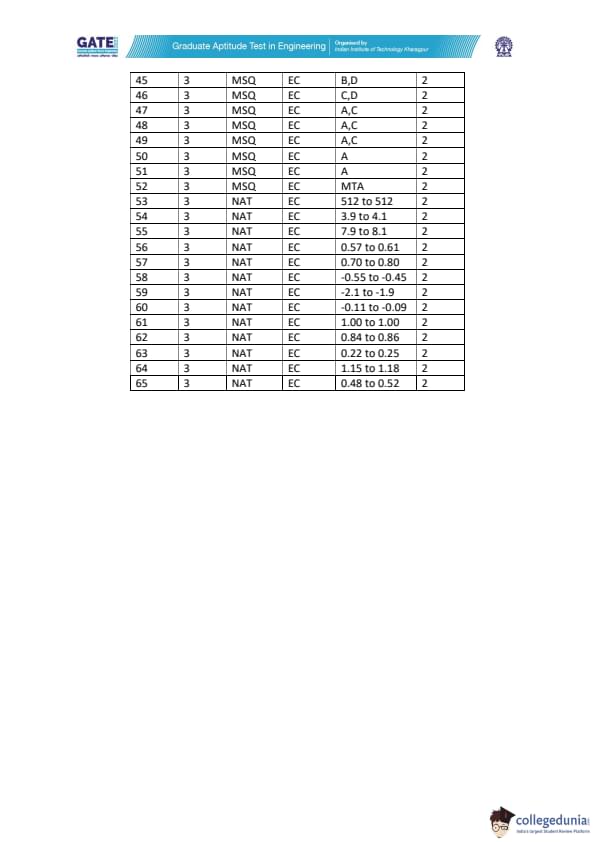
GATE 2022 Electronics and Communications Engineering (EC) Question Paper with Solutions PDF is now available for download. IIT Kharagpur conducted the GATE 2022 EC on 6th February 2022 for a 3 hours duration (9:00 AM to 12 PM). The overall difficulty level of GATE 2022 EC question paper was rated moderate to tough. The General Aptitude section carried the highest weightage in the exam. The Communication System carried the greatest weightage from the core Electrical and Communication Engineering section. The Signal and System section had the least weightage in the exam.
GATE 2022 Electronics and Communications Engineering (EC) Question Paper with Solutions
| GATE 2022 Electronics and Communications Engineering (EC) Question Paper | Check Solutions |

Mr. X speaks _____ Japanese _____ Chinese.
A sum of money is to be distributed among P, Q, R, and S in the proportion 5 : 2 : 4 : 3, respectively.
If R gets ₹1000 more than S, what is the share of Q (in ₹)?
A trapezium has vertices marked as P, Q, R, and S (in that order anticlockwise). The side PQ is parallel to side SR. Further, it is given that, PQ = 11 cm, QR = 4 cm, RS = 6 cm, and SP = 3 cm. What is the shortest distance between PQ and SR (in cm)?
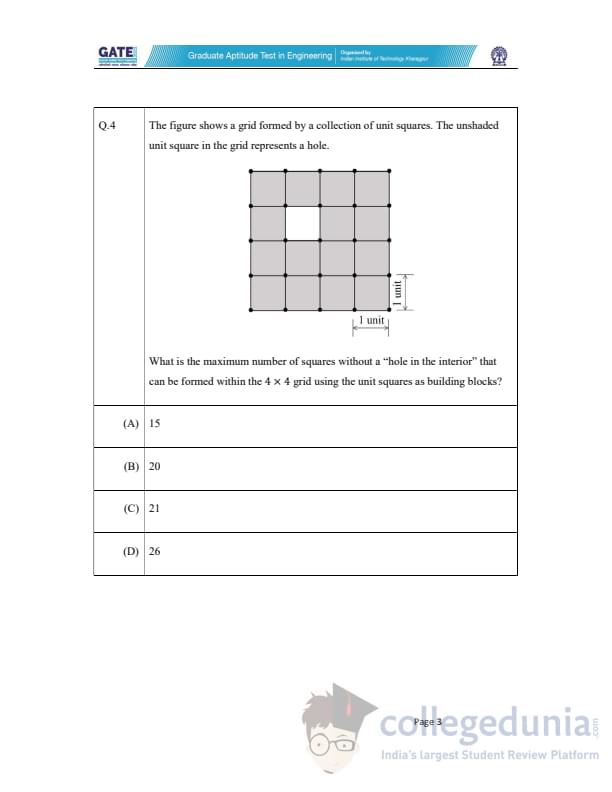
The figure shows a grid formed by a collection of unit squares. The unshaded unit square in the grid represents a hole. What is the maximum number of squares without a "hole in the interior" that can be formed within the 4 \(\times\) 4 grid using the unit squares as building blocks?

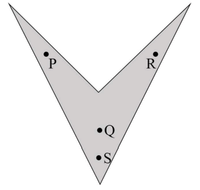
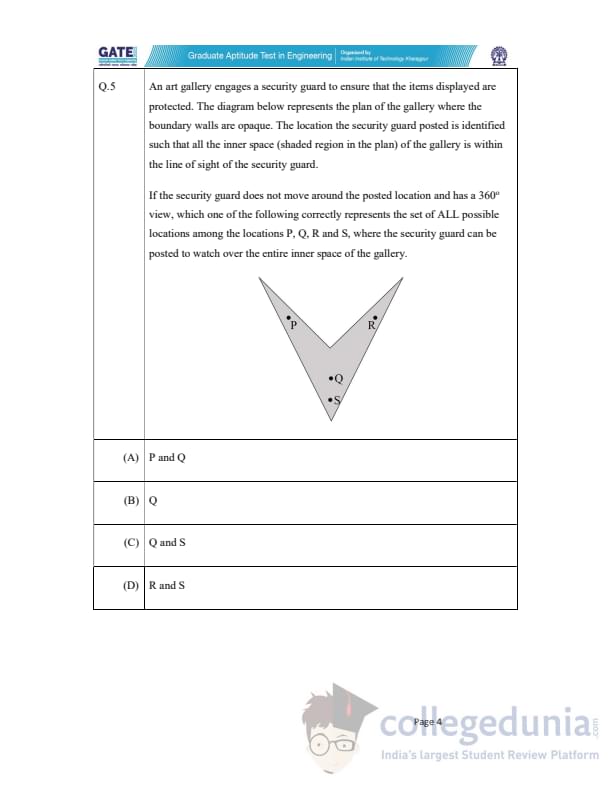
An art gallery engages a security guard to ensure that the items displayed are protected. The diagram below represents the plan of the gallery where the boundary walls are opaque. The location the security guard posted is identified such that all the inner space (shaded region in the plan) of the gallery is within the line of sight of the security guard.
If the security guard does not move around the posted location and has a 360° view, which one of the following correctly represents the set of ALL possible locations among the locations P, Q, R and S, where the security guard can be posted to watch over the entire inner space of the gallery?
Mosquitoes pose a threat to human health. Controlling mosquitoes using chemicals may have undesired consequences. In Florida, authorities have used genetically modified mosquitoes to control the overall mosquito population. It remains to be seen if this novel approach has unforeseen consequences.
Which one of the following is the correct logical inference based on the information in the above passage?
Consider the following inequalities.
(i) 2x - 1 \(>\) 7
(ii) 2x - 9 \(<\)1
Which one of the following expressions below satisfies the above two inequalities?
Four points \( P(0, 1), Q(0, -3), R(-2, -1), \) and \( S(2, -1) \) represent the vertices of a quadrilateral. What is the area enclosed by the quadrilateral?
In a class of five students P, Q, R, S and T, only one student is known to have copied in the exam. The disciplinary committee has investigated the situation and recorded the statements from the students as given below.
Statement of P: R has copied in the exam.
Statement of Q: S has copied in the exam.
Statement of R: P did not copy in the exam.
Statement of S: Only one of us is telling the truth.
Statement of T: R is telling the truth.
The investigating team had authentic information that S never lies.
Based on the information given above, the person who has copied in the exam is:
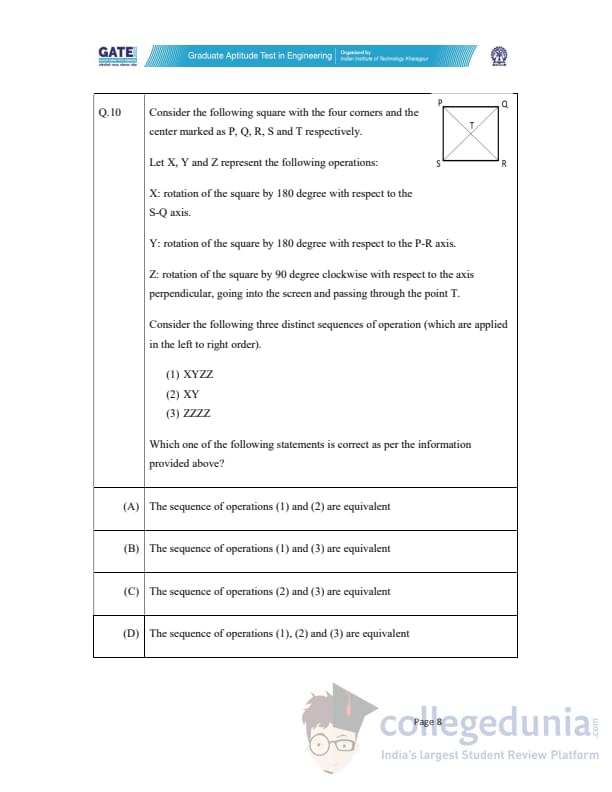
Consider the following square with the four corners and the center marked as P, Q, R, S and T respectively.
Let X, Y, and Z represent the following operations:
X: rotation of the square by 180 degree with respect to the S-Q axis.
Y: rotation of the square by 180 degree with respect to the P-R axis.
Z: rotation of the square by 90 degree clockwise with respect to the axis perpendicular, going into the screen and passing through the point T.
Consider the following three distinct sequences of operation (which are applied in the left to right order).
(1) XYZ
(2) XY
(3) ZZZZ

Which one of the following statements is correct as per the information provided above?
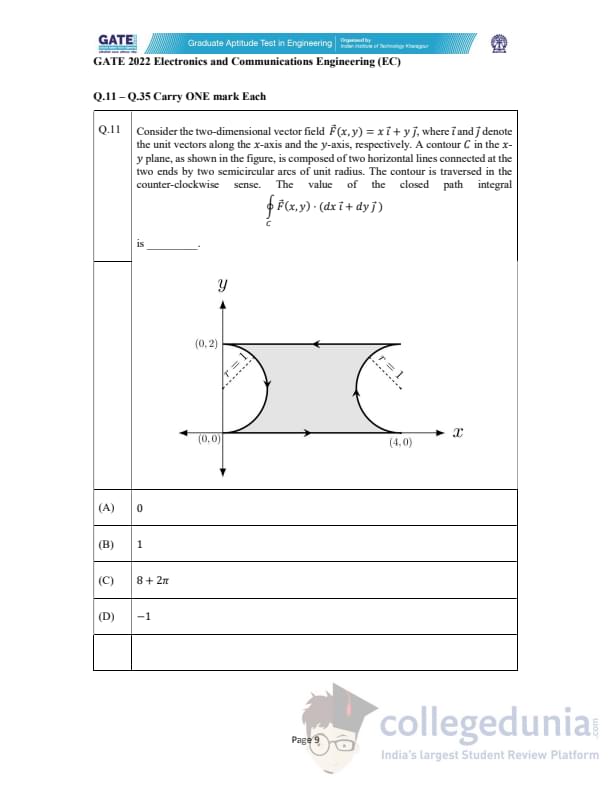
Consider the two-dimensional vector field \(\vec{F}(x,y)=x\,\hat{i}+y\,\hat{j}\), where \(\hat{i}\) and \(\hat{j}\) denote the unit vectors along the \(x\)-axis and the \(y\)-axis, respectively. A contour \(C\) in the \(xy\)-plane, as shown in the figure, is composed of two horizontal lines connected at the two ends by two semicircular arcs of unit radius. The contour is traversed in the counter-clockwise sense. The value of the closed path integral \[ \oint_{C} \vec{F}(x,y)\cdot(dx\,\hat{i}+dy\,\hat{j}) \]
is ________.

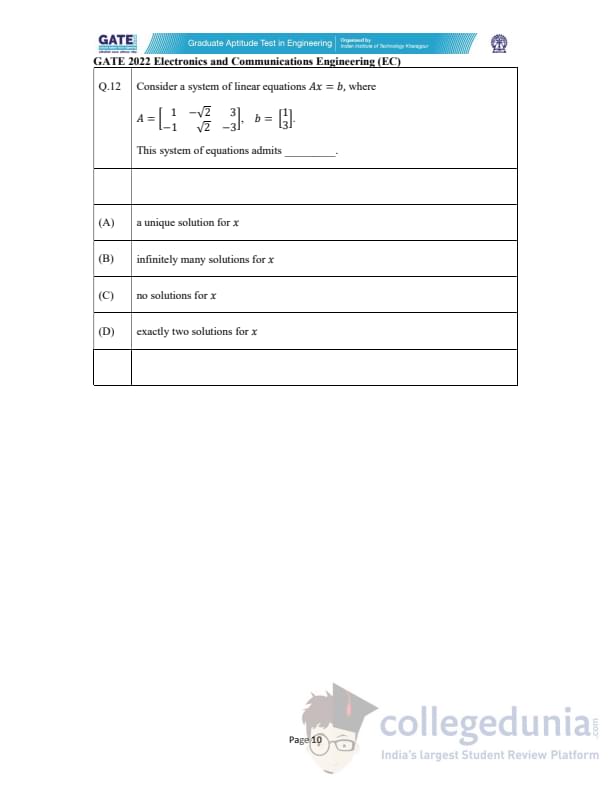
Consider a system of linear equations \(Ax = b\), where
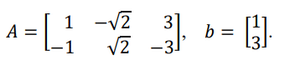
This system of equations admits ________.
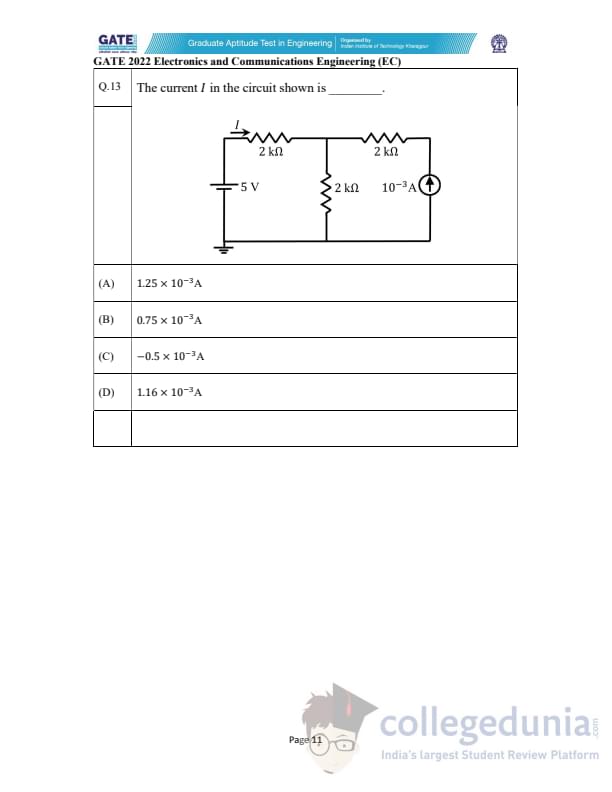
The current \(I\) in the circuit shown is ________.

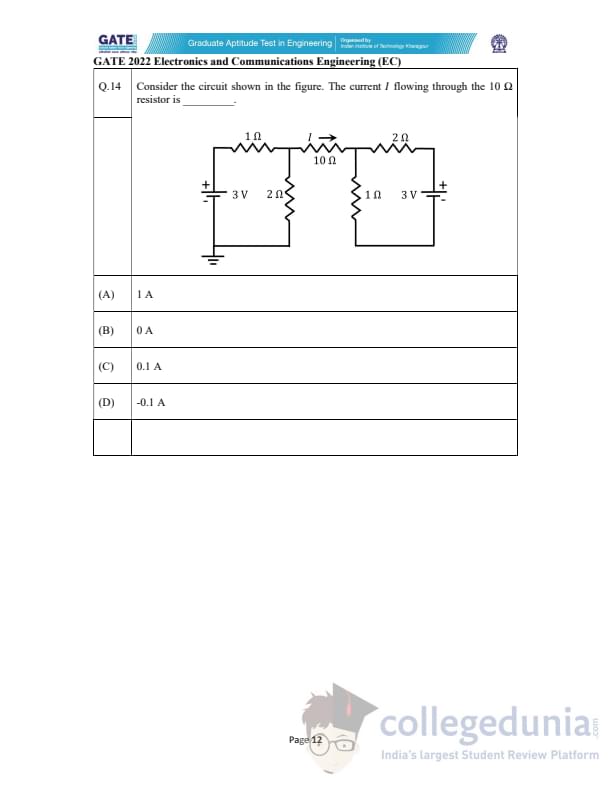
Consider the circuit shown in the figure. The current \(I\) flowing through the 10 \(\Omega\) resistor is ________.

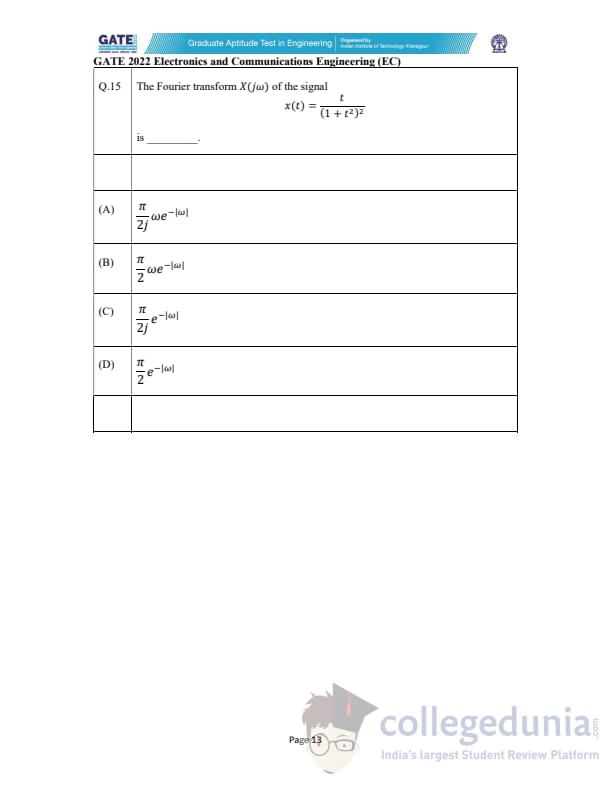
The Fourier transform \(X(j\omega)\) of the signal \[ x(t)=\frac{t}{(1+t^{2})^{2}} \]
is ________.
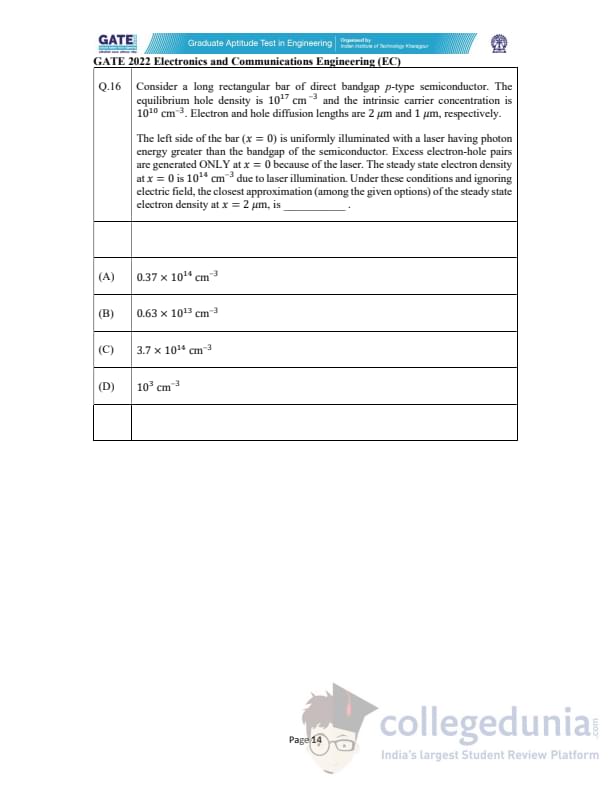
Consider a long rectangular bar of direct bandgap \(p\)-type semiconductor. The equilibrium hole density is \(10^{17}\,cm^{-3}\) and the intrinsic carrier concentration is \(10^{10}\,cm^{-3}\). Electron and hole diffusion lengths are \(2\,\mu\)m and \(1\,\mu\)m, respectively.
The left side of the bar (\(x=0\)) is uniformly illuminated with a laser having photon energy greater than the bandgap of the semiconductor. Excess electron-hole pairs are generated ONLY at \(x=0\) because of the laser. The steady state electron density at \(x=0\) is \(10^{14}\,cm^{-3}\) due to laser illumination. Under these conditions and ignoring electric field, the closest approximation (among the given options) of the steady state electron density at \(x=2\,\mum\) is _______.
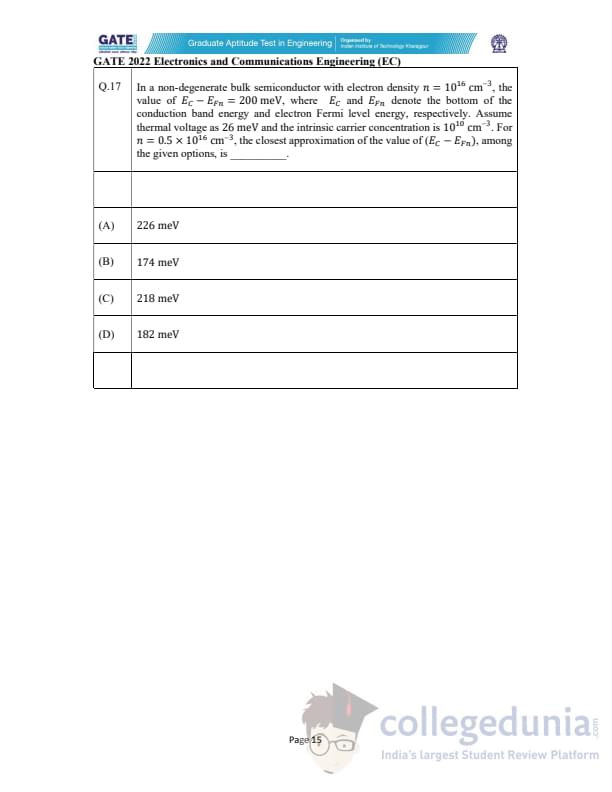
In a non-degenerate bulk semiconductor with electron density \(n = 10^{16}\) cm\(^{-3}\), the value of \((E_C - E_{Fn}) = 200\) meV, where \(E_C\) and \(E_{Fn}\) denote the conduction band edge and electron Fermi level, respectively. Assume thermal voltage as 26 meV and intrinsic carrier concentration as \(10^{10}\) cm\(^{-3}\). For \(n = 0.5 \times 10^{16}\) cm\(^{-3}\), the closest approximation of \((E_C - E_{Fn})\), among the given options, is ________.
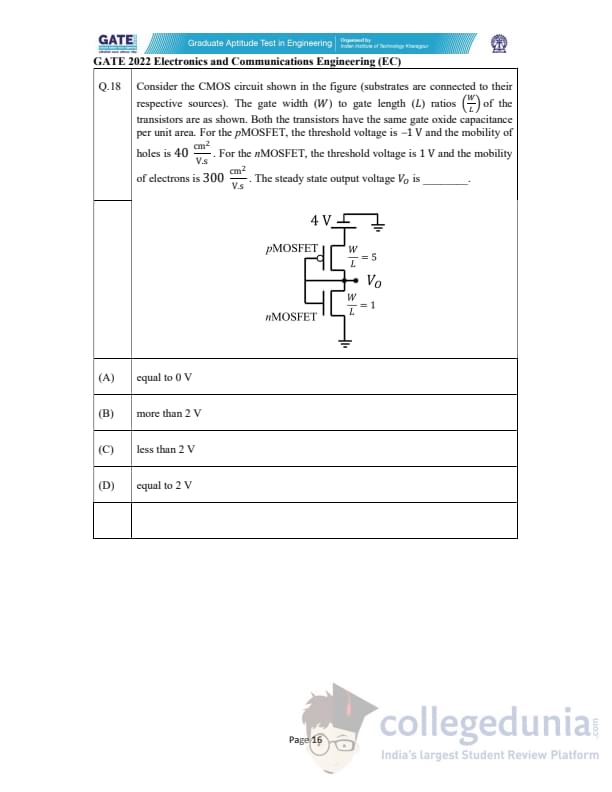
Consider the CMOS circuit shown in the figure (substrates are connected to their respective sources). The gate width \((W)\) to gate length \((L)\) ratios of the transistors are as shown. Both the transistors have the same gate oxide capacitance per unit area. For the pMOSFET, the threshold voltage is \(-1\ V\) and the mobility of holes is \(40\ cm^2/(V·s)\). For the nMOSFET, the threshold voltage is \(1\ V\) and the mobility of electrons is \(300\ cm^2/(V·s)\). The steady state output voltage \(V_O\) is ________.

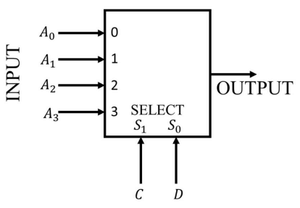
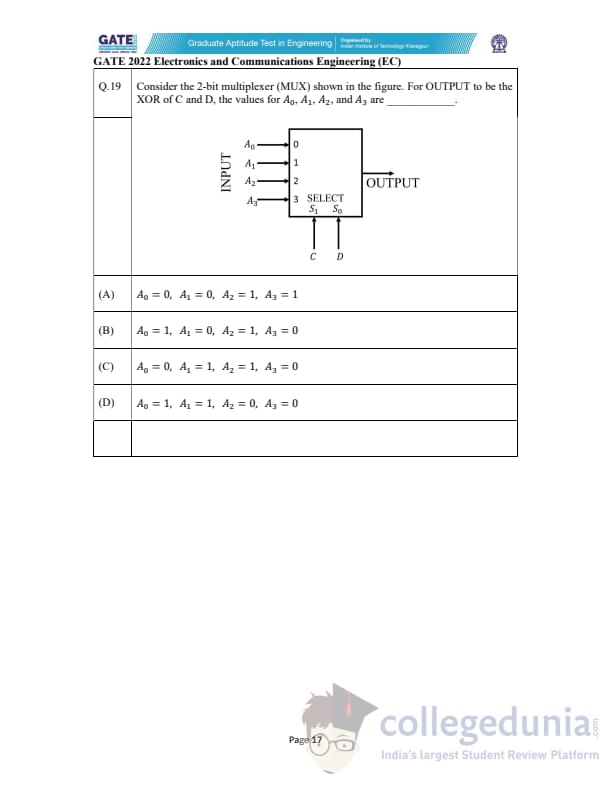
Consider the 2-bit multiplexer (MUX) shown in the figure. For OUTPUT to be the XOR of C and D, the values for \(A_0, A_1, A_2,\) and \(A_3\) are ________.
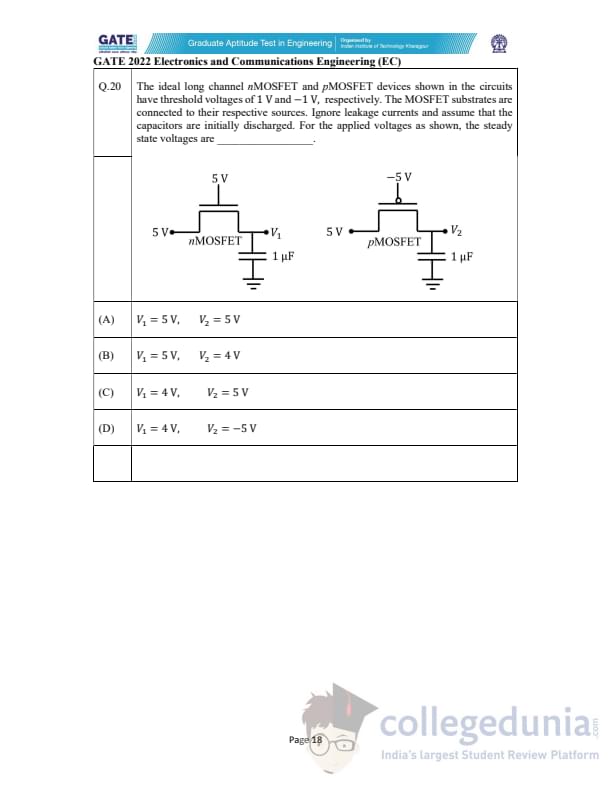
The ideal long-channel nMOSFET and pMOSFET devices shown have threshold voltages of \(1 V\) and \(-1 V\), respectively. The MOSFET substrates are connected to their sources. Ignore leakage currents and assume that the capacitors are initially discharged. For the applied voltages as shown, the steady-state voltages are ________.

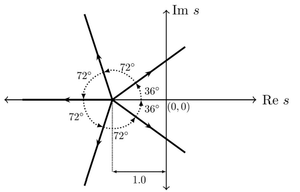
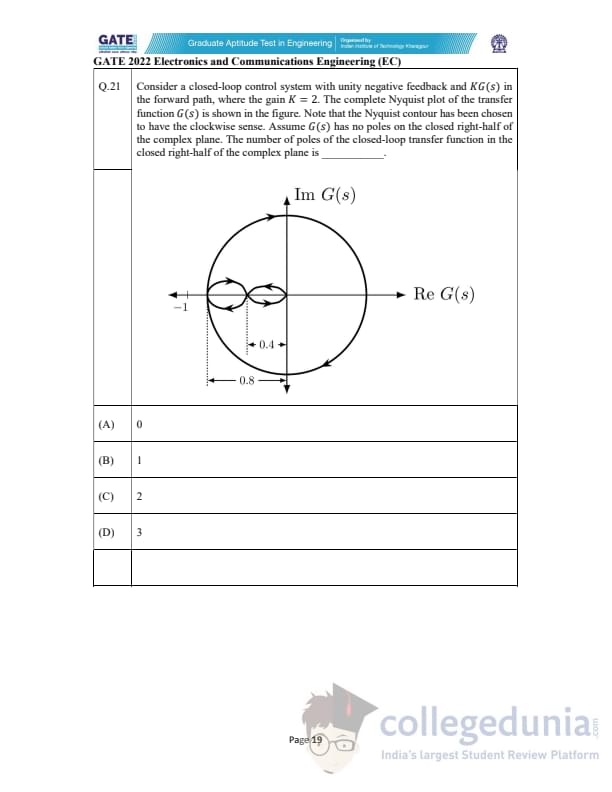
Consider a closed-loop control system with unity negative feedback and \(K G(s)\) in the forward path, where the gain \(K = 2\). The complete Nyquist plot of the transfer function \(G(s)\) is shown in the figure. Note that the Nyquist contour has been chosen to have the clockwise sense. Assume \(G(s)\) has no poles on the closed right-half of the complex plane. The number of poles of the closed-loop transfer function in the closed right-half of the complex plane is ______.

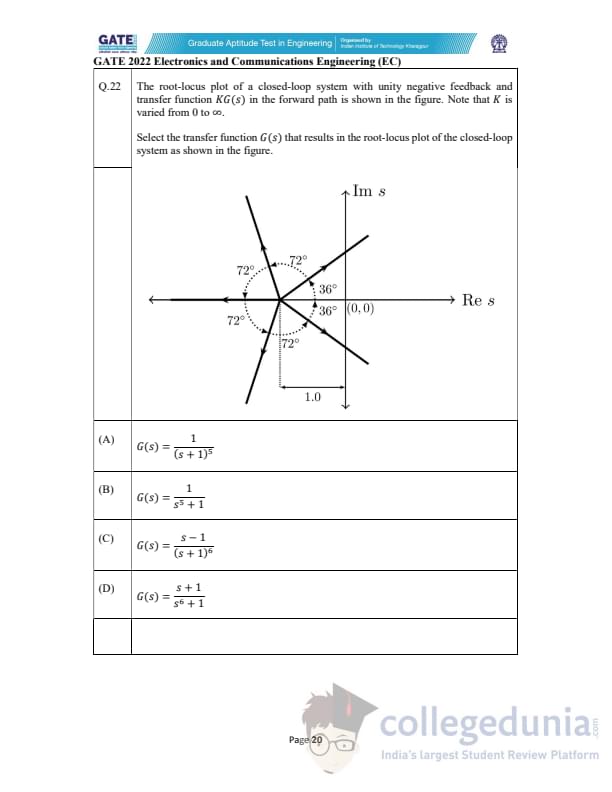
The root-locus plot of a closed-loop system with unity negative feedback and transfer function \(KG(s)\) in the forward path is shown in the figure. Note that \(K\) is varied from 0 to \(\infty\). Select the transfer function \(G(s)\) that results in the shown root-locus.
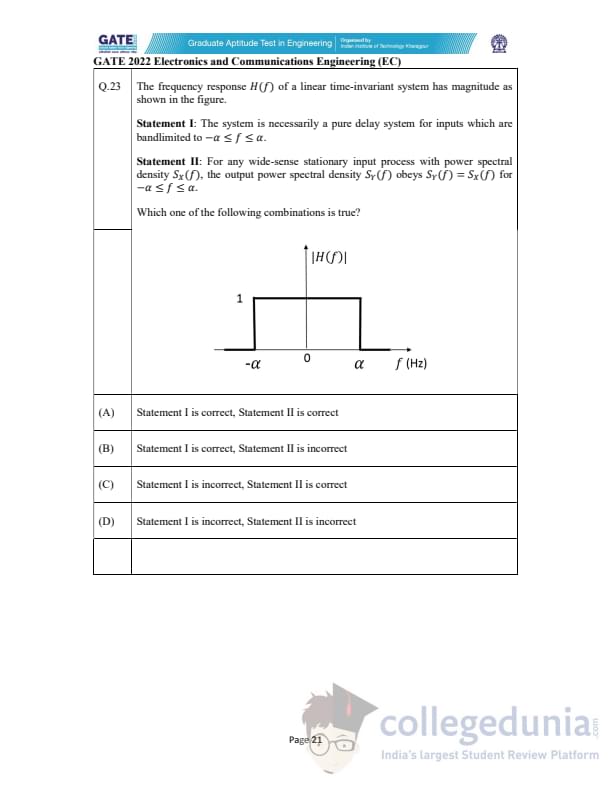
The frequency response \(H(f)\) of a linear time-invariant system has magnitude as shown in the figure.
Statement I: The system is necessarily a pure delay system for inputs which are bandlimited to \(-\alpha \le f \le \alpha\).
Statement II: For any wide-sense stationary input process with power spectral density \(S_X(f)\), the output power spectral density \(S_Y(f)\) obeys \(S_Y(f) = S_X(f)\) for \(-\alpha \le f \le \alpha\).
Which one of the following combinations is true?

In a circuit, there is a series connection of an ideal resistor and an ideal capacitor. The conduction current (in Amperes) through the resistor is \(2\sin(t + \pi/2)\). The displacement current (in Amperes) through the capacitor is ________.
Consider the PDE \[ a\,\frac{\partial^{2} f(x,y)}{\partial x^{2}} \;+\; b\,\frac{\partial^{2} f(x,y)}{\partial y^{2}} \;=\; f(x,y), \]
where \(a\) and \(b\) are distinct positive real numbers. Select the combinations of real parameters \(\xi\) and \(\eta\) such that \[ f(x,y)=e^{\,(\xi x+\eta y)} \]
is a solution of the PDE.
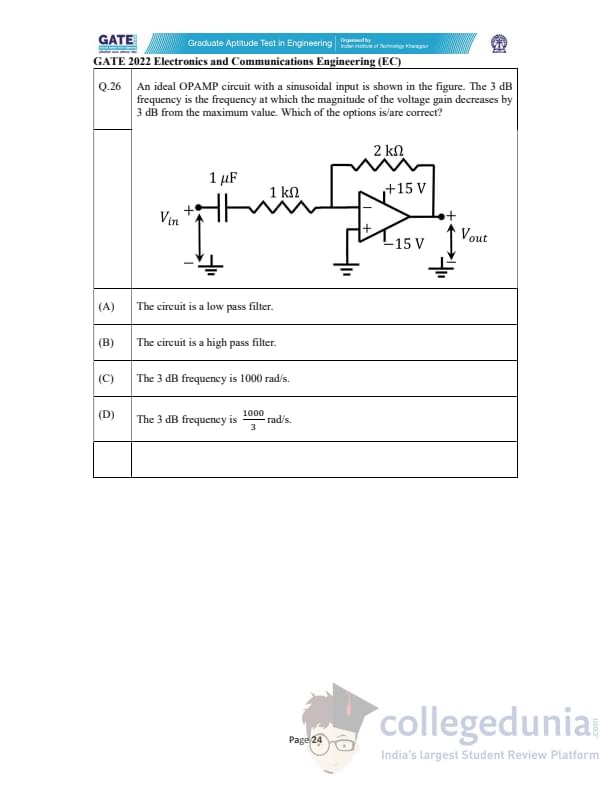
An ideal OPAMP circuit with a sinusoidal input is shown in the figure. The 3 dB frequency is the frequency at which the magnitude of the voltage gain decreases by 3 dB from the maximum value. Which of the options is/are correct?

Select the Boolean function(s) equivalent to \(x + yz\), where \(x\), \(y\), and \(z\) are Boolean variables, and \(+\) denotes logical OR.
Select the correct statement(s) regarding CMOS implementation of NOT gates.
Let \(H(X)\) denote the entropy of a discrete random variable \(X\) taking \(K\) possible distinct real values. Which of the following statements is/are necessarily true?
Consider the following wave equation \[ \frac{\partial^2 f(x,t)}{\partial t^2} = 10000 \frac{\partial^2 f(x,t)}{\partial x^2} \]
Which of the given options is/are solution(s) to the given wave equation?
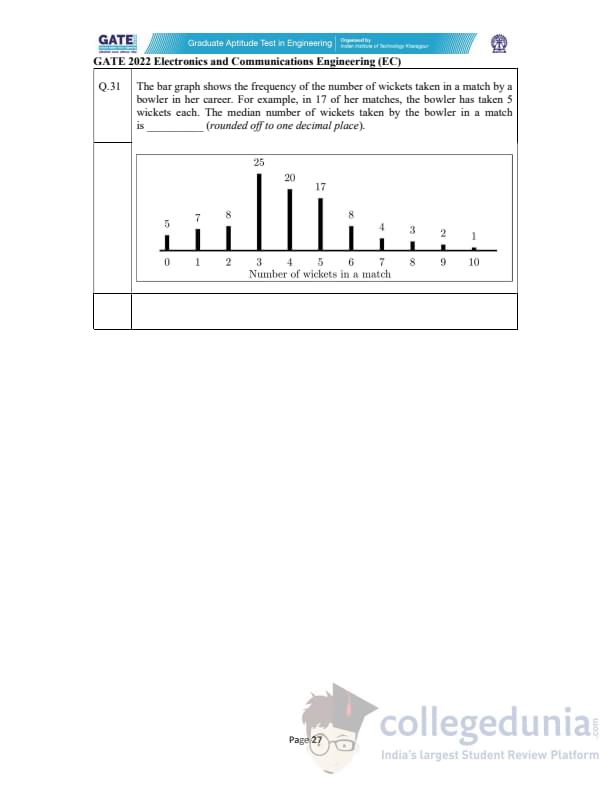
The bar graph shows the frequency of wickets taken by a bowler in her career.
The median number of wickets taken in a match is _____ (rounded off to one decimal place).

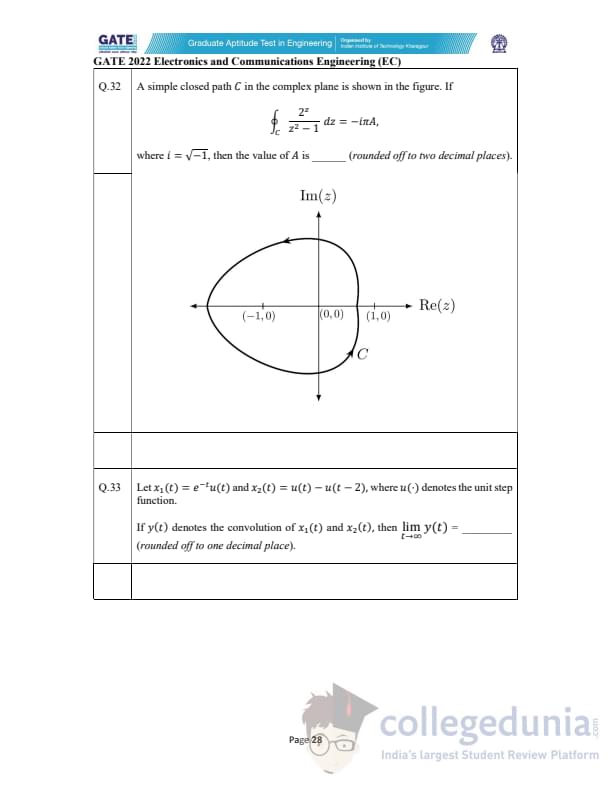
A simple closed path \(C\) is shown in the complex plane. If \[ \oint_C \frac{2z}{z^2 - 1}\, dz = -i\pi A, \]
where \(i = \sqrt{-1}\), find \(A\) (rounded to two decimals).

Let \(x_1(t)=e^{-t}u(t)\) and \(x_2(t)=u(t)-u(t-2)\).
If \(y(t)\) is the convolution \(x_1(t)x_2(t)\), find \[ \lim_{t\to\infty} y(t) \]
(rounded to one decimal place).
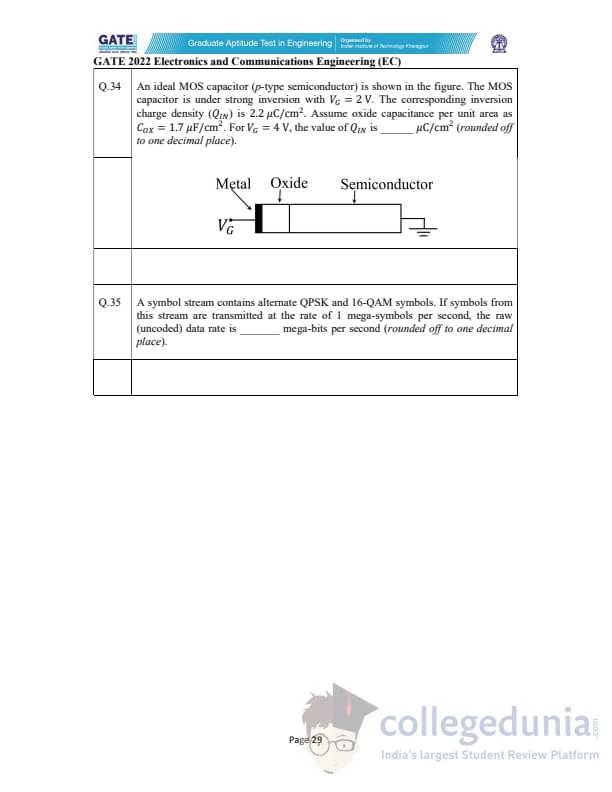
An ideal MOS capacitor (p-type semiconductor) is under strong inversion with \(V_G = 2\) V.
The inversion charge density is \(Q_{IN} = 2.2\ \muC/cm^2\).
Assume oxide capacitance per unit area \(C_{ox} = 1.7\ \muF/cm^2\).
For \(V_G = 4\) V, the value of \(Q_{IN}\) is ______ \(\mu\)C/cm\(^2\) (rounded to one decimal place).

A symbol stream contains alternate QPSK and 16-QAM symbols.
If transmitted at 1 mega-symbol per second, the raw data rate is _____ Mbps
(rounded off to one decimal place).
The function \(f(x)=8\log_e x - x^2 + 3\) attains its minimum over the interval \([1,e]\) at \(x=\) ______.
Let \(\alpha, \beta\) be non-zero real numbers and \(v_1, v_2\) be two non-zero vectors of size \(3 \times 1\). Suppose \(v_1^T v_2 = 0\), \(v_1^T v_1 = 1\), \(v_2^T v_2 = 1\). Let \[ A = \alpha v_1 v_1^T + \beta v_2 v_2^T. \]
The eigenvalues of \(A\) are ______.
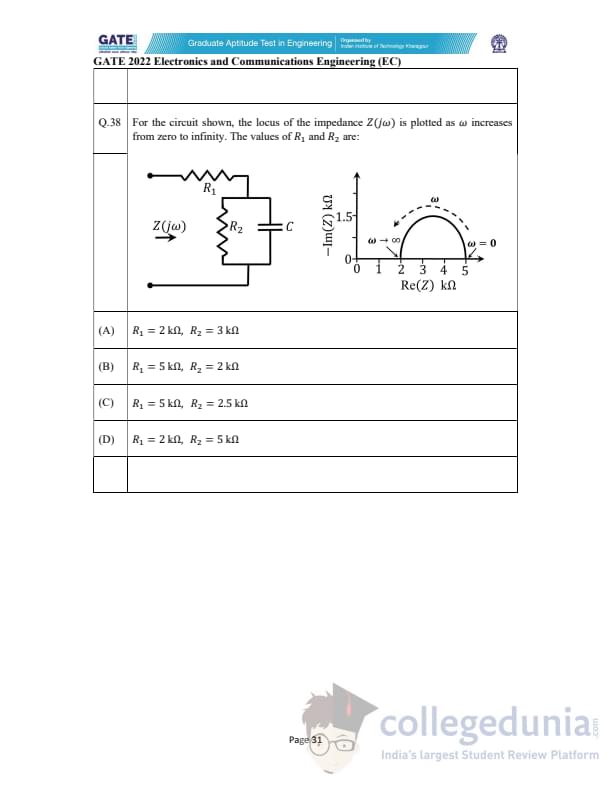
For the circuit shown, the locus of the impedance \(Z(j\omega)\) is plotted as \(\omega\) increases from zero to infinity. The values of \(R_1\) and \(R_2\) are:

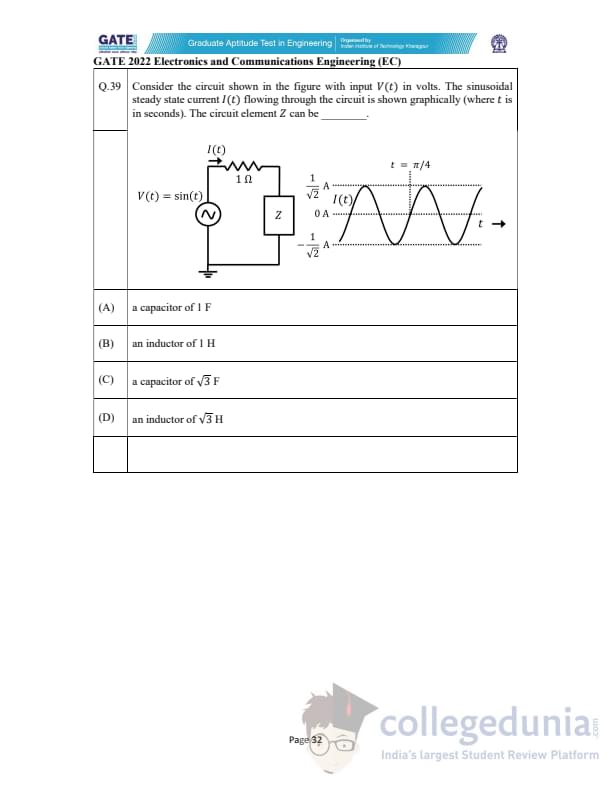
Consider the circuit shown in the figure with input \(V(t)\) in volts. The sinusoidal steady state current \(I(t)\) flowing through the circuit is shown graphically. The circuit element \(Z\) can be ________.

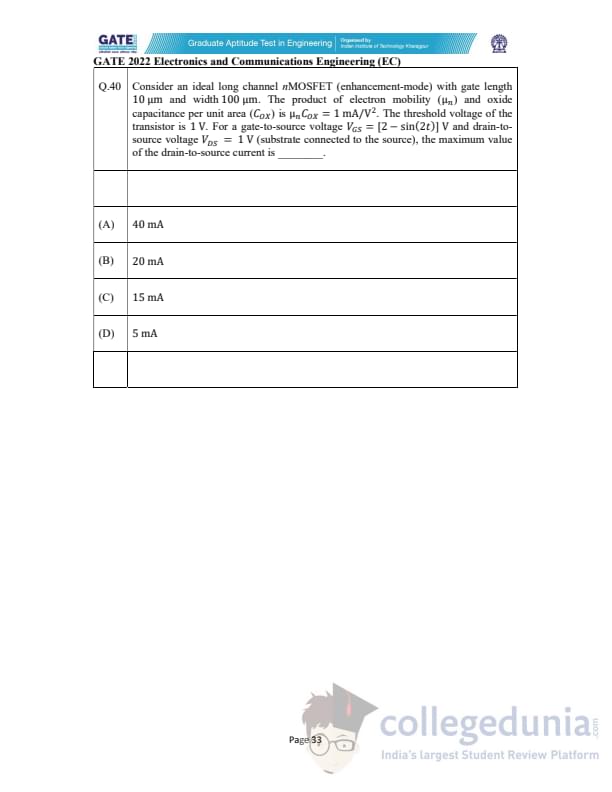
Consider an ideal long channel nMOSFET (enhancement-mode) with gate length 10 \(\mu\)m and width 100 \(\mu\)m. The product of electron mobility (\(\mu_n\)) and oxide capacitance per unit area (\(C_{OX}\)) is \(\mu_n C_{OX} = 1\ mA/V^2\). The threshold voltage of the transistor is 1 V. For a gate-to-source voltage \(V_{GS} = [2 - \sin(2t)]\) V and drain-to-source voltage \(V_{DS} = 1\) V (substrate connected to source), the maximum value of the drain-to-source current is ________.
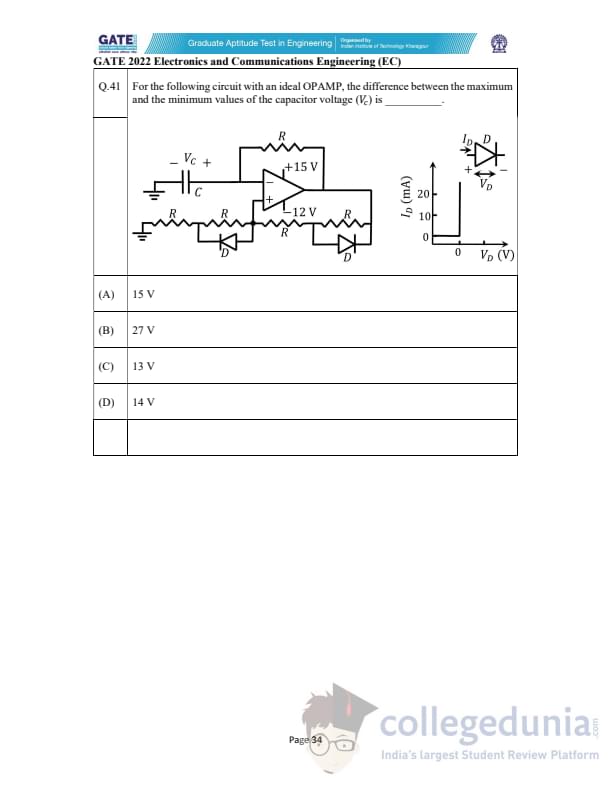
For the following circuit with an ideal OPAMP, the difference between the maximum and minimum values of the capacitor voltage \((V_C)\) is ________.

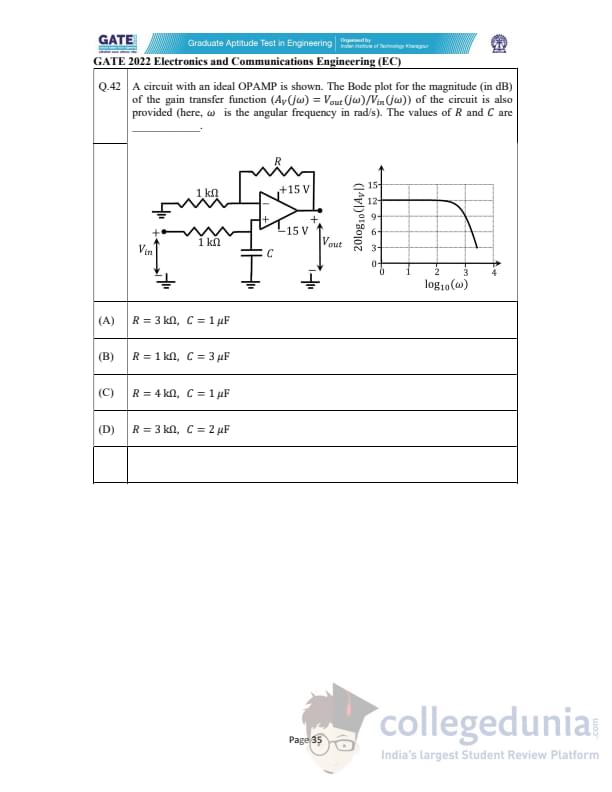
A circuit with an ideal OPAMP is shown. The Bode plot for the magnitude (in dB) of the gain transfer function \(A_V(j\omega)=V_{out}(j\omega)/V_{in}(j\omega)\) of the circuit is also provided (here, \(\omega\) is the angular frequency in rad/s). The values of \(R\) and \(C\) are ______.

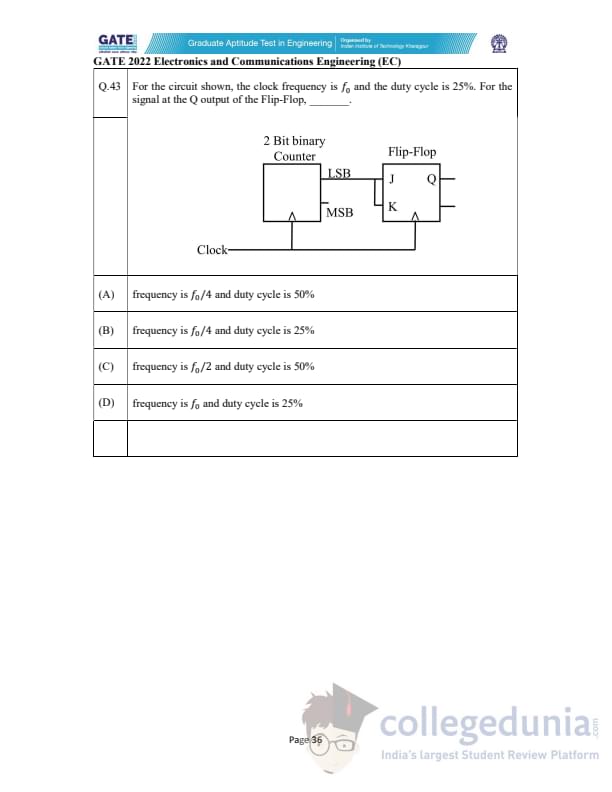
For the circuit shown, the clock frequency is \(f_0\) and the duty cycle is 25%. For the signal at the Q output of the Flip-Flop, ________.
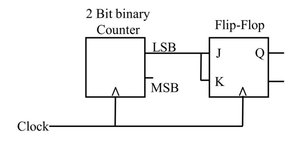
Consider an even polynomial \(p(s)\) given by \[ p(s) = s^4 + 5s^2 + 4 + K, \]
where \(K\) is an unknown real parameter. The complete range of \(K\) for which \(p(s)\) has all its roots on the imaginary axis is ________.
Consider the following series: \[ \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} \frac{n^{d}}{c^{n}} \]
For which of the following combinations of \(c, d\) values does this series converge?
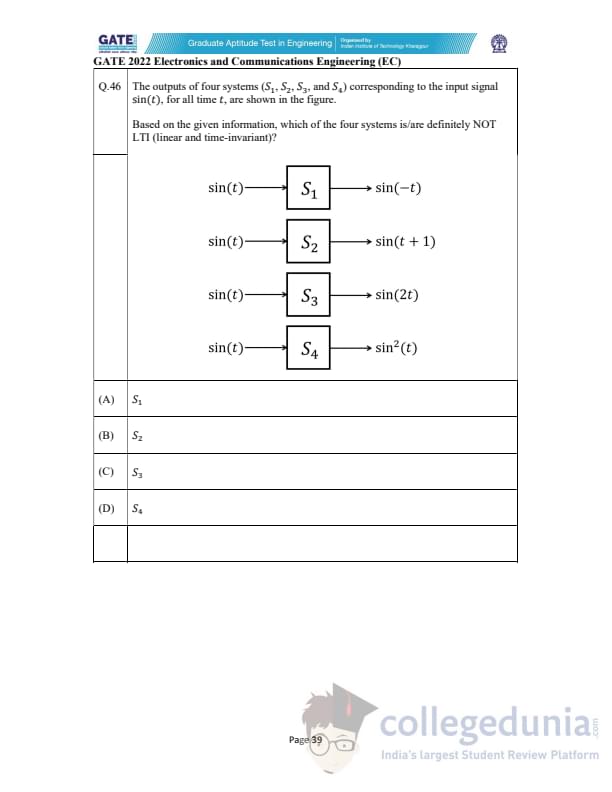
The outputs of four systems \((S_1, S_2, S_3, S_4)\) corresponding to the input signal \(\sin(t)\), for all time \(t\), are shown. Based on the given information, which of the four systems is/are definitely NOT LTI (linear and time-invariant)?

Select the CORRECT statement(s) regarding semiconductor devices.
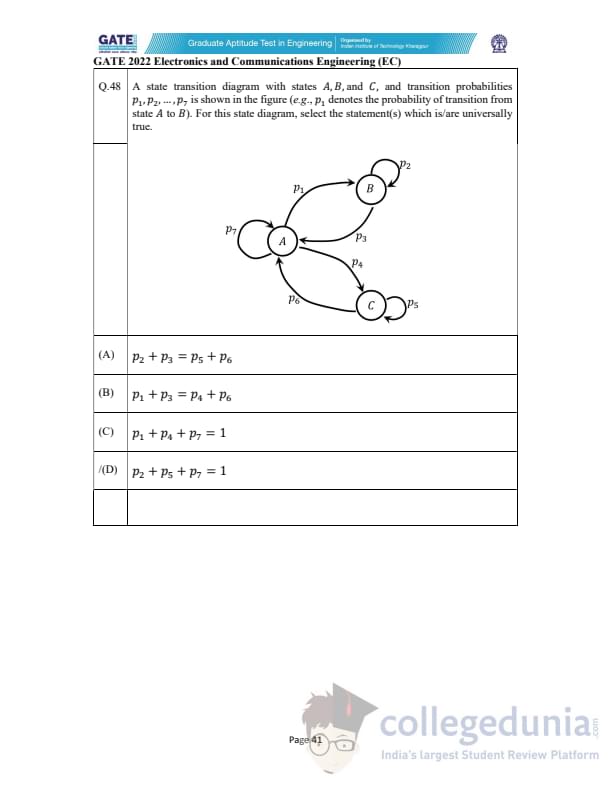
A state transition diagram with states \(A\), \(B\), and \(C\), and transition probabilities \(p_1, p_2, \ldots, p_7\) is shown in the figure (e.g., \(p_1\) denotes the probability of transition from state \(A\) to \(B\)). For this state diagram, select the statement(s) which is/are universally true.

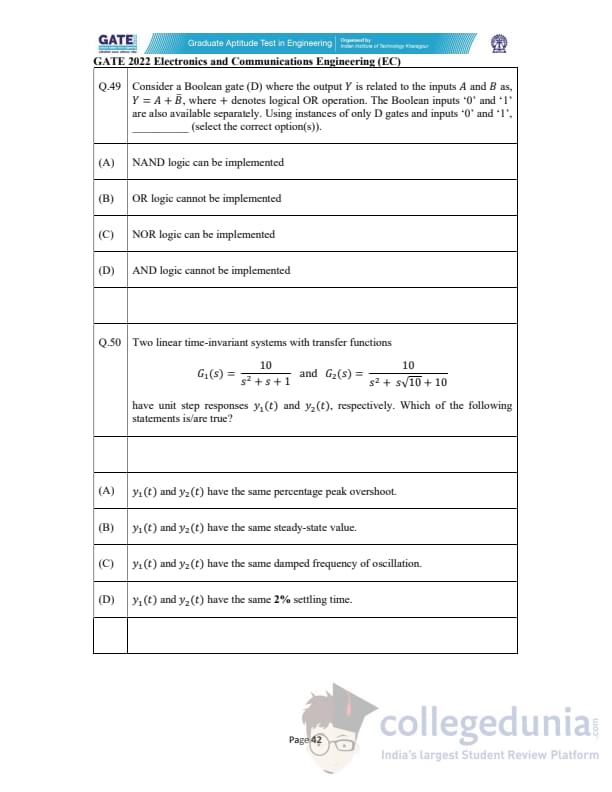
Consider a Boolean gate (D) where the output \(Y\) is related to the inputs \(A\) and \(B\) as \[ Y = A + \overline{B}, \]
where \(+\) denotes logical OR. The Boolean inputs ‘0’ and ‘1’ are also separately available. Using only D gates and inputs ‘0’ and ‘1’, ________ (select the correct option(s)).
Two linear time-invariant systems with transfer functions \[ G_1(s) = \frac{10}{s^2 + s + 1}, \qquad G_2(s) = \frac{10}{s^2 + s\sqrt{10} + 10} \]
have unit step responses \(y_1(t)\) and \(y_2(t)\), respectively. Which of the following statements is/are true?
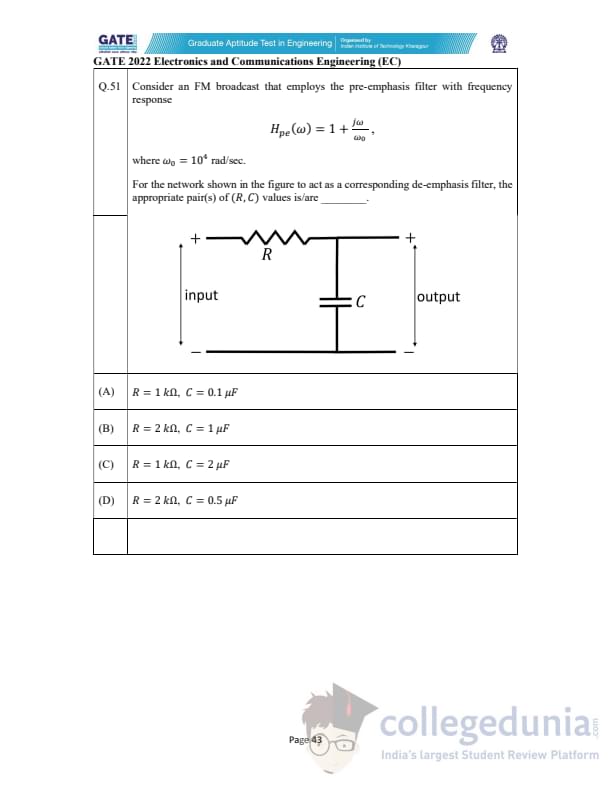
Consider an FM broadcast that employs the pre-emphasis filter with frequency response \[ H_{pe}(\omega) = 1 + \frac{j\omega}{\omega_0}, \]
where \(\omega_0 = 10^{4}\) rad/s.
For the network shown in the figure to act as a corresponding de-emphasis filter, the appropriate pair(s) of \((R, C)\) values is/are ________.

A waveguide consists of two infinite parallel plates (perfect conductors) at a separation of \(10^{-4}\,cm\), with air as the dielectric. Assume the speed of light in air to be \(3\times10^{8}\,m/s\). The frequency/frequencies of TM waves which can propagate in this waveguide is/are ________.
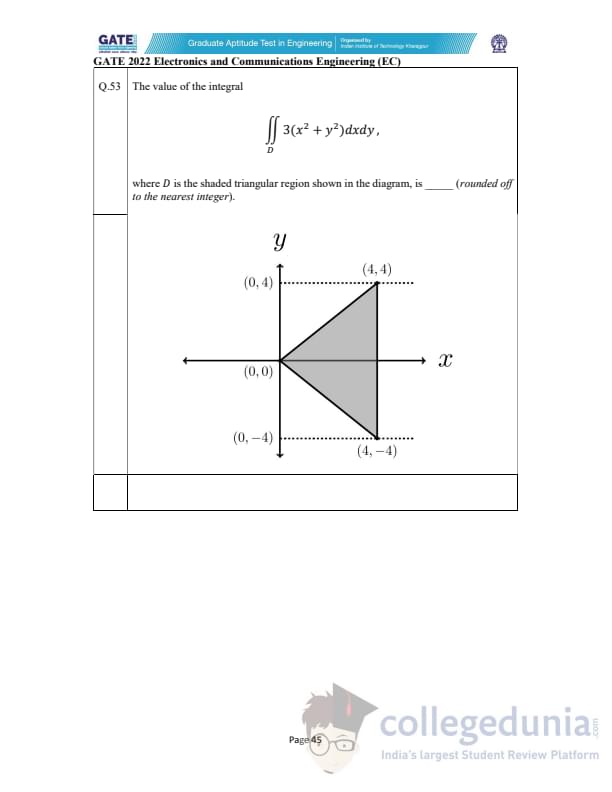
The value of the integral \[ \iint_D 3(x^2 + y^2)\, dx\, dy, \]
where \(D\) is the shaded triangular region, is _____ (rounded off to the nearest integer).

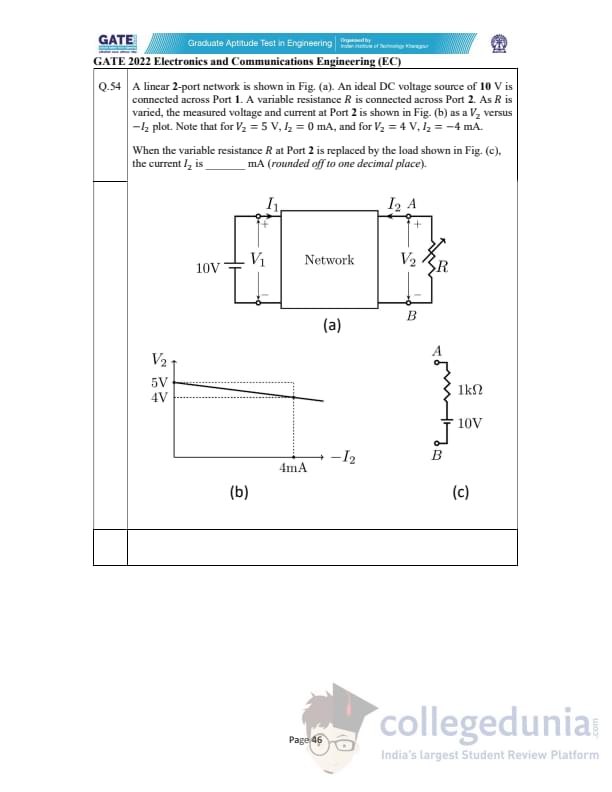
A linear 2-port network is shown. From the \(V_2\)–\((-I_2)\) plot:
when \(V_2 = 5\) V, \(I_2 = 0\) mA, and when \(V_2 = 4\) V, \(I_2 = -4\) mA.
Port 2 is now connected to the load in Fig. (c).
Find the current \(I_2\) (rounded to one decimal place).

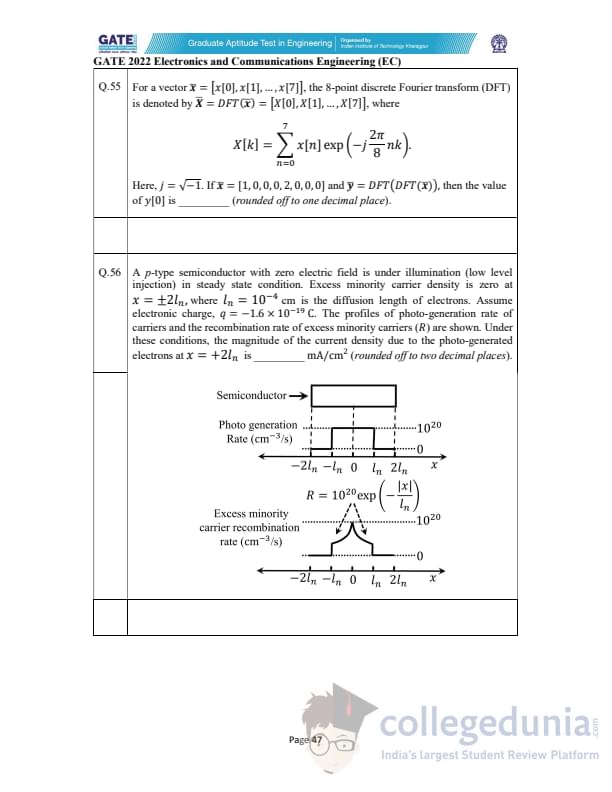
For a vector \(\bar{x} = [x[0], x[1], ..., x[7]]\), the 8–point DFT is \(\bar{X} = DFT(\bar{x}) = [X[0], X[1], ..., X[7]]\) where \[ X[k] = \sum_{n=0}^{7} x[n]\exp\left(-j\,\frac{2\pi}{8}nk\right). \]
If \(\bar{x} = [1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0]\) and \(\bar{y} = DFT(DFT(\bar{x}))\),
the value of \(y[0]\) is _____ (rounded off to one decimal place).
A p-type semiconductor in steady state has excess minority carriers zero at \(x=\pm 2L_n\),
with \(L_n = 10^{-4}\) cm. Electron charge \(q = -1.6\times 10^{-19}\) C.
The recombination rate profile is \[ R = 10^{20} \exp\left(-\frac{|x|}{L_n}\right)\ cm^{-3}s^{-1}. \]
The magnitude of electron current density at \(x=+2L_n\) is _____ mA/cm\(^2\) (rounded to two decimals).

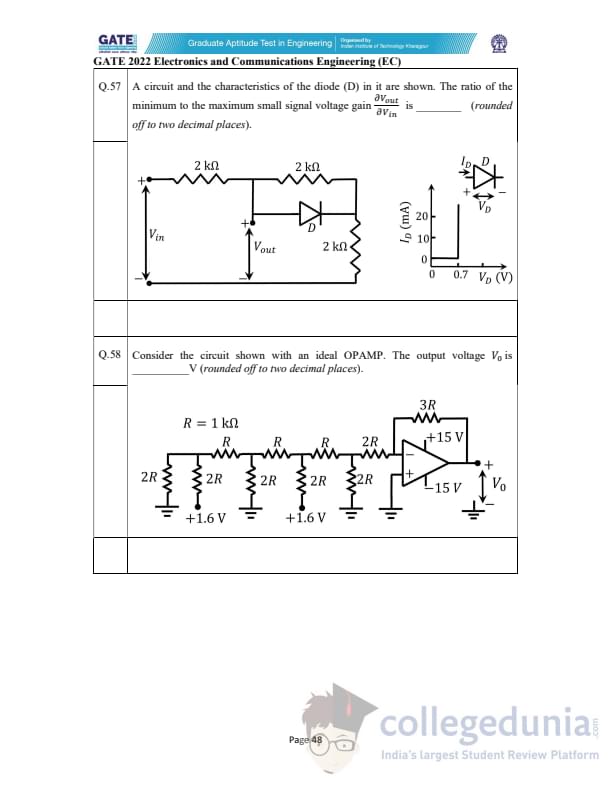
A circuit with a diode is shown. The ratio of the minimum to maximum small-signal voltage gain \[ \frac{\partial V_{out}}{\partial V_{in}} \]
is to be found (rounded to two decimals).

Consider the shown ideal OPAMP circuit. Find the output voltage \(V_0\) (rounded to two decimals).

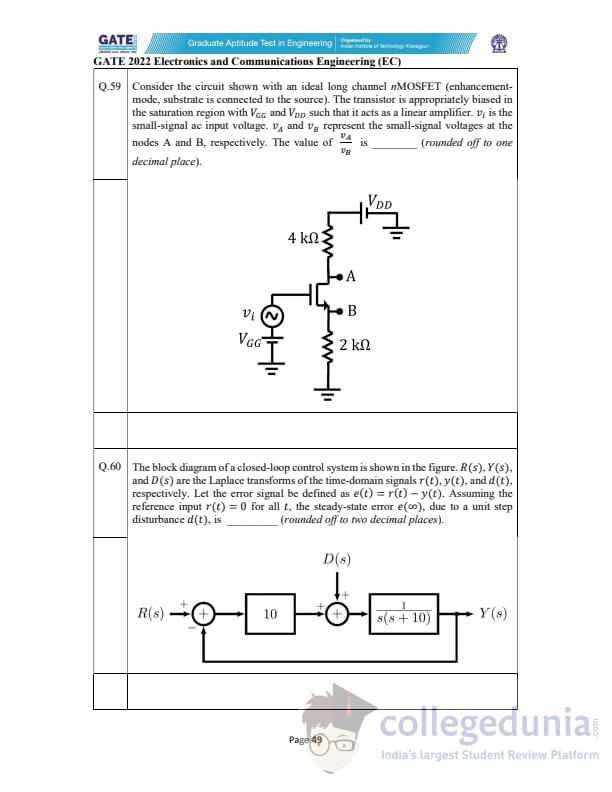
For the circuit shown with an ideal long-channel nMOSFET biased in saturation, \(v_A\) and \(v_B\) are the small-signal voltages at nodes A and B.
The value of \(\dfrac{v_A}{v_B}\) is ______ (rounded off to one decimal place).

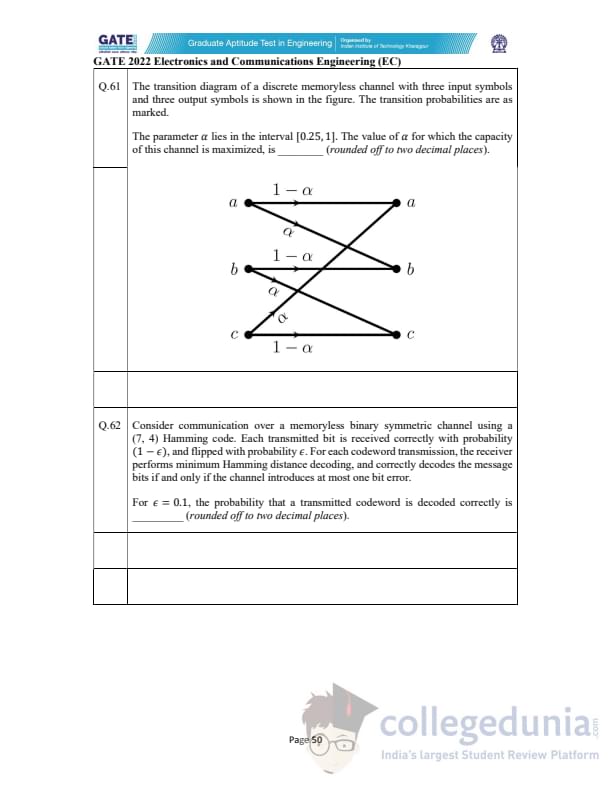
For the closed-loop control system shown, with \(r(t)=0\),
the steady-state error \(e(\infty)\) due to a unit step disturbance \(d(t)\) is ______
(rounded off to two decimal places).

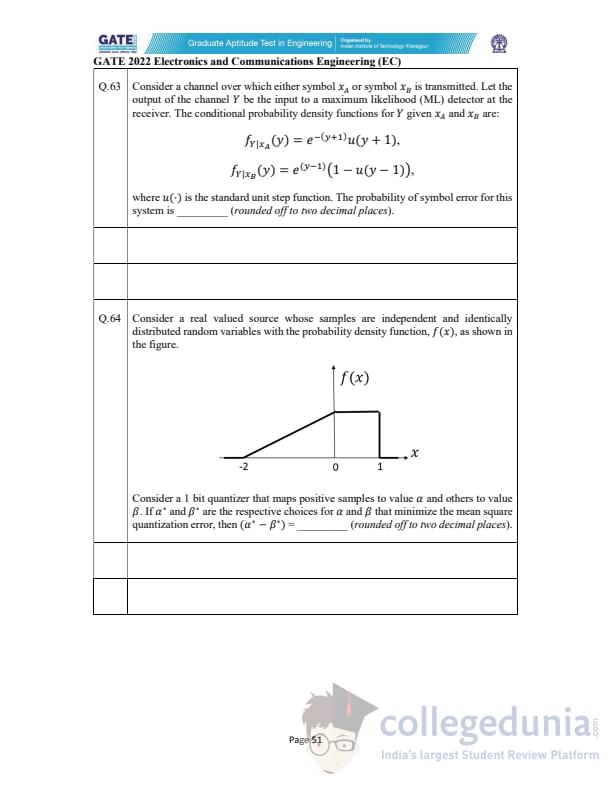
A discrete memoryless channel with three inputs and outputs has transition probabilities as shown.
The parameter \(\alpha \in [0.25,1]\).
Find the value of \(\alpha\) that maximizes channel capacity (rounded to two decimals).
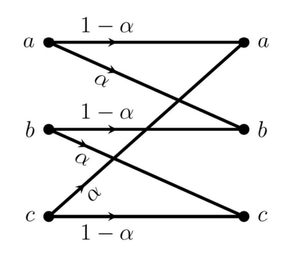
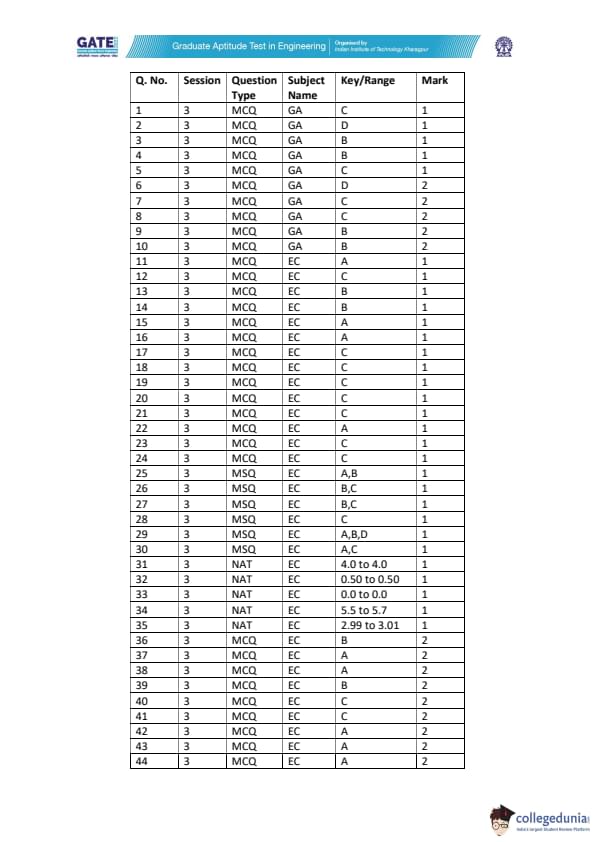
A (7,4) Hamming code is used over a BSC with flip probability \(\epsilon = 0.1\).
A transmitted codeword is decoded correctly if at most one bit error occurs.
Find the probability of correct decoding (rounded to two decimals).
Consider a channel where either symbol \(x_A\) or symbol \(x_B\) is transmitted.
The conditional PDFs of \(Y\) given \(x_A\) and \(x_B\) are:
\[ f_{Y|x_A}(y) = e^{-(y+1)}u(y+1), \qquad f_{Y|x_B}(y) = e^{(y-1)}\left(1 - u(y-1)\right), \]
where \(u(\cdot)\) is the unit step function.
The probability of symbol error is ______ (rounded off to two decimal places).
Question 64:
Consider a real valued source whose samples are independent and identically distributed random variables with the probability density function, f(x), as shown in the figure.

Consider a 1 bit quantizer that maps positive samples to value \(\alpha\) and others to value \(\beta\). If \(\alpha\)∗ and \(\beta\)∗ are the respective choices for \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) that minimize the mean square quantization error, then \((\alpha^* - \beta^*)\) = _________ (rounded off to two decimal places).
View Solution
PDF description from the figure:
- Linear from \(x=-2\) to \(x=0\), rising to maximum.
- Constant from \(x=0\) to \(x=1\).
Compute probabilities:
Total area must be 1.
Area of triangle (\(-2\) to \(0\)): \[ \frac{1}{2}(2)(1) = 1. \]
Area of rectangle (\(0\) to \(1\)): \[ 1 \times 1 = 1. \]
Normalize PDF: divide by 2.
Thus: \[ P(x<0) = \frac{1}{2}, \quad P(x>0) = \frac{1}{2}. \]
Optimum quantizer outputs are conditional means:
\[ \beta^\ = E[x|x<0], \qquad \alpha^\ = E[x|x>0]. \]
Compute \(\alpha^
): \[ \alpha^\ = E[x|0
): Shape is linear from \(-2\) to \(0\): \[ f(x) \propto (x+2). \]
Normalized on \([-2,0]\): \[ f(x) = \frac{x+2}{2}. \]
\[ \beta^\ = \int_{-2}^{0} x \frac{x+2}{2} dx = \frac{1}{2}\int_{-2}^{0}(x^2+2x)dx. \]
Compute integral: \[ \int(x^2+2x)dx = \frac{x^3}{3} + x^2. \]
Evaluate from -2 to 0:
At 0 → 0.
At -2 → \[ \frac{-8}{3} + 4 = \frac{4}{3}. \]
Thus: \[ \beta^\ = -\frac{1}{2}\cdot\frac{4}{3} = -\frac{2}{3} \approx -0.67. \]
Difference: \[ \alpha^\ - \beta^\ = 0.5 - (-0.67) \approx 1.17. \]
Thus: \[ \boxed{1.17} \quad (acceptable range: 1.15–1.18) \]
Quick Tip: For optimal quantizers, outputs equal conditional means of each region.
In an electrostatic field, the displacement vector is \[ \vec{D}(x,y,z) = (x^3\,\vec{i} + y^3\,\vec{j} + xy^2\,\vec{k})\ C/m^2. \]
A cube of side 1 m is centered at the origin with vertices at \((\pm 0.5, \pm 0.5, \pm 0.5)\).
Find the electric charge enclosed within the cube (rounded to two decimals).















Quick Links:
GATE 2022 EC Paper Analysis
All the candidates were supposed to attempt a total of 65 questions to score 100 marks in GATE 2022 EC question paper.
- IIT Kharagpur listed 14 MSQs (Multiple Choice Questions), 18 NATs (National Testing Agency), and 33 MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions).
- A total of 47 questions were listed from the core EC subject.
- The remaining 18 questions were related to the Engineering Mathematics and General Aptitude sections.
- The Signal and System topic carried only 4 questions carrying 6 marks. It accounted for the lowest weightage in GATE 2022 EC question paper.
- The General Aptitude section carried 10 questions of 15 marks
- The difficulty level of the General Aptitude was moderate
- 8 questions carrying 13 marks appeared from Engineering Mathematics section
Have a look at the below-mentioned table to see the details of the topics and number of questions and marks carried by the topics asked in the exam-
| Topics/Sections | 1 Mark Question | 2 Marks Questions | Marks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Theory | 2 | 3 | 8 |
| Analog Circuits | 4 | 3 | 10 |
| Digital Circuits | 3 | 4 | 11 |
| Control System | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| Signal and System | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| Communication System | 3 | 5 | 13 |
| Electromagnetics | 4 | 1 | 6 |
| Electronic Devices and Circuits | 2 | 3 | 8 |
| Engineering Mathematics | 3 | 5 | 13 |
| General Aptitude | 5 | 5 | 15 |
| Total | 30 | 35 | 100 |
Also Check:
Also Check:
GATE Previous Year Question Papers
| GATE 2023 Question Papers | GATE 2022 Question Papers | GATE 2021 Question Papers |
| GATE 2020 Question Papers | GATE 2019 Question Papers | GATE 2018 Question Papers |
Also Check:





Comments