
Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Resonance can be defined as the phenomenon of the increased amplitude of vibration of a system or an object when an external force or external vibrating system has a frequency similar to the natural frequency of the system under consideration. Resonance is characterised by an increase in the amplitude of the vibration. It can be a result of an external periodic force that has a similar frequency or an external vibrating system with a matching frequency. Resonance usually takes place when the matching vibrations of an object increase the amplitude of an object’s oscillations.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Resonance, Simple Harmonic Motion, Frequency, Amplitude, Oscillation, Wavelength, Velocity, Vibration, Sound, Waves, Electromagnetic Spectrum
What is Resonance?
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Resonance is a phenomenon that gets induced by either an external periodic force or an external vibrating system which is having a specific frequency matching the natural frequency of vibration of the system under consideration. It is a special case of Simple Harmonic Motion. This causes the amplitude of the vibration to increase. There are various common examples which illustrate this phenomenon.
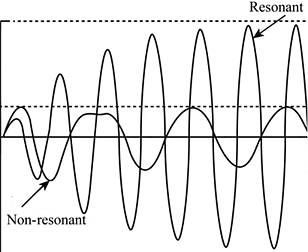
Resonance
Every system of objects which is under oscillatory motion has a natural frequency of oscillation. Similarly, periodic forces also have a particular frequency. When the frequencies match, it leads to resonance. Some common examples of resonance are the motion of the swing, the vibration of bridges, etc. The basic concept behind all these examples is the application of a periodic force with a similar frequency to that of the swing or the bridge.
Read More:
Types of Resonance
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The different types of resonance are :
Mechanical Resonance
Mechanical resonance is the phenomenon by which the amplitude of vibration of a mechanical system increases. This happens when its frequency matches the system’s natural frequency. Mechanical resonance is of great importance in designing buildings.
Engineers have to ensure that the components of the building do not have mechanical resonance frequencies similar to driving vibrational frequencies of motors and other oscillatory parts.
This is done to avoid a resonance disaster in the building. In major buildings dampers are used to cancel the effects of resonance. Although the structures are designed at the resonant frequency which mostly never occurs. Construction in earthquake-prone regions requires careful analysis of the vibratory motion of the earth.
Acoustic Resonance
Acoustic resonance is concerned with acoustic instruments. Acoustic instruments produce sounds in the hearing range of humans. Acoustic instruments use resonators like strings of a violin which produce resonance and amplify the sound produced. It can also lead to the failure of the instrument at the resonant frequency. For example, a wine glass can be broken by producing a resonating frequency. Although such resonating frequency is difficult to achieve.

Resonance in a Tuning Fork
Electrical Resonance
In case of electrical circuits, when inductive reactance equals the capacitive reactance, then the condition is called electrical resonance. Another case is when the impedance becomes minimum or zero and maximum in series and parallel circuits respectively.
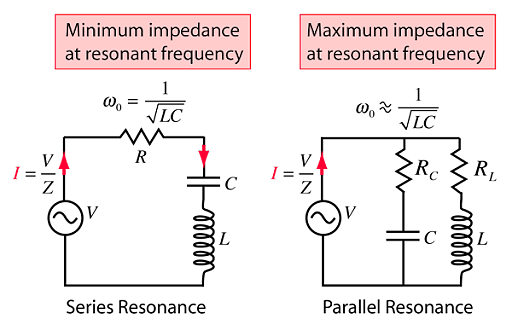
Electrical Resonance
For LC oscillations in electric circuits,
Resonant frequency = 1/\(\sqrt{LC}\)
- L = Inductance
- C= Capacitance
Optical Resonance
Optical resonators are used in optical instruments like parametric oscillators and interferometers. Resonators like the optical cavity are a major part of lasers. For certain resonant frequencies, these optical resonators produce standing waves. Optical resonators like optical cavities have a higher value of the Q factor.

Optical Resonance
Orbital Resonance
Celestial bodies like planets of the solar system exert gravitational forces on each other. This mutual gravitational effect is enhanced or amplified when the exertion of force is periodic. This phenomenon of the amplified effect of gravitational forces on the planetary bodies in their orbits is called orbital resonance.
Orbital Resonance
Orbital resonance has an important role to play in deciding the orbital stability of planets in their celestial motion.
Atomic Resonance
Resonance phenomenons like Nuclear Magnetic Resonance are used by researchers to study molecular physics and crystalline structures. At the atomic and molecular levels, the NMR technique is used for magnetic resonance imaging which is of great importance in the medical field. Similar to NMR is Electron paramagnetic resonance also called the electron spin resonance.

Atomic Resonance
Examples of Resonance
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Some of the real-life examples of resonance are as follows.
Musical Instruments
When any musical instrument is played by producing a disturbance and using a resonator, standing waves are created which make the instrument vibrate at its natural frequency. Each instrument has its specified natural frequency of vibration which are also known as harmonics. If another instrument is played at the same frequency then due to resonance the vibratory amplitude of the first one increases. This is the phenomenon of resonance.
Swing
The swing is a very common example of resonance that we see in daily lives. The motion of the swing tells us the importance of periodically frequent forces. Once the swing attains its natural frequency of motion, then only a small amount of force is required periodically to maintain its motion. If the force applied is irregular or higher in magnitude then the motion of the swing will break. Each time a small force hits, the swing goes higher.

Resonance in Swing
Bridge
A major example is when people march on a bridge in tandem. If the frequency of the falling footsteps of the soldiers matches with the natural frequency of vibration of the bridge, then resonance will take place increasing the amplitude of vibration which may result in the collapse of the bridge. This is the reason why soldiers are asked to break their steps while passing a bridge.
Calculation of Resonant Frequency
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The frequency at which a system achieves the state of resonance is called the resonant frequency. At this frequency, the system vibrates at the highest amplitude. The resonant frequency allows the motion of vibration or oscillation to go on for a long time. Mathematically the resonant frequency is given by:
| f = v / λ |
Where,
- f → frequency
- v → wave velocity
- λ → wavelength
Previous Year Questions
- In the circuit shown, the symbols have their usual meanings … [BITSAT 2018]
- An electrical cable having a resistance of … [WBJEE 2009]
- A coil of inductance 8.4 mH and resistance … [JEE Advanced 1999]
- A coil of resistance 10Ω … [VITEEE 2011]
- For a coil having L = 2 mH, current flow through … [NEET 2001]
- A vehicle, with a horn of frequency n is moving with a velocity … [NEET 1998]
- With the propogation of a longitudinal wave through a material medium … [NEET 1992]
- The frequency of sinusoidal wave y … [NEET 1992]
- For production of beats the two sources must have … [NEET 1992]
- A siren emitting a sound of frequency 800 Hz … [NEET 2016]
- A tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz … [NEET 2010]
- In a hall, a person receives direct sound waves from a source … [BHU UET]
- Which of the following electromagnetic radiations have the longest wavelength … [NEET 1989]
- 4.0 g of a gas occupies 22.4 litres at NTP … [NEET 2015]
- A standing wave having 3 nodes and 2 antinodes … [NEET 1998]
Things to Remember
- Resonance can be defined as the phenomenon of the increased amplitude of vibration of a system or an object when an external force or external vibrating system has a frequency similar to the natural frequency of the system under consideration.
- The different types of resonance are mechanical, acoustic, atomic, orbital, electrical and optical.
- Mechanical resonance is the phenomenon by which the amplitude of vibration of a mechanical system increases. It is of great importance in designing buildings.
- Optical resonators are used in optical instruments like parametric oscillators and interferometers. These resonators help achieve the state of resonance.
- Atomic resonance is very useful in the medical field. Techniques like NMR and Electron Paramagnetic Resonance are some of the well-known techniques.
- The frequency at which a system achieves the state of resonance is called the resonant frequency. At this frequency, the system vibrates at the highest amplitude. Mathematically it is given as f = v / λ, where v is the wave velocity and λ is the wavelength.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques. Define resonance. Give three examples where we experience resonance in real life. (5 Marks)
Ans. Resonance can be defined as the phenomenon of the increased amplitude of vibration of a system or an object when an external force or external vibrating system has a frequency similar to the natural frequency of the system under consideration. Resonance is characterised by an increase in the amplitude of the vibration. It can be a result of an external periodic force that has a similar frequency or an external vibrating system with a matching frequency.
Some daily life examples of resonance are :
- When any musical instrument is played by producing a disturbance and using a resonator, standing waves are created which make the instrument vibrate at its natural frequency. If another instrument is played at the same frequency then due to resonance the vibratory amplitude of the first one increases.
- The swing is a very common example of resonance that we see in daily lives. Once the swing attains its natural frequency of motion, then only a small amount of force is required periodically to maintain its motion. If the force applied is irregular or higher in magnitude then the motion of the swing will break.
- A very common case is soldiers marching on a bridge. If the frequency of the falling footsteps of the soldiers matches with the natural frequency of vibration of the bridge, then resonance will take place increasing the amplitude of vibration which may result in the collapse of the bridge. This is the reason why soldiers are asked to break their steps while passing a bridge.
Ques. What is Mechanical Resonance? (2 Marks)
Ans. Mechanical resonance is the phenomenon by which the amplitude of vibration of a mechanical system increases. This happens when its frequency matches the system’s natural frequency. Mechanical resonance is of great importance in designing buildings. Engineers have to ensure that the components of the building do not have mechanical resonance frequencies similar to driving vibrational frequencies of motors and other oscillatory parts. This is done to avoid a resonance disaster in the building.
Ques. What is Acoustic resonance? (2 Marks)
Ans. Acoustic resonance is concerned with acoustic instruments. Acoustic instruments produce sounds in the hearing range of humans. Acoustic instruments use resonators like strings of a violin which produce resonance and amplify the sound produced. It can also lead to the failure of the instrument at the resonant frequency.
Ques. How to calculate Resonant Frequency? (2 Marks)
Ans. The frequency at which a system achieves the state of resonance is called the resonant frequency. At this frequency, the system vibrates at the highest amplitude. The resonant frequency allows the motion of vibration or oscillation to go on for a long time.
Mathematically the resonant frequency is given by
f = v / λ
Where,
f → frequency
v → wave velocity
λ → wavelength
Ques. What is Electrical resonance and Optical resonance? (2 Marks)
Ans. In case of electrical circuits, when inductive reactance equals the capacitive reactance, then the condition is called electrical resonance. Another case is when the impedance becomes minimum or zero and maximum in series and parallel circuits respectively.
Optical resonators are used in optical instruments like parametric oscillators and interferometers. Resonators like the optical cavity are a major part of lasers. For certain resonant frequencies, these optical resonators produce standing waves.
Ques. Why are soldiers asked to break steps while crossing a bridge? (3 Marks)
Ans. Soldiers marching through a bridge are asked to break steps to avoid resonance with the bridge’s natural frequency. When the soldiers march in tandem the frequency of their footsteps falling on the bridge surface may match with the natural oscillating frequency of the bridge. If the frequencies match then the bridge will oscillate with increased amplitude. This can lead to the collapse of the bridge. Hence the soldiers are asked to break their footsteps. This helps in breaking the effect of resonance by making the force application irregular.
Ques. Define resonant frequency. (2 Marks)
Ans. The frequency at which a system achieves the state of resonance is called the resonant frequency. At this frequency, the system vibrates at the highest amplitude. The resonant frequency allows the motion of vibration or oscillation to go on for a long time.
Mathematically the resonant frequency is given by
f = v / λ
Here
- f = frequency
- v = wave velocity
- and λ = wavelength
Ques. What basic conditions are required for resonance? (3 Marks)
Ans. The basic criteria which must be satisfied for resonance to take place are :
- A system or an object which has a natural frequency of oscillation.
- A driving force which has a frequency similar to the natural frequency of the oscillating system.
- Friction, viscosity and resistance of any kind should be the least.
Ques. Write the advantages and disadvantages of resonance. (4 Marks)
Ans. Advantages:
- Atomic resonance techniques like NMR and Electron Paramagnetic Resonance are used in the medical field.
- Orbital resonance is used to predict the stability of electrons inside the atom.
- Resonators are used in musical instruments.
- Resonance causes the motion of the swing.
Disadvantages:
- Resonance can lead to the collapse of structures if any external force is applied like an earthquake or soldiers marching in tandem on a bridge and its frequency matches the frequency of oscillation of the structure.
- Resonance can lead to discomfort in building apartments in case of earthquakes. If the frequency of the earth’s vibration matches the design frequency of the building it may also lead to collapse.
Ques. Differentiate between periodic and oscillatory motion. (3 Marks)
Ans.
| Periodic Motion | Oscillatory Motion |
|---|---|
| Periodic motion repeats itself after regular intervals. | Oscillatory motion is the to and fro movement of a body about a fixed position. |
| The time period associated with the periodic motion is a definite interval of time. | An oscillation having a definite period is called a periodic oscillation. |
| Examples: Movement of hands of a clock | Examples: Swinging of swing, vibration in strings, etc. |
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:







Comments