
Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Difference between Alternator and Generator is based on its movements and spins. Two types of equipment used for generating electricity are known as Alternators and Generators. An alternator produces electricity and can charge cars. Generators, on the other hand, are used for the large-scale production of electricity.
Alternators are used in modern internal combustion engine automobiles to charge the battery. They are also used to power the electrical system when its engine is running. A generator turns mechanical energy into electrical energy. Generators provide electricity to devices and appliances when they are not connected to the power grid.
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms: Alternator, Generator, Mechanical energy, Output Current, Electricity, Magnetic flux, Electrical Energy, Alternating current, Magnetic field, Ac generator
What is an Alternator?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A machine that produces alternating current, by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy is known as an Alternator. Hence, it is called the Synchronous generator or an AC generator. The spinning of the magnetic field inside the wire’s windings in an Alternator produces electricity.
Alternator speed is reduced to reduce the Output Current from the alternator. Upon running it at low speeds, the efficiency of an Alternator can decrease and its output current can be decreased by increasing the temperature.
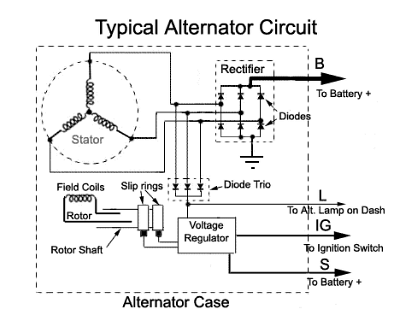
Alternator
Alternators can be classified into many types on the basis of their design and applications, such as Automotive-type alternator, Marine type alternator, Brushless type alternator and Diesel-electric locomotive type’s alternator, etc. Alternators use only the needed energy and hence contribute to conserving them.
Read More:
| Related Links | ||
|---|---|---|
| AC Voltage Applied to a Resistor | AC Voltage Applied to an Inductor | Power in Alternating Current |
| Transformers | NCERT Solutions Chapter 7 Alternating Current | Oscillations |
What is a Generator?
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The machines that provide electricity during power cuts from the power grid are called electrical generators. A generator produces electricity by spinning the armature or windings of wire inside a fixed magnetic field.
Hence, Generators are used on a large scale to provide backup electricity for appliances that need electricity to run at offices and homes. This type of power source is used mostly at places where power supply from grids is not possible such as in farming operations and mining.

Generator
A generator converts kinetic energy into electricity, so it works as an electric engine. Electricity is procured in a gasoline-powered generator by the internal combustion engine driving the rotating shaft and turning the armature. Generators tend to use different kinds of sources for producing electricity such as wind energy, water energy, etc.
They are also used in places such as construction sites and large development areas where electricity is not easily accessible. However, Some electrical generators are portable and small as well and big generators which need proper and permanent installation are available as well.
Industrial generators are capable of producing a lot of power and hence are capable of maintaining electricity to large manufacturing facilities. Some other kinds of generators are bi-fuel generators, diesel generators, propane generators, and natural gas generators.
Difference between Alternator And Generator
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Difference between Alternator and Generator has been tabulated below:
| Factors | Alternator | Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A device in which mechanical energy is converted into AC electrical energy. | A device in which mechanical energy is converted into AC or DC electrical energy. |
| Output Current | It induces an alternating current. | It can generate either direct or alternating current. |
| Efficiency of Energy | They are very efficient. | They are less efficient. |
| Output | They have a higher output. | They have a lower output. |
| Conservation of Energy | Energy is conserved in them as they use only the required amount of energy. | They conserve less energy as they use all the energy that is produced. |
| Polarization After Installation | There is no Polarization required. | Polarization is required after installation. |
| Magnetic Field | The magnetic field in an alternator rotates inside the stator. | The magnetic field in a generator is stationary or fixed where the armature winding spins. |
| Armature Movement | The armature is stationary. | The armature is rotating. |
| Input Supply | Input supply is taken from the stator. | Input supply is taken from the rotor. |
| RPM (Rotation Per Minute) Range | They have a wide range of RPM. | They have a low range of RPM. |
| Voltage Generation | Voltage is only produced when needed. | Voltage is produced at all times. |
| Size | They are generally smaller in size. | They are generally larger and require more space to fit in. |
| Brush Efficiency | The brushes last longer. | The brushes last lesser. |
| Charging of a Dead Battery | They never charge a dead battery | They can be used for charging a dead battery. |
| Uses | They are used in the automobile industry as a charging system for the battery. | They are widely used to produce large-scale electricity. |
Things to Remember
- A mechanics of alternator converts the energy which is mechanical from a major mover into the AC.
- The generator converts the energy which is mechanical from the first cause into a DC or AC.
- The induced current in the alternator is AC.
- Both the AC and DC power is generated by A Generator.
- The alternator features a magnetic flux with a rotating field.
- The generator features a magnetic flux which may be a rotating field for the high voltage generation and therefore the voltage which is that the low and a stationary magnetic flux is employed.
- Input supply in a generator is taken from the rotor.
- Input supply in an alternator is taken from the stator.
Read More:
Sample Questions
Ques. How to reduce the eddy current losses? (1 Mark)
Ans. To reduce current losses one shall laminate the core with a varnish or a paper to insulate it from each other.
Ques. What are the advantages of the stationary armature and rotating field system? (2 Marks)
Ans. The advantages of the stationary armature and rotating field system are listed below:
- It becomes easy to install the stationary armature coils.
- It becomes easy to achieve The peripheral speed.
- Only two slip rings are used.
Ques. What are the losses in a generator? (2 Marks)
Ans. The losses in a Generator are listed below:
- Windage loss
- Friction loss
- Rotor copper
- Stator iron
- Stator copper
Ques. What are the advantages of the stationary armature and rotating field in an AC generator? (3 Marks)
Ans. The advantages of the rotating field and stationary armature in an AC generator are listed below:
- It becomes easy to Collect output from the stationary armature.
- We can use higher voltage for the stationary armature.
- It becomes easy to supply low voltage excitation to the rotor, When the armature is stationary, through the slip rings.
Ques. What are the advantages of parallel operations of alternators? (3 Marks)
Ans. Parallel operations of alternators have several advantages, some of them are listed below:
- The parallel operations provide a continuous connection to its consumers, if a breakdown of an alternator occurs at the place.
- This arrangement of alternators is economical and makes the operation efficient.
- The extra alternators are arranged parallel to each other, Hence, the installation of extra alternators in times of need is easy.
- The arrangement helps in meeting the need of an outsized alternator through multiple alternators and their arrangement in simultaneous operation.
Ques. (a) What do you understand by the terms ‘direct current’ and ‘alternating current’?
(b) Name some sources of direct current and some of alternating current.
(c) State an important advantage of alternating current over direct current.
(d) What is the frequency of A.C. supply in India? (3 Marks)
Ans. (a) If the current flows in one direction only, it is known as direct current; and if the current reverses direction after equal intervals of time, it is called alternating current.
(b) Source of DC are dry cell, car battery, DC generator etc.
Sources of AC are AC generators, bicycle dynamos etc.
(c) An important advantage of AC over DC is that AC can be transmitted over long distances without much loss of electrical energy.
(d) 50Hz.
Ques. (a) In what respect does the construction of an A.C. generator differ from that of a D.C. generator?
(b) What normally drives the alternators in a Thermal Power Station ? What fuels can be used to heat water in the boiler? (3 Marks)
Ans. (a). Construction-wise, the only difference between a D.C. generator and an A.C. generator is in the way the two ends of the generator coil are linked to the outer circuit. In a D.C. generator we connect the two ends of the coil to a commutator consisting of two half rings of copper. In an A.C. generator we connect the two ends of the coil to two full rings of copper called slip rings. There is no commutator in an A.C. generator.
(b) Generally, the alternators in a Thermal Power Station are driven by the power of high pressure steam. To heat water in the boiler, fuels like coal or natural gas can be used.
Ques. What factors do the generated EMF in an alternator depend upon? (1 Mark)
Ans. Generated EMF depends on the number of armature coil turns, magnetic field strength, and the speed of the rotating field.
Ques. What is the power factor? (2 Marks)
Ans. The ratio between kilowatts (kW) and kilovolt amps (kVa) that is drawn from an electrical load is a power factor. The generator's connected load determines it. Generators, which have higher power factors, are more efficient in transfer energy to the connected load, while generators with a lower power factor are not as efficient and result in increased power costs.
Ques. What happens when an alternator is said to be over excited? (3 Marks)
Ans. An overexcited alternator always supplies lagging current to the connected load, which means that load is of lagging nature. Lagging load take active and reactive power from the supply or alternator. Therefore, reactive power flows outwards from an over-excited alternator.
Important Points:
- Under excited alternator works at the leading power factor
- The normal excited alternator works at the unity power factor
- The overexcited alternator works at lagging power factor
For Synchronous motor its opposite of alternator,
- Under excited synchronous motor works at lagging power factor
- The normal excited synchronous motor works at the unity power factor
- The overexcited synchronous motor works at a leading power factor
Previous Year Questions
- RMS value of AC is _______ of the peak value… [VITEEE 2006]
- The instantaneous values of alternating current and voltages in a circuit... [JIPMER 2003]
- The average power dissipated in the A.C. circuit is 2 watts. If a current... [KCET 2014]
- An alternating voltage of 220 V, 50 Hz frequency is applied across... [VITEEE 2018]
- An inductive circuit contains a resistance of 10 Ω and... [VITEEE 2011]
- An AC supply gives 30 Vrms which is fed on... [JIPMER 2003]
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Do Check Out:






Comments