GATE 2022 Aerospace Engineering (AE) Question Paper with Solutions PDFs can be downloaded from this page. The exam was successfully concluded by IIT Kharagpur on 13th February, 2022 in Afternoon Session (2:30 PM to 5:30 PM). The overall difficulty level of the question paper was found to be difficult. Aerodynamics and Structures carried the highest weightage in the exam, while Space Mechanics holds the least weightage.
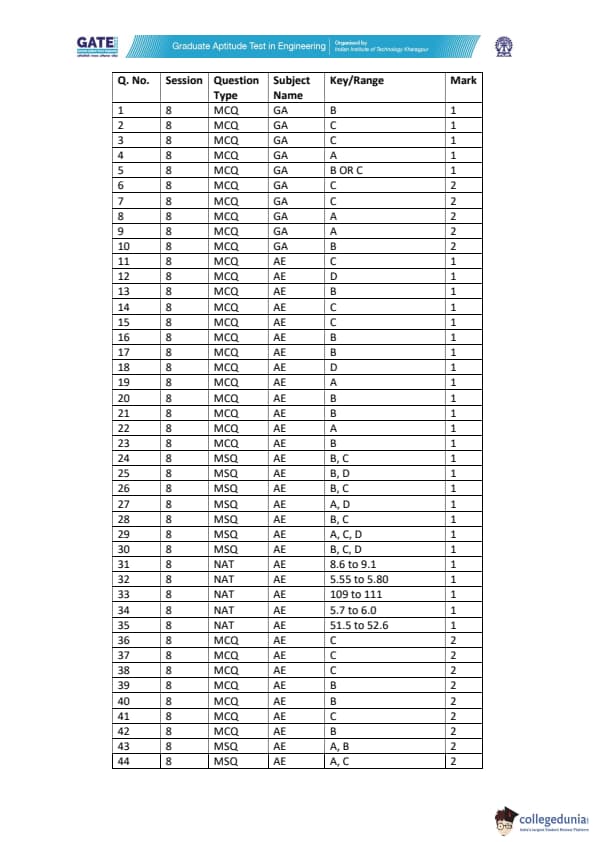
GATE 2022 Aerospace Engineering (AE) Question Paper with Solutions
| GATE 2022 Aerospace Engineering (AE) Question Paper | Check Solutions |

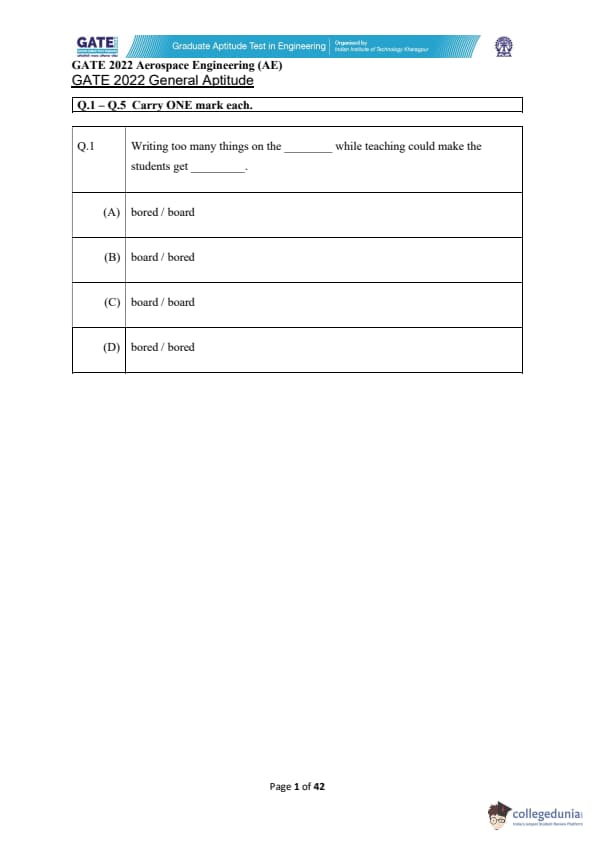
Writing too many things on the \hspace{2cm} while teaching could make the students get \hspace{2cm}.
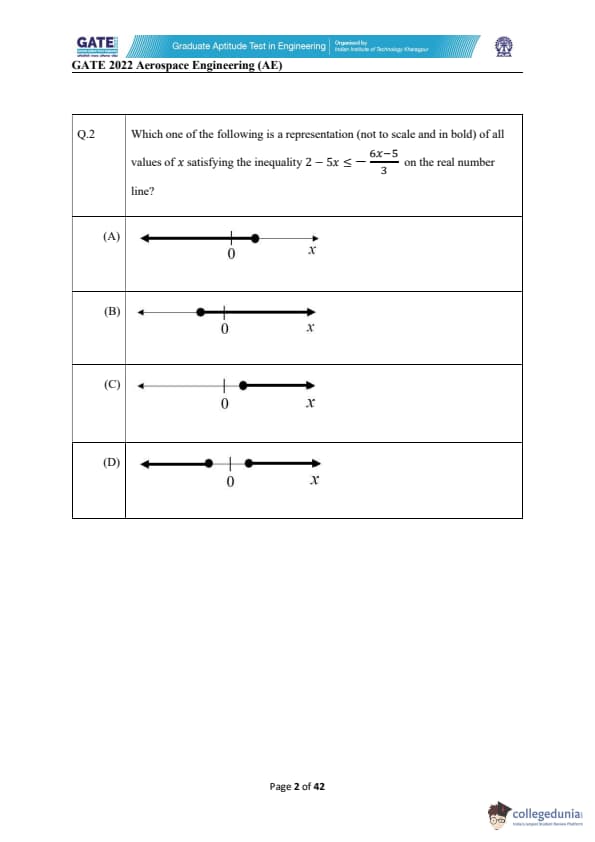
Which one of the following is a representation (not to scale and in bold) of all values of \( x \) satisfying the inequality \( 2 - 5x \leq \frac{-6x - 5}{3} \) on the real number line?

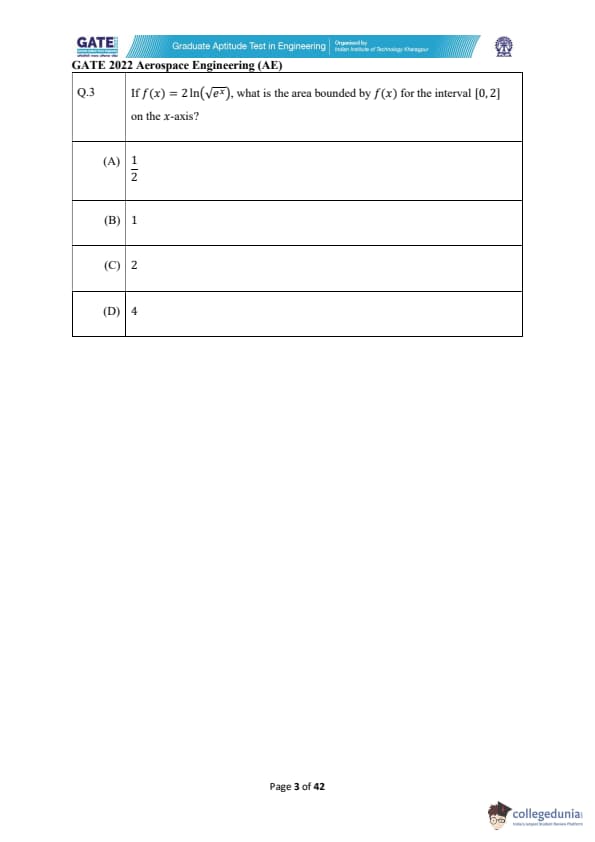
If \( f(x) = 2 \ln(\sqrt{e^x}) \), what is the area bounded by \( f(x) \) for the interval \([0, 2]\) on the x-axis?
A person was born on the fifth Monday of February in a particular year.
Which one of the following statements is correct based on the above information?
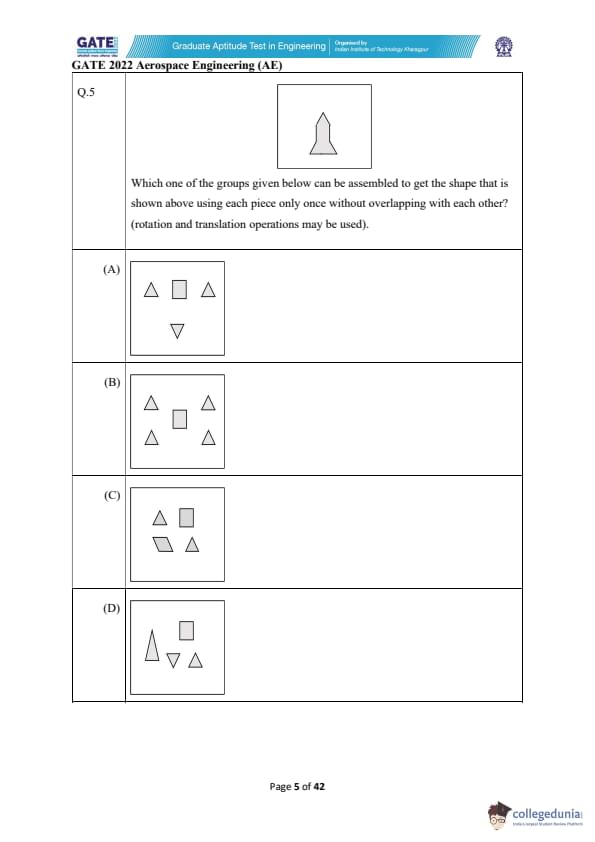
Which one of the groups given below can be assembled to get the shape that is shown above using each piece only once without overlapping with each other? (rotation and translation operations may be used).


Fish belonging to species S in the deep sea have skins that are extremely black (ultra-black skin). This helps them not only to avoid predators but also sneakily attack their prey. However, having this extra layer of black pigment results in lower collagen on their skin, making their skin more fragile.
For the past \( m \) days, the average daily production at a company was 100 units per day.
If today’s production of 180 units changes the average to 110 units per day, what is the value of \( m \)?
Consider the following functions for non-zero positive integers, \( p \) and \( q \):
\[ f(p, q) = p \times p \times p \times \cdots \times p = p^q \quad ; \quad f(p, 1) = p \] \[ g(p, q) = ppppp\cdots (up to q terms) \quad ; \quad g(p, 1) = p \]
Which one of the following options is correct based on the above?
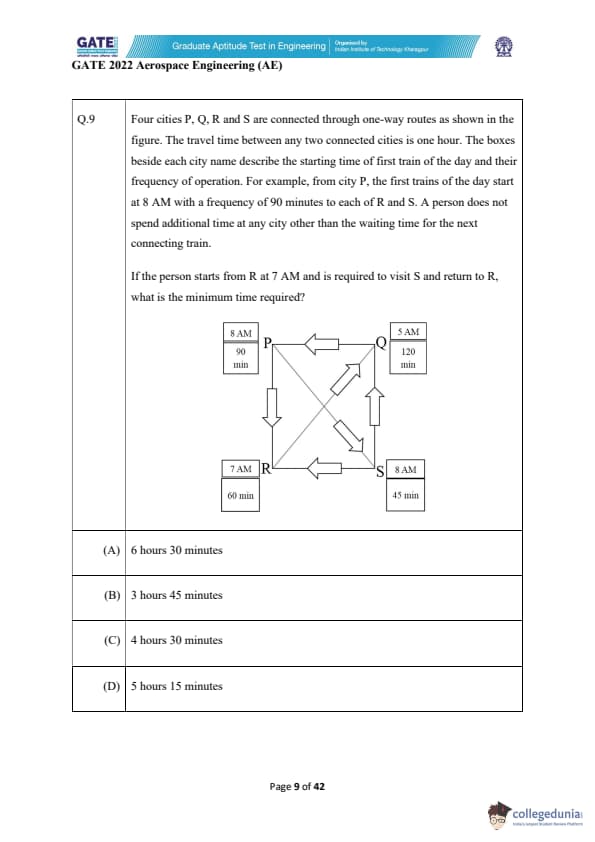
Four cities P, Q, R, and S are connected through one-way routes as shown in the figure. The travel time between any two connected cities is one hour. The boxes beside each city name describe the starting time of the first train of the day and their frequency of operation. For example, from city P, the first trains of the day start at 8 AM with a frequency of 90 minutes to each of R and S. A person does not spend additional time at any city other than the waiting time for the next connecting train.
If the person starts from R at 7 AM and is required to visit S and return to R, what is the minimum time required?

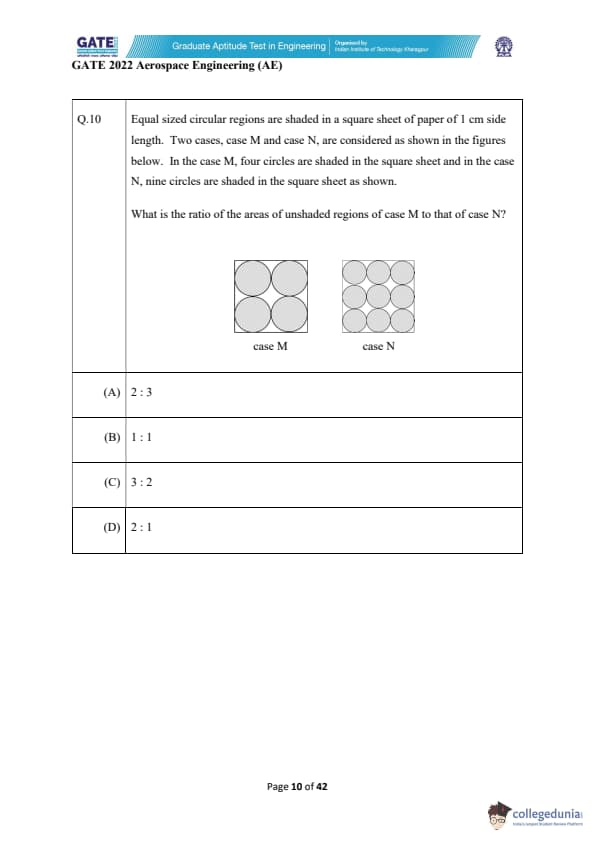
Equal sized circular regions are shaded in a square sheet of paper of 1 cm side length. Two cases, case M and case N, are considered as shown in the figures below. In the case M, four circles are shaded in the square sheet and in the case N, nine circles are shaded in the square sheet as shown.
What is the ratio of the areas of unshaded regions of case M to that of case N?

The equation of the straight line representing the tangent to the curve \(y = x^2\) at the point (1, 1) is
Let \(\hat{i}, \hat{j}, \hat{k}\) be the unit vectors in the x, y, and z directions, respectively. If the vector \(\hat{i} + \hat{j}\) is rotated about positive \(\hat{k}\) by \(135^\circ\), one gets
Let \(x\) be a real number and \(i=\sqrt{-1}\). Then the real part of \(\cos(ix)\) is
The point of maximum entropy on a Fanno-curve in a Temperature–Entropy (T–s) diagram represents the
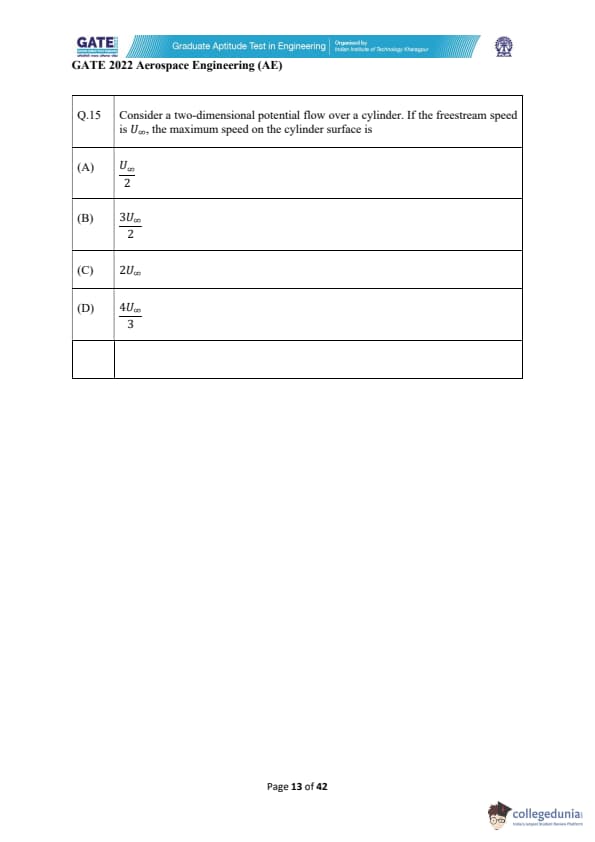
Consider a two-dimensional potential flow over a cylinder. If the freestream speed is \(U_{\infty}\), the maximum speed on the cylinder surface is
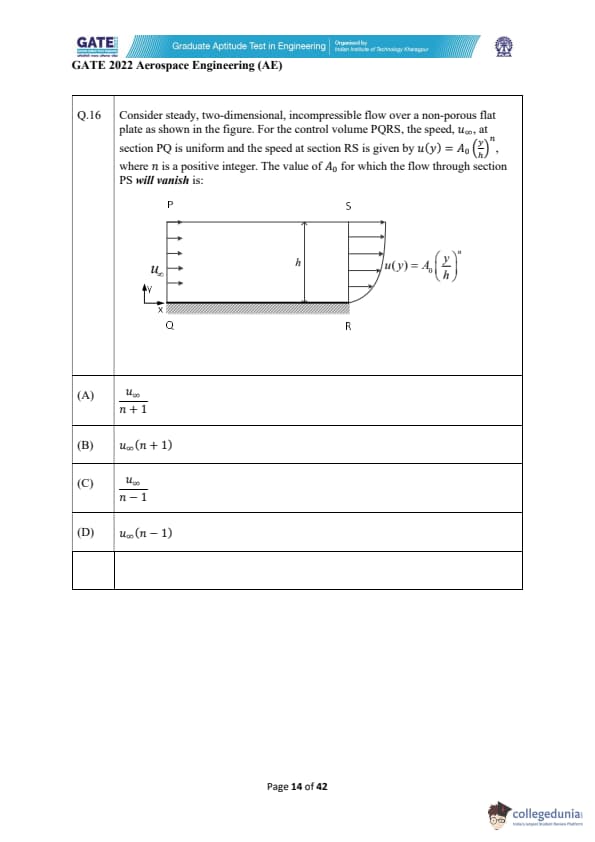
Consider steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow over a non-porous flat plate as shown in the figure. For the control volume PQRS, the speed \(u_{\infty}\) at section PQ is uniform and the speed at section RS is given by \(u(y)=A_0\left(\frac{y}{h}\right)^n\), where \(n\) is a positive integer. The value of \(A_0\) for which the flow through section PS will vanish is:

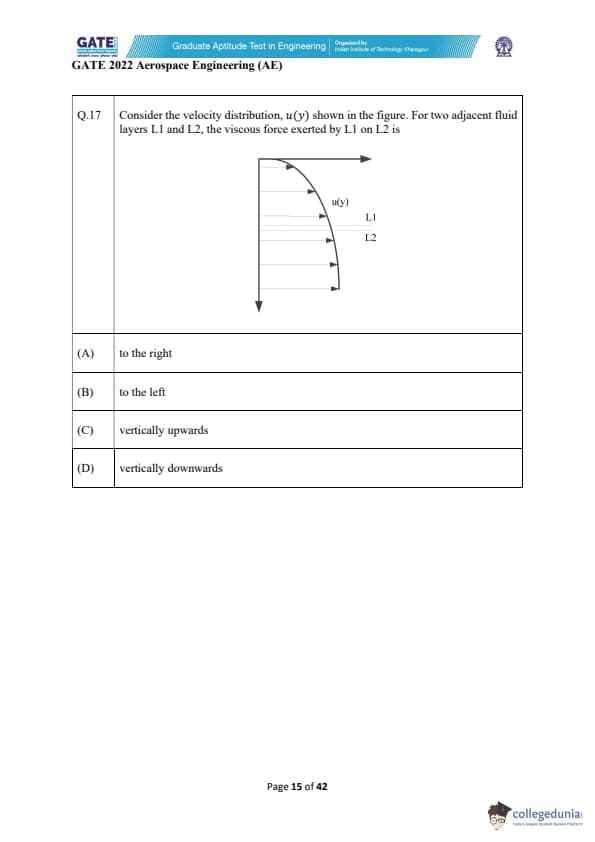
Consider the velocity distribution \(u(y)\) shown in the figure. For two adjacent fluid layers L1 and L2, the viscous force exerted by L1 on L2 is _________.

The service ceiling of an airplane is the altitude
Regarding the horizontal tail of a conventional airplane, which one of the following statements is true?
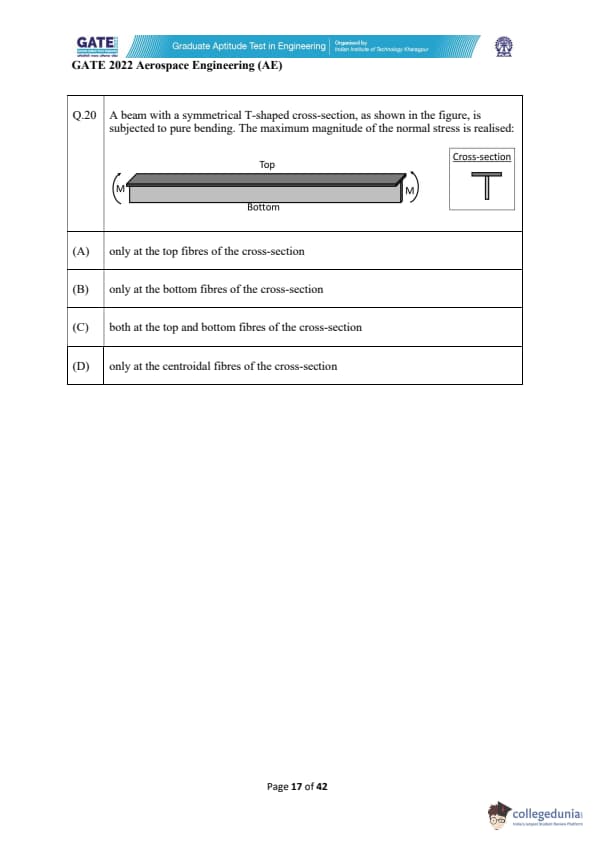
A beam with a symmetrical T-shaped cross-section, as shown in the figure, is subjected to pure bending. The maximum magnitude of the normal stress is realised:

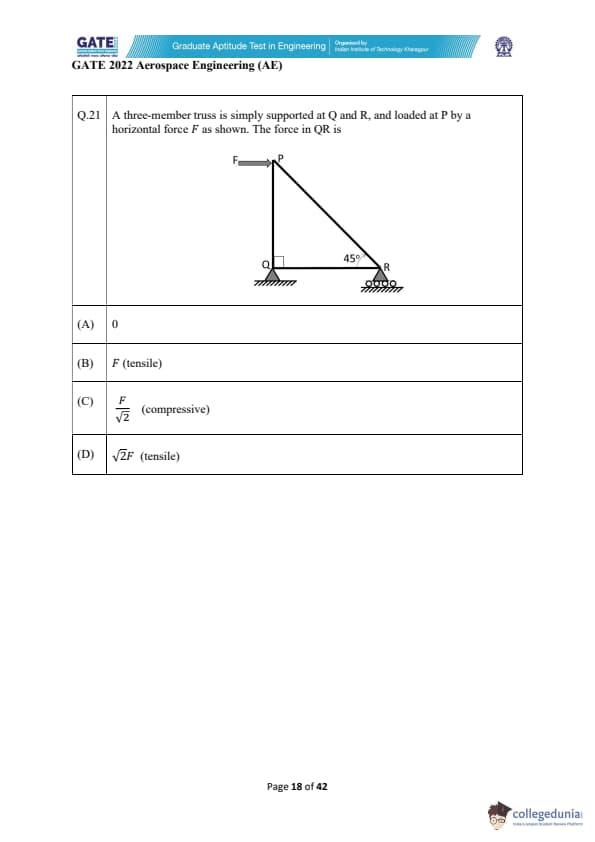
A three-member truss is simply supported at Q and R, and loaded at P by a horizontal force \( F \) as shown. The force in QR is

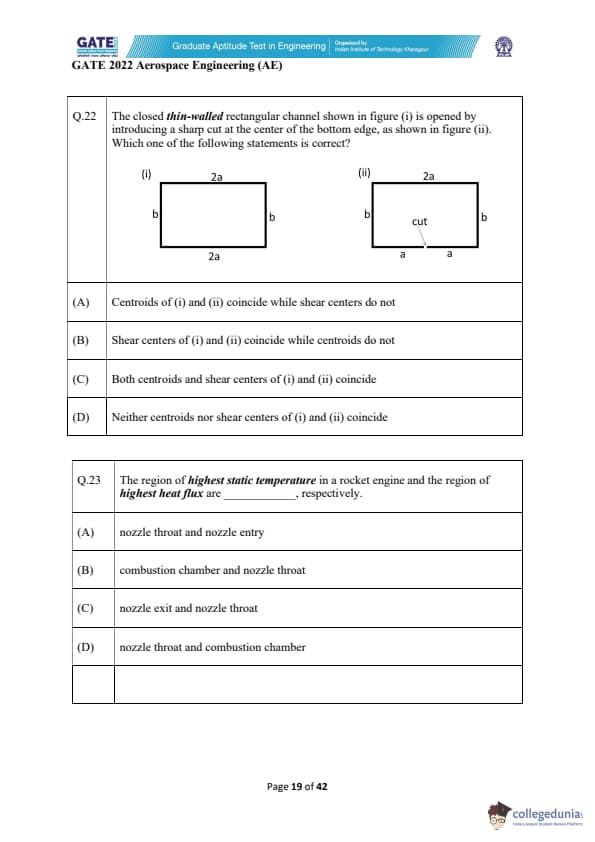
The closed thin-walled rectangular channel shown in figure (i) is opened by introducing a sharp cut at the center of the bottom edge, as shown in figure (ii). Which one of the following statements is correct?

The region of highest static temperature in a rocket engine and the region of highest heat flux are _______, respectively.
If \(\hat{a}, \hat{b}, \hat{c}\) are three mutually perpendicular unit vectors, then \(\hat{a} \cdot (\hat{b} \times \hat{c})\) can take the value(s):
Across an oblique shock wave in a calorifically perfect gas,
NACA 2412 airfoil has
For International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) up to 11 km, which of the following statement(s) is/are true?
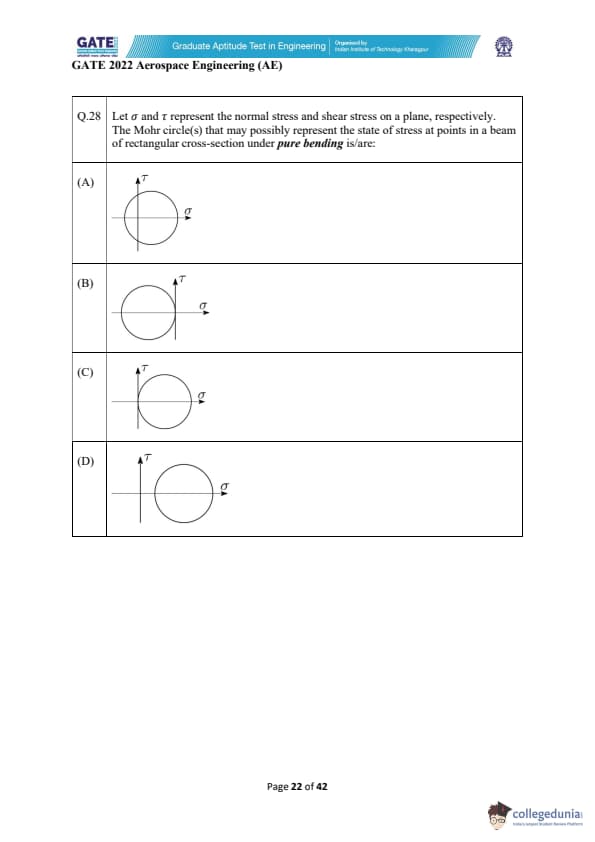
Let \(\sigma\) and \(\tau\) represent the normal stress and shear stress on a plane, respectively. The Mohr circle(s) that may possibly represent the state of stress at points in a beam of rectangular cross-section under \textit{pure bending is/are:

An isotropic linear elastic material point under plane strain condition in the x–y plane always obeys:
A high-pressure-ratio multistage axial compressor encounters an extreme loading mismatch during starting. Which of the following technique(s) can be used to alleviate this problem?
The arc length of the parametric curve: \( x=\cos\theta,\; y=\sin\theta,\; z=\theta \) from \( \theta=0 \) to \( \theta=2\pi \) is equal to _________ (round off to one decimal place).
An unpowered glider is flying at a glide angle of 10 degrees. Its lift-to-drag ratio is _________ (round off to two decimal places).
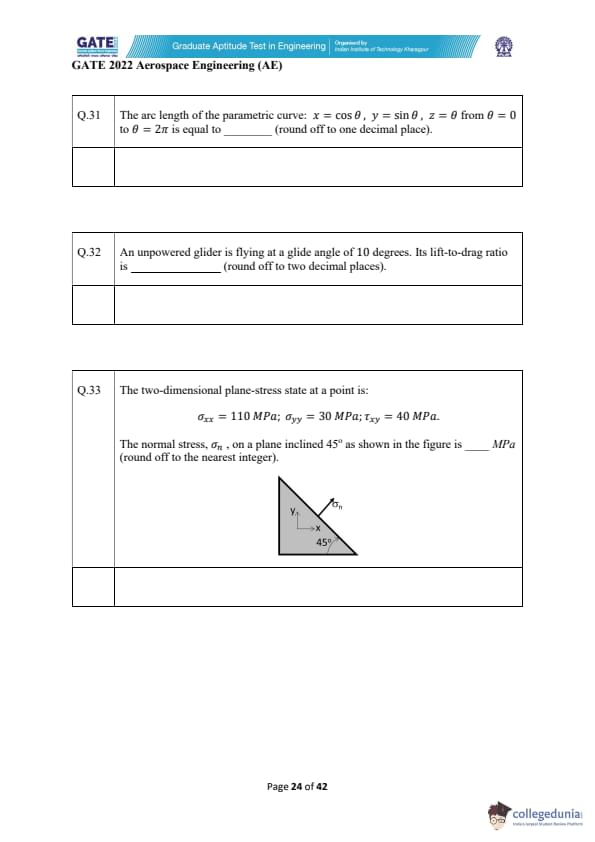
The two-dimensional plane-stress state at a point is: \[ \sigma_{xx} = 110\,MPa,\quad \sigma_{yy} = 30\,MPa,\quad \tau_{xy} = 40\,MPa. \]
The normal stress \(\sigma_n\) on a plane inclined at \(45^\circ\) as shown is (round off to the nearest integer).

In a static test, a turbofan engine with bypass ratio of 9 has core hot exhaust speed 1.5 times that of fan exhaust speed. The engine is operated at a fuel–air ratio of \(f=0.03\). Both the fan and the core streams have no pressure thrust. The ratio of fan thrust to thrust from the core engine is (round off to one decimal place).
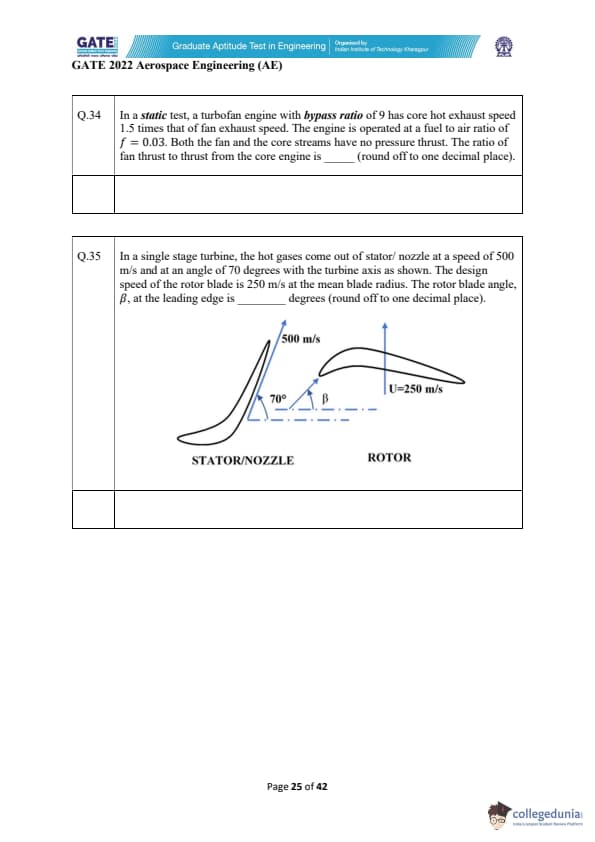
In a single stage turbine, the hot gases come out of stator/nozzle at a speed of 500 m/s and at an angle of 70 degrees with the turbine axis as shown. The design speed of the rotor blade is 250 m/s at the mean blade radius. The rotor blade angle, \( \beta \), at the leading edge is _________ degrees (round off to one decimal place).

The height of a right circular cone of maximum volume that can be enclosed within a hollow sphere of radius \(R\) is
Consider the differential equation \(\frac{d^2y}{dx^2} - 2 \frac{dy}{dx} + y = 0\). The boundary conditions are \(y = 0\) and \(\frac{dy}{dx} = 1\) at \(x = 0\). Then the value of \(y\) at \(x = \frac{1}{2}\) is
Consider the partial differential equation \(\frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial x^2} + \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial y^2} = 0\) where \(x, y\) are real.
If \(f(x, y) = a(x)b(y)\), where \(a(x)\) and \(b(y)\) are real functions, which one of the following statements can be true?
A cylindrical object of diameter 900 mm is designed to move axially in air at 60 m/s. Its drag is estimated on a geometrically half-scaled model in water, assuming flow similarity.
Co-efficients of dynamic viscosity and densities for air and water are \(1.86 \times 10^{-5}\) Pa-s, 1.2 kg/m\(^3\) and \(1.01 \times 10^{-3}\) Pa-s, 1000 kg/m\(^3\) respectively.
Drag measured for the model is 2280 N. Drag experienced by the full-scale object is ___ N (rounded off to the nearest integer).
Consider a conventional subsonic fixed-wing airplane. \(e\) is the Oswald efficiency factor and \(AR\) is the aspect ratio. Corresponding to the minimum \(\left(\frac{C_D}{C_L^{3/2}}\right)\), which of the following relations is true?
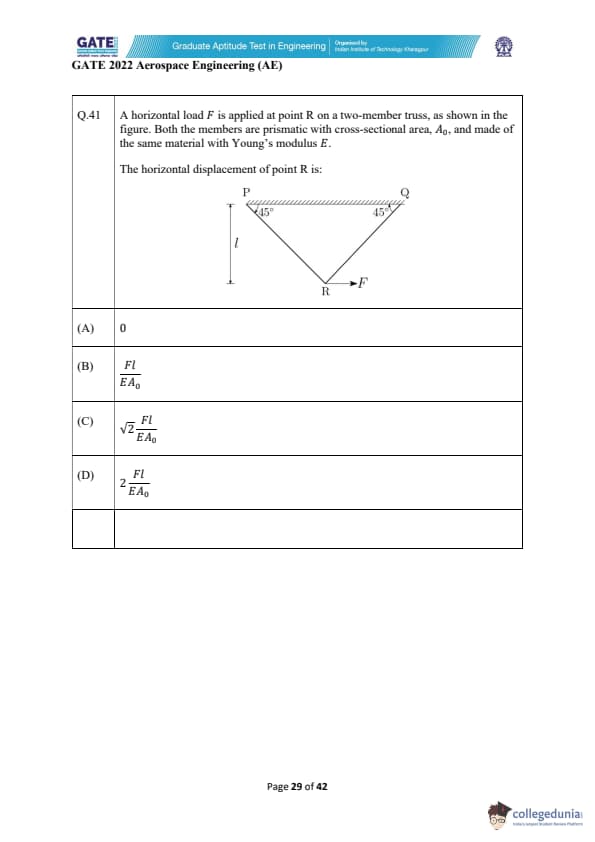
A horizontal load \(F\) is applied at point R on a two-member truss, as shown in the figure. Both the members are prismatic with cross-sectional area \(A_0\), and made of the same material with Young's modulus \(E\).
The horizontal displacement of point R is:

Which of the following is NOT always true for a combustion process taking place in a closed system?
The real function \( y = \sin^2(|x|) \) is
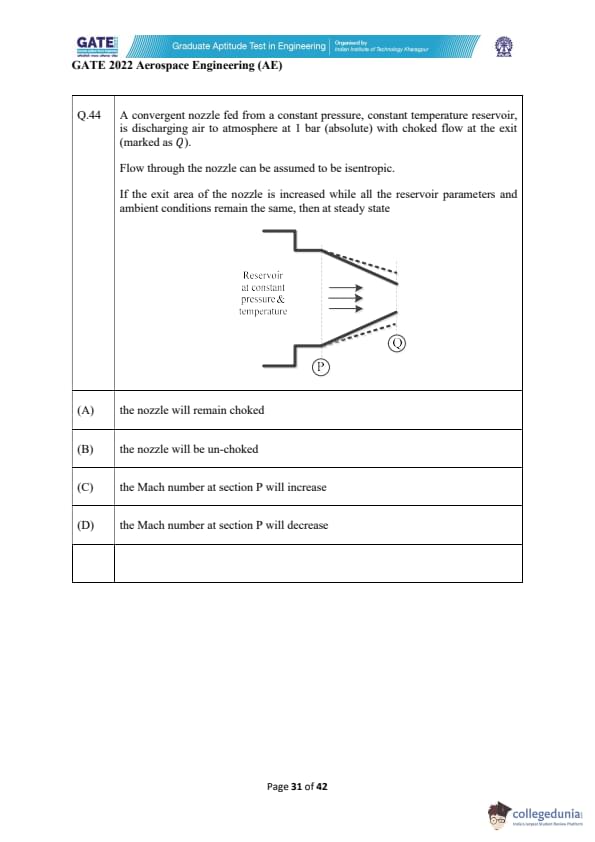
A convergent nozzle fed from a constant pressure, constant temperature reservoir, is discharging air to atmosphere at 1 bar (absolute) with choked flow at the exit (marked as \(Q\)).
Flow through the nozzle can be assumed to be isentropic.
If the exit area of the nozzle is increased while all the reservoir parameters and ambient conditions remain the same, then at steady state

For a conventional airplane in straight, level, constant velocity flight condition, which of the following condition(s) is/are possible on Euler angles (\(\phi, \theta, \psi\)), angle of attack (\(\alpha\)) and the sideslip angle (\(\beta\))?
Consider a high Earth-orbiting satellite of angular momentum per unit mass \(\vec{h}\) and eccentricity \(e\). The mass of the Earth is \(M\) and \(G\) is the universal gravitational constant.
The distance between the satellite’s center of mass and the Earth’s center of mass is \(r\), the true anomaly is \(\theta\), and the phase angle is zero.
Which of the following statements is/are true?
A rocket operates at an absolute chamber pressure of 20 bar to produce thrust \(F_1\).
The hot exhaust is optimally expanded to 1 bar (absolute pressure) using a convergent-divergent nozzle with exit to throat area ratio \(\left(\frac{A_e}{A_t}\right)\) of 3.5 and thrust coefficient, \(C_{F,1} = 1.42\).
The same rocket when operated at an absolute chamber pressure of 50 bar produces thrust \(F_2\) and the thrust coefficient is \(C_{F,2}\).
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
The vector field \( \vec{v} = x^3 \hat{i} + y^3 \hat{j} + z^3 \hat{k} \) is a vector field where \( \hat{i}, \hat{j}, \hat{k} \) are the base vectors of a Cartesian coordinate system.
Using the Gauss divergence theorem, the value of the outward flux of the vector field over the surface of a sphere of unit radius centered at the origin is _________ (rounded off to one decimal place).
The largest eigenvalue of the given matrix is: \[ \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 1
1 & 0 & 1
1 & 1 & 0
\end{bmatrix} \]
A rotational velocity field in an air flow is given as \( \vec{V} = a y \hat{i} + b x \hat{j} \), with \( a = 10 \, s^{-1} \), \( b = 20 \, s^{-1} \).
The air density is 1.0 kg/m\(^3\) and the pressure at \( (x, y) = (0, 0) \) is 100 kPa.
Neglecting gravity, the pressure at \( (x, y) = (6 \, m, 8 \, m) \) is _________ kPa (rounded off to the nearest integer).
Consider a circulation distribution over a finite wing given by the equation below.
\[ \Gamma(y) = \begin{cases} \Gamma_0 \left(1 - \frac{2y}{b}\right) & if 0 \leq y \leq \frac{b}{2},
\Gamma_0 \left(1 + \frac{2y}{b}\right) & if -\frac{b}{2} \leq y \leq 0, \end{cases} \]
The wingspan \( b \) is 10 m, the maximum circulation \( \Gamma_0 \) is 20 m\(^2\)/s, density of air is 1.2 kg/m\(^3\), and the free stream speed is 80 m/s.
The lift over the wing is _________ N (rounded off to the nearest integer).
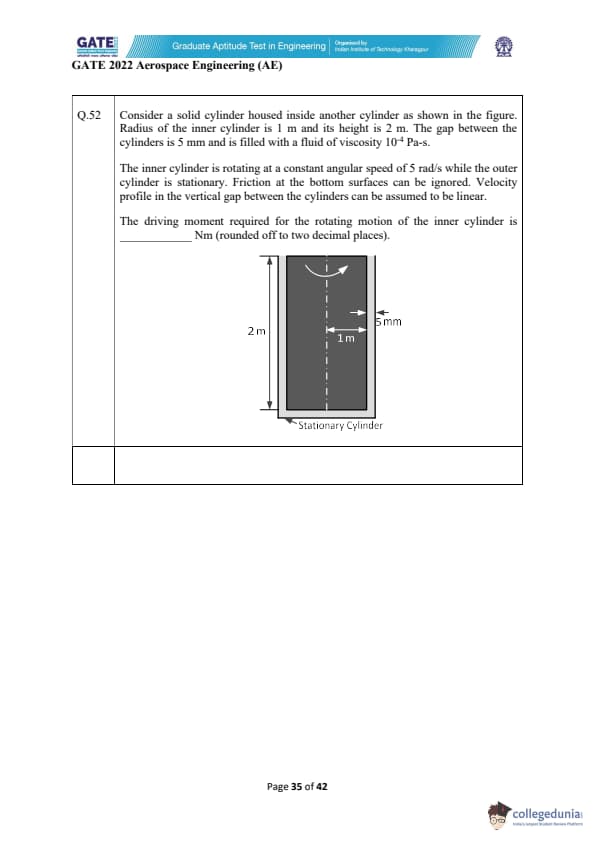
Consider a solid cylinder housed inside another cylinder as shown in the figure. Radius of the inner cylinder is 1 m and its height is 2 m. The gap between the cylinders is 5 mm and is filled with a fluid of viscosity \( 10^{-4} \) Pa-s.
The inner cylinder is rotating at a constant angular speed of 5 rad/s while the outer cylinder is stationary. Friction at the bottom surfaces can be ignored. Velocity profile in the vertical gap between the cylinders can be assumed to be linear.
The driving moment required for the rotating motion of the inner cylinder is _________ Nm (rounded off to two decimal places).

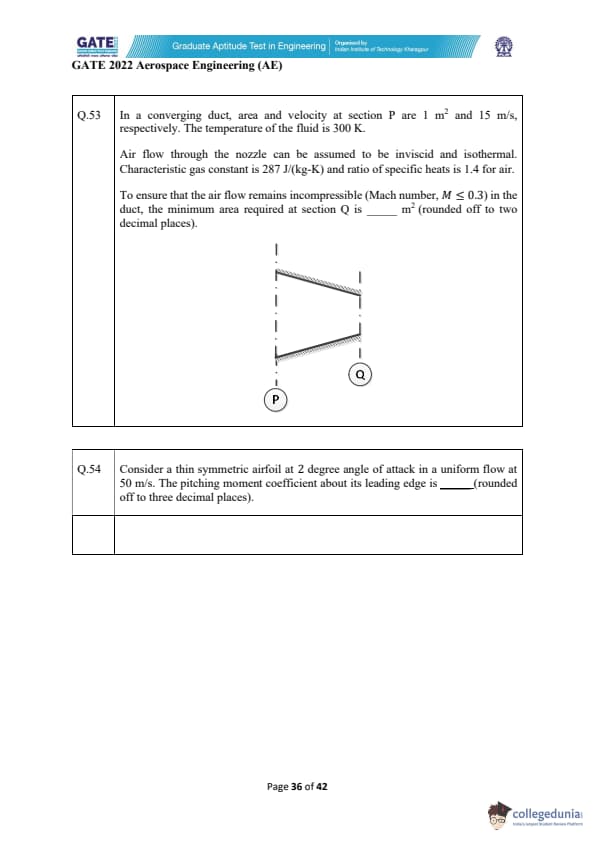
In a converging duct, area and velocity at section P are 1 m\(^2\) and 15 m/s, respectively. The temperature of the fluid is 300 K.
Air flow through the nozzle can be assumed to be inviscid and isothermal. Characteristic gas constant is 287 J/(kg-K) and the ratio of specific heats is 1.4 for air.
To ensure that the air flow remains incompressible (Mach number, \( M \leq 0.3 \)) in the duct, the minimum area required at section Q is _________ m\(^2\) (rounded off to two decimal places).

Consider a thin symmetric airfoil at a 2 degree angle of attack in a uniform flow at 50 m/s. The pitching moment coefficient about its leading edge is _________ (rounded off to three decimal places).
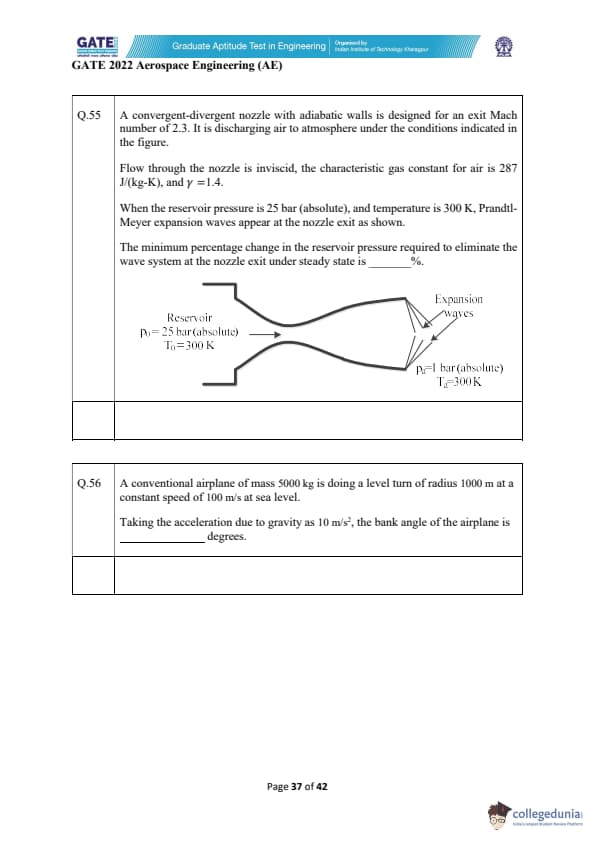
A convergent-divergent nozzle with adiabatic walls is designed for an exit Mach number of 2.3. It is discharging air to atmosphere under the conditions indicated in the figure.
Flow through the nozzle is inviscid, the characteristic gas constant for air is 287 J/(kg-K), and \( \gamma = 1.4 \).
When the reservoir pressure is 25 bar (absolute), and temperature is 300 K, Prandtl-Meyer expansion waves appear at the nozzle exit as shown.
The minimum percentage change in the reservoir pressure required to eliminate the wave system at the nozzle exit under steady state is _________ %.

A conventional airplane of mass 5000 kg is doing a level turn of radius 1000 m at a constant speed of 100 m/s at sea level.
Taking the acceleration due to gravity as 10 m/s\(^2\), the bank angle of the airplane is _________ degrees.
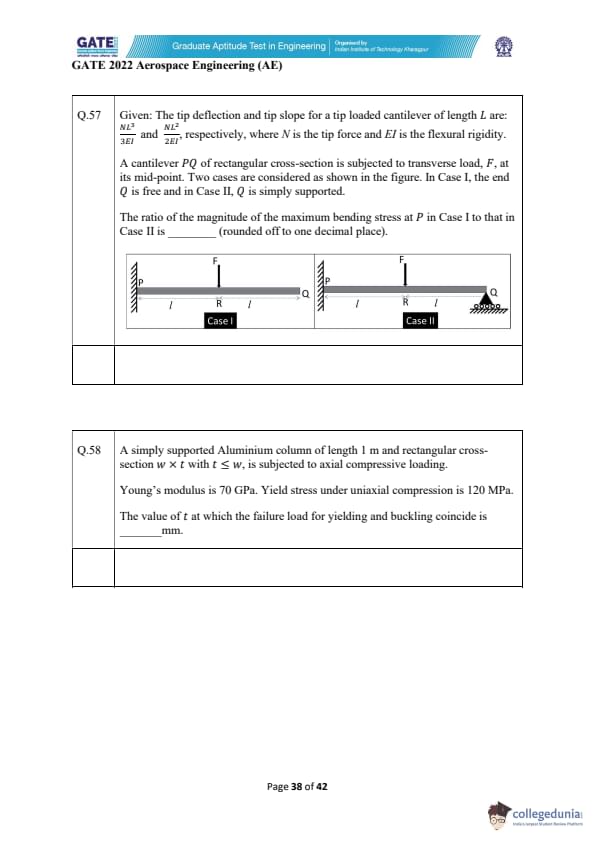
Given: The tip deflection and tip slope for a tip-loaded cantilever of length \( L \) are: \[ \delta = \frac{NL^3}{3EI} \quad and \quad \theta = \frac{NL^2}{2EI}, \]
where \( N \) is the tip force and \( EI \) is the flexural rigidity.
A cantilever \( PQ \) of rectangular cross-section is subjected to transverse load, \( F \), at its mid-point. Two cases are considered as shown in the figure. In Case I, the end \( Q \) is free and in Case II, \( Q \) is simply supported.
The ratio of the magnitude of the maximum bending stress at \( P \) in Case I to that in Case II is _________ (rounded off to one decimal place).

A simply supported Aluminium column of length 1 m and rectangular cross-section \( w \times t \) with \( t \leq w \), is subjected to axial compressive loading.
Young’s modulus is 70 GPa. Yield stress under uniaxial compression is 120 MPa.
The value of \( t \) at which the failure load for yielding and buckling coincide is _________ mm.
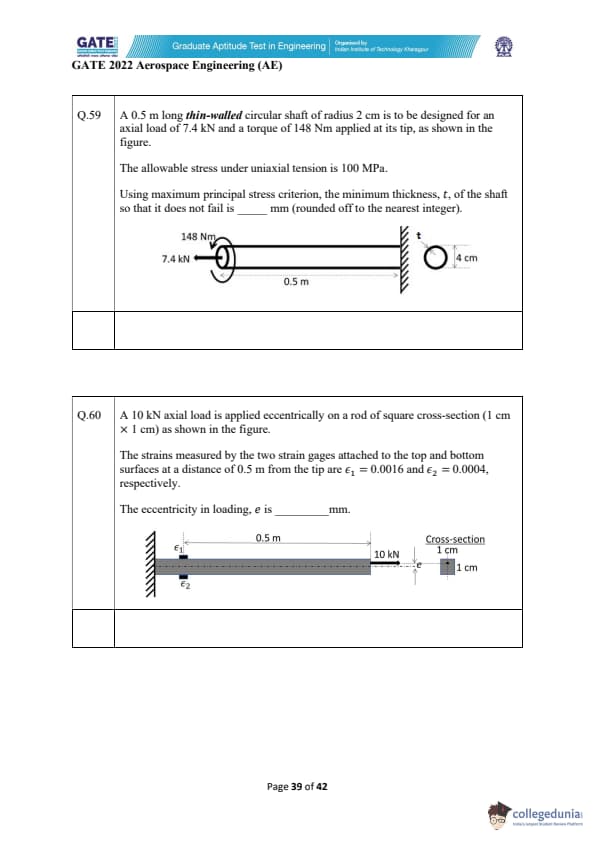
A 0.5 m long thin-walled circular shaft of radius 2 cm is to be designed for an axial load of 7.4 kN and a torque of 148 Nm applied at its tip, as shown in the figure.
The allowable stress under uniaxial tension is 100 MPa.
Using the maximum principal stress criterion, the minimum thickness, \( t \), of the shaft so that it does not fail is _________ mm (rounded off to the nearest integer).

A 10 kN axial load is applied eccentrically on a rod of square cross-section (1 cm \(\times\) 1 cm) as shown in the figure.
The strains measured by the two strain gages attached to the top and bottom surfaces at a distance of 0.5 m from the tip are \( \varepsilon_1 = 0.0016 \) and \( \varepsilon_2 = 0.0004 \), respectively.
The eccentricity in loading, \( e \), is _________ mm.

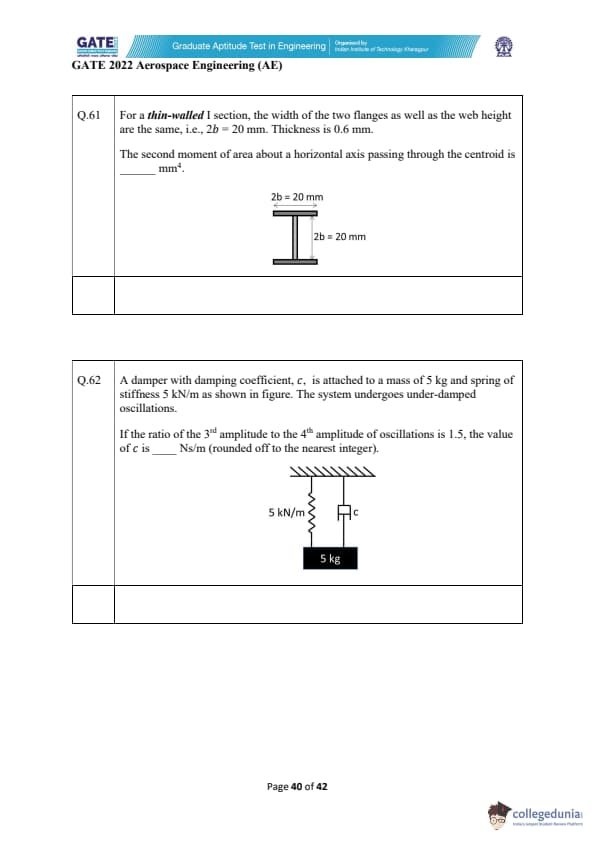
For a thin-walled I section, the width of the two flanges as well as the web height are the same, i.e., \( 2b = 20 \, mm \). Thickness is 0.6 mm.
The second moment of area about a horizontal axis passing through the centroid is _________ mm\(^4\).

A damper with damping coefficient, \( c \), is attached to a mass of 5 kg and spring of stiffness 5 kN/m as shown in the figure. The system undergoes under-damped oscillations.
If the ratio of the 3rd amplitude to the 4th amplitude of oscillations is 1.5, the value of \( c \) is _________ Ns/m (rounded off to the nearest integer).

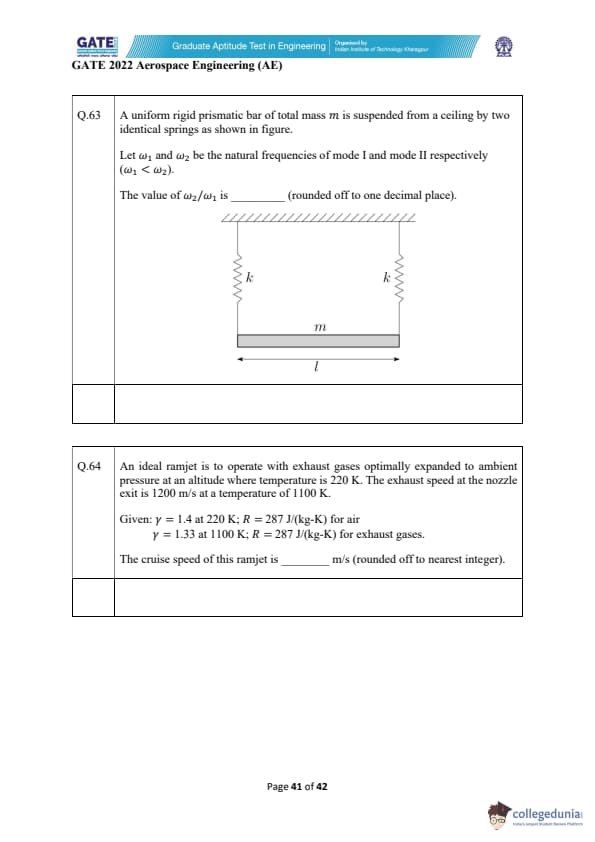
A uniform rigid prismatic bar of total mass \( m \) is suspended from a ceiling by two identical springs as shown in the figure.
Let \( \omega_1 \) and \( \omega_2 \) be the natural frequencies of mode I and mode II respectively (with \( \omega_1 < \omega_2 \)).
The value of \( \omega_2/\omega_1 \) is _________ (rounded off to one decimal place).

An ideal ramjet is to operate with exhaust gases optimally expanded to ambient pressure at an altitude where temperature is 220 K. The exhaust speed at the nozzle exit is 1200 m/s at a temperature of 1100 K.
Given: \( \gamma = 1.4 \) at 220 K; \( R = 287 \, J/(kg-K) \) for air; \( \gamma = 1.33 \) at 1100 K; \( R = 287 \, J/(kg-K) \) for exhaust gases.
The cruise speed of this ramjet is _________ m/s (rounded off to nearest integer).
A multistage axial compressor takes in air at 1 atm, 300 K and compresses it to a minimum of 5 atm.
The mean blade speed is 245 m/s and work coefficient, \( \frac{\Delta c \, \theta}{U} \), is 0.55 for each stage.
For air, use \( C_p = 1005 \, J/(kg-K) \), \( R = 287 \, J/(kg-K) \), and \( \gamma = 1.4 \).
If the compression is isentropic, the number of stages required is _________ (rounded off to the next higher integer).















Quick Links:
GATE 2022 AE Detailed Paper Analysis
The listed questions in GATE 2022 AE were related to 7 topics including General Aptitude and Engineering Mathematics. The below-mentioned table is showing the details of the important topics as per the carried questions-
| Sections/Topics | Question Frequency |
|---|---|
| General Aptitude | 10 |
| Flight Mechanics | 7 |
| Space Mechanics | 1 |
| Engineering Mathematics | 11 |
| Propulsion | 8 |
| Aerodynamics | 14 |
| Structures | 14 |
| Total | 65 |
- The General Aptitude section was rated moderate to tough, while the subject-specific section was rated a difficult section to attempt
Also Check:
GATE 2022 AE Question Details
There were three types of questions (MCQs, MSQs, and NATs) that constituted the question paper of GATE 2022 AE. Kindly follow the below-mentioned table in order to get details of MCQs, MSQs, and NATs as per the carried marks-
| Question Types | Question Frequency | Carried Marks |
|---|---|---|
| No. Of 1 mark MCQs | 18 | 18 |
| No. Of 2 marks MCQs | 12 | 24 |
| No. Of 1 mark MSQs | 7 | 7 |
| No. Of 2 marks MSQs | 5 | 10 |
| No. Of 1 mark NATs | 5 | 5 |
| No. Of 2 marks NATs | 18 | 36 |
| Total | 65 | 100 |
- MCQs hold the maximum weightage in the exam, while NATs hold the least weightage
GATE 2022 AE: Exam Pattern and Marking Scheme
- GATE 2022 AE asked both MCQs and NATs. It was held online via CBT mode
- As per the specified marking scheme by IIT Delhi, from the final score, ⅓ and ⅔ marks would be reduced for each wrong MCQ carried 1 and 2 marks
- Wrong attempted NATs were not supposed to bring any kind of deduction in the final achieved marks
GATE Previous Year Question Papers
| GATE 2022 Question Papers | GATE 2021 Question Papers | GATE 2020 Question Papers |
| GATE 2019 Question Papers | GATE 2018 Question Papers | GATE 2017 Question Papers |





Comments