GATE 2023 Ecology and Evolution Question Paper PDF is available here for download. IIT Kanpur conducted GATE 2023 Ecology and Evolution exam on February 11, 2023 in the Afternoon Session from 02:30 PM to 05:30 PM. Students have to answer 65 questions in GATE 2023 Ecology and Evolution Question Paper carrying a total weightage of 100 marks. 10 questions are from the General Aptitude section and 55 questions are from Core Discipline.
GATE 2023 Ecology and Evolution Question Paper with Solutions PDF
| GATE 2023 Ecology and Evolution Question Paper with Solutions | Download | Check Solutions |

“You are delaying the completion of the task. Send ______ contributions at the earliest.”
References : _____ :: Guidelines : Implement (By word meaning)
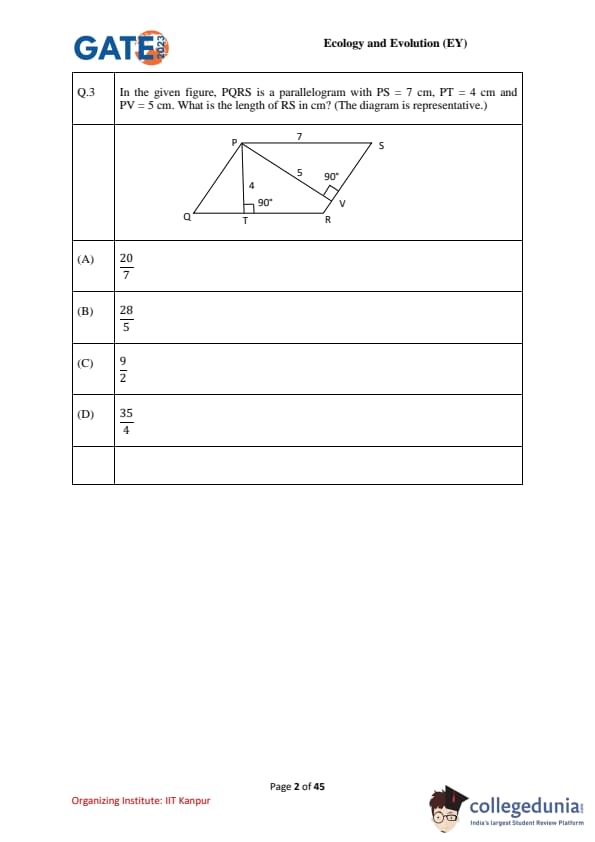
In the given figure, \(PQRS\) is a parallelogram with \(PS = 7 \,cm\), \(PT = 4 \,cm\) and \(PV = 5 \,cm\). What is the length of \(RS\) in cm? (The diagram is representative.)

In 2022, June Huh was awarded the Fields medal, which is the highest prize in Mathematics.
When he was younger, he was also a poet. He did not win any medals in the International Mathematics Olympiads. He dropped out of college.
Based only on the above information, which one of the following statements can be logically inferred with certainty?
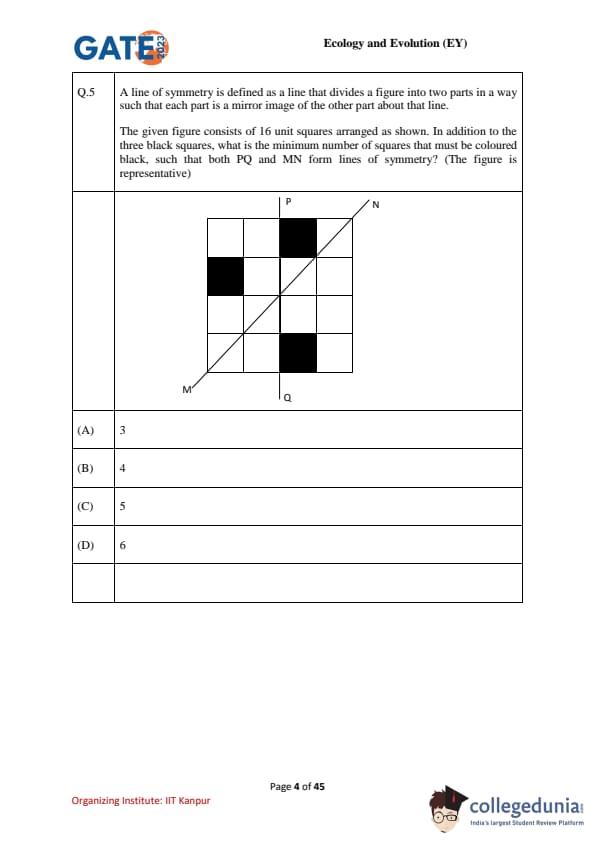
A line of symmetry is defined as a line that divides a figure into two parts such that each part is a mirror image of the other.

The figure consists of 16 unit squares (4×4 grid). Three squares are already black. In addition to these, what is the minimum number of squares that must be coloured black so that both \(PQ\) (vertical axis) and \(MN\) (diagonal axis) are lines of symmetry?
Human beings are one among many creatures that inhabit an imagined world. In this imagined world, some creatures are cruel. If it is given that the statement “Some human beings are not cruel creatures” is FALSE, then which set of statements can be logically inferred with certainty?
(i) All human beings are cruel creatures.
(ii) Some human beings are cruel creatures.
(iii) Some creatures that are cruel are human beings.
(iv) No human beings are cruel creatures.
To construct a wall, sand and cement are mixed in the ratio \(3:1\). The cost (per unit) of sand and cement are in the ratio \(1:2\). If the total cost of sand and cement is \(Rs. 1000\), what is the cost (in rupees) of the cement used?
The World Bank has declared that it does not plan to offer new financing to Sri Lanka until the country has an adequate macroeconomic policy framework in place. It has also noted that Sri Lanka needs to adopt reforms to tackle the root causes of its crisis. Based on the passage, which statement can be inferred with certainty?
The coefficient of \(x^4\) in the polynomial \((x-1)^3(x-2)^3\) is equal to _____.
Which one of the following shapes can be used to tile (completely cover by repeating) a flat plane, extending to infinity in all directions, without leaving any empty spaces in between them? The copies of the shape used to tile are identical and are not allowed to overlap.
Which one of the following is an example of mechanical potential energy?
A research team studies the probability of crop damage by wild boar in crop fields. For each field, they record \(\,1\) if damage was observed and \(\,0\) if not. Which distribution is most appropriate to analyse the probability of crop damage?
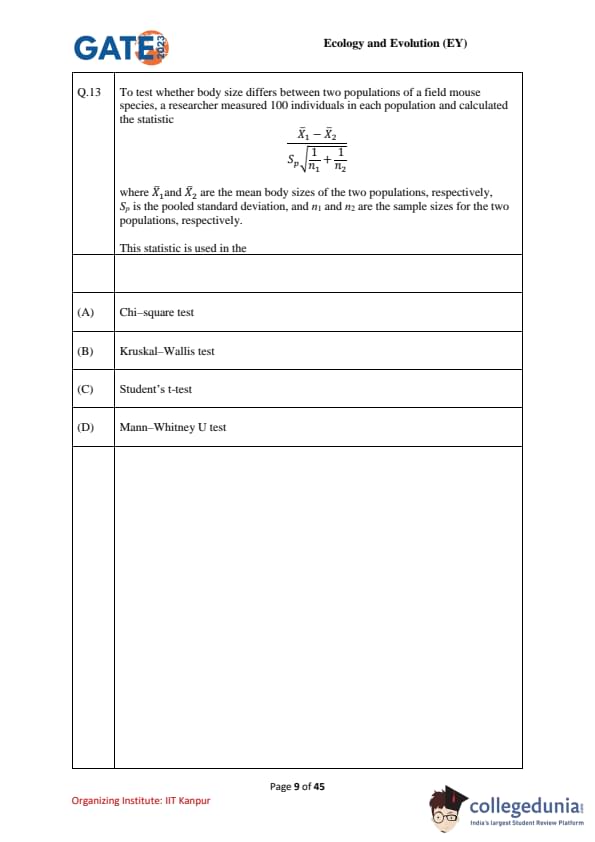
To test whether body size differs between two populations of a field mouse species, a researcher measured 100 individuals in each population and calculated the statistic \[ t \;=\; \frac{\overline{X}_1 - \overline{X}_2}{S_p\,\sqrt{\tfrac{1}{n_1}+\tfrac{1}{n_2}}} \]
where \(\overline{X}_1\) and \(\overline{X}_2\) are the sample means, \(S_p\) is the pooled standard deviation, and \(n_1,n_2\) are the sample sizes.
Which ecological process best explains the observation that seedling establishment increases with distance from the parent tree in a forest?
In the early 20th century, which scientist made fundamental contributions to both evolution and statistics?
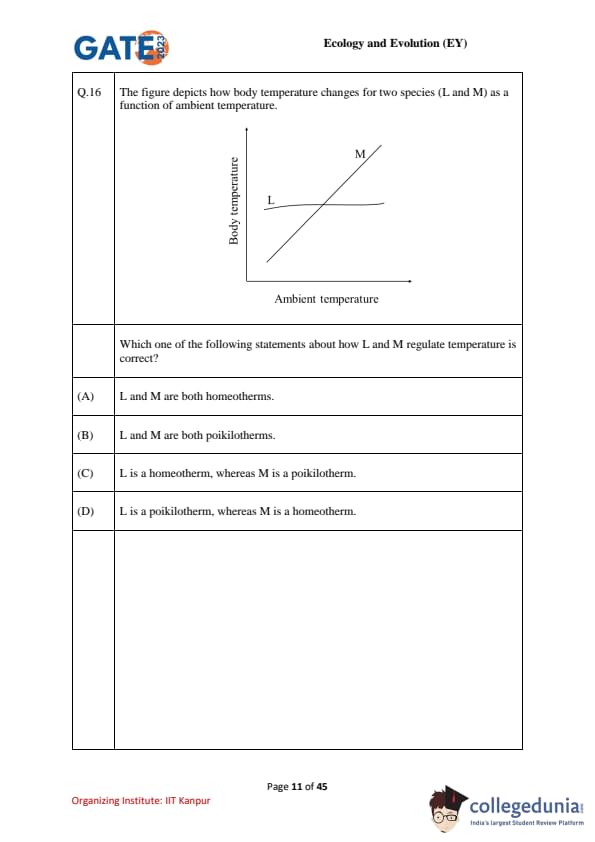
The figure shows body temperature vs. ambient temperature for two species (L and M). Which statement about temperature regulation is correct?

You are a deep–sea organism and potential mates are several hundreds of kilometers away. Which kind of mating signal is most likely to help them locate you?
Which option shows the correct order of biological organization levels? (B – biomes; E – ecosystems; P – populations; I – individuals; C – communities)
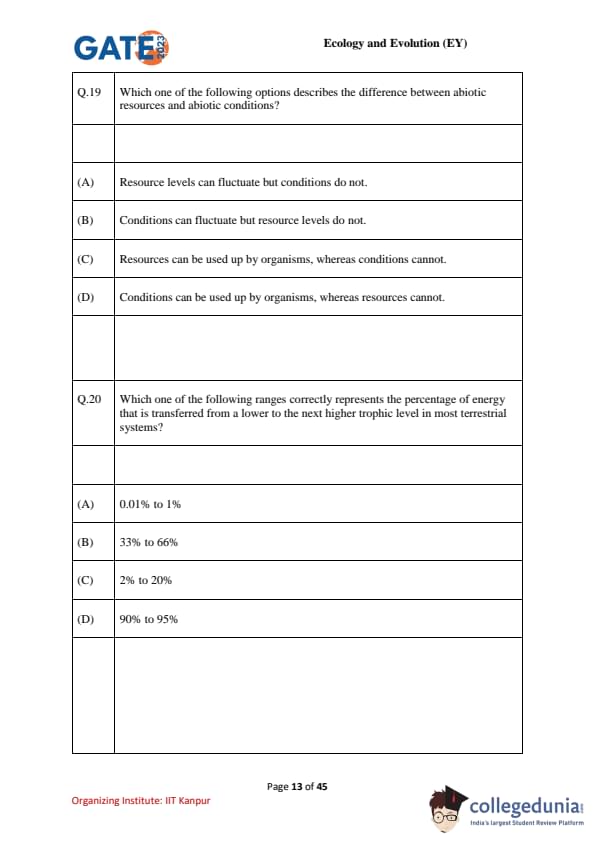
Which one of the following options describes the difference between abiotic resources and abiotic conditions?
Which of the following ranges correctly represents the percentage of energy transferred from a lower to the next higher trophic level in most terrestrial systems?
Whales and dolphins are hypothesized to have evolved along the northern shore of the Tethys Sea, prior to the Indian plate’s collision with the Eurasian plate. To which of the following animals are these aquatic mammals most closely related?
Which one of the following options represents the correct order of decreasing average net primary productivity (NPP; g\,m\(^{-2}\)\,yr\(^{-1}\)) in natural ecosystems?
The increase in mean global temperature since the Industrial Revolution falls in the range of:
Which one of the following endangered species has been the subject of a reintroduction plan in India?
Compared with bony fish, many shark species show steeper population declines in response to heavy fishing pressure. Which one of the following options explains this?
Which one or more of the following options describe(s) how ferns differ from angiosperms and gymnosperms?
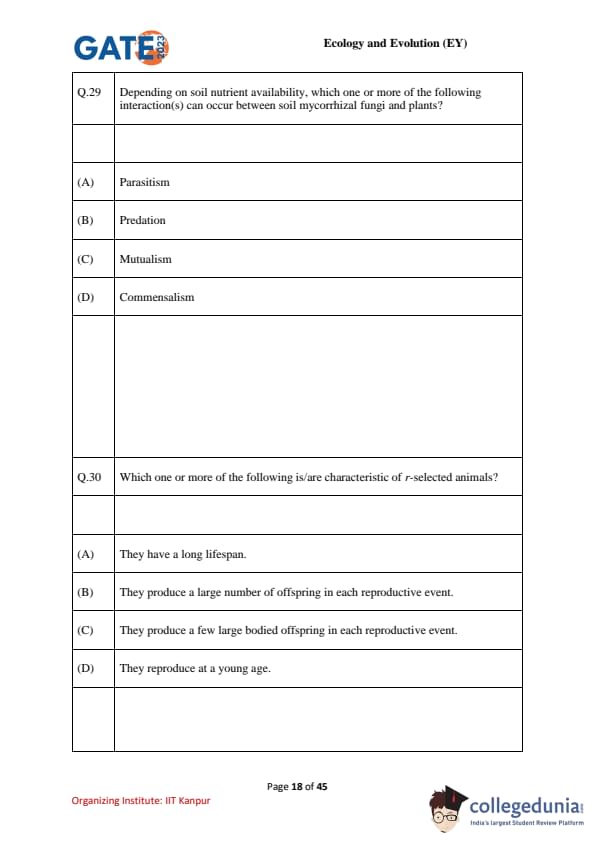
Depending on soil nutrient availability, which one or more of the following interaction(s) can occur between soil mycorrhizal fungi and plants?
Which one or more of the following is/are characteristic of r-selected animals?
Which one or more of the following represent(s) benefits of Batesian mimicry to the mimic?
Which one or more of the following is/are developmental feature(s) of hatchlings of an altricial bird species?
You have a biased coin with the probability of getting a head being \(p=0.6\). The probability of getting at least \(1\) head in \(n=3\) tosses is \(\_\_\_\_\). (Rounded off to three decimal places)
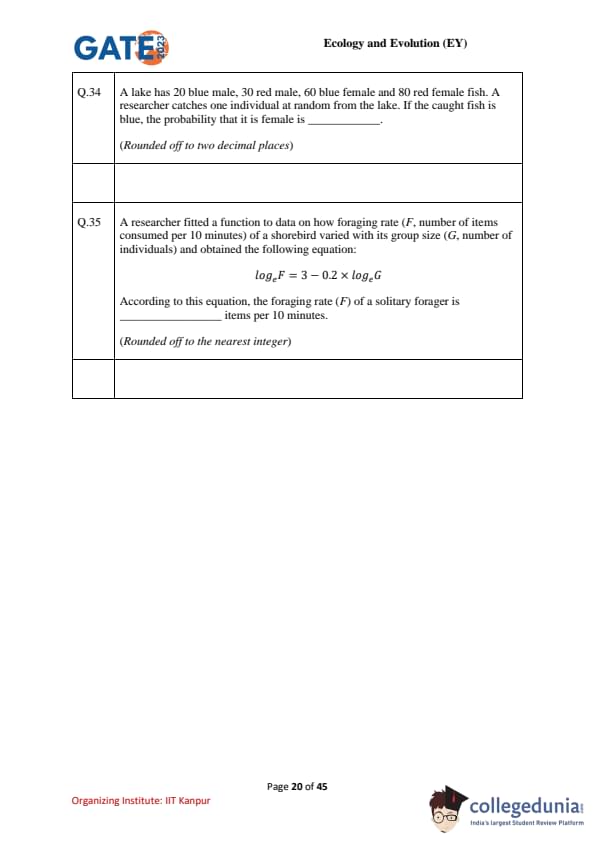
A lake has \(20\) blue males, \(30\) red males, \(60\) blue females, and \(80\) red females. A researcher catches one individual at random. If the caught fish is blue, the probability that it is female is \(\_\_\_\_\). (Rounded off to two decimal places)
A researcher fitted a function to show how foraging rate \(F\) (items per 10 min) varies with group size \(G\) (number of individuals): \[ \log_e F \;=\; 3 - 0.2\,\log_e G. \]
According to this equation, the foraging rate \(F\) of a solitary forager is \(\_\_\_\_\) items per 10 minutes. (Rounded to the nearest integer)
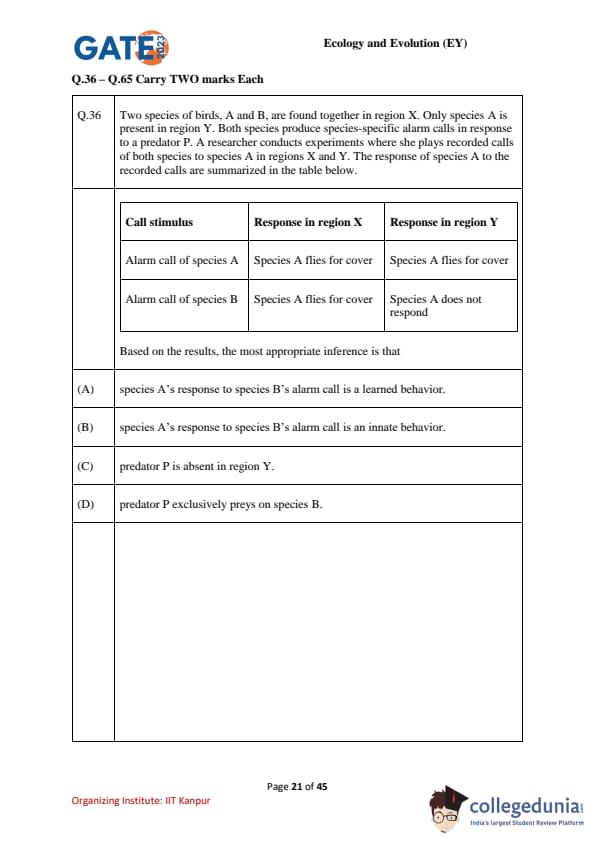
Two species of birds, A and B, are found together in region X. Only species A is present in region Y. Both species produce species-specific alarm calls to a predator \(P\). A researcher plays back recorded calls of both species to species A in regions X and Y. The responses of species A are summarized below.
Call stimulus & Response in region X & Response in region Y
Alarm call of species A & Species A flies for cover & Species A flies for cover
Alarm call of species B & Species A flies for cover & Species A does not respond
Based on the results, the most appropriate inference is that
The table below lists different insects and taxonomic orders. Choose the option that matches each animal to its correct taxonomic order.
Animal Taxonomic order
P) Moths i) Hemiptera
Q) True bugs ii) Orthoptera
R) Crickets iii) Coleoptera
S) Beetles iv) Lepidoptera
v) Diptera
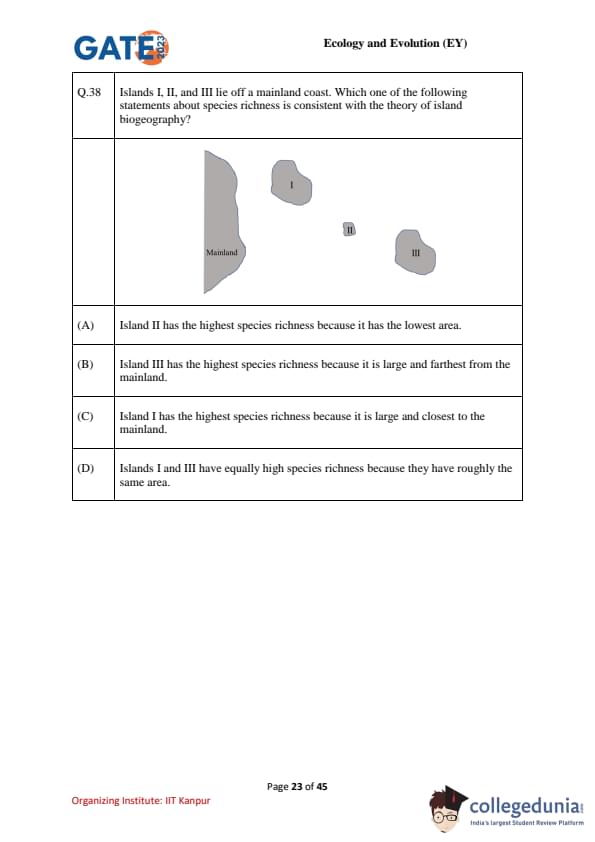
Islands I, II, and III lie off a mainland coast (see figure). Which statement about species richness is consistent with the theory of island biogeography?

In a polygynous hummingbird species, males defend and monopolize nectar–rich plants (resource). Females visit these plants for nectar and the defending male will have access to all visiting females for mating. Under which scenario is polygyny expected to be the highest?

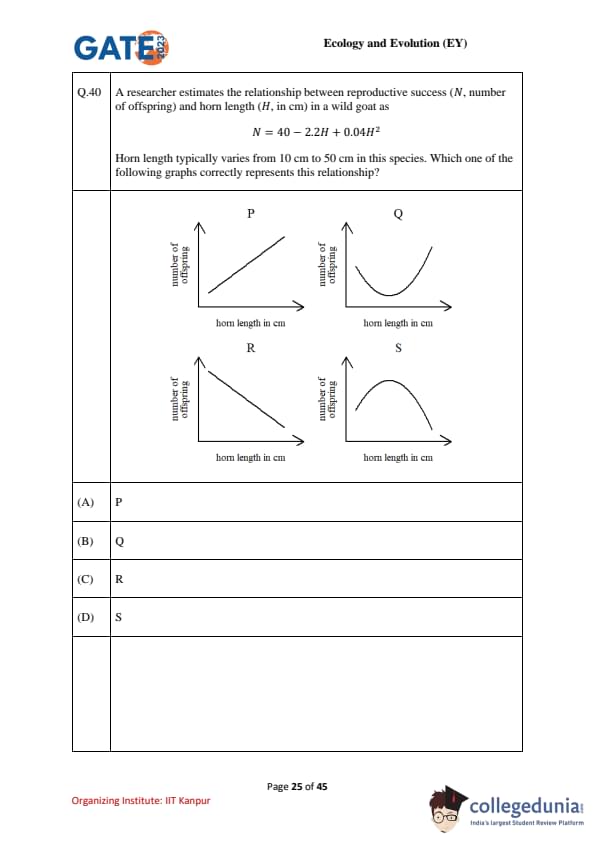
A researcher estimates the relationship between reproductive success \(N\) (number of offspring) and horn length \(H\) (cm) in a wild goat as \[ N \;=\; 40 \;-\; 2.2H \;+\; 0.04H^{2}. \]
Horn length typically varies from \(10\) cm to \(50\) cm. Which graph (P, Q, R, S) correctly represents this relationship?

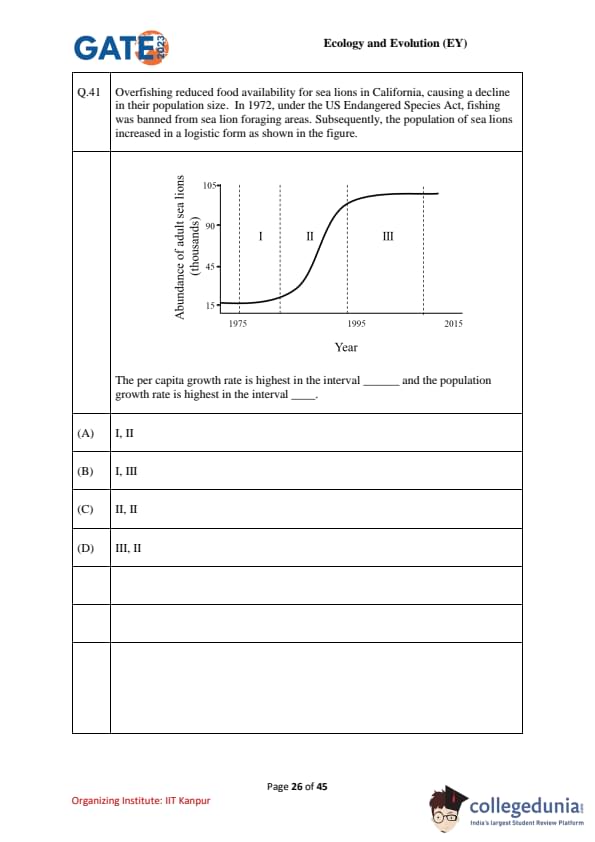
Overfishing reduced food availability for sea lions in California, causing a decline in their population size. In 1972, under the US Endangered Species Act, fishing was banned from sea lion foraging areas. Subsequently, the population of sea lions increased in a logistic form as shown in the figure.

The per capita growth rate is highest in the interval and the population growth rate is highest in the interval .
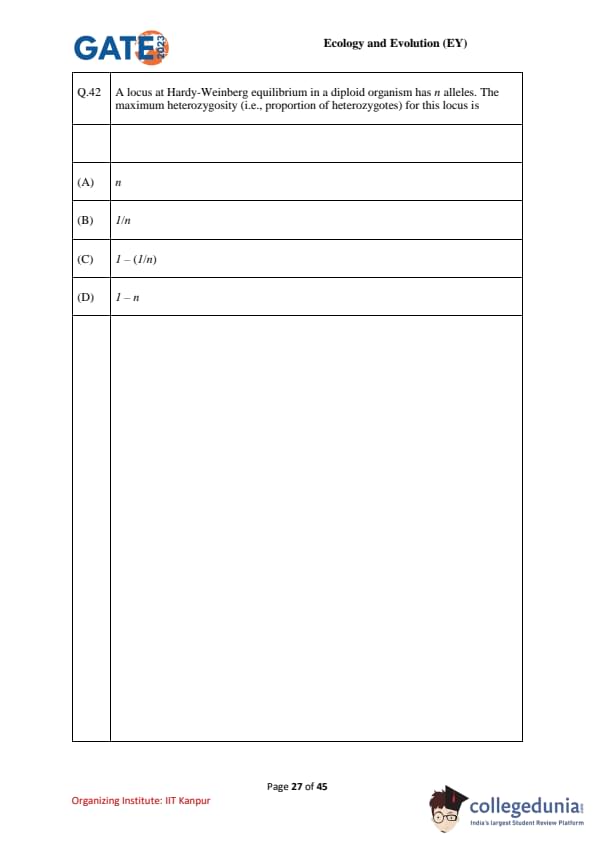
A locus at Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium in a diploid organism has \(n\) alleles. The maximum heterozygosity (i.e., proportion of heterozygotes) for this locus is
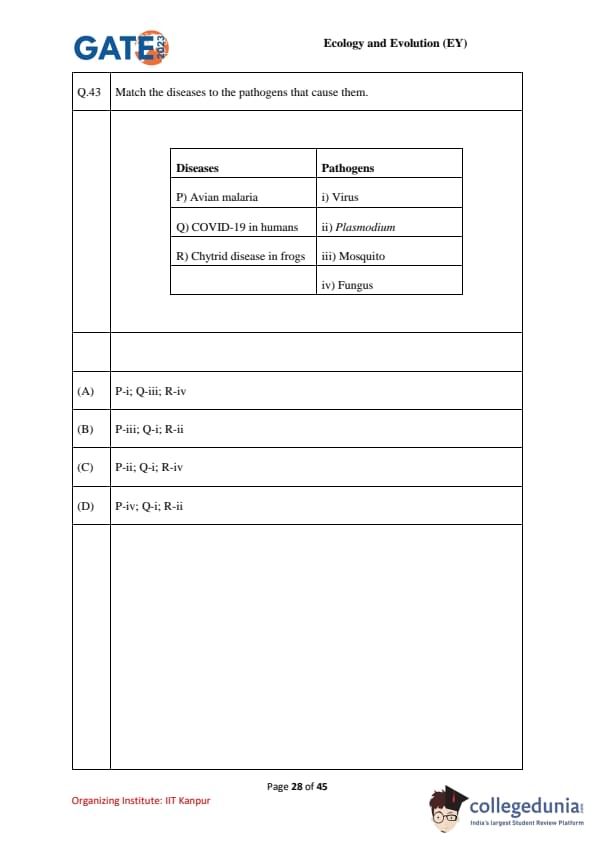
Match the diseases to the pathogens that cause them.
Diseases Pathogens
P) Avian malaria i) Virus
Q) COVID-19 in humans ii) Plasmodium
R) Chytrid disease in frogs iii) Mosquito
iv) Fungus
The production of anthocyanin pigments in pea flowers requires the presence of at least one dominant allele in each of two independently assorting genes, C and P.
The presence of anthocyanin results in purple flowers, whereas its absence gives white flowers.
A cross between two double heterozygous (CcPp) plants is performed.
What is the expected ratio of plants with purple flowers to plants with white flowers?
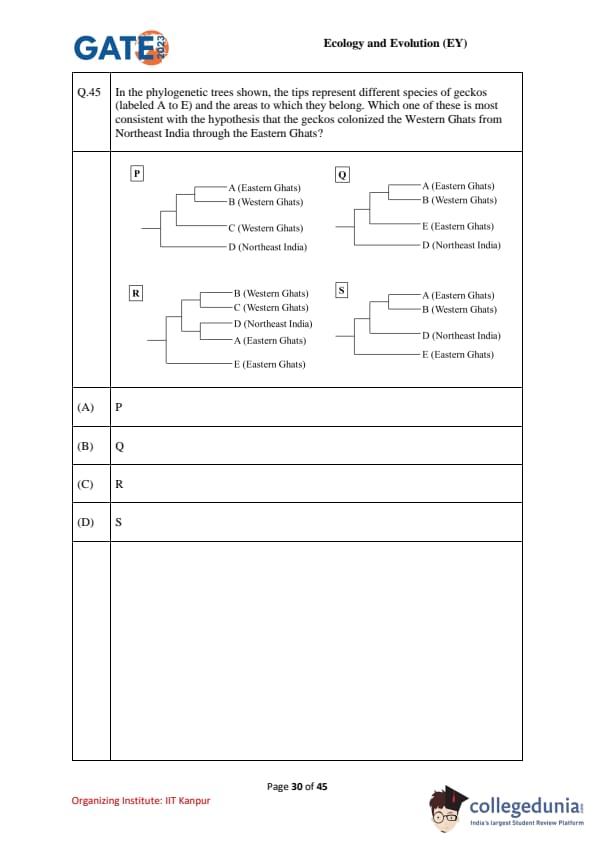
In the phylogenetic trees shown, the tips represent different species of geckos (A–E) and the areas they belong to.
Which tree is most consistent with the hypothesis that geckos colonized the Western Ghats from Northeast India through the Eastern Ghats?

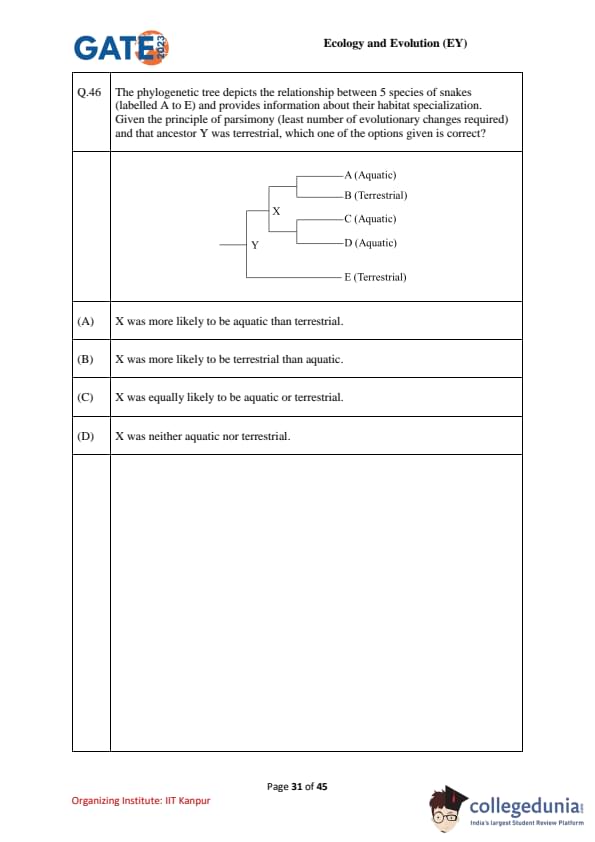
The phylogenetic tree depicts relationships among five snake species (A–E) and their habitat specializations (Aquatic or Terrestrial). Given parsimony (least number of changes) and that ancestor Y was terrestrial, which option about ancestor X is correct?

Speciation in Western Ghats snakes is predominantly allopatric. To quantify diversification most cost- and time-efficiently, how should a researcher sample?
All else equal, which population size \(N\) and migration rate \(m\) yield the most genetic differentiation between populations (largest \(F_{st}\))? Given \(F_{st}=\dfrac{1}{4Nm+1}\).
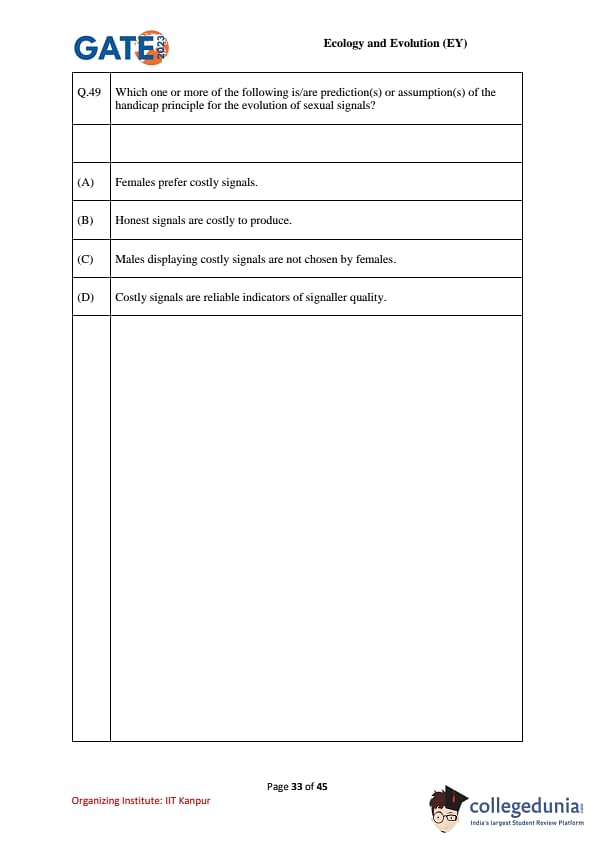
Which one or more of the following is/are prediction(s) or assumption(s) of the handicap principle for the evolution of sexual signals?
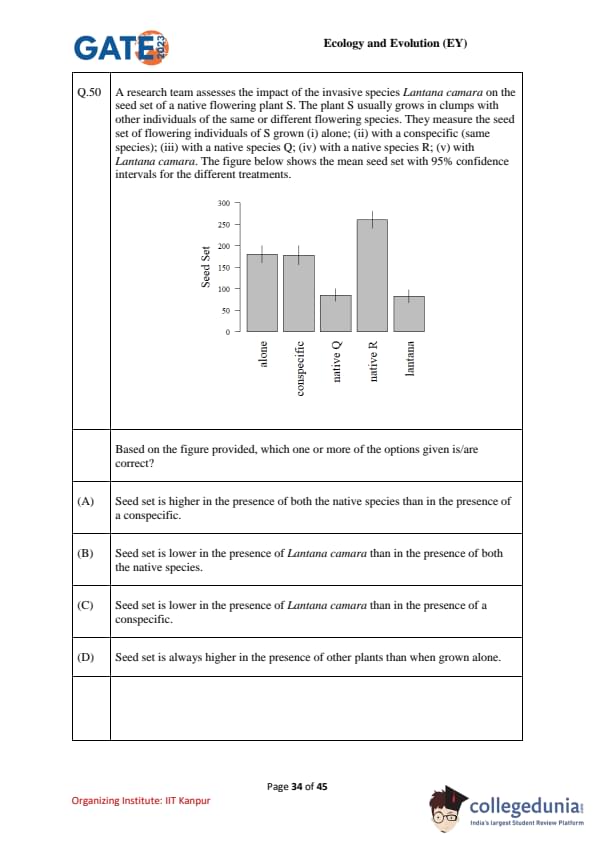
A research team tests how neighbours affect the seed set of a native plant \(S\): grown (i) alone, (ii) with a conspecific, (iii) with native Q, (iv) with native R, (v) with Lantana camara. The bar plot shows mean seed set with 95% CIs. Based on the figure, which option(s) are correct?

There are two palatable prey species, Q and R, for an insectivorous bird. The bird searches for and consumes only species Q. According to optimal foraging theory, which condition(s) can explain the bird choosing to forage only for Q?
SLOSS debate: With the same total area, which option(s) describe a conservation benefit} of protecting several small patches rather than one large patch?
Which one or more options is/are example(s) of niche partitioning between species?
In an assemblage of coexisting wild cat species, the size of canine teeth was found to be strikingly different between species. Which one or more of the following statements explain(s) this observation?
The Biological Species Concept (BSC) defines species as groups of interbreeding natural populations that are reproductively isolated from other such groups. Which one or more of the following options could pose challenges for defining species using the BSC?
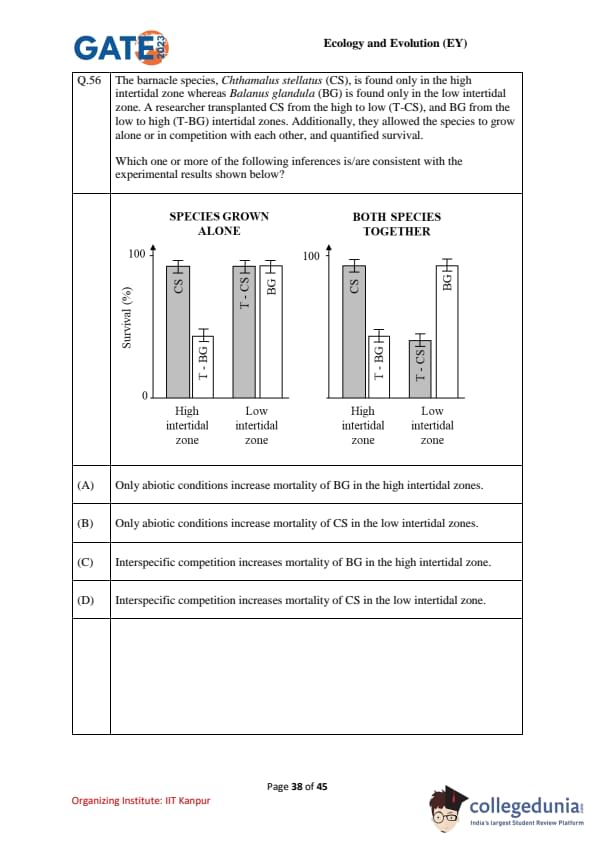
Two barnacles: Chthamalus stellatus (CS, naturally high intertidal) and Balanus glandula (BG, naturally low intertidal). Each species was grown (i) alone and (ii) together, and also transplanted: CS to low (T–CS) and BG to high (T–BG). Survival (%) was recorded. Which inference(s) are consistent with the results?

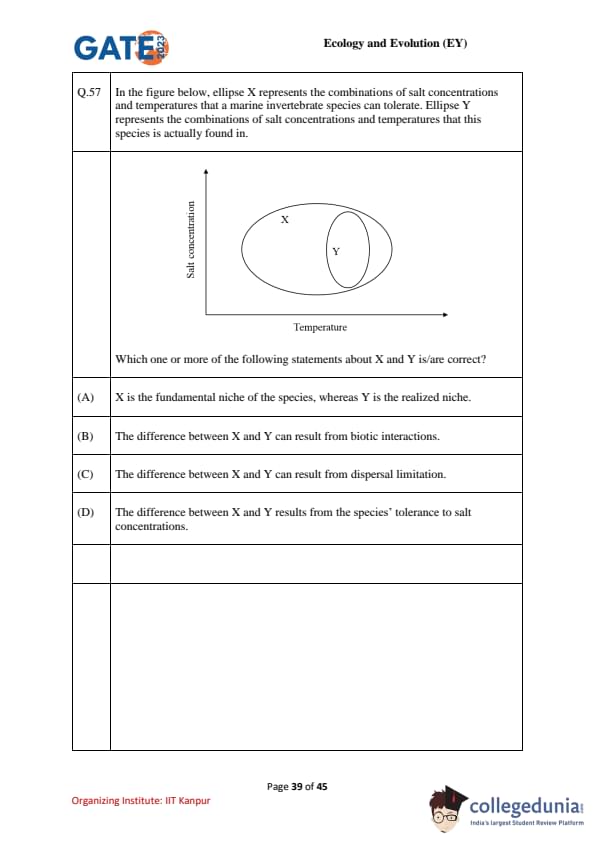
In the figure, ellipse X represents the combinations of salt concentrations and temperatures a marine invertebrate species can tolerate (its potential physiological range). Ellipse Y represents the combinations of salt concentrations and temperatures where the species is actually found. Which one or more of the following statements about X and Y is/are correct?

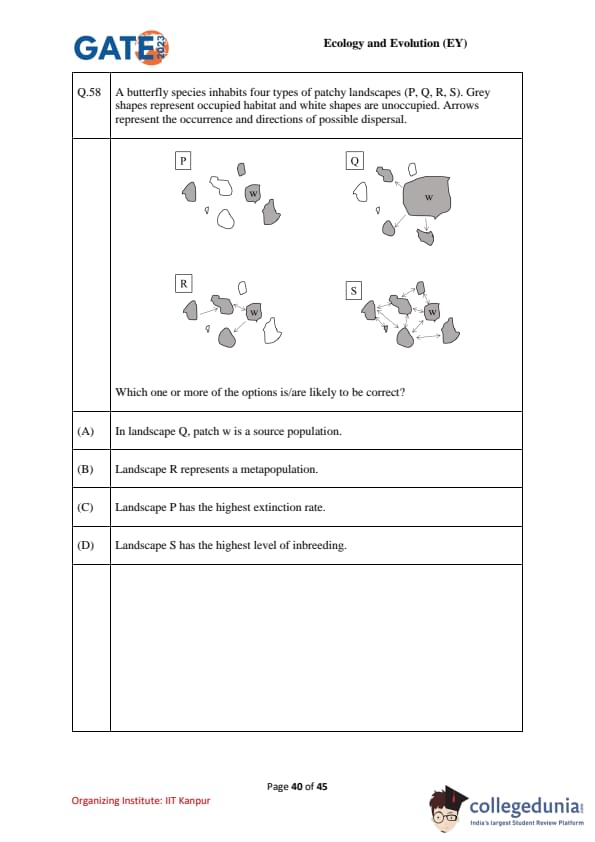
A butterfly species inhabits four patchy landscapes (P, Q, R, S). Grey shapes = occupied patches, white = unoccupied. Arrows = directions of dispersal. Which one or more of the options is/are correct?

A new food-requesting behaviour has been observed in bonnet macaques in Bandipur National Park. The macaques extend their hand and make a cooing sound towards humans, resulting in food given to them. If this behaviour is to increase in frequency in the population by natural selection, which condition(s) are necessary?
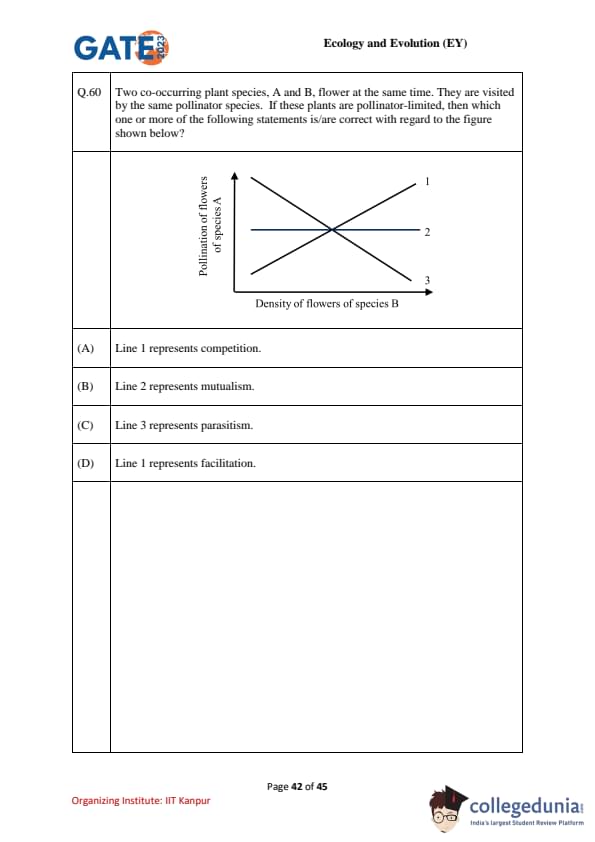
Two co-occurring plant species, A and B, flower at the same time and share the same pollinator species. If these plants are pollinator-limited, then which one or more of the following statements is/are correct with regard to the figure shown below?

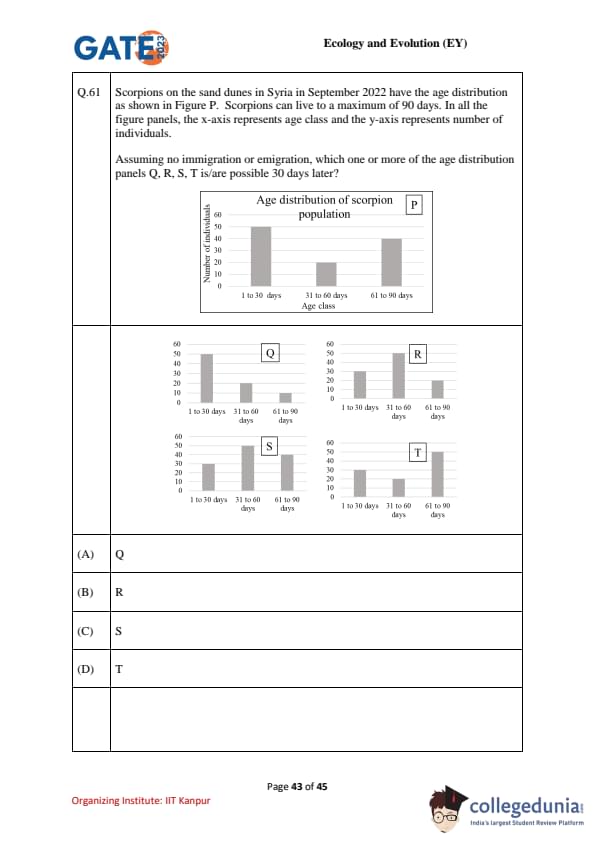
Scorpions on Syrian sand dunes in Sept 2022 show the age distribution in panel P (age classes: 1–30 d, 31–60 d, 61–90 d; y-axis = number of individuals). Scorpions live to a maximum of 90 days. Assuming no immigration or emigration}, which one or more of the age-distribution panels Q, R, S, T is/are possible 30 days later?

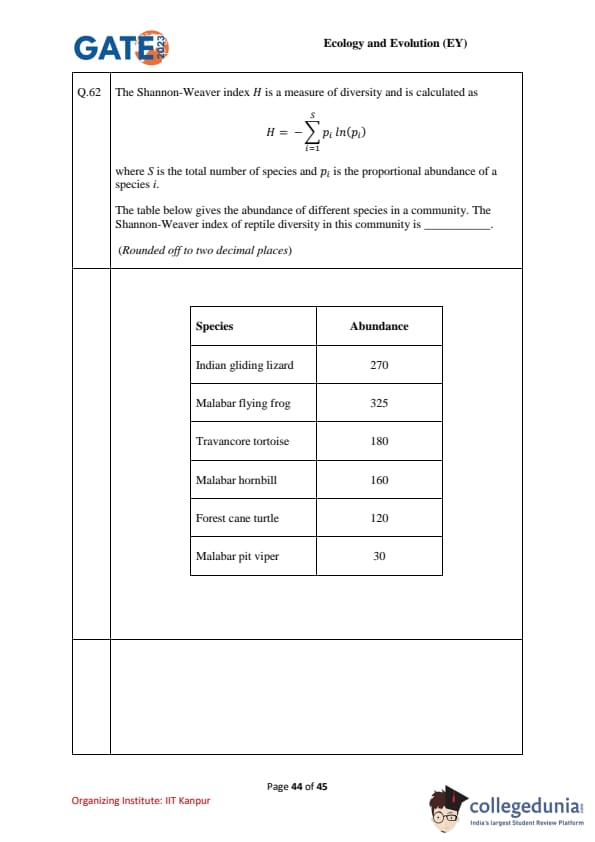
The Shannon–Weaver index \(H\) is \(H=-\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^{S} p_i\ln(p_i)\), where \(S\) is the number of species and \(p_i\) is the proportional abundance of species \(i\).
The table lists abundances of different species in a community. Compute the Shannon–Weaver index of reptile diversity in this community (round to two decimals).
Species Abundance
Indian gliding lizard 270
Malabar flying frog 325
Travancore tortoise 180
Malabar hornbill 160
Forest cane turtle 120
Malabar pit viper 30
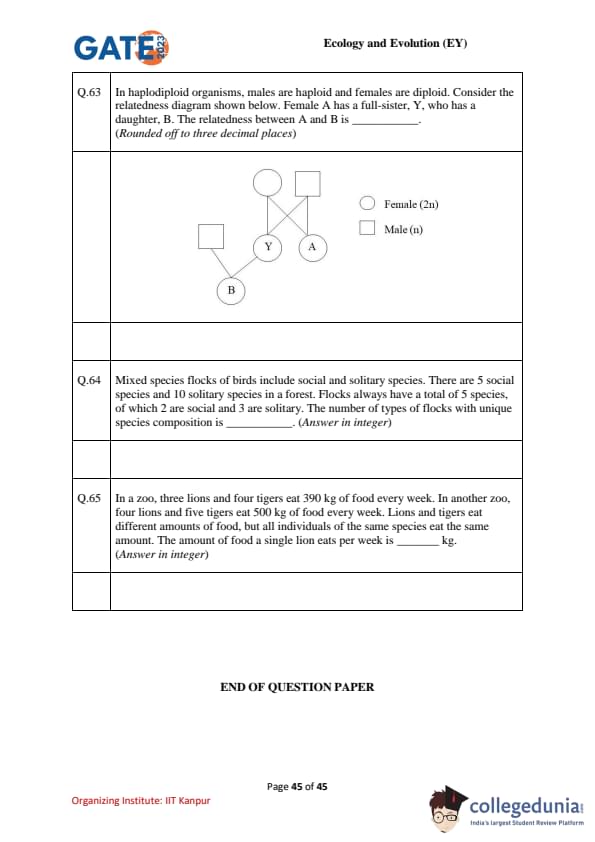
In haplodiploid organisms, males are haploid and females are diploid. In the pedigree, female A has a full-sister Y; Y has a daughter B. Compute the genetic relatedness between A and B (round to three decimals).

Mixed-species flocks contain exactly 5 species: 2 social (from 5 available) and 3 solitary (from 10 available). How many distinct species-composition types are possible? (Answer in integer)
In Zoo 1, \(3\) lions and \(4\) tigers eat \(390\) kg/week. In Zoo 2, \(4\) lions and \(5\) tigers eat \(500\) kg/week. All lions eat the same amount \(L\) kg/week and all tigers the same amount \(T\) kg/week. Find \(L\) (Answer in integer).














Also Check:
| Previous Year GATE Ecology and Evolution Question Papers | GATE 2023 Ecology and Evolution Paper Analysis |
| GATE Ecology and Evolution Exam Pattern | GATE Ecology and Evolution Syllabus |





Comments