JEE Main reduced syllabus from past years indicates that around 15% of the topics have been removed from the JEE Main syllabus PDF. However, 85% of the JEE Main syllabus remains consistent with earlier versions.
- Topics like "Capacitors and Capacitance," "Communication Devices," etc. have been reduced from JEE Main Physics syllabus.
- From JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus, topics like "States of Matter," "Surface Chemistry," and "Environmental Chemistry" have been reduced.
- The mathematics syllabus for JEE Main has shown a reduction in topics like "Mathematical Induction," "Mathematical Reasoning," and some of the topics in "Three-Dimensional Geometry."
JEE Main syllabus 2026 is yet to be released and is expected to remain the same as that in 2025 syllabus for JEE Main.
Also Read
Key Summary
- Around 15% of the JEE Main syllabus has been reduced across different subjects.
- 85% of the JEE Main syllabus 2026 has remained the same.
- From the JEE Main Physics syllabus, removed chapters include Capacitors and Capacitance, Communication Devices, etc.
- From Chemistry, chapters like States of Matter, Surface Chemistry, and Environmental Chemistry have been removed.
- Mathematical Reasoning and some of the topics in Three-Dimensional Geometry have been removed from JEE Main Mathematics syllabus
Which Chapters have been removed from JEE Main 2026?
The National Testing Agency (NTA) has revised the JEE Main syllabus in 2024, removing certain chapters and topics to better align with the NCERT curriculum. This year, the JEE Main syllabus 2026 is expected to remain the same.
Below is a subject-wise breakdown of the removed content in 2024:
| Subject | Chapter/Topic | Change |
|---|---|---|
| Physics | Communication Systems | Entire chapter removed |
| Experimental Skills | Specific topics removed | |
| Chemistry | States of Matter | Entire chapter removed |
| Surface Chemistry | Entire chapter removed | |
| s-Block Elements | Entire chapter removed | |
| Hydrogen | Entire chapter removed | |
| Environmental Chemistry | Entire chapter removed | |
| Polymers | Entire chapter removed | |
| Chemistry in Everyday Life | Entire chapter removed | |
| General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals | Entire chapter removed | |
| Atomic Structure | Topics on Thomson and Rutherford's atomic models and their limitations were removed | |
| Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry | Topics on physical quantities and their measurements, precision, accuracy, and significant figures were removed | |
| Mathematics | Mathematical Reasoning | Entire chapter removed |
| Mathematical Induction | Entire chapter removed | |
| Three-Dimensional Geometry | Specific topics removed |
- JEE Main 2026 Syllabus - Updated
- Is the JEE 2026 syllabus the same as the 2025?
- Comparison Analysis of JEE 2025 and JEE 2024
- Subject-Wise Changes in the JEE Main 2026 Syllabus
4.1 Key Changes in the JEE Main 2026 Exam Syllabus
4.2 Comparison of Syllabus Changes Over the Years (2025-2021)
4.3 Comparison of Weightage Over the Years (2025-2021)
4.4 Change and Updation in JEE Mains 2026 Syllabus of Paper 1 and Paper 2
4.5 Will JEE Main 2026 be tough?
4.6 Factors Influencing the Difficulty Level of JEE Main 2026
- JEE Main Syllabus 2026
5.1 JEE Main Syllabus 2026 for Physics
5.2 JEE Main Syllabus 2026 for Chemistry
5.3 JEE Main Syllabus 2026 for Mathematics
- JEE Main Reduced Syllabus FAQs
JEE Main Reduced Syllabus- Deleted Chapters
Candidates can go through the youtube video below to check the deleted chapters in JEE Main syllabus for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics.
JEE Main 2026 Syllabus - Updated
Candidates can check and download the JEE Main syllabus PDF in the table below.
| JEE Main Syllabus PDFs | Links |
|---|---|
| JEE Main 2026 Physics Syllabus PDF | Download PDF here |
| JEE Main 2026 Math Syllabus PDF | Download PDF here |
| JEE Main 2026 Chemistry Syllabus PDF | Download PDF here |
Is the JEE 2026 syllabus the same as the 2025?
The JEE Main 2026 syllabus is expected to remain nearly unchanged from the syllabus of 2025. In 2024, the NTA removed some topics from Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics.
- For Physics, the removal of topics such as "Capacitors and Capacitance," "Communication Devices," etc., and some experimental skills are undertaken.
- In Chemistry, the chapters "States of Matter," "Surface Chemistry," and "Environmental Chemistry" have been removed.
- Mathematics also reduced "Mathematical Induction," "Mathematical Reasoning," and some of the topics in "Three-Dimensional Geometry."
Comparison Analysis of JEE 2025 and JEE 2024
A comparison analysis between JEE Main 2024 and JEE Main 2025 is discussed in the table below.
- JEE Main 2025 was difficult compared to JEE Main 2024, with Mathematics as the most demanding section.
- Physics and Chemistry sections of JEE Main 2025 were moderate in difficulty level.
JEE Main Difficulty Level- 2024-25
| Subject | JEE Main 2024 | JEE Main 2025 | Change Observed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physics | Moderate to Easy | Moderate | Easier due to more direct questions |
| Chemistry | Moderate | Moderate | Increased focus on conceptual application |
| Mathematics | Moderate | Difficult | Shift towards application-based problems |
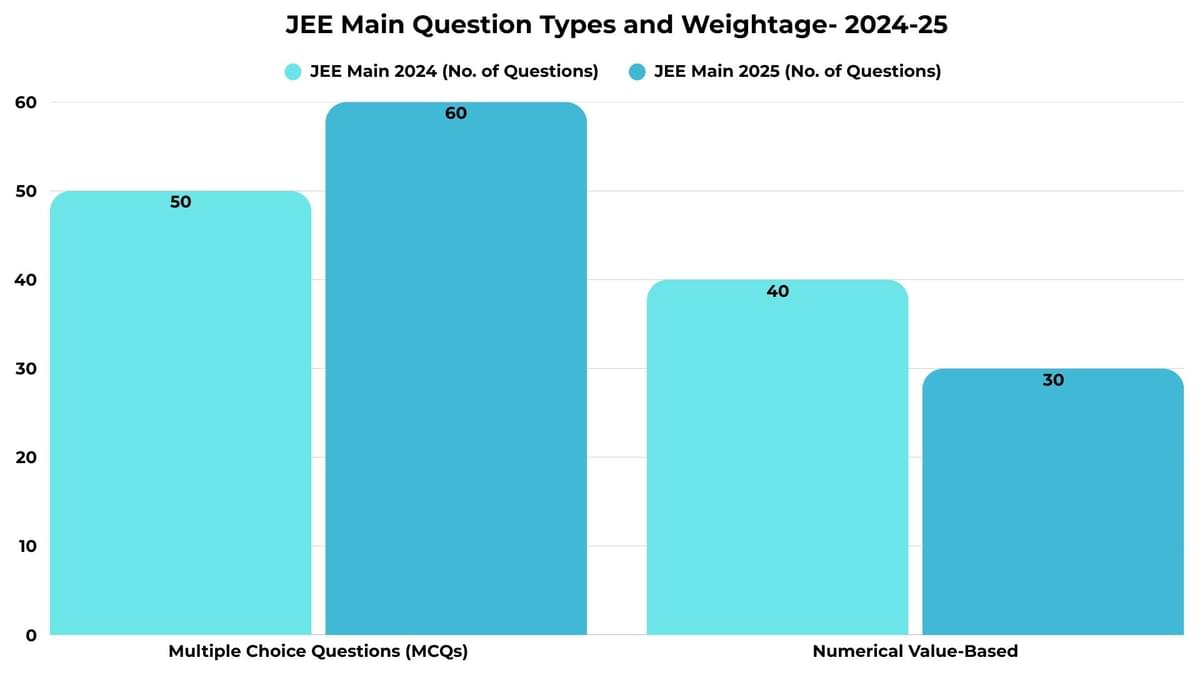
JEE Main Question Types and Weightage- 2024-25
As per the JEE Main 2025 paper analysis, 60 questions were asked as MCQs, with 20 MCQs from each section. However, 30 questions were asked as Numerical Value Based questions, out of which students were required to solve only 15 questions, with 5 questions from each section.
| Question Type | JEE Main 2024 (No. of Questions) | JEE Main 2025 (No. of Questions) |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) | 50 | 60 |
| Numerical Value-Based | 40 | 30 |
JEE Main High Weightage Topics- 2024-25
| Subject | JEE Main 2024 Top-Weight Chapters | JEE Main 2025 Top-Weight Chapters |
|---|---|---|
| Physics | Optics, Modern Physics | Optics, Rotational Motion, Units and Measurements, Electrostatics |
| Chemistry | Physical Chemistry, Biomolecules | Organic Chemistry, Coordination Compounds, Equilibrium |
| Mathematics | Algebra, Probability & Statistics | Calculus, Algebra |

Read More
- JEE Main Chapter Wise Weightage
- JEE Main Practice Papers
JEE Main Scoring Pattern- 2024-25
- The average score decreased from around 160 to 120 due to increased overall difficulty.
- Regional patterns showed better preparation among students from Rajasthan and Maharashtra.
| Parameter | JEE Main 2024 | JEE Main 2025 | Change Observed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Score | 160 | 120 | Slight improvement |
| High-Scoring Regions | Maharashtra, South India | Rajasthan, Maharashtra | Region-specific trends observed |
JEE Main Key Changes and Updates
- Balanced Mathematics: Application-based problems were emphasized more, providing a fairer distribution of easy, moderate, and difficult questions.
- Conceptual Chemistry: Increased focus on Physical Chemistry and Biomolecules required a deeper understanding of concepts.
- Increased Numerical Questions: More numerical questions demanded better calculation skills, reducing reliance on theoretical memorization.
- Physics Modernization: Shifting from classical mechanics to modern topics aligned with global academic trends.
“JEE Main 2024 introduced changes to make the exam more conceptual and skill-oriented, balancing difficulty across subjects. Students well-versed with NCERTs and adept at numerical problem-solving performed better.”
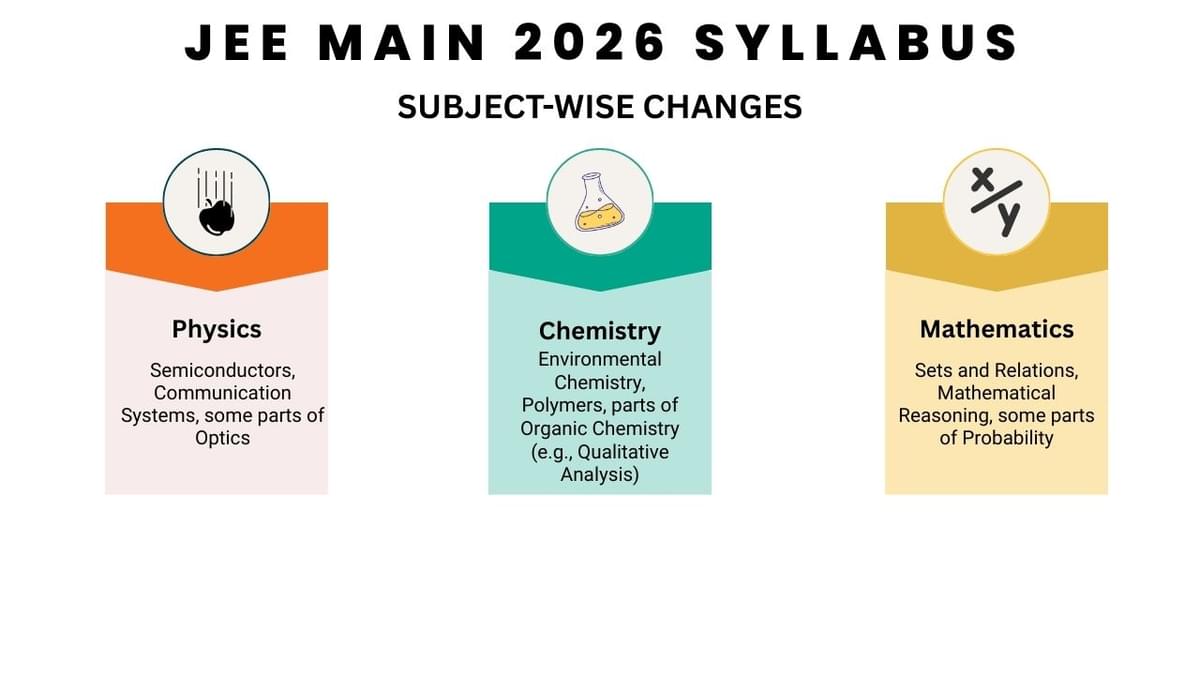
Subject-Wise Changes in the JEE Main 2026 Syllabus
As per the changes introduced in the JEE Main syllabus in the past years, Students can check the topics reduced from each subject of JEE Main 2026 below.
- From Physics, Semiconductors, Communication Systems, and some parts of Optics were removed.
- From Chemistry, Environmental Chemistry, Polymers, and parts of Organic Chemistry (e.g., Qualitative Analysis) are removed.
- From Mathematics, Sets and Relations, Mathematical Reasoning, and some parts of Probability were removed.
Changes in JEE Main Physics Syllabus
| Topic Status | Topics Removed | Key Topics Retained | Approximate Weightage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Removed Topics | Semiconductors, Communication Systems, some parts of Optics | Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Electrodynamics, Modern Physics | 35% |
| Content Change | 15% reduction in total syllabus | Greater emphasis on foundational concepts | - |
Changes in JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
| Topic Status | Topics Removed | Key Topics Retained | Approximate Weightage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Removed Topics | Environmental Chemistry, Polymers, parts of Organic Chemistry (e.g., Qualitative Analysis) | Physical Chemistry (basics), Inorganic Chemistry (Periodic Table, Bonding), Organic Chemistry (General Reactions) | 35% |
| Content Change | 18% reduction in total syllabus | Focused on high-impact areas | - |
Changes in JEE Main Mathematics Syllabus
| Topic Status | Topics Removed | Key Topics Retained | Approximate Weightage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Removed Topics | Sets and Relations, Mathematical Reasoning, and some parts of Probability | Calculus, Algebra, Coordinate Geometry | 30% |
| Content Change | 12% reduction in total syllabus | Retained topics essential for engineering studies | - |
Also Read
Key Changes in the JEE Main 2026 Exam Syllabus
- Physics: The chapters on "Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents" and "Optics" have been merged into a single chapter.
- Chemistry: The entire chapter on "P Block Elements" has been split into two chapters, specifically "Group 13 to Group 17 Elements and Group 18 Elements". The chapters on "Coordination Compounds" and "Environmental Chemistry" have been included in a single chapter.
- Mathematics: The chapter "Sets, Relations and Functions" has been divided into two chapters, "Sets and Relations" and "Functions". Three chapters on "Vectors and Three-Dimensional Geometry", "Linear Programming" have been amalgamated into one chapter.
Comparison of Syllabus Changes Over the Years (2025-2021)
| Year | Key Changes in Syllabus | Data Insights |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 | Significant reduction (12-18%) across subjects, aligning with NEP recommendations. | Streamlined syllabus targets conceptual clarity and reduced redundancy. |
| 2024 | Pilot reduction of less than 5% in certain areas to test response. | Over 1.2 million students benefited from reduced ambiguity in syllabus content. |
| 2023 | Introduction of slight topic-specific weightage adjustments. | Inclusion of modern topics like Machine Learning concepts in Physics. |
| 2022 | Restored to pre-pandemic levels, with minor tweaks. | 95% of the syllabus matched with NCERT curriculum. |
| 2021 | Slight adjustments due to COVID-19, and optional internal choices introduced in exams. | Reduction primarily focused on relieving students impacted by pandemic disruptions. |
Comparison of Weightage Over the Years (2025-2021)
JEE Main weightage of various subjects has shown a slight change over the years.
- Weightage of Physics in JEE Main syllabus was 32% in 2021, 33% in 2022, & 2024, 34% in 2023, and 35% in 2025.
- The weightage of JEE Main Chemistry was highest, 36% in 2021, and lowest in 2023 (33%).
- Mathematics weightage in JEE Main question paper was 32% in 2021 & 2022, 33% in 2023 & 2024, and 30% in 2025.
| Subject | 2025 Weightage (%) | 2024 Weightage (%) | 2023 Weightage (%) | 2022 Weightage (%) | 2021 Weightage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physics | 35 | 33 | 34 | 33 | 32 |
| Chemistry | 35 | 34 | 33 | 35 | 36 |
| Mathematics | 30 | 33 | 33 | 32 | 32 |
Also Read
Change and Updation in JEE Mains 2026 Syllabus of Paper 1 and Paper 2
The JEE Main 2026 syllabus for both Paper 1 (B.E./B.Tech) and Paper 2 (B.Arch/B.Planning) has undergone significant updates in the past years.
- JEE Main syllabus has witnessed a 15-25% reduction in syllabus in the past years.
- Mathematics weightage in JEE Main paper 1 has increased, and witnessed a decrease in JEE Main paper 2.
- The weightage of JEE Main physics syllabus has shown a reduction in Paper 1 of JEE Main.
| Category | Paper 1 | Paper 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Syllabus Reduction | 25% Reduction | 15% Reduction |
| Mathematics Weightage | 35% (Increased) | 35% (Reduced) |
| Physics Weightage | 22.5% (Reduced) | NA |
| Chemistry Weightage | 22.5% (Reduced) | NA |
| Drawing Weightage | NA | 20% (Increased) |
Will JEE Main 2026 be tough?
The difficulty level of JEE Main 2026 will depend on multiple factors, including changes in the syllabus, question patterns, and student preparedness. As per the JEE Main difficulty level from past years, JEE Main 2024 was moderate to difficult, and JEE Main was comparatively tougher than JEE Main 2024.
Factors Influencing the Difficulty Level of JEE Main 2026
Reduced Syllabus
- Effect: Given that it has removed 11 chapters and many topics across Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics, the syllabus is leaner, perhaps less heavy for students.
- Expectation: The attention to the core concepts should be followed by conceptually deeper, more application-based questions to make up for this reduced syllabus.Pattern and Distribution of Questions
- NTA's Trend: JEE Main has maintained a good balance of easy, moderate, and difficult questions over the years. If this trend continues, the overall difficulty level is unlikely to increase sharply.
- Insights: ~25% easy, ~50% moderate, and ~25% difficult questions, which is expected to stay consistent. Past papers have shown this trend.
Increased Competition
- Data Insights: The number of JEE Main applicants has witnessed an upward trend, with almost 1.4 million students registering in 2024. With the competition heating up, scoring well can only be achieved through thoughtful preparation, irrespective of whether the exam is tough or not.
Weightage Redistribution
- Effect: If topics are reduced, there might be increased weightage of the remaining syllabus towards the high-priority chapters such as Calculus, Thermodynamics, and Organic Chemistry. These are usually considered tricky subjects.
Strict NCERT
- Benefit: The curriculum is very much in conformity with NCERT textbooks, therefore not requiring additional resources as much. It makes preparing for students dependent mainly on schooling easier.
Also Read
JEE Main Syllabus 2026
Below is the detailed chapter-wise syllabus for JEE Main 2025, categorized by subject. The syllabus reflects the latest updates, excluding topics that have been officially removed.
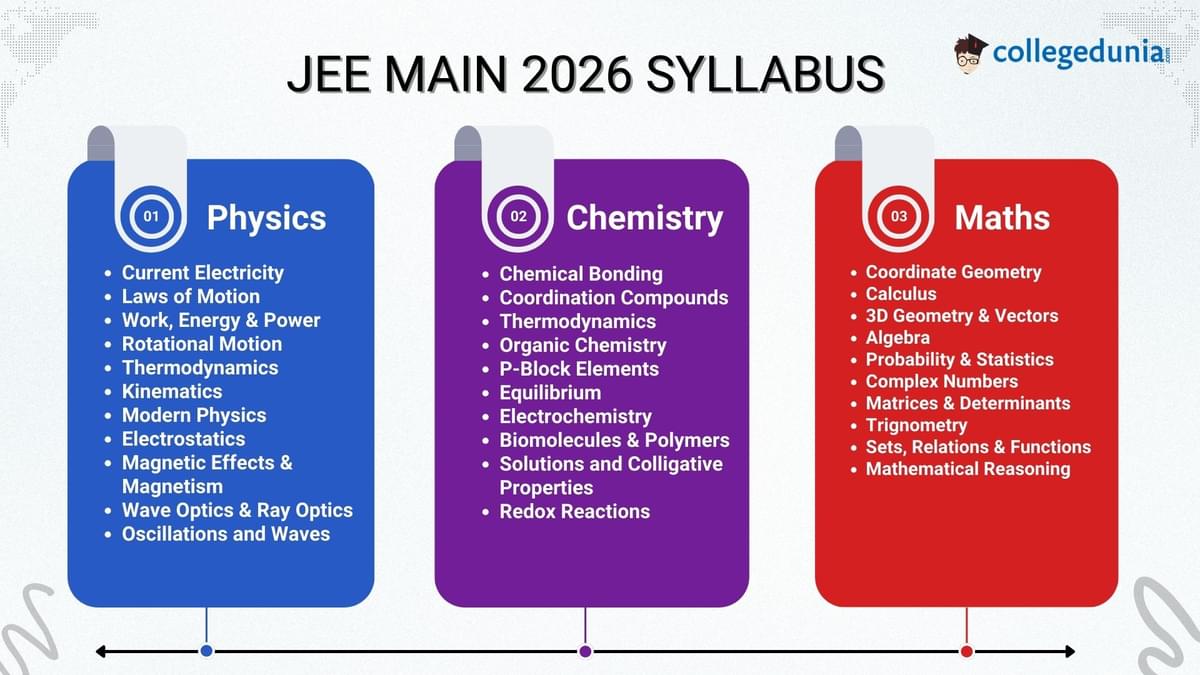
JEE Main Syllabus 2026 for Physics
The Physics syllabus is divided into Class 11 and Class 12 topics.
| Unit | Topics |
|---|---|
| Physics and Measurement | Units and dimensions, SI units, error analysis, dimensional analysis. |
| Kinematics | Motion in a straight line, motion in a plane, velocity, acceleration, vectors. |
| Laws of Motion | Newton's laws, friction, dynamics of uniform circular motion. |
| Work, Energy, and Power | Work-energy theorem, conservation of energy, power, collisions. |
| Rotational Motion | Moment of inertia, torque, angular momentum, dynamics of rotational motion. |
| Gravitation | Kepler's laws, gravitational potential energy, escape velocity. |
| Properties of Matter | Elasticity, viscosity, fluid dynamics, surface tension. |
| Thermodynamics | First law, second law, Carnot engine, specific heats. |
| Kinetic Theory of Gases | Molecular speeds, degrees of freedom, ideal gas law. |
| Oscillations and Waves | SHM, damped and forced oscillations, sound waves, Doppler effect. |
| Electrostatics | Coulomb’s law, electric field, Gauss’s law, potential, capacitors. |
| Current Electricity | Ohm’s law, series-parallel circuits, Kirchhoff’s laws, and potentiometer. |
| Magnetism | Biot-Savart law, Ampere's law, bar magnets, Earth’s magnetism. |
| Electromagnetic Induction | Faraday’s law, Lenz’s law, AC generator, transformers. |
| Optics | Reflection, refraction, interference, diffraction, polarization. |
| Modern Physics | Photoelectric effect, Bohr’s model, radioactivity, semiconductors. |
JEE Main Syllabus 2026 for Chemistry
The Chemistry syllabus includes Physical, Organic, and Inorganic Chemistry.
JEE Main Syllabus 2026 for Physical Chemistry
| Unit | Topics |
|---|---|
| Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry | Mole concept, stoichiometry, laws of chemical combination. |
| States of Matter | Gas laws, kinetic theory, intermolecular forces. |
| Atomic Structure | Quantum numbers, Bohr’s model, Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. |
| Chemical Bonding | Hybridization, molecular orbital theory, VSEPR theory. |
| Thermodynamics | Enthalpy, entropy, Gibbs free energy, spontaneous reactions. |
| Equilibrium | Chemical and ionic equilibria, Le Chatelier’s principle. |
| Redox Reactions | Oxidation-reduction, balancing redox reactions. |
| Solutions | Colligative properties, Raoult's law, molality, molarity. |
JEE Main Syllabus 2026 for Inorganic Chemistry
| Unit | Topics |
|---|---|
| Periodic Table | Trends in periodic properties: electronegativity, ionization energy. |
| s-Block Elements | Group 1 and Group 2 elements: properties, compounds, and applications. |
| p-Block Elements | Groups 13-18: properties, chemical reactions, compounds like oxides, halides. |
| d- and f-Block Elements | Transition metals, oxidation states, coordination compounds. |
| Metallurgy | Principles of extraction, refining methods. |
JEE Main Syllabus 2026 for Organic Chemistry
| Unit | Topics |
|---|---|
| Hydrocarbons | Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, aromatic hydrocarbons. |
| Haloalkanes and Haloarenes | Reactions, mechanisms, physical and chemical properties. |
| Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers | Preparation, reactions, and properties. |
| Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids | Nucleophilic addition, reactions with ammonia derivatives. |
| Polymers | Classification, properties, and uses. |
Also Read
JEE Main Syllabus 2026 for Mathematics
| Unit | Topics |
|---|---|
| Sets, Relations, and Functions | Types of relations and functions, domain, range, and co-domain. |
| Complex Numbers | Polar form, roots of complex numbers, properties. |
| Matrices and Determinants | Properties, inverse, applications to linear equations. |
| Quadratic Equations | Roots, nature of roots, solving inequalities. |
| Permutations and Combinations | Basics of counting principle, binomial theorem. |
| Sequences and Series | Arithmetic, geometric progression, harmonic progression. |
| Calculus | Limits, continuity, differentiability, integration, applications. |
| Coordinate Geometry | Straight lines, circles, ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas. |
| Probability | Conditional probability, Bayes' theorem, random variables. |
Also Read
JEE Main Reduced Syllabus FAQs
Ques. Is the Syllabus Reduced for JEE Main 2026?
Ans. As of now, the JEE Main syllabus is expected to remain unchanged. With the recent introduction of the revised JEE Main 2026 Exam Pattern by the NTA, where optional questions from Section B have been removed, aspirants are now speculating about potential changes in the JEE Main 2026 Syllabus.
- The syllabus includes topics from three core subjects—Mathematics, Physics, and Chemistry—aligned primarily with the NCERT Class 11 and 12 curriculum.
- For aspirants asking, “Is the JEE Main 2026 syllabus reduced?”, it is crucial to stay vigilant and updated. Any official announcements from the NTA regarding syllabus revisions will directly impact preparation strategies.
Ques. Which topics are removed from JEE 2025?
Ans. As per the JEE Main reduced syllabus from past years, students can check the chapters and topics removed from the JEE Main syllabus in the table below.
| JEE Main Section | JEE Main Reduced Topics |
|---|---|
| Physics | Semiconductors, Communication Systems, and some parts of Optics |
| Chemistry | Environmental Chemistry, Polymers, and parts of Organic Chemistry (e.g., Qualitative Analysis) |
| Mathematics | Sets and Relations, Mathematical Reasoning, and some parts of Probability |
Ques. In which year was the JEE Mains syllabus reduced?
Ans. JEE Main syllabus was revised in 2025 with the removal of some chapters and topics from each section of the JEE Main syllabus 2026. As per the analysis, around 15% of the JEE Main syllabus is reduced, and 85% of the JEE Main syllabus is the same as in past years.
Ques. How much percentile is required for NIT?
Ans. As per the JEE Main cutoff analysis from past years, students must score more than 90 percentile to get admission to IITs and NITs. For top branches like CSE at IITs and NITs, students must score more than 95 percentile to secure admission.
Ques. What is removed from JEE 2025 syllabus?
Ans. Various topics from the JEE Main syllabus for Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics have been removed. Students can check the topics removed from the JEE Main syllabus below.
- Physics- Semiconductors, Communication Systems, and some parts of Optics.
- Chemistry- Environmental Chemistry, Polymers, and parts of Organic Chemistry (e.g., Qualitative Analysis).
- Mathematics- Sets and Relations, Mathematical Reasoning, and some parts of Probability.
Ques. How to download JEE Main syllabus PDF?
Ans. To download the JEE Main 2026 syllabus, students can follow the steps listed below.
- Go to the official website of JEE Main 2026.
- On the official website, click on the link for JEE Main syllabus.
- JEE Main 2026 syllabus wil be displayed on the screen.
- Students can download JEE Main 2026 syllabus for future reference.





Comments