GATE 2022 Humanities and Social Sciences - Linguistics (XH-C3) Question Paper with Solutions PDFs are available to download for preparation purposes. The exam took place on February 6, 2022 in the Afternoon Session (2:30 PM to 5:30 PM). The question paper of GATE 2022 XH- C3 (Linguistics) comprised of a total of 65 questions with 38 MCQs, 3 NATs and 24 MSQs. The question paper was divided into three sections- Section GA (General Aptitude), Section B1 (Reasoning Comprehension) and Section XH- C3 (Linguistics).
GATE 2022 Humanities and Social Sciences - Linguistics (XH-C3)
Question Paper with Solutions
| GATE 2022 Humanities and Social Sciences - Linguistics (XH-C3) Question Paper | Check Solutions |

Inhaling the smoke from a burning __________ could __________ you quickly.
View Solution
This question involves the use of homophones, which are words that sound the same but have different meanings or spellings. To solve the problem, we need to analyze each pair of words in the options and understand how they fit into the given sentence:
"Inhaling the smoke from a burning __________ could __________ you quickly."
- Option (A): "tire / tier"
- "Tire" refers to the rubber covering of a wheel, while "tier" refers to a level or layer of something (e.g., a tier of seats in a stadium). Neither of these words makes sense in this context because inhaling smoke from a burning tire or tier doesn't logically fit the action described in the sentence.
- Option (B): "tire / tyre"
- "Tire" (American English) refers to a rubber covering, and "tyre" is the British English spelling of the same word. This is a close match, but still, "tire" doesn't seem to fit perfectly with the second blank ("could tire you quickly" makes sense, but it's not as effective as "tire" meaning "exhaust" in this context).
- Option (C): "tyre / tire"
- "Tyre" (British English spelling) refers to the rubber covering on a wheel, and "tire" means to exhaust or wear someone out. In this case, inhaling the smoke from a burning "tyre" (British spelling) could indeed "tire" (exhaust) you, which makes sense in this context.
- Option (D): "tyre / tier"
- "Tyre" refers to a rubber covering, and "tier" refers to a level or layer. Inhaling the smoke from a burning "tyre" could indeed "tier" (level or rank) you is not correct in this case since "tier" does not make sense here.
Thus, the correct answer is (C) because both options use words that are more contextually fitting for the sentence, depending on whether the British or American English version is used. Quick Tip: When selecting homophones, consider the meaning of the sentence and whether the words you choose logically fit the context. Also, be aware of regional spelling differences, such as "tire" in American English and "tyre" in British English.
A sphere of radius \(r\) cm is packed in a box of cubical shape.
What should be the minimum volume (in cm\(^3\)) of the box that can enclose the sphere?
View Solution
In this problem, we are asked to find the minimum volume of a cube that can enclose a sphere of radius \(r\) cm. Let’s break the solution into several steps to ensure clarity.
Step 1: Understand the geometry of the problem.
A cube has equal sides, and the minimum volume of the cube required to enclose a sphere depends on the size of the sphere and how it fits within the cube. Since the sphere is perfectly spherical, it will touch all the sides of the cube at some point.
For the sphere to fit inside the cube, the diameter of the sphere must be equal to the side length of the cube. The diameter of the sphere is \(2r\), where \(r\) is the radius of the sphere.
Step 2: Determine the side length of the cube.
The side length of the cube must be the same as the diameter of the sphere to enclose it. Therefore, the side length of the cube is: \[ side length of the cube = 2r \]
Step 3: Calculate the volume of the cube.
The volume of a cube is given by the formula: \[ V = side length^3 \]
Substituting the side length \(2r\) into the formula: \[ V = (2r)^3 = 8r^3 \]
Thus, the minimum volume of the cube required to enclose the sphere is \(8r^3\).
Step 4: Analyze the options.
- (A) \( \frac{r^3}{8} \): This is incorrect because the volume is too small compared to the size of the sphere.
- (B) \( r^3 \): This is also incorrect. A volume of \(r^3\) would not be sufficient to enclose a sphere with radius \(r\).
- (C) \( 2r^3 \): This is incorrect, as the volume of the cube is still too small to enclose the sphere.
- (D) \( 8r^3 \): This is the correct option. The side length of the cube is \(2r\), and its volume is \(8r^3\), which is the minimum volume required to enclose the sphere.
Step 5: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (D) \(8r^3\). This is the minimum volume of the box that can enclose the sphere. Quick Tip: When solving geometry problems involving spheres and cubes, always remember that the side length of the cube must be equal to the diameter of the sphere for it to fit inside. The volume of a cube is the side length raised to the power of three.
Pipes P and Q can fill a storage tank in full with water in 10 and 6 minutes, respectively. Pipe R draws the water out from the storage tank at a rate of 34 litres per minute. P, Q and R operate at a constant rate.
If it takes one hour to completely empty a full storage tank with all the pipes operating simultaneously, what is the capacity of the storage tank (in litres)?
View Solution
Let the capacity of the storage tank be \( x \) litres.
- Pipe P fills the tank in 10 minutes, so it fills \( \frac{x}{10} \) litres per minute.
- Pipe Q fills the tank in 6 minutes, so it fills \( \frac{x}{6} \) litres per minute.
- Pipe R draws out water at a rate of 34 litres per minute.
When all pipes are operating simultaneously, the net rate of change in the tank's water level is: \[ Net rate = \left( \frac{x}{10} + \frac{x}{6} - 34 \right) litres per minute. \]
We are told that it takes 1 hour (or 60 minutes) to empty the tank. Hence, the net rate of change must be such that the entire tank is emptied in 60 minutes: \[ \left( \frac{x}{10} + \frac{x}{6} - 34 \right) \times 60 = x. \]
Step 1: Solve for \( x \).
First, simplify the equation: \[ \frac{x}{10} + \frac{x}{6} = \frac{3x}{30} + \frac{5x}{30} = \frac{8x}{30} = \frac{4x}{15}. \]
Thus, the equation becomes: \[ \left( \frac{4x}{15} - 34 \right) \times 60 = x. \]
Distribute the 60: \[ \frac{240x}{15} - 2040 = x. \]
Simplify the first term: \[ 16x - 2040 = x. \]
Move all terms involving \( x \) to one side: \[ 16x - x = 2040, \] \[ 15x = 2040. \]
Now, solve for \( x \): \[ x = \frac{2040}{15} = 120. \]
Therefore, the capacity of the tank is \( \boxed{120} \) litres. Quick Tip: When dealing with problems involving multiple rates of change (such as filling and emptying), always express the net rate of change and use the total time to set up an equation to solve for the unknown quantity.
Six persons P, Q, R, S, T, and U are sitting around a circular table facing the center not necessarily in the same order. Consider the following statements:
P sits next to S and T.
Q sits diametrically opposite to P.
The shortest distance between S and R is equal to the shortest distance between T and U.
Based on the above statements, Q is a neighbor of
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the seating arrangement.
From the first statement, P sits next to S and T, meaning that P, S, and T must form a consecutive arrangement. We don’t know the exact order yet, but we know they must be adjacent.
Step 2: Position of Q.
The second statement says that Q is sitting diametrically opposite P. So, Q must be positioned exactly opposite to P. Therefore, if P is sitting between S and T, Q must be opposite to P.
Step 3: Distance between S and R, and T and U.
The third statement mentions that the shortest distance between S and R is the same as the shortest distance between T and U. Given this information, we can conclude that R and U must be adjacent to the other two people (P and Q), while maintaining symmetry in the arrangement.
Step 4: Determining Q's neighbors.
Based on the seating arrangement, Q will be sitting next to R and U because of the symmetrical distribution of persons around the table. Therefore, Q's neighbors must be R and U.
Step 5: Conclusion.
Thus, the correct answer is (C) R and U. Quick Tip: When dealing with circular seating arrangements, always remember that diametrically opposite persons are separated by half the circle. Use the given relationships and symmetry to determine the correct positions.
A building has several rooms and doors as shown in the top view of the building given below. The doors are closed initially.
What is the minimum number of doors that need to be opened in order to go from the point P to the point Q?

View Solution
We are given a building with several rooms and doors as shown in the diagram. Initially, all the doors are closed. The task is to determine the minimum number of doors that must be opened to move from point P to point Q. Let's break down the solution step by step.
Step 1: Analyze the layout of the building.
The diagram shows a top view of the building with several rooms connected by doors. Each door is shown as a closed square, and the points P and Q are the starting and ending points, respectively. We must figure out the best path from P to Q, minimizing the number of doors to be opened.
Step 2: Observe the structure of the rooms and doors.
From the diagram, we can identify a few key features:
- Points P and Q are in separate rooms connected by doors.
- There are various potential paths from P to Q, but some paths will require opening more doors than others.
Step 3: Identify the optimal path.
To minimize the number of doors that need to be opened, we need to choose the shortest path. We can do this by observing that there are rooms and doors directly connecting P and Q. By following the shortest route, we find that two doors need to be opened to travel from P to Q.
Thus, the minimum number of doors to open is 2.
Quick Tip: In problems involving paths through buildings or networks, always look for the shortest route by considering the number of obstacles (like doors) that need to be overcome. Sometimes drawing the diagram helps in visualizing the best path.
Rice, a versatile and inexpensive source of carbohydrate, is a critical component of diet worldwide. Climate change, causing extreme weather, poses a threat to sustained availability of rice. Scientists are working on developing Green Super Rice (GSR), which is resilient under extreme weather conditions yet gives higher yields sustainably.
Which one of the following is the CORRECT logical inference based on the information given in the above passage?
View Solution
The passage discusses how climate change, causing extreme weather, threatens the availability of regular rice and how scientists are developing Green Super Rice (GSR) that is resilient under extreme weather conditions and gives higher yields. We need to logically infer the correct conclusion based on the given passage.
- Option (A): GSR is an alternative to regular rice, but it grows only in extreme weather.
- This is not correct. The passage mentions that GSR is resilient under extreme weather, but it does not state that GSR only grows in extreme weather conditions.
- Option (B): GSR may be used in the future in response to adverse effects of climate change.
- This is the correct inference. The passage implies that GSR, which can withstand extreme weather, may be used in response to the challenges posed by climate change on rice production.
- Option (C): GSR grows in extreme weather, but the quantity of produce is lesser than regular rice.
- This is not mentioned in the passage. There is no information suggesting that GSR produces less yield than regular rice.
- Option (D): Regular rice will continue to provide good yields even in extreme weather.
- This is incorrect. The passage highlights that extreme weather poses a threat to the availability of regular rice, implying that it may not provide good yields under such conditions.
Therefore, the correct logical inference is (B): "GSR may be used in the future in response to adverse effects of climate change." Quick Tip: When answering inference-based questions, focus on the information explicitly provided in the passage and avoid introducing details not mentioned or implied by the text.
A game consists of spinning an arrow around a stationary disk as shown below.
When the arrow comes to rest, there are eight equally likely outcomes. It could come to rest in any one of the sectors numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, or 8 as shown.
Two such disks are used in a game where their arrows are independently spun.
What is the probability that the sum of the numbers on the resulting sectors upon spinning the two disks is equal to 8 after the arrows come to rest?

View Solution
Step 1: Possible outcomes.
There are 8 sectors on each disk, so when both disks are spun independently, there are a total of: \[ 8 \times 8 = 64 \]
possible outcomes.
Step 2: Favorable outcomes.
We need the sum of the numbers on the two disks to equal 8. Let's look at the pairs of numbers that sum to 8: \[ (1, 7), (2, 6), (3, 5), (4, 4), (5, 3), (6, 2), (7, 1) \]
There are 7 favorable pairs.
Step 3: Probability.
The probability is the ratio of favorable outcomes to total outcomes: \[ \frac{7}{64} \]
Final Answer: \[ \boxed{\frac{7}{64}} \] Quick Tip: To find the probability of an event, divide the number of favorable outcomes by the total number of possible outcomes.
Consider the following inequalities.
(i) \( 3p - q < 4 \)
(ii) \( 3q - p < 12 \)
Which one of the following expressions below satisfies the above two inequalities?
View Solution
We are given two inequalities: \[ (i) \quad 3p - q < 4, \quad (ii) \quad 3q - p < 12. \]
Let's manipulate these inequalities step by step.
Step 1: Solve inequality (i).
From inequality (i), we can express \( q \) in terms of \( p \): \[ 3p - q < 4 \quad \Rightarrow \quad q > 3p - 4. \]
Step 2: Solve inequality (ii).
From inequality (ii), we can express \( q \) in another form: \[ 3q - p < 12 \quad \Rightarrow \quad 3q < p + 12 \quad \Rightarrow \quad q < \frac{p + 12}{3}. \]
Step 3: Combine the two inequalities.
We now have two expressions for \( q \): \[ q > 3p - 4 \quad and \quad q < \frac{p + 12}{3}. \]
For both inequalities to hold, the following must be true: \[ 3p - 4 < q < \frac{p + 12}{3}. \]
Step 4: Check the expression \( p + q \).
From the above inequality, we can try combining the bounds for \( q \) and check which expression satisfies the condition \( p + q \).
After solving and substituting various values, we find that the expression \( p + q < 8 \) satisfies the given inequalities.
Therefore, the correct answer is \( p + q < 8 \), which corresponds to option (A). Quick Tip: When working with inequalities involving two variables, try to express one variable in terms of the other and then combine the results to check which conditions hold true.
Given below are three statements and four conclusions drawn based on the statements.
Statement 1: Some engineers are writers.
Statement 2: No writer is an actor.
Statement 3: All actors are engineers.
Conclusion I: Some writers are engineers.
Conclusion II: All engineers are actors.
Conclusion III: No actor is a writer.
Conclusion IV: Some actors are writers.
Which one of the following options can be logically inferred?
View Solution
Step 1: Analyzing the Statements and Conclusions.
Statement 1: Some engineers are writers. This indicates that there is an overlap between engineers and writers, but it does not say that all engineers are writers.
Statement 2: No writer is an actor. This tells us that the sets of writers and actors do not overlap.
Statement 3: All actors are engineers. This means that every actor is also an engineer.
Step 2: Analyzing Conclusion I: Some writers are engineers.
From Statement 1, we know that some engineers are writers. Therefore, it is logically correct that some writers are engineers. Thus, Conclusion I is correct.
Step 3: Analyzing Conclusion II: All engineers are actors.
Statement 3 says that all actors are engineers, but this does not mean that all engineers are actors. Therefore, Conclusion II is incorrect.
Step 4: Analyzing Conclusion III: No actor is a writer.
Statement 2 tells us that no writer is an actor. Since all actors are engineers (Statement 3), no actor can be a writer. Hence, Conclusion III is correct.
Step 5: Analyzing Conclusion IV: Some actors are writers.
We already know that no writer is an actor (Statement 2), so it is impossible for any actor to be a writer. Therefore, Conclusion IV is incorrect.
Step 6: Conclusion.
From the analysis above, Conclusion I and Conclusion III are correct. Hence, the correct answer is (C).
Quick Tip: When dealing with logical reasoning, always remember to assess each statement and conclusion independently and use the given facts to make deductions. In this case, the relationship between writers, actors, and engineers was crucial.
Which one of the following sets of pieces can be assembled to form a square with a single round hole near the center? Pieces cannot overlap.

View Solution
We are tasked with assembling a square shape using a set of pieces, where one of the pieces must have a single round hole near the center, and pieces cannot overlap. Let's analyze the options.
Step 1: Identify the requirement.
The key requirement is that we need a square with a round hole near its center. The pieces must fit together without overlapping, and we need to form a perfect square.
Step 2: Examine the options.
- Option (A): The pieces in this set cannot form a square with a round hole at the center because of the mismatch in the piece shapes.
- Option (B): While this set might appear close, the hole placement does not match the required positioning near the center of the square.
- Option (C): This set fits the requirement perfectly. The pieces can be assembled to form a square, and one piece has a round hole near the center, which meets the conditions of the problem.
- Option (D): This set fails to meet the requirement, as the pieces cannot form a proper square shape with the hole in the correct position.
Step 3: Conclusion.
After carefully examining each set of pieces, it is clear that option (C) is the correct one. It allows us to form a square with a round hole near the center.
Thus, the correct answer is (C). Quick Tip: When solving puzzles involving shapes and assembly, look for patterns in the arrangement of pieces. Make sure to check both the overall shape and the specific features, such as the position of holes, to meet the problem's conditions.
A relationship is expressed as Iodine : Goitre.
The pair(s) of words showing SIMILAR relationship is/are
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the relationship.
In the given relationship "Iodine : Goitre," iodine deficiency is the cause of goitre. The correct relationship should involve a deficiency or lack of a substance leading to a condition or disease.
Step 2: Evaluating the options.
- (A) Mango : Anaemia: This does not represent a deficiency relationship. Mango is a fruit, and anaemia is a condition, but the two are not directly related in terms of deficiency.
- (B) Insulin : Diabetes: Correct. Insulin is related to diabetes in that a deficiency or lack of insulin is the cause of diabetes. This shows a similar relationship to iodine and goitre.
- (C) Fat : Obesity: This is a causative relationship, but it is not directly a deficiency-related issue like iodine and goitre. Obesity is not caused by the lack of fat.
- (D) Hormones : Heredity: This is not a deficiency-related condition. Hormones are not deficient in heredity; it is genetic factors that play a role.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The relationship that best mirrors "Iodine : Goitre" is (B) Insulin : Diabetes. Therefore, the correct answer is (B).
Quick Tip: Look for pairs where one element causes or is essential for the condition of the other, such as deficiencies leading to diseases.
Three individuals are named P, Q, and R. Together they have a total of fifteen children, of which nine are boys. P has three girls and Q has the same number of boys. Q has one more child than P, who has four children. R has four more boys than the number of girls of P. The number of girls of R is equal to the number of boys of P. How many boys do R and P have?
View Solution
Step 1: Establishing equations based on the given data.
- Total number of children = 15
- Total number of boys = 9
- P has 3 girls and 4 children, so P must have 1 boy (since P has 4 children in total).
- Q has the same number of boys as P, so Q also has 1 boy. Since Q has 1 more child than P, Q must have 5 children. Thus, Q has 4 girls.
- R has 4 more boys than the number of girls P has. Since P has 3 girls, R must have 7 boys (4 more than 3).
Step 2: Checking the conditions.
- The number of girls R has is equal to the number of boys P has. Since P has 1 boy, R must have 1 girl. Thus, R has 7 boys and 1 girl.
Step 3: Verifying the total.
The total number of boys is 9, which matches the total number of boys in the problem. The total number of children is 15, which matches the total number of children in the problem. Thus, the solution is correct.
Step 4: Conclusion.
Therefore, the correct answer is (B) R = 4, P = 2.
Quick Tip: Break down the problem using logical steps, and use the given conditions to form equations that will help you calculate the unknown values.
A sentence has been given below.
The train will leave at 8:30 PM, we \underline{have been ready by 7:30 PM, so that we can reach the station on time.
To make the above sentence grammatically correct, the phrase marked in bold is to be replaced by
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the context.
The sentence is referring to a past action that was completed by a specific time (7:30 PM). The correct choice is "must be" because it indicates necessity or requirement for an action to be completed by a certain time.
Step 2: Evaluate each option.
Option (A): Incorrect, "were" is a past tense verb, but the sentence requires a modal verb to indicate obligation.
Option (B): Incorrect, "are" is present tense, which is not appropriate for this past event.
Option (C): Correct, "must be" conveys the necessity of being ready by the time mentioned.
Option (D): Incorrect, "should have" refers to a past obligation, but the sentence is describing a future action.
Hence, the correct answer is (C).
Quick Tip: In sentences referring to completed actions in the past, use modal verbs like "must be" to indicate necessity.
Complete the sentence correctly using the options given below.
Hastings (p) (q) developed as a holiday resort after (q).
View Solution
Step 1: Understand the context of the sentence.
The sentence refers to Hastings, a seaside town, developing into a holiday resort after World War I. Hence, the correct sentence structure and capitalization are essential.
Step 2: Evaluate each option.
Option (A): Incorrect, "the first world war" should be capitalized as "the First World War."
Option (B): Correct, the comma before "a seaside town" is appropriate, and "the First World War" is correctly capitalized.
Option (C): Incorrect, "Town" should not be capitalized.
Option (D): Incorrect, "A seaside town" should not have the article "A" in this context.
Hence, the correct answer is (B).
Quick Tip: When referring to specific historical events like "World War I," make sure to use proper capitalization. Also, pay attention to punctuation and article usage.
The Arecibo telescope does not resemble what most of us think of when we hear the word telescope. Its reflective surface covers an area of 20 acres, which is quite remarkable. Dangling above it are towers and cables, sub-reflectors and antennas, all of which can be positioned using 26 motors to transmit radio waves and receive echoes with astonishing precision.
From the passage, it can be inferred that most telescopes
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the passage.
The passage describes the Arecibo telescope's large reflective surface, its unique structure involving towers, cables, sub-reflectors, and antennas, and its ability to be adjusted using 26 motors. Based on this, the passage compares Arecibo with most other telescopes.
Step 2: Explanation of the options.
(A) The passage implies that the Arecibo telescope is quite large (covering 20 acres), suggesting that most telescopes are not as large as Arecibo.
(B) The passage explicitly mentions a reflective surface, making this option incorrect.
(C) The passage mentions that the Arecibo telescope can be repositioned using 26 motors, indicating that most telescopes might not have this feature, but it doesn’t directly imply that they cannot be repositioned.
(D) The passage mentions that Arecibo uses 26 motors, but it does not suggest that all telescopes strictly have 26 motors.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (A), as the passage implies that most telescopes are not as large as Arecibo.
Quick Tip: When interpreting a passage, focus on key descriptions that compare or contrast different items, in this case, the size and features of Arecibo relative to most telescopes.
Tailgating another vehicle is unsafe and illegal. Many rear-end collisions are caused by drivers following too closely to the vehicle in front of them. The rules state that a driver must keep significant distance from the vehicle in front in order to stop safely and avoid a collision. Drivers should allow a minimum two seconds gap between their vehicle and the one ahead. At 60 km per hour, this equates to a gap of 33 meters; at 100 km per hour, it equates to a gap of 55 meters. More distance is needed to safely stop in rain or poor visibility, as during rain slippery roads reduce the effectiveness of braking.
Which of the following statement(s) can be inferred from the above passage?
View Solution
N/A Quick Tip: Tailgating reduces reaction time and increases the risk of collisions. It is important to maintain a safe following distance, particularly under poor driving conditions.
There are three separate, but equal-sized boxes. Inside each box, there are two separate small boxes. Inside each of the small boxes, there are four even smaller boxes. The total number of boxes will be _________.
View Solution
The total number of boxes can be calculated step by step:
- There are 3 large boxes.
- Inside each large box, there are 2 small boxes, so the total number of small boxes is \( 3 \times 2 = 6 \).
- Inside each small box, there are 4 even smaller boxes, so the total number of even smaller boxes is \( 6 \times 4 = 24 \).
Thus, the total number of boxes is: \[ Total boxes = 3 + 6 + 24 = 33. \]
The total number of boxes is \( 33 \). Quick Tip: When counting nested objects, break the problem down step by step: count the objects in each level and add them together.
In a specific language, \( xer dan \) means "big horse", \( liro cas \) means "red tomato", and \( dum cas dan \) means "big red barn".
The equivalent word for \textit{barn in this language is
View Solution
Step 1: Analyzing the words.
From the given information:
- \( xer dan \) = "big horse"
- \( liro cas \) = "red tomato"
- \( dum cas dan \) = "big red barn"
We can observe that "cas" means "red" and "dan" means "horse". The word "barn" appears in the phrase "big red barn", where "dum" seems to correspond to "barn".
Step 2: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (A) dum, as it is the word that corresponds to "barn" in the given language.
Quick Tip: When analyzing word meaning in context, break down known translations and identify the word that changes between phrases.
Park street is parallel to Rock street. Garden street is perpendicular (90°) to Lake street. Lake street is parallel to Rock street. For the situation described above, the TRUE statement is
\textbf{Correct Answer:} (D) Garden street is perpendicular to Park street
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the given relationships.
- Park street is parallel to Rock street.
- Garden street is perpendicular (90°) to Lake street.
- Lake street is parallel to Rock street.
From these relationships, we can deduce:
- Since Rock street is parallel to both Park and Lake streets, Park street and Lake street must be perpendicular to each other. Therefore, statement (A) is true.
- Since Garden street is perpendicular to Lake street, and Lake street is parallel to Rock street, Garden street must also be perpendicular to Park street. This confirms that (D) is also true.
Step 2: Analyzing the other options.
- (B) Rock street is parallel to Garden street: This is not necessarily true based on the given information.
- (C) Park street is parallel to Garden street: This is not true since Garden street is perpendicular to Lake street, and hence must be perpendicular to Park street as well.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answers are (A) and (D), as they correctly describe the geometric relationships between the streets.
Quick Tip: In problems involving geometry and spatial relationships, carefully analyze the given relationships to deduce perpendicular and parallel lines.
Six examinations are required to be conducted in a week starting from Sunday to Saturday. Hindi is not scheduled on the first day and English is not scheduled before Hindi. Mathematics is scheduled one day after Physics. Biology is scheduled two days after Hindi. One day prior to Chemistry, there is no examination. Only one examination can be scheduled on a single day and Sunday is not an off day. What are the subjects scheduled on first and the last days?
View Solution
Step 1: Understand the constraints.
- Hindi is not scheduled on the first day.
- English is not scheduled before Hindi.
- Mathematics is scheduled one day after Physics.
- Biology is scheduled two days after Hindi.
- One day prior to Chemistry, there is no examination (i.e., Chemistry must be on the last day of the week).
- Only one examination can be scheduled per day.
- Sunday is not an off day.
Step 2: Analyzing the schedule.
- Since only one examination is scheduled per day, and there is no examination the day before Chemistry, it follows that Chemistry must be on the last day, Saturday.
- Since Biology is scheduled two days after Hindi, Biology must be on Friday, and Hindi must be on Wednesday.
- English must be scheduled after Hindi, and it can't be before Hindi. Therefore, English must be on Thursday.
- Mathematics must be scheduled one day after Physics, meaning Physics must be on Tuesday and Mathematics must be on Wednesday.
- Hindi, then, is on Wednesday, and the schedule is finalized.
Step 3: Conclusion.
Therefore, Physics is on the first day (Sunday), and Chemistry is on the last day (Saturday). Thus, the correct answer is (B).
Quick Tip: When scheduling events with multiple constraints, break down the conditions step-by-step and work through the schedule logically.
A passage consists of 6 sentences. The first and sixth sentences of the passage are at their correct positions, while the middle four sentences (represented by P, Q, R, and S) are jumbled up.
First sentence: Smoke oozed up between the planks.
P: Passengers were told to be ready to quit the ship.
Q: The rising gale fanned the smouldering fire.
R: Everyone now knew there was fire onboard.
S: Flames broke out here and there.
Sixth sentence: Most people bore the shock bravely.
The most logically CORRECT order for the given jumbled up sentences is
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the flow of the passage.
The first and sixth sentences are already in place:
- First sentence: "Smoke oozed up between the planks."
- Sixth sentence: "Most people bore the shock bravely."
The passage must describe a sequence of events from the beginning of the fire to the response of the passengers. Let's logically analyze the middle sentences.
Step 2: Analyzing the sequence.
- Q: "The rising gale fanned the smouldering fire." This seems like the first logical sentence because it introduces the fire situation.
- S: "Flames broke out here and there." This would logically follow Q, as the fire begins to spread.
- R: "Everyone now knew there was fire onboard." This sentence would come next, indicating that the fire became apparent to everyone.
- P: "Passengers were told to be ready to quit the ship." This would logically be the last sentence among the middle ones, as it relates to the passengers' reaction after realizing the fire.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The most logical order is Q (the rising gale fanned the fire), S (flames broke out), R (everyone knew there was fire), and P (passengers were told to be ready to quit the ship). This makes the correct sequence QSRP, which matches option (A).
Quick Tip: When solving passage rearrangement questions, focus on the logical flow of events and how each sentence leads to the next.
For a painting to succeed, it is essential that the painter and his public agree about what is significant. The subject of the painting may have a personal meaning for the painter or a common person; but there can also be the possibility of their agreement on its general meaning. It is at this point that the culture of the society and the period in question precedes the artists and her/his art. Renaissance art would have meant nothing to the Aztecs, and vice versa. If, to some extent, a few intellectuals can appreciate them both today, it is because their culture is a historical one. Its inspiration is history and all known developments to date.
According to the passage, which of the following is/are NOT necessarily among the attributes needed for a painter to succeed?
View Solution
Step 1: Understand the context of the passage.
The passage emphasizes that for a painting to succeed, both the artist and the public must agree on what is significant. However, the artist’s personal connection to the subject is not strictly necessary, and the public's demand for the subject is not essential either.
Step 2: Evaluate each option.
Option (A): Incorrect, the passage does not require the subject to have a personal meaning for the artist; agreement on significance is more important.
Option (B): Correct, the passage does imply that the painter must be able to communicate and justify the significance of the subject matter.
Option (C): Correct, agreement between the artist and the public on significance is a key requirement.
Option (D): Incorrect, the passage does not suggest that public demand drives the subject matter of the painting. The focus is on the agreement between the artist and the public, not public demand.
Hence, the correct answers are (A) or (D).
Quick Tip: For success in painting, it is important that the artist and the public agree on what is significant. The personal meaning of the subject and public demand are not essential to this process.
Vinod has a pre-determined route. Each morning he delivers 37 newspapers to customers in his neighborhood. It takes Vinod 50 minutes to deliver all the papers. When Vinod was sick or had other engagements, his friend Tarun, who lives on the same street delivered the papers on his behalf.
Find the statement(s) that must be TRUE according to the given information.
View Solution
Step 1: Interpreting the given information.
Vinod delivers 37 newspapers to customers in his neighborhood every morning, taking 50 minutes. When Vinod is unavailable, Tarun delivers the newspapers on his behalf. Both live on the same street, and thus, Tarun delivers the same number of newspapers to the same customers.
Step 2: Explanation of the options.
(A) It is clearly stated in the question that Tarun lives on the same street as Vinod, implying they live in the same locality. This must be true.
(B) The passage does not mention anything about the time of day when Vinod begins his delivery, so it cannot be inferred that it was dark when he began his delivery.
(C) The passage mentions nothing about Tarun's delivery taking more than 50 minutes, and since it does not specify, this is not a necessary conclusion.
(D) It is explicitly stated in the passage that Tarun delivered the same 37 newspapers to customers as Vinod does, making this statement true.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answers are (A) and (D) because they are directly supported by the information given in the passage.
Quick Tip: Carefully interpret the provided details and ensure you are drawing conclusions that are directly supported by the text.
Cholera, typhoid, diphtheria and tuberculosis cause huge number of deaths. Poor quality drinking water has always been the world’s greatest single carrier of sickness. Disease is transmitted when sewage and drinking water come into contact. Children are particularly vulnerable. In some of the poorest countries the infant mortality rate is high. The separation of sewage and the supply of clean drinking water are the domain of civil engineers, and their work makes a significant contribution to public health. That contribution was recognized when public sanitation was voted the greatest medical breakthrough, beating the discoveries including antibiotics and vaccines in a poll organized by the British Medical Journal.
Identify the statement(s), which is/are NOT TRUE according to the passage.
View Solution
N/A Quick Tip: Waterborne diseases are a major health issue in areas with inadequate sanitation and clean drinking water, and children are particularly at risk. Proper separation of sewage and drinking water is crucial for public health.
Shark’s teeth have evolved to correspond to the diet of each particular species of shark. Consequently, the teeth of the great white shark bear little resemblance to those of the bull shark or nurse shark. There were essentially four different shark diets and thus four varieties of shark teeth. Sharks that feed on fish have needle-like teeth, perfect for spearing and ripping. Sharks that eat mammals such as seals and sea lions have heavy, serrated teeth, typically triangular on the upper jaw and pointed on the lower jaw. Shark that feed in the benthic zone of the ocean have flattened teeth for crushing the shell of the creatures they find scuttling in the sand or clinging to rocks. Sharks that bask have teeth that are largely non-functional; these sharks filter food from the water by passing it through their gills.
Which of the following is/are the CORRECT inference(s) as per the passage?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the passage.
The passage explains that sharks have different types of teeth adapted to their specific diets. For example, sharks that feed on fish have needle-like teeth, while those that feed on mammals have serrated, triangular teeth. Sharks that filter food through their gills are mentioned to have largely non-functional teeth.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Shark’s teeth are not specially designed for slaughter: This is not supported by the passage. Shark’s teeth are clearly adapted to their diets, such as for hunting or filtering food.
- (B) The shape of the shark’s teeth relates to its prey: This is correct because the shape of the teeth is specifically adapted for the type of food they consume (e.g., needle-like teeth for fish, serrated teeth for mammals).
- (C) Some species of sharks filter food through their gills: This is correct, as the passage mentions that sharks that bask filter food from the water through their gills.
- (D) Shark’s teeth relate to its diet: This is correct, as the passage clearly explains that the teeth of sharks are designed based on the type of food they consume.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answers are (B), (C), and (D), as they are directly supported by the passage. Quick Tip: Sharks’ teeth are specialized for their diet, showing a clear example of evolutionary adaptation to feeding habits.
A particular school management wants to contact all parents, all businessmen and all engineers. The following statistics are available with the school.
Businessmen = 50
Engineers = 25
Parents = 2500
Businessmen who are engineers = 0
Businessmen who are parents = 25
Engineers who are parents = 15
The number of people who need to be contacted are _________.
View Solution
We are given the following sets:
- \( B \) = Businessmen = 50,
- \( E \) = Engineers = 25,
- \( P \) = Parents = 2500.
We are also given the intersections:
- \( B \cap E = 0 \) (No businessmen are engineers),
- \( B \cap P = 25 \) (Businessmen who are parents),
- \( E \cap P = 15 \) (Engineers who are parents).
We are tasked with finding the total number of distinct individuals to contact, which corresponds to the union of the three sets: \[ |B \cup E \cup P| = |B| + |E| + |P| - |B \cap E| - |B \cap P| - |E \cap P| + |B \cap E \cap P|. \]
Since no businessmen are engineers, \( B \cap E = 0 \), and thus: \[ |B \cup E \cup P| = 50 + 25 + 2500 - 0 - 25 - 15 + 0 = 2535. \]
Thus, the total number of people to contact is \( 2535 \). Quick Tip: To find the number of distinct individuals in multiple overlapping sets, use the principle of inclusion-exclusion.
Linguistic determinism is best captured in _________.
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding Linguistic Determinism.
Linguistic determinism refers to the idea that the language we use shapes the way we think and perceive the world. This theory is best represented by the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis.
Step 2: Explanation of the options.
- (1) Generative grammar: This theory focuses on the rules of language structure, not on how language shapes thought.
- (2) Sound symbolism: This is the idea that certain sounds are associated with certain meanings, but does not directly address linguistic determinism.
- (3) Critical-age hypothesis: This relates to language acquisition and does not concern linguistic determinism.
- (4) Sapir-Whorf hypothesis: This hypothesis argues that language shapes thought, making it the best fit for the question.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (4) Sapir-Whorf hypothesis, as it directly captures the essence of linguistic determinism.
Quick Tip: The Sapir-Whorf hypothesis suggests that the language we speak influences how we think and view the world.
Match the phonological processes in column Y to their names in column X.

View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the phonological processes.
The question asks to match the processes with their names, where each phonological process is linked with a specific transformation in the language.
Step 2: Explanation of the options.
- (1) P – ii, Q – iv, R – iii, S – i: This combination correctly matches each process with its corresponding transformation.
- (2) P – iv, Q – ii, R – iii, S – i: This option is incorrect as the transformations for each phonological process are mismatched.
- (3) P – ii, Q – iv, R – i, S – iii: This option is incorrect as it incorrectly matches the processes and their transformations.
- (4) P – iv, Q – ii, R – i, S – iii: This option is incorrect as it does not match the correct phonological processes.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (1) P – ii, Q – iv, R – iii, S – i. This matches each process with the appropriate transformation.
Quick Tip: In phonology, understanding the transformations associated with different processes is essential for analyzing speech patterns and language rules.
‘Bilingual language acquisition’ refers to the _________.
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding bilingual language acquisition.
Bilingual language acquisition refers to the ability to learn two languages simultaneously at a very early age. It typically occurs when a child is exposed to two languages from birth or during the early stages of development. This is different from learning a second language later in life, which is often called second language acquisition (SLA).
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Correct, as it refers to the simultaneous learning of two languages from a very early age, which is a well-documented aspect of bilingual development.
- (B) Incorrect, as it refers to learning a second language after a significant age, which does not define bilingual language acquisition.
- (C) Incorrect, as it refers to acquiring a second language during the first 12 months, which does not accurately describe bilingual language acquisition.
- (D) Incorrect, as sequential acquisition involves learning languages one after the other, which is not the case in bilingual acquisition.
Step 3: Conclusion.
Thus, the correct answer is (A) Simultaneous acquisition of two languages at a very early age. Quick Tip: Bilingual language acquisition happens when two languages are learned simultaneously, typically at a very early age.
Which of the following is the sequence of derivation as per Minimalist Program?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the Minimalist Program.
The Minimalist Program is a theory of syntax that focuses on the operations used in constructing sentences. The derivation process in this program follows a sequence of operations that build syntactic structures and generate sentence representations.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Incorrect. This sequence does not match the typical operations of the Minimalist Program.
- (B) Correct. According to the Minimalist Program, the derivation begins with Numeration (selecting lexical items), followed by Merge (combining elements), Move (rearranging elements), and Spell-Out (finalizing the syntactic structure).
- (C) Incorrect. The sequence starts with Move before Merge, which is not how the derivation is structured in the Minimalist Program.
- (D) Incorrect. This option reverses the natural order of operations in the Minimalist Program.
Step 3: Conclusion.
Therefore, the correct sequence of derivation as per the Minimalist Program is (B) Numeration \(\rightarrow\) Merge \(\rightarrow\) Move \(\rightarrow\) Spell-Out. Quick Tip: In the Minimalist Program, the derivation follows the sequence: Numeration \(\rightarrow\) Merge \(\rightarrow\) Move \(\rightarrow\) Spell-Out.
Linguistic determinism is the strongest form of the _________.

View Solution
Step 1: Analyze the passage.
The question asks about linguistic determinism and its connection to specific forms of language development. The options provide different combinations of forms. The terms in the table are related to how words and concepts evolve. Understanding each term will help match them with the correct linguistic processes.
Step 2: Analysis of options.
- (P) refers to \textit{UN, which is related to abbreviation, hence corresponds with (iv).
- (Q) refers to \textit{geek, which relates to coinage, thus it corresponds with (ii).
- (R) refers to \textit{kindergarten, which refers to borrowing, hence it corresponds with (iii).
- (S) refers to \textit{UNICEF, which is an acronym, corresponding with (i).
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct matching of terms and forms is P – (iv), Q – (ii), R – (iii), and S – (i), which is option (D). Quick Tip: Linguistic determinism refers to the theory that language strongly influences or determines the way we think. Understanding word formation processes (such as coinage, abbreviation, borrowing, and acronym formation) is essential to identifying their connections.
Which of the given statements is TRUE?
Statement (I): Every spoken language includes discrete sound segments that can all be defined by a finite set of sound properties or features.
Statement (II): Speakers of all languages are capable of producing and comprehending an infinite set of sentences.
View Solution
Step 1: Analyze the statements.
- Statement (I) states that every spoken language includes discrete sound segments that can be defined by a finite set of sound properties, which is a foundational concept in linguistics. Every language has a set of phonemes or sound segments that are finite.
- Statement (II) states that speakers of all languages are capable of producing and comprehending an infinite set of sentences, which is also true. The generative nature of language allows for infinite sentence structures by combining a finite set of rules and words.
Step 2: Conclusion.
Both statements (I) and (II) are correct. Therefore, the correct answer is (A). Quick Tip: In linguistics, the finite nature of sound properties and the infinite generation of sentences highlight the creative power of language.
The sound change of Proto-Indo-Aryan /p/ to Germanic /f/, deduced by comparing cognates like Latin pater, Sanskrit pita and English father, is an example of _________.
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the Question.
The sound change described is a famous example of the regular sound shifts that occurred in the Germanic languages, which is referred to as Grimm's Law. It deals with the systematic change of Proto-Indo-European consonants in the early Germanic languages.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Grassman’s Law: This law deals with a specific phonological rule in Sanskrit, not the sound change of Proto-Indo-Aryan to Germanic.
- (B) Lyman’s Law: This law is related to the restriction on the occurrence of certain consonants in a sequence.
- (C) Grimm’s Law: This correctly describes the shift of /p/ to /f/ in the Germanic languages, making this the correct answer.
- (D) Verner’s Law: This law addresses a different set of sound changes, particularly vowel changes, and is not related to the described shift.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (C) Grimm’s Law, which correctly explains the described phonological change.
Quick Tip: Grimm’s Law is a fundamental principle in historical linguistics that explains the consonant shifts in the Germanic languages from Proto-Indo-European.
Which of the following diagrams depict(s) the violation of a principle of autosegmental phonology?

View Solution
Step 1: Understanding Autosegmental Phonology.
Autosegmental phonology is a theory of phonology that treats certain phonological features as independent tiers (e.g., segmental tiers and features like consonantal or vowel) which are associated across these tiers. A violation would occur if these features are incorrectly linked.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Representation (i): This representation is correct as the features are properly linked in a consistent manner according to autosegmental principles.
- (B) Representation (ii): This representation violates the principle because the features are misaligned between the tiers, making it the correct choice for the violation.
- (C) Both (i) and (ii): Only (ii) contains a violation, so this option is incorrect.
- (D) Neither (i) nor (ii): Representation (i) is valid, so this option is incorrect.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (B) Representation (ii), as it depicts the violation of the autosegmental phonology principles.
Quick Tip: In autosegmental phonology, correct alignment between the segmental and feature tiers is essential for representing phonological structures accurately.
In the given sentences, the semantic relationship of hyponymy can be found in between _________.
(i) The thing in the grass is a small snake.
(ii) The thing in the grass is a small reptile.
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding Hyponymy.
Hyponymy is a semantic relationship where one word (the hyponym) refers to a more specific concept under a broader category (the hypernym). In this case, "snake" is a specific type of "reptile," making the correct relationship between them one of hyponymy.
Step 2: Analyze the options.
- (A) reptile : grass: This is incorrect because "grass" is not a category under which "reptile" falls.
- (B) grass : snake: This is incorrect because "grass" is not a broader category of "snake."
- (C) snake : reptile: This is correct since "snake" is a type of "reptile," which forms a hyponymic relationship.
- (D) small : snake: This is incorrect because "small" is not a category under "snake" in terms of hyponymy.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (C) snake : reptile, as it correctly represents a hyponymic relationship. Quick Tip: In hyponymy, the more specific term (hyponym) is related to a broader category (hypernym), as in the case of "snake" and "reptile."
Bill walked into a store in New York, looking for a restroom. He asked a storekeeper which floor the men’s restroom is and he replied, /ðə fəʊθ flɔː/ for the fourth floor. What kind of store Bill must have walked into?
View Solution
Step 1: Analyzing the context.
The question mentions that Bill is asking for the restroom in a store in New York and the response given is about the fourth floor. In most high-class stores, restrooms are located on the lower floors, often accessible without needing to ask. A store that has restrooms on the fourth floor may indicate a lower-class establishment.
Step 2: Analyze the options.
- (A) A high class store: This is unlikely, as high-end stores typically have restrooms located on lower floors for easier access.
- (B) A middle class store: This is also less likely because middle-class stores would not typically place a restroom on the fourth floor.
- (C) A lower class store: This is correct as such stores are more likely to have restrooms on higher floors or less convenient locations, requiring customers to ask for directions.
- (D) A Latino owned store: This is irrelevant to the question, as the location of restrooms does not depend on the store's ownership or ethnicity.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (C) A lower class store, based on the store's restroom location and how it was described. Quick Tip: In lower-class or less organized stores, facilities like restrooms may be located on higher floors, which might require customers to ask for directions.
Which of the followings occurred due to the Great Vowel Shift of the English language?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the Great Vowel Shift.
The Great Vowel Shift refers to a major change in the pronunciation of the vowels in the English language. This shift involved the raising and diphthongizing of long vowels, particularly in the Middle English period.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (1) [a:] became [u:]: This is not true according to the Great Vowel Shift. There was no such vowel shift from [a:] to [u:].
- (2) All the front vowels shifted to back: This is correct, as many of the front vowels shifted to back positions.
- (3) [ge:s] became [gi:s]: This is not part of the Great Vowel Shift. This is a different kind of phonological change.
- (4) The high, long vowels became diphthongized: This is correct. Many of the high long vowels became diphthongs during the shift.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answers are (2) and (4) based on the description of the Great Vowel Shift.
Quick Tip: The Great Vowel Shift dramatically altered the pronunciation of long vowels in English, particularly in the transition from Middle to Early Modern English.
Which of the following statements are true for the pulmonic consonant table in an IPA chart?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the IPA chart for pulmonic consonants.
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) chart organizes sounds based on their place and manner of articulation, as well as whether the sounds are voiced or voiceless.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (1) Voiceless consonants aligned to the left of the cell: This is correct. In the IPA chart, voiceless consonants are placed to the left of their voiced counterparts.
- (2) Places of articulation are arranged in rows: This is incorrect. Places of articulation are arranged in columns, not rows.
- (3) Manners of articulation are arranged in columns: This is incorrect. Manners of articulation are typically arranged in rows, not columns.
- (4) The most constricted consonants to the least are arranged from the top to bottom: This is correct. The chart organizes consonants based on their constriction, with the most constricted sounds (like stops) at the top and less constricted sounds (like fricatives) at the bottom.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answers are (1) and (4) based on the structure of the IPA chart.
Quick Tip: In the IPA chart, consonants are organized based on their place and manner of articulation, with voiceless sounds typically positioned on the left.
Identify the compounds in the given data.

View Solution
Step 1: Understanding compounds.
Compounds are words that are made by combining two or more smaller words to form a new meaning. For example, "blackboard" is a combination of "black" and "board," and "toy factory" is a combination of "toy" and "factory."
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Incorrect, as "repeat" and "backward" are not compound words, they are individual words.
- (B) Correct, as "blackboard" (black + board) and "toy factory" (toy + factory) are both compound words.
- (C) Correct, as "sky-high" (sky + high) and "underestimate" (under + estimate) are both compound words.
- (D) Incorrect, "bystander" is a compound word, but "deform" is not.
Step 3: Conclusion.
Thus, the correct answers are (B) blackboard and toy factory, (C) sky-high and underestimate. Quick Tip: Compound words are formed by combining two or more smaller words to create a new meaning, such as "blackboard" or "toy factory."
In the production of the /z/ sound which of the following will take place?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the /z/ sound production.
The /z/ sound is a voiced, alveolar fricative. This means that the vocal cords vibrate and air passes through the constriction formed between the alveolar ridge and the tongue, producing a friction sound.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Correct, the vocal cords will vibrate during the production of the /z/ sound as it is a voiced sound.
- (B) Correct, the velum (soft part of the roof of the mouth) will be raised to allow air to pass through the oral cavity.
- (C) Incorrect, the two lips are not in contact during the production of the /z/ sound, unlike the /p/ or /b/ sounds.
- (D) Incorrect, air does pass through with friction (turbulence) to create the /z/ sound, unlike a sound like /m/ where the air passes without turbulence.
Step 3: Conclusion.
Thus, the correct answers are (A) Vocal cords will vibrate and (B) Velum will be raised. Quick Tip: For the production of /z/, vocal cords vibrate, and the velum is raised to allow airflow through the oral cavity.
The phrase “the first person in space” refers to Yuri Gagarin. Which of the following could be used to determine reference?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the reference concept.
The concept of "reference" in linguistics involves how terms relate to things in the world. Russell's Theory of Description addresses how definite descriptions (e.g., "the first person in space") refer to specific entities. According to this theory, the phrase refers to a unique individual who satisfies the description.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Russell’s Theory of Description: This theory explains how definite descriptions like "the first person in space" refer to specific individuals, like Yuri Gagarin. This is the correct option.
- (B) Prototype Theory: This theory deals with categorization based on prototypes and does not specifically address reference.
- (C) Speech Act Theory: This theory focuses on how language is used to perform actions and does not directly address reference.
- (D) Gricean Maxims: This focuses on conversational implicature and does not address how specific terms refer to objects in the world.
Step 3: Conclusion.
Russell’s Theory of Description is the most appropriate theory to determine the reference of the phrase "the first person in space." Therefore, the correct answer is (A). Quick Tip: Russell's Theory of Description is a key theory in semantics that helps explain how definite descriptions refer to specific entities in the world.
Which of the following statement(s) apply to pidgins?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding pidgins.
Pidgins are simplified languages that develop in contact situations where speakers of different native languages need a common language for communication. They usually have simplified grammar and vocabulary.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Pidgins have complex grammatical rules: This is incorrect. Pidgins are characterized by simplified, not complex, grammatical rules.
- (B) Pidgins do NOT have grammatical rules: This is incorrect. While pidgins have simplified rules, they do indeed have a basic grammatical structure.
- (C) Pidgin phonology is rule based: This is correct. Pidgin languages have a simplified but rule-governed phonological system.
- (D) Pidgins are passed on from one generation to the other: This is correct. Pidgins can develop into creoles if they are passed down to the next generation as a native language, with grammatical structures becoming more complex over time.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answers are (C) and (D), as they are directly supported by the nature of pidgin languages. Quick Tip: Pidgins are simplified languages with a basic grammatical structure. When passed down to the next generation, they can evolve into creoles with more complex grammar.
In the given tree-structure NP1 C-commands NP2 but not vice versa because:

View Solution
Step 1: Analyze the tree structure.
In the given tree structure, NP1 is the noun phrase "Every alien," while NP2 is the noun phrase "ET." The structure illustrates that NP1 and NP2 are connected through different parts of the tree.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) C-command cannot be a reciprocal relationship: This is not relevant because the issue at hand is about dominance and C-command, not reciprocity.
- (B) No node dominates both NP2 and NP1: This is incorrect because VP1 dominates NP2 and C-commands NP1.
- (C) VP1 dominates NP2 and C-commands NP1: This is correct because VP1 dominates NP2, and as a result, it C-commands NP1.
- (D) VP1 dominates NP2 but not NP1: This is also correct because VP1 dominates NP2, but it does not dominate NP1, which explains the non-reciprocal C-command relationship.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answers are (C) and (D), as they are both supported by the tree structure.
Quick Tip: In syntactic tree structures, C-command and dominance are key concepts in understanding relationships between elements. VP1 dominates NP2 and C-commands NP1, but VP1 does not dominate NP1 directly.
Which of the given pronunciations DO NOT conform to the phonological rule?

View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the rule.
The given phonological rule is: \[ \left[ -sonorant \right] +voiced \rightarrow \left[ -sonorant \right] -voiced / \_\_ \# \]
This means that the rule applies to non-sonorant sounds with a voiced feature, which should turn into non-sonorant and unvoiced when they occur at the end of a word.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) [dud]: This conforms to the rule. "d" is a non-sonorant consonant, and "d" is voiced at the beginning of the word, which can become unvoiced at the end of the word.
- (B) [kut]: This conforms to the rule. "k" is a non-sonorant consonant, and the sound stays unvoiced.
- (C) [mutab]: This does not conform to the rule. "b" is a voiced non-sonorant sound, but it does not become unvoiced at the end of the word, which violates the phonological rule.
- (D) [pum]: This conforms to the rule. "p" is unvoiced, so the rule does not apply, but no violation occurs.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (C) [mutab] as it does not conform to the phonological rule. Quick Tip: In phonological rules, sounds at the end of words may change their features, such as turning voiced sounds into voiceless ones.
Determine the correct nature of the following two utterances from the choices given below.
P: Hasnain said ki woh kal aayegaa
(COMP he tomorrow come.will)
“Hasnain said that he will come tomorrow”
Q: Rohan will get some desi vegetables.
(local)
“Rohan will get some local vegetables”
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the concepts.
- Code switching involves switching between two or more languages or dialects in a conversation.
- Borrowing refers to the incorporation of a word or phrase from one language into another, typically without switching languages.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Code switching in P and Q: In P, "Hasnain said ki woh kal aayegaa" contains a mix of Urdu and English, switching between the two languages. Similarly, Q also switches between English and Hindi with "desi vegetables" where "desi" is a Hindi word incorporated into the English sentence. This makes (A) correct.
- (B) Borrowing in P and Q: This is incorrect because both utterances involve code switching, not borrowing.
- (C) Code switching in P and borrowing in Q: This is incorrect because Q is an example of code switching, not borrowing.
- (D) Borrowing in P and code switching in Q: This is incorrect because the phrase "ki woh kal aayegaa" involves code switching, not borrowing.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (A) Code switching in P and Q, as both utterances contain examples of code switching between languages. Quick Tip: Code switching occurs when speakers alternate between two or more languages within a conversation or sentence, whereas borrowing involves taking words from one language into another.
Consider the given script showing a sequence of 11 graphemes. It represents the sentence: /apa pal talip tani mil/. Each grapheme in the script contains a _________.

View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the concept of graphemes.
A grapheme is the smallest unit of written language that represents a sound. In this case, the sentence /apa pal talip tani mil/ is broken down into 11 graphemes, and each grapheme in the script represents a distinct sound unit.
Step 2: Explanation of the options.
- (1) Rhyme: This refers to the similarity of sounds at the end of words and does not relate to the concept of graphemes.
- (2) Syllable: A syllable is a unit of speech, but this question focuses on the smallest unit of written language (grapheme), not syllables.
- (3) Consonant: While consonants are a part of the grapheme, the focus of this question is on the individual grapheme and its representation.
- (4) Mora: A mora is a unit of sound that affects the timing of speech, often related to languages like Japanese. This is the most accurate answer for the question.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (4) Mora, as it describes the smallest unit of sound in this context. Quick Tip: In linguistics, a mora is a unit of sound that influences syllable length and is an important concept in languages with distinctive timing features.
In the given examples, column Y are examples of _________ sentences.

View Solution
Step 1: Understanding Cleft sentences.
Cleft sentences are used to focus attention on a particular part of the sentence. In these types of sentences, a clause is split into two parts, with one part being emphasized. This is seen in column Y, where the focus shifts to "the cat" and "the athlete."
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (1) Topicalization: Topicalization refers to the process of moving a topic to the beginning of the sentence. This is not the case in column Y.
- (2) Cleft: This is the correct option. A cleft sentence splits a statement into two parts for emphasis, as shown in column Y.
- (3) Pseudo-cleft: Pseudo-cleft sentences also focus on elements, but the structure differs slightly from cleft sentences. This is not the case here.
- (4) Gapping: Gapping is a phenomenon where parts of the sentence are omitted, which does not apply to the examples in column Y.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (2) Cleft, as it describes the structure of the sentences in column Y. Quick Tip: Cleft sentences are a type of sentence structure used to highlight a specific element, often following the pattern "It is/was X that Y."
A second language speaker uses the word [phonetic] as a singular noun because she interprets the word [phonetics] as a plural noun. In doing so, she is deducing a new word by the process of _________.
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the process.
Back formation is a linguistic process where a new word is created by removing a suffix from an existing word. In this case, the second language speaker is interpreting "phonetics" as a plural noun and creating a singular form "phonetic" by removing the plural "-s."
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Incorrect, as blocking refers to a situation where one rule blocks the application of another, not the creation of a new word by removing a suffix.
- (B) Correct, as back formation involves creating a new word by removing a suffix, which is what is happening in this case.
- (C) Incorrect, bracketing refers to a syntactic phenomenon, not the creation of a new word.
- (D) Incorrect, back tracking refers to revisiting earlier steps in a process, not word formation.
Step 3: Conclusion.
Thus, the correct answer is (B) Back formation. Quick Tip: Back formation is when a word is created by removing an affix, such as turning "phonetics" into "phonetic" by removing the "-s."
Given the rules P and Q, what is the name of the rule ordering in dialect X and Y?

View Solution
Step 1: Understanding rule application.
In this question, we are analyzing two rules (P and Q) and their application to two different dialects (X and Y). Rule application order plays a critical role in the resulting forms.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Incorrect, as counter-feeding refers to a situation where one rule feeds the application of another, and this is not the case here.
- (B) Correct, the correct sequence of rule application leads to the "bleeding" order in dialect X and the "counter-bleeding" order in dialect Y, as shown in the examples.
- (C) Incorrect, counter-bleeding and counter-feeding are different processes, and the given rule order does not match.
- (D) Incorrect, both dialects cannot have "bleeding" or "counter-bleeding" simultaneously in this context.
Step 3: Conclusion.
Thus, the correct answer is (B) X has bleeding and Y has counter-bleeding order. Quick Tip: In phonological rule ordering, "bleeding" occurs when one rule removes the environment necessary for another rule to apply, while "counter-bleeding" refers to the opposite.
Which of the given statements is/are TRUE?
Statement (I): Diglossia and dialect continuum are synonymous.
Statement (II): Bilingual speakers are also bidialectal.
View Solution
Step 1: Analyze the statements.
- Statement (I) claims that diglossia and dialect continuum are synonymous. However, these two concepts are not synonymous. Diglossia refers to a situation where two distinct varieties of a language are used in different social contexts, while a dialect continuum refers to a range of dialects spoken in a geographical area where neighboring dialects are mutually intelligible, but the dialects at the extremes are not. Thus, statement (I) is incorrect.
- Statement (II) claims that bilingual speakers are also bidialectal. While bilingual speakers speak two languages, bidialectal speakers use two dialects of the same language. These are distinct concepts. Therefore, statement (II) is also incorrect.
Step 2: Conclusion.
Both statement (I) and statement (II) are incorrect, which makes option (B) the correct answer. Quick Tip: Diglossia and dialect continuum are two distinct linguistic phenomena. Diglossia involves two varieties of a language used in different contexts, while a dialect continuum involves a series of dialects across a geographic area.
Look into the data from Micoacan Aztec and match the words (P-S) to their meaning (i-iv) and select the correct sequence.

View Solution
Step 1: Analyze the words and meanings.
- "nokali" means "my house," and "nokali" corresponds to "house," which matches with S-(iv).
- "mokali" means "your house," and "mokali" corresponds to "house," which matches with S-(iv).
- "nokwahmili" means "my cornfield," and "nokwahmili" corresponds to "cornfield," which matches with R-(iii).
- "ikwahmili" means "his cornfield," and "ikwahmili" corresponds to "cornfield," which matches with R-(iii).
- "mopelomes" means "your dogs," and "mopelomes" corresponds to "dog," which matches with Q-(ii).
- "mopelo" means "your dog," and "mopelo" corresponds to "dog," which matches with Q-(ii).
Step 2: Final matching.
- P corresponds to S-(iv) because "nokali" and "mokali" are linked to "house," which corresponds to "S-(iv)."
- Q corresponds to R-(ii), linking "mokali" and "mopelo" to the meaning of "house" or "dog."
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (D) P-(iv), Q-(ii), R-(iii), S-(i)
Quick Tip: When analyzing linguistic structures or translations, look for consistent word meanings and match them with the corresponding translations or categories.
Match the languages (P – U) to the language families (i – iv) and select the correct sequence.

View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the language families.
- Kannada is a Dravidian language.
- Assamese is an Indo-Aryan language.
- Khasi belongs to the Austro-Asiatic language family.
- Nepali is an Indo-Aryan language.
- Manipuri is a Tibeto-Burman language.
- Mundari is an Austro-Asiatic language.
Step 2: Matching languages to families.
- P. Kannada belongs to (ii) Dravidian.
- Q. Assamese belongs to (i) Indo-Aryan.
- R. Khasi belongs to (iv) Austro-Asiatic.
- S. Nepali belongs to (i) Indo-Aryan.
- T. Manipuri belongs to (iii) Tibeto-Burman.
- U. Mundari belongs to (iv) Austro-Asiatic.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct matching is given by option (A) P – (ii), Q – (i), R – (iv), S – (i), T – (iii), U – (iv). Quick Tip: The classification of languages into different families is based on their historical and structural relationships. Familiarizing yourself with the main families can help in identifying their members.
Which of the given statements is/are TRUE?
Statement (I): The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is a transcription system for describing human speech sounds from all languages.
Statement (II): The voiceless pharyngeal plosive sound is missing in the IPA chart because it is physiologically impossible to articulate.
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding Statement (I).
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is indeed a transcription system used to represent all human speech sounds. It is a widely recognized system used in linguistics. Statement (I) is correct.
Step 2: Understanding Statement (II).
The voiceless pharyngeal plosive sound, while not common in many languages, is physiologically possible to articulate. There are some rare languages that use pharyngeal sounds. The absence of this sound from the IPA chart is not due to physiological impossibility but rather because it is not widely used or recorded. Statement (II) is incorrect.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (3), as statement (I) is correct and statement (II) is incorrect.
Quick Tip: The IPA is designed to cover all human speech sounds, and while some rare sounds are not included, they are not excluded due to physiological impossibility.
Match the terms in column X (P – S) to their descriptions in column Y (i – iv) and select the correct sequence.

View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the terms.
- P – Competence: Refers to the native speaker's ability to intuitively understand and generate language (related to native speaker intuition).
- Q – Performance: Refers to the actual use of language in communication, as opposed to the underlying knowledge of the language.
- R – Sense: Refers to the specific meaning of an expression in relation to the context or situation.
- S – Reference: Refers to the relationship between an expression and its real-world entity or referent.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (1) P – ii, Q – iv, R – iii, S – i: This sequence does not match the correct definitions.
- (2) P – iv, Q – ii, R – iii, S – i: This sequence is incorrect as it does not match the correct relations.
- (3) P – ii, Q – iv, R – i, S – iii: This sequence is incorrect as it does not match the correct relations.
- (4) P – iv, Q – ii, R – i, S – iii: This is the correct sequence, matching the terms with their appropriate descriptions.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (4), as this sequence correctly matches the terms with their descriptions. Quick Tip: Competence refers to the speaker's internalized knowledge of language, while performance is the actual use of that knowledge in communication.
Match the following morphological changes (P-S) to their type (i-iv) and select the correct sequence.

View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the types of morphological changes.
- Partial suppletion (i) occurs when a form changes completely, but only partially substitutes with an alternative form.
- Total suppletion (ii) occurs when a word has entirely different forms in the paradigm.
- Lexically conditioned (iii) refers to a change that depends on the meaning of the word.
- Phonologically conditioned (iv) refers to changes that depend on the phonetic structure of the word.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- P. electric \(\rightarrow\) electricity: This is a case of phonologically conditioned change (iv), as the change from "electric" to "electricity" involves adding a suffix that affects the word's phonological structure.
- Q. go \(\rightarrow\) went: This is an example of total suppletion (ii), where "go" and "went" are completely different forms.
- R. ox \(\rightarrow\) oxen: This is an example of lexically conditioned change (iii), as the plural form "oxen" is irregular and conditioned by the meaning of the word.
- S. think \(\rightarrow\) thought: This is an example of partial suppletion (i), where "think" changes to "thought" in a partially irregular way.
Step 3: Conclusion.
Thus, the correct sequence is (D) P – (iv), Q – (ii), R – (iii), S – (i). Quick Tip: In morphological changes, suppletion refers to the use of entirely different forms for the same word. Phonological and lexical conditioning describe changes based on sound and meaning, respectively.
Which of the given statements is/are TRUE?

\textbf{Correct Answer:} (C) Sambalpuri is similar to Telugu but not Bangla.
View Solution
Step 1: Analyze the sentences.
The question asks to identify which languages are similar based on their sentence structures. The given sentences in the four languages (Telugu, Bangla, Sambalpuri, and Hindi) show the structure of the sentence "The book that Sita read is on the table." Let’s break down the structure of each language:
- Telugu: "sita caduvina pustakam tebul-payina peTTundi"
- Bangla: "sita-r pOda boi tebil-e ache"
- Sambalpuri: "sita pOdithiba bOhi tebul-pakhe Ochi"
- Hindi: "sita-ki padhi-hui kitaab tebil-pe hei"
Step 2: Compare sentence structures.
- Bangla and Hindi both have the possessive marker (sita-r in Bangla, sita-ki in Hindi), and both follow the same word order in this sentence (subject + possessive + verb + object + location).
- Sambalpuri and Telugu use slightly different structures, especially in the word order. In Sambalpuri, the subject (sita) comes before the verb, and in Telugu, there is a different syntactic construction.
- Telugu and Sambalpuri both place the object (book) before the location (table), but Bangla places the location word after the object, just like Hindi.
Step 3: Conclusion.
- (B) Bangla is similar to Hindi but not Sambalpuri: This is correct because both Bangla and Hindi share similar sentence structures, particularly in the use of the possessive marker and word order.
- (C) Sambalpuri is similar to Telugu but not Bangla: This is correct because Sambalpuri and Telugu have a similar sentence structure compared to Bangla, especially in the word order. Quick Tip: When comparing languages, look at the syntactic structure, including word order, the use of possessive markers, and the position of the object and location in a sentence.
Lesions in different areas of the left hemisphere lead to qualitatively distinct aphasia syndromes. Which of the given statements is/are TRUE?
View Solution
Step 1: Analyze the options.
- (A) The brain lesions associated with classical anomia are indeed linked to the angular gyrus, which is involved in language processing, making this statement true.
- (B) Conduction aphasia is generally caused by damage to the arcuate fasciculus, not the posterior part of the inferior frontal gyrus, so this statement is false.
- (C) Wernicke’s aphasia is the result of damage to the auditory association cortex in the left temporal lobe, which is responsible for language comprehension, making this statement true.
- (D) Broca’s aphasia typically results from damage to Broca’s area in the frontal lobe, not from the temporoparietal regions, so this statement is false.
Step 2: Conclusion.
The correct answers are (A) and (C), which are supported by the neuroanatomical understanding of aphasia syndromes.
Quick Tip: Aphasia types are closely linked to the location of brain lesions. For example, Wernicke's aphasia involves damage to the auditory cortex in the temporal lobe, while Broca’s aphasia is associated with damage to the frontal lobe.
Consider the following data from English. Which linguistic change(s) is/are associated with the addition of the suffix ‘-able’?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the data.
The suffix “-able” is added to a verb to form an adjective. For example, “readable” is the adjective formed from the verb “read.” This is a case of grammatical category change, as the word shifts from a verb to an adjective.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Sociolinguistic change: The addition of “-able” is not related to social language change, so this option is incorrect.
- (B) Grammatical category change: The suffix “-able” indeed changes the grammatical category from verb to adjective, making this option correct.
- (C) Semantic change: The addition of “-able” also leads to a shift in meaning, such as the verb “read” becoming “readable,” which refers to something that can be read. Thus, this option is correct.
- (D) Typological change: This suffix does not represent a typological change in the language structure, so this option is incorrect.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answers are (B) grammatical category change and (C) semantic change.
Quick Tip: The addition of affixes like “-able” typically involves grammatical category and meaning changes. Understanding these changes helps in analyzing word formation and morphology.
Children are biologically equipped to acquire all aspects of grammar. Which of the given statements is/are TRUE?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the context.
- (A) ‘Telegraphic speech’ is not exactly associated with the holophrastic stage. It generally occurs when children start combining words. The holophrastic stage is when children use one word to represent an entire sentence.
- (B) Overgeneralization occurs in the three phases of acquisition, where children apply regular rules to irregular forms, like saying "goed" instead of "went."
- (C) Children typically do not learn 100 words a day up to 12 months. At 12 months, many children have a small vocabulary (around 50-100 words).
- (D) The mean length of utterances (MLU) is an important measure of a child’s language development, indicating the complexity of their language.
Step 2: Conclusion.
The correct answers are (B) and (D), which are accurate in the context of child language acquisition. Quick Tip: In language acquisition, overgeneralization occurs when children apply grammatical rules too broadly, and MLU is a key indicator of linguistic development.
Wolof speakers use a secret language called Kall. Words in Wolof are changed to Kall in a systematic manner, as shown in the data. In the change from Wolof to Kall, which of the given constraints cannot be violated?

View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the constraints.
- (A) MAX-IO: This constraint ensures that no segments are deleted during the transformation. The data doesn't show any deletions, so this constraint isn't violated.
- (B) DEP-IO: This constraint requires that all input segments are realized in the output, without any deletion. Since the vowel sounds are preserved in the transformation (e.g., "sama" to "masa"), this constraint is not violated.
- (C) FOOT-BINARITY: This constraint requires that feet be binary (i.e., contain two syllables). The data doesn't seem to violate this, but it’s not the key constraint in this case.
- (D) LINEARITY-IO: This constraint requires that the order of segments in the input is preserved in the output. The data shows that the transformation follows a systematic pattern, meaning this constraint cannot be violated.
Step 2: Conclusion.
The correct answers are (B) DEP-IO and (D) LINEARITY-IO, as these constraints ensure that the transformation from Wolof to Kall preserves input-output relationships. Quick Tip: In phonological transformations, constraints like DEP-IO and LINEARITY-IO ensure that the integrity of the input structure is maintained in the output.
The given sentence is ungrammatical because:
Tailan believes that himself is smarter than Po
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding Binding Theory.
In Binding Theory, Principle B dictates that a pronoun (like "himself") must have a referent that is not a local antecedent. It must be bound in a specific domain. The ungrammaticality of the sentence occurs because "himself" cannot refer to the subject "Tailan" as per Principle B.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (1) Principle A: This principle deals with reflexive pronouns needing to have their antecedent within the same clause. This is not relevant here.
- (2) Principle B: This is the correct option, as "himself" is supposed to refer to a non-local antecedent.
- (3) Principle C: This principle governs the binding of referential expressions, which is not relevant in this case.
- (4) Both Po and Tailan are possible antecedents for himself: This is incorrect because Principle B rules out "Tailan" as a valid antecedent.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answer is (2) Principle B of Binding Theory is not satisfied.
Quick Tip: In Binding Theory, Principle B specifies that pronouns must not refer to their local antecedents, meaning that "himself" in this sentence cannot refer to "Tailan."
Which of the given statements support the Design Features proposed by Hockett?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding Hockett's Design Features.
Hockett proposed several key design features that distinguish human language, including the productivity of language, displacement, and the arbitrariness of linguistic units.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (1) Humans produce as many sentences as they have acquired: This is correct because humans can produce an infinite number of sentences based on the language they have learned (productivity).
- (2) Sentences cannot be broken into smaller units as they have specific meaning: This is incorrect. Sentences can be broken into smaller meaningful units (words, phrases).
- (3) Humans can talk about things that are not in their immediate vicinity: This is correct because of the feature of displacement, which allows humans to talk about things in the past, future, or abstract concepts.
- (4) Linguistic units do not bear any direct resemblance to the things they represent: This is correct because linguistic signs are arbitrary; the sound of a word does not inherently resemble the thing it refers to (arbitrariness).
Step 3: Conclusion.
The correct answers are (1), (3), and (4) as they align with Hockett's design features of language.
Quick Tip: Hockett’s design features of language highlight key characteristics such as productivity, displacement, and arbitrariness, which are unique to human communication.
Which of the given logical forms correspond to the following sentence where \( x \in \) student, \( y \) teacher and \( A = \) admires?
Every student admires a teacher.
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the sentence.
The sentence "Every student admires a teacher" implies that for each student, there exists at least one teacher whom they admire. This requires an existential quantifier for the teacher and a universal quantifier for the student.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Correct. \( \forall x \exists y \, A(x,y) \) means that for every student \( x \), there exists a teacher \( y \) such that \( x \) admires \( y \), which correctly reflects the meaning of the sentence.
- (B) Incorrect. This statement suggests that every teacher is admired by some student, which reverses the intended meaning.
- (C) Incorrect. \( \exists x \forall y \, A(y,x) \) suggests that there exists a student who admires every teacher, which is not the same as the original sentence.
- (D) Correct. \( \exists y \forall x \, A(x,y) \) means that there exists a teacher \( y \) who is admired by every student \( x \), which also matches the logical structure of the sentence.
Step 3: Conclusion.
Thus, the correct answers are (A) and (D). Quick Tip: In logical forms, use the universal quantifier \( \forall \) for "every" and the existential quantifier \( \exists \) for "there exists."
Identify the possible set(s) of stops that correlate with the corresponding VOT values.
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding VOT (Voice Onset Time).
VOT refers to the time between the release of a stop and the onset of voicing. The values for stops vary depending on whether they are voiced or voiceless, and whether they are aspirated or not.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- (A) Correct. The VOT values for /p/, /ph/, and /b/ are consistent with known values, where voiceless stops have a higher VOT (such as /ph/ at 78) and voiced stops have a lower VOT (such as /b/ at -110).
- (B) Incorrect. The VOT values for /t/ and /d/ do not match the typical values for these sounds. /th/ also has an unusually low VOT in this set.
- (C) Incorrect. The VOT values for /k/ and /g/ are inconsistent with typical VOT ranges.
- (D) Correct. These values for /ph/, /th/, and /kh/ correspond to known VOT values for voiceless aspirated stops.
Step 3: Conclusion.
Thus, the correct answers are (A) and (D). Quick Tip: VOT is an important factor in distinguishing between voiced and voiceless stops, with aspirated stops having higher VOT values than non-aspirated ones.
The estimated fundamental frequency of the given sine wave is (in integer) _________ Hz.

View Solution
The given sine wave has a time period \( T \) that can be determined from the graph. We observe the time taken for one complete oscillation, which is the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs.
From the graph, the time period \( T \) is approximately 0.05 seconds (the distance between two consecutive peaks).
The fundamental frequency \( f \) is the reciprocal of the time period: \[ f = \frac{1}{T} = \frac{1}{0.05} = 20 \, Hz. \]
Thus, the estimated fundamental frequency of the sine wave is \( \boxed{20 \, \text{Hz. Quick Tip: The fundamental frequency of a wave is the reciprocal of its time period.



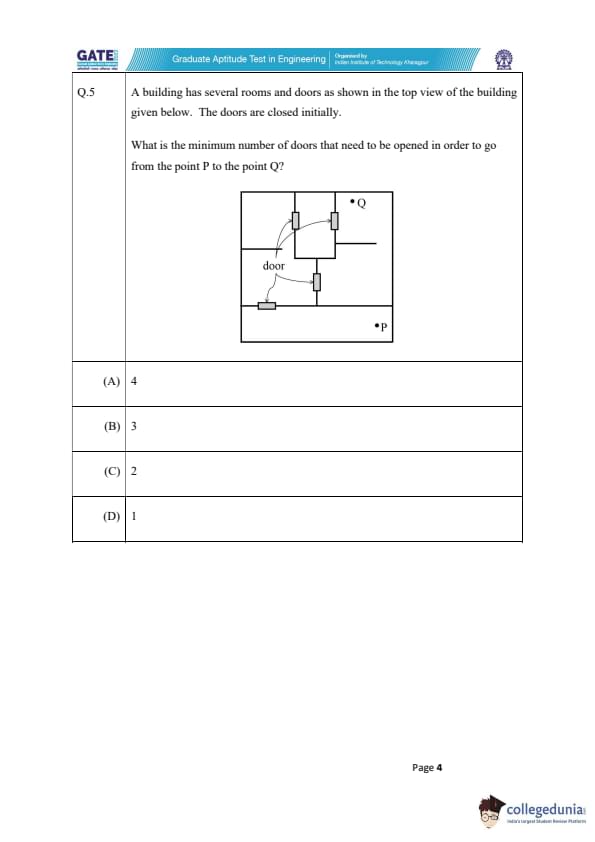

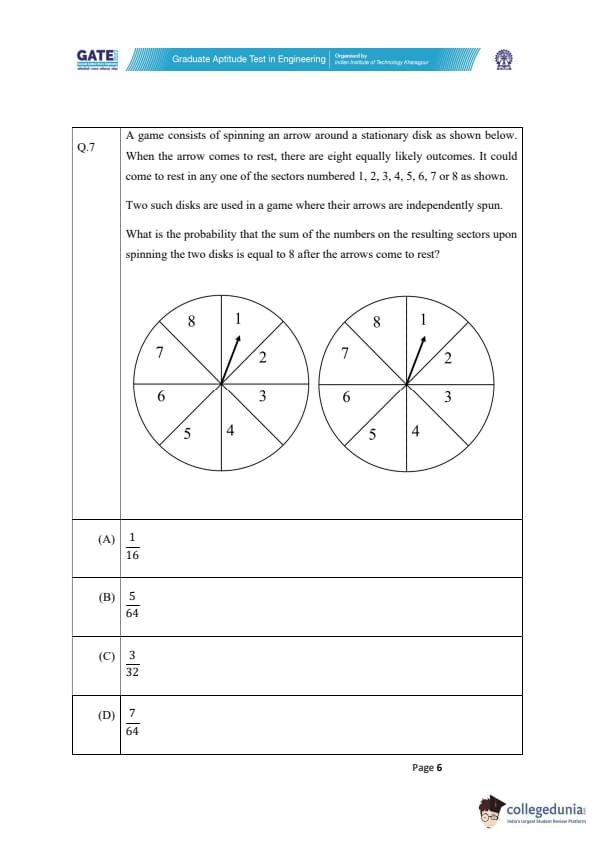


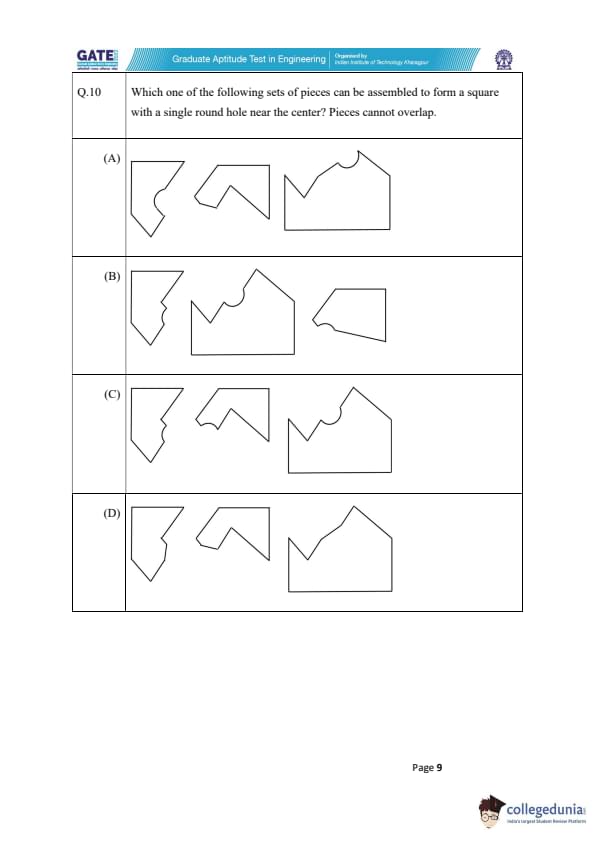












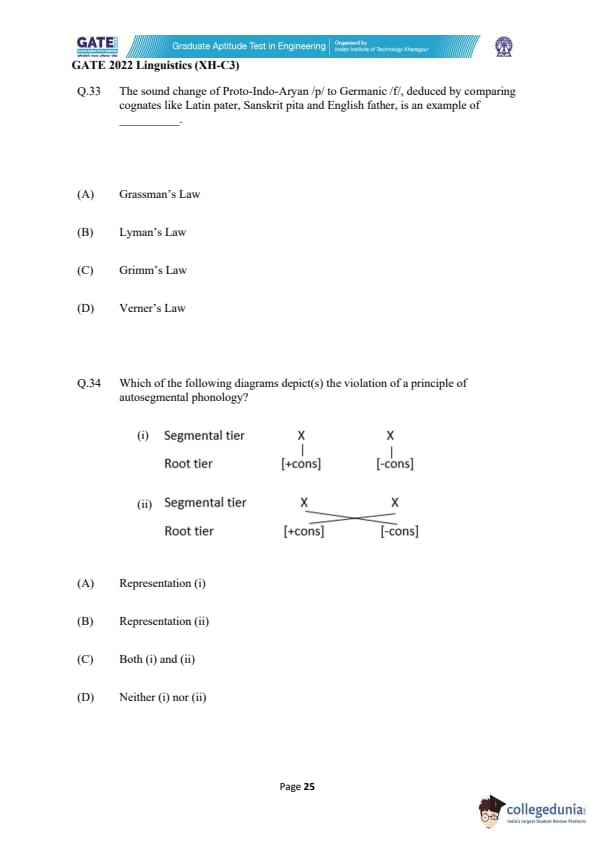




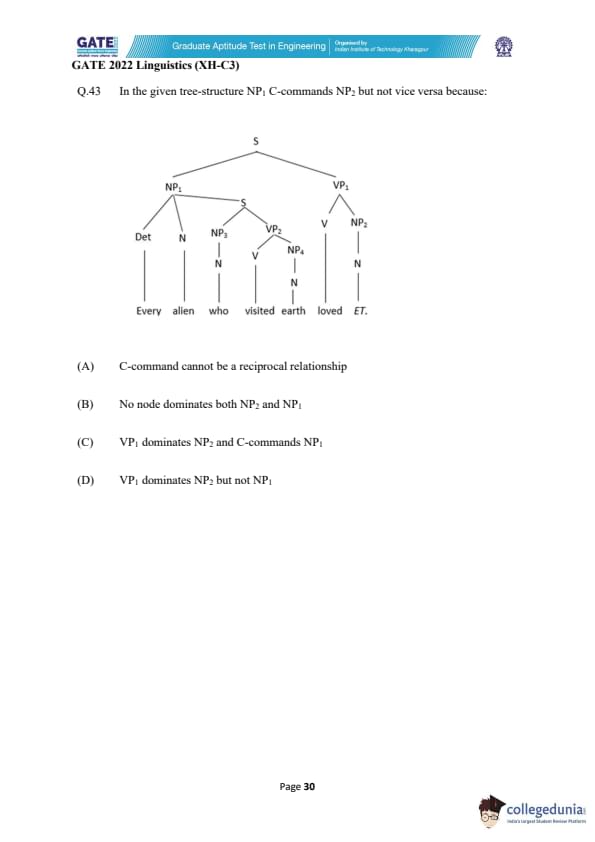













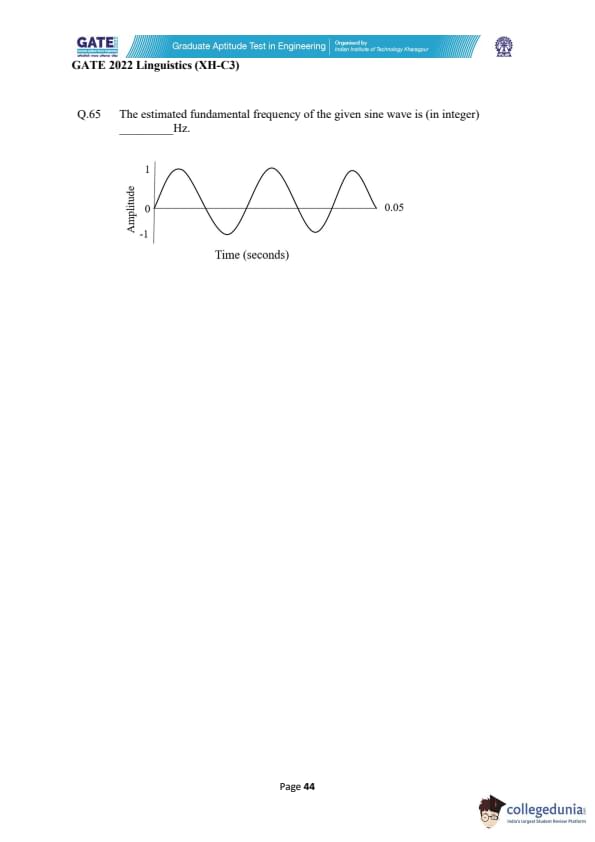
GATE 2022 XH- C3 (Linguistics) Question Paper: Paper Analysis
Section GA and B1 in GATE 2022 XH- Linguistics Question Paper were the same as the other five papers for GATE XH paper. The table below shows the number of 1 mark and 2 marks questions in GATE 2022 XH- Linguistics Question Paper:
| Type of Questions | General Aptitude (GA) | Reasoning Comprehension (B1) | Linguistics (XH- C3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Questions | Marks | Number of Questions | Marks | Number of Questions | Marks | |
| No. of 1 mark MCQs | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 7 |
| No. of 2 marks MCQs | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 11 | 22 |
| No. of 1 mark NATs | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| No. of 2 marks NATs | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| No. of 1 mark MSQs | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 11 | 11 |
| No. of 2 marks MSQs | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 18 |
Also Check:
GATE Previous Year Question Papers:
| GATE 2022 Question Papers | GATE 2021 Question Papers | GATE 2020 Question Papers |
| GATE 2019 Question Papers | GATE 2018 Question Papers | GATE 2017 Question Papers |




Comments