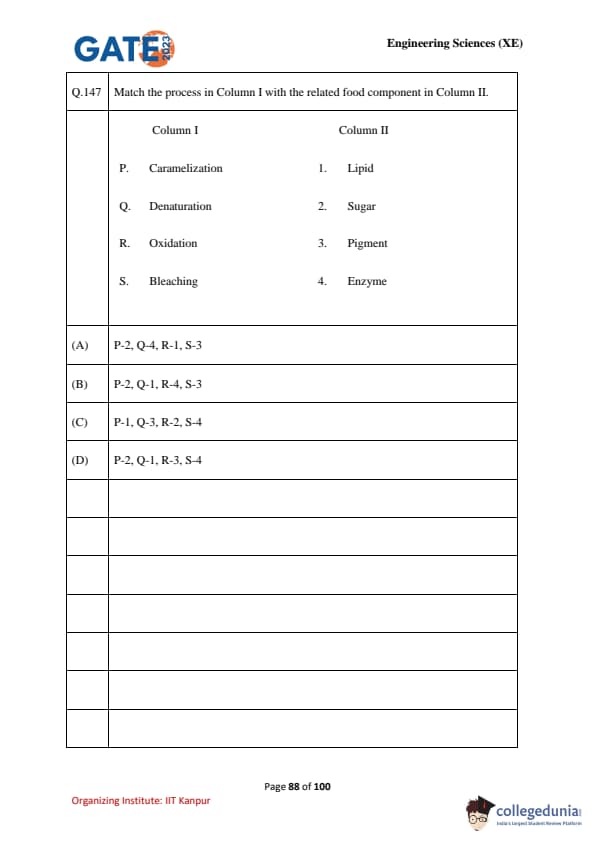
Match the process in Column I with the related food component in Column II.
\begin{tabular{|c|l|c|l|
Column I & Process & Column II & Food Component
P & Caramelization & 1 & Lipid
Q & Denaturation & 2 & Sugar
R & Oxidation & 3 & Pigment
S & Bleaching & 4 & Enzyme
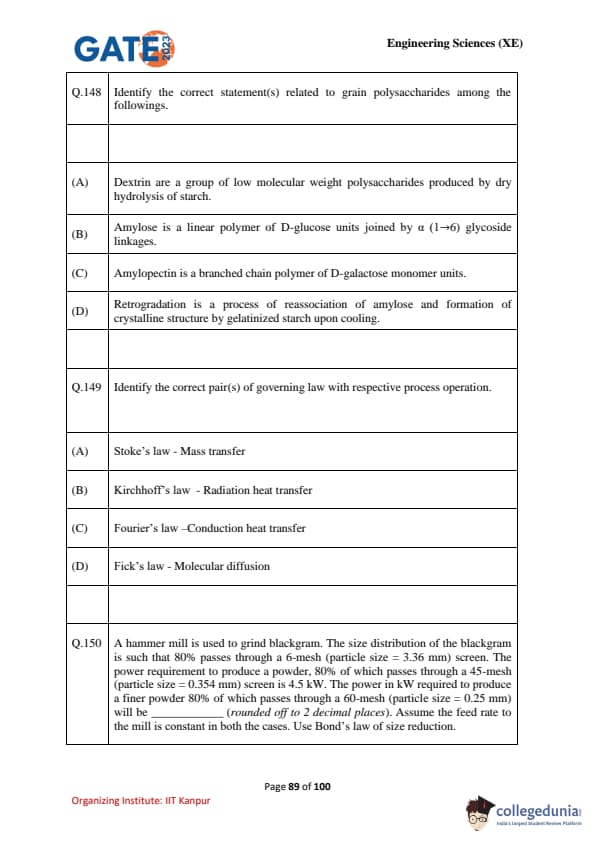
Identify the correct statement(s) related to grain polysaccharides among the followings.
Identify the correct pair(s) of governing law with respective process operation.
A hammer mill is used to grind blackgram. The size distribution is such that 80% passes through a 6-mesh (3.36 mm) screen.
The power required to produce a powder where 80% passes through a 45-mesh (0.354 mm) screen is 4.5 kW.
Find the power in kW required to produce a finer powder, 80% of which passes through a 60-mesh (0.25 mm) screen.
Use Bond’s law of size reduction.
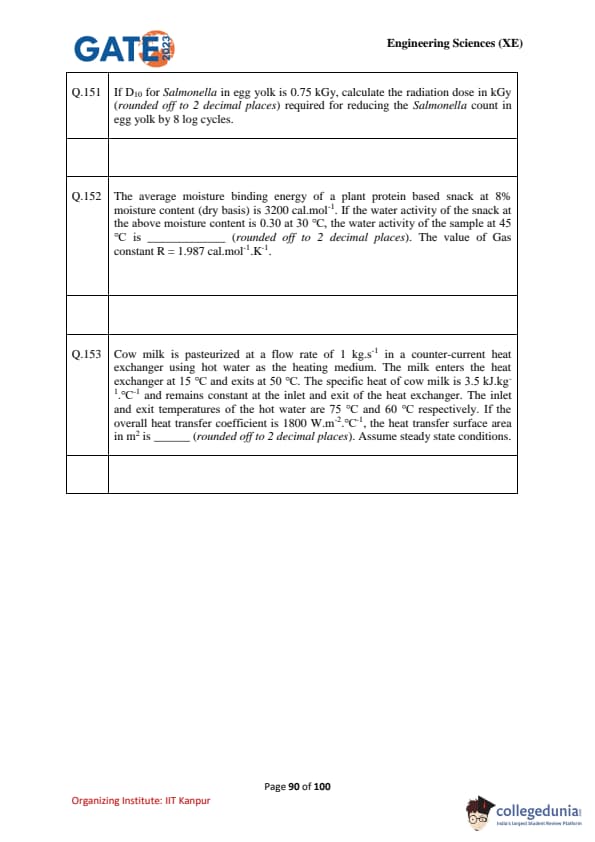
If \(D_{10}\) for Salmonella in egg yolk is 0.75 kGy, calculate the radiation dose in kGy (rounded off to 2 decimal places) required for reducing the Salmonella count in egg yolk by 8 log cycles.
The average moisture binding energy of a plant protein-based snack at 8% moisture content (dry basis) is 3200 cal.mol\(^{-1}\). If the water activity of the snack at the above moisture content is 0.30 at 30°C, the water activity of the sample at 45°C is ............. (rounded off to 2 decimal places). Use \(R = 1.987\) cal.mol\(^{-1}\).K\(^{-1}\).
Cow milk is pasteurized at a flow rate of 1 kg.s\(^{-1}\) in a counter-current heat exchanger using hot water as the heating medium. The milk enters at 15°C and exits at 50°C. The specific heat of milk is 3.5 kJ.kg\(^{-1}\).°C\(^{-1}\).
Hot water enters at 75°C and exits at 60°C. Overall heat transfer coefficient \(U = 1800\) W.m\(^{-2}\).°C\(^{-1}\).
Find the heat transfer surface area in m\(^2\) (rounded off to 2 decimal places). Assume steady-state.
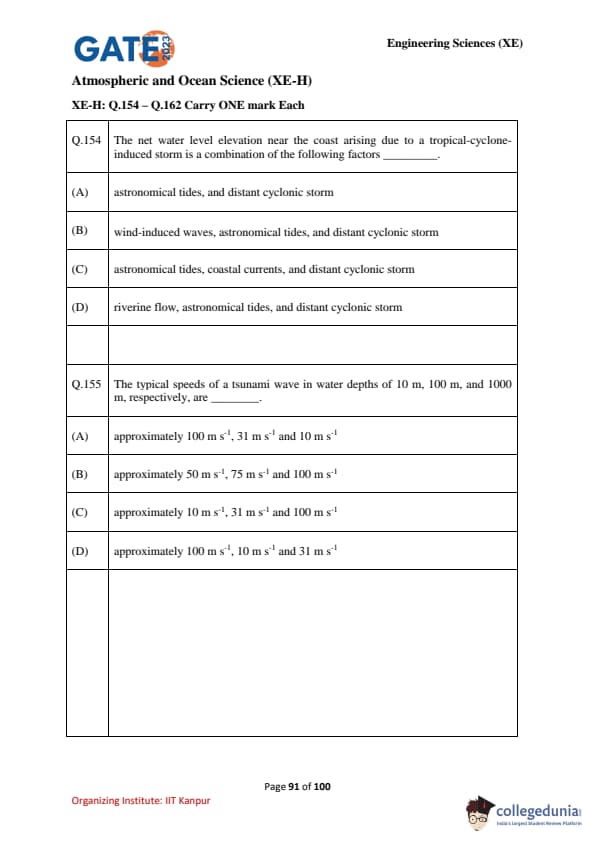
The net water level elevation near the coast arising due to a tropical-cyclone-induced storm is a combination of the following factors ................
The typical speeds of a tsunami wave in water depths of 10 m, 100 m, and 1000 m, respectively, are ................
Which classification of tides best represents the west coast of India?
The variation in geostrophic winds with height, at the atmospheric boundary layer, considering variation in pressure gradient as a function of height, is referred to as ..................
Consider the following options and pick out the right choice. The solubility of a gas in sea water increases with ...............
From the list given below, identify the organism type in the biological pump that takes up carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into the ocean.
The amount of CO\(_2\) that can be absorbed ............... when the temperature of seawater decreases.
Which among the following gases has the highest global warming potential?
What will happen to the speed of a balanced flow as one moves across the isobar along a particular latitude?
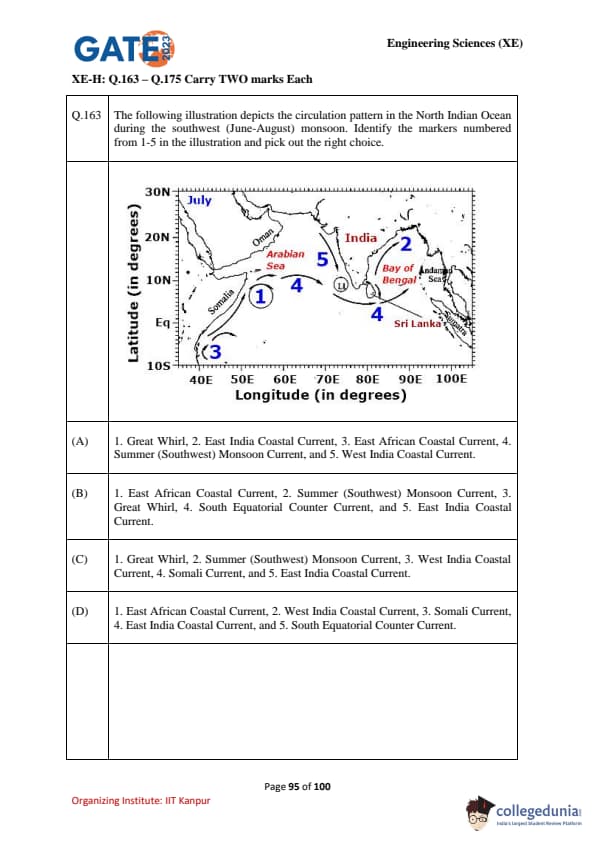
The following illustration depicts the circulation pattern in the North Indian Ocean during the southwest (June–August) monsoon. Identify the markers numbered from 1–5 in the illustration and pick out the right choice.
From the following list identify the region that has low chlorophyll and low nutrients.
Match the following physical phenomena from the perspective of monsoonal circulation:
\begin{tabular{|c|l|c|l|
Column-1 & Phenomenon & Column-2 & Region
a) & Reversal of East–West temperature gradient with seasons & i & Over the tropics
b) & Reversal of North–South temperature gradient with seasons & ii & Indian Ocean
c) & Surface cooling and deepening of mixed layer & iii & Over mid-latitudes
d) & Northward movement of south equatorial current & iv & Arabian Sea
Choose the correct statement(s) in context to Ekman spiral from the following:
Which of the following is/are associated with winter rainfall over India?
If the global albedo is increased from 0.3 to 0.4, the global radiative equilibrium temperature (in K) would decrease by .......... (rounded off to one decimal place).
(Consider no greenhouse effect, solar constant = 1360 W/m\(^2\), Stefan–Boltzmann constant = \(5.67 \times 10^{-8}\) W m\(^{-2}\) K\(^{-4}\)).
When a parcel of dry air rises at a rate of 2 cm s\(^{-1}\) vertically, what should be the rate of heating per unit mass in J s\(^{-1}\) kg\(^{-1}\) (due to radiation, conduction, etc.) in order to maintain the air parcel at a constant temperature?
(Consider \(g = 9.8 \, m/s^2\), rounded off to three decimal places).
Two balls each of 5 cm in diameter are placed 200 m apart on a horizontal frictionless plane at 45° N. The balls are impulsively propelled directly at each other with equal speeds. What must be the speed in m/s so that the two balls just miss each other?
(Take \(\Omega = 7.29 \times 10^{-5} \, rad/s\), rounded off to two decimal places).
A parcel of dry air having an initial temperature of 30 °C at 1000 hPa level is lifted adiabatically. At what pressure (in hPa) its density reduces by half?
(Take \(C_p/C_v = 0.71\), rounded off to two decimal places).
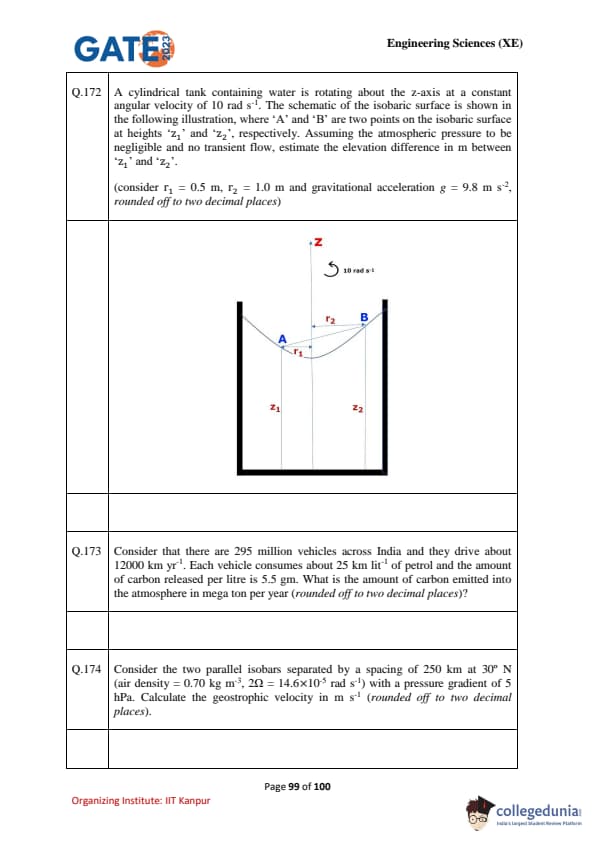
A cylindrical tank containing water is rotating about the z-axis at a constant angular velocity of 10 rad s\(^{-1}\). The schematic of the isobaric surface is shown below, where ‘A’ and ‘B’ are two points on the isobaric surface at heights \(z_1\) and \(z_2\), respectively. Assuming negligible atmospheric pressure and no transient flow, estimate the elevation difference in m between \(z_1\) and \(z_2\).
(Given: \(r_1 = 0.5 \, m\), \(r_2 = 1.0 \, m\), \(g = 9.8 \, m/s^2\), \(\omega = 10 \, rad/s\)).
There are 295 million vehicles across India driving about 12000 km yr\(^{-1}\). Each vehicle consumes about 25 km l\(^{-1}\) of petrol, and the amount of carbon released per litre is 5.5 g. What is the amount of carbon emitted into the atmosphere in mega tons per year?
Two parallel isobars are separated by 250 km at 30°N with air density = 0.70 kg/m\(^3\), Coriolis parameter \(f = 2\Omega \sin \phi\) (where \(\Omega = 14.6 \times 10^{-5}\) rad/s), and pressure gradient = 5 hPa. Calculate the geostrophic velocity in m/s.
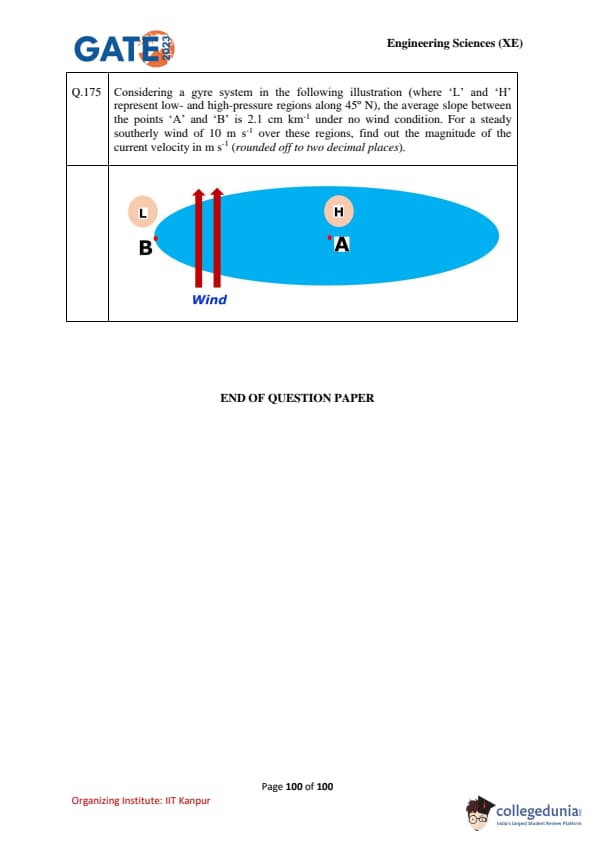
Considering a gyre system (shown in the figure) where ‘L’ and ‘H’ represent low- and high-pressure regions along 45°N, the average slope between points ‘A’ and ‘B’ is 2.1 cm km\(^{-1}\) under no-wind condition. For a steady southerly wind of 10 m s\(^{-1}\) over these regions, find out the magnitude of the current velocity in m s\(^{-1}\) (rounded off to two decimal places).
























Also Check:
| Previous Year GATE Engineering Sciences Question Papers | GATE 2023 Engineering Sciences Paper Analysis |





Comments