Muskan Shafi Education Content Expert
Education Content Expert
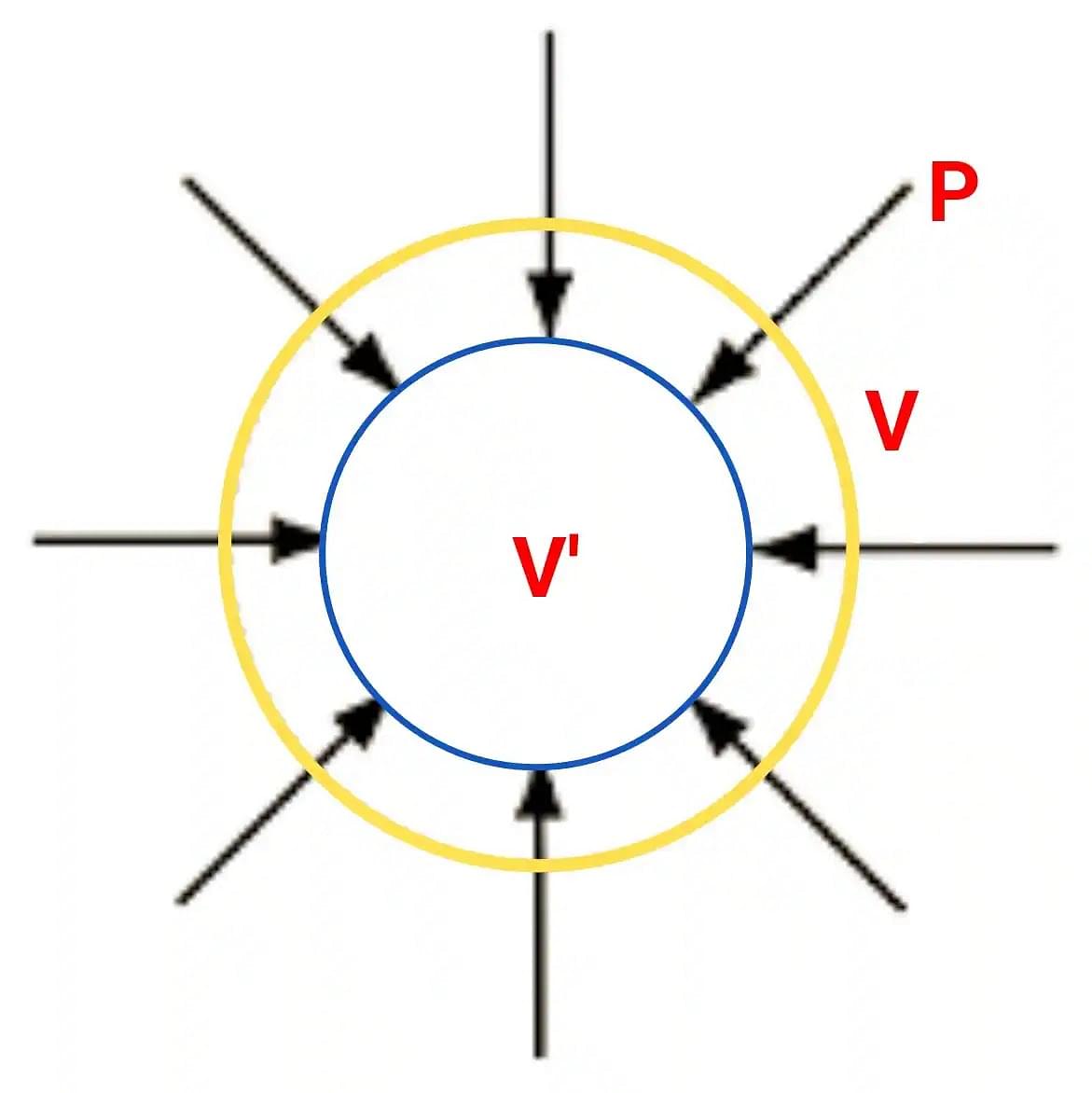
Bulk Modulus is a measure of the resistance of a substance to uniform compression. It is the change in the volume of a body produced when it undergoes compression on all sides. It is a numerical constant used to specify the elastic characteristics of a solid or fluid on application of pressure.
- Bulk Modulus is defined as the proportion of volumetric stress to volumetric strain.
- It is denoted by the letter ‘K’ or ‘B’.
- It is measured in the units of Pascals (Pa).
- Bulk Modulus gives a measure of how incompressible a solid is.
Read More: NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids
Key Terms: Bulk Modulus, Bulk Modulus of Elasticity, Elastic Moduli, Bulk Modulus Formula, Stress, Strain, Pressure, Young’s Modulus
What is Bulk Modulus?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Bulk Modulus is a numerical constant that determines the elastic properties of a solid or fluid when subjected to uniform compression. It is one of the three mechanical properties of solids along with Shear Modulus and Young’s Modulus.
- Bulk Modulus describes how resistant a substance is to compression.
- It is also referred to as ‘Volume Strain Modulus’.
- Volume strain is the difference in the volume of an object divided by the original volume.
- Bulk modulus is defined as the change in the relative volume of an object when stress is uniformly applied to the surface of the object.
- It is denoted by ‘K’ or ‘B’ and is measured in Pascals or Newtons per Square Meter (N/m2).
Bulk Modulus
Elastic Moduli
Modulus of Elasticity is defined as the ratio between stress and strain. Young’s Modulus, Shear Modulus, and Bulk Modulus are three major elastic moduli.
| Elastic Moduli | Definition |
|---|---|
| Bulk Modulus | It is the ratio of volumetric stress to volumetric strain and is denoted by B. |
| Young’s Modulus | It is the ratio of longitudinal stress to longitudinal strain and is denoted by Y. |
| Shear Modulus | It is the ratio of shear stress to shear strain and is denoted by G or S. |
Read More:
Bulk Modulus of Materials
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
Bulk modulus is a measure of the compressibility of a material. The higher the bulk modulus, the lower the compressibility of the material. The bulk modulus of all three states of matter, i.e. solids, liquids, and gases are listed in the table below:
Read More: Mechanical Properties of Solids Important Questions
Bulk Modulus of Elasticity Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Bulk Modulus gives a description of the elastic properties of a material since it returns to its original volume once the pressure is released. It is the ratio of volumetric stress to volumetric strain.
Bulk Modulus Formula is given as follows:
| \(K = {\Delta \ P\over \Delta \ V/V}\) |
Where
- K: Bulk Modulus
- ΔP: Change in the Pressure or Force Applied Per Unit Area.
- v: Initial Volume of the Material.
- ΔV: Change in the Volume of the Material due to the compression.
Solved ExampleExample: Calculate the bulk modulus of a material that experienced a change of pressure of 5 x 104 N/m2 and its volume goes from 4 cm3 to 3.9 cm3. Solution: Given that,
Using the Vulk Modulus Formula, K = ΔP / (ΔV/V) K = (5 x 104 N/m2) / ((4 cm3 – 3.9 cm3)/4 cm3) = 0.125 x 104 N/m2 K = 1.25 x 104 N/m2 Thus, the bulk modulus of the material is 1.25 x 104 N/m2. |
Read More: Important MCQs on Mechanical Properties of Solids
Uses of Bulk Modulus
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
Bulk modulus is used to measure the incompressibility of a material. For instance, the value of K for steel is 1.6×1011 N/m2 and the value of K for glass is 4×1010N/m2. Here, k for steel is more than three times the value of K for glass. This indicates that glass is more compressible than steel.
If we try to find the result of the value of a diamond and compare it with the value of glass and steel, then
- Atmospheric Pressure = 1.01×105 N/m2
- Bulk Modulus of Bone = 1.5×1010 N/m2
- Pressure at Deep Point = 1.09×108 N/m2
Check More:
Solved Examples on Bulk Modulus
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Here are a few solved examples on Bulk Modulus to understand the formula better:
Example 1: The bulk modulus for water is given 2.1GPa. Compute the change in volume of 200ml water that is subjected to a stress of 2MPa.
Solution: Given that,
- Bulk modulus of water = 2.1GPa
- Volume of the water = 200ml
- Pressure exerted = P = 2MPa
Using the Bulk Modulus Formula,
B = ΔP/(ΔV/V)
- B = 2.1 GPa = 2.1 x 109 Pa.
- V = 200 ml = 2 x 10-6 ml.
- P = 2MPa = 200 x 106 Pa.
B = - (1/p) (ΔV/V) = ΔV = pV/B
B = (2 x 106 x 200 x 10-6) = 2.1 x109
B = 0.19 ml
Example 2: Using Bulk Modulus Formula, calculate the bulk modulus of a body that practices a change in stress of 4x104N/m2 and its volume changes from 5cm3 to 4.8cm3.
Solution: It is given that,
- The volume of the body = 5cm3
- The pressure exerted = P = 4 x 104N/m2
- The change in volume of the body = ΔV = 5 - 4.8 = 0.2 cm3
Using the Vulk Modulus Formula,
B=ΔP/(ΔV/V) = PV × VB = ΔP ΔV=PVV
Substituting the values,
B = ΔP/(ΔV/V) = 4×104 × 50.2 = 106 N/m2
Handwritten Notes on Class 11 Mechanical Properties of Solids
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
Here are the handwritten notes on the Mechanical Properties of Solids and related concepts:















Things to Remember
- Bulk Modulus is one of the three mechanical properties of solids along with Young’s Modulus and Shear Modulus.
- It describes the elastic properties of a solid or fluid when it is under pressure on all surfaces.
- The volume of material reduces when pressure is applied and returns to its initial volume when the pressure is removed.
- Bulk modulus is used to measure the incompressibility of a material.
- ‘K’ or ‘B’ are used to denote bulk modulus which is measured in Pascals.
- Bulk Modulus Formula is given as K = ΔP/(ΔV/V).
Previous Years’ Questions
- Bulk modulus of water is 2×10 9 N/m2. The change in pressure… (Punjab PMET 2011)
- The bulk modulus of a perfectly rigid body is…
- The bulk modulus of a fluid is inversely proportional to… (JIPMER 1996)
- Bulk modulus of elasticity (K) represents incompressibility…
- How does the isothermal bulk modulus…
- The relationship between Young's modulus Y, bulk modulus…
- Young modulus of a perfectly rigid body is… (KCET 2020)
- The relation between Shear modulus (G) , Young modulus… (J & K CET 2019)
- The dimension of the modulus of rigidity is… (AIIMS 1994)
- The ratio of shearing stress to the shearing strain is defined…
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the dimensional formula of Bulk Modulus? (1 Mark)
Ans. The dimensional formula of the bulk modulus is [ML-1 T-2].
Ques. What is the use of Bulk Modulus? (1 Mark)
Ans. Bulk modulus of elasticity is an elastic modulus used to determine the compressibility of the material.
Ques. What is Bulk Modulus? (3 Marks)
Ans. Bulk Modulus is the ratio of volumetric stress to the volumetric strain of material. It is denoted by either K or B. It is a measure of how compressible a material is, thus, the higher the bulk modulus, the lower will be the compressibility of the material, and vice versa. It has the same units as pressure as strain is unitless. Thus, the unit of measurement of Bulk Modulus is Pascals (Pa).
Ques. What factors affect Bulk Modulus? (2 Marks)
Ans. Bulk Modulus is affected by temperature. The higher the temperature, the lower would be the bulk modulus. It means the lower the temperature of a fluid, the more difficult it is to compress. Entrained gas, especially air, affects the bulk modulus of fluids drastically. The more entrained gas is there in a fluid, the lower will be the bulk modulus.
Ques. The pressure in an ammonium testing system is found to be 255 MPa. What will be the change in volume of the copper piece in percentage when subjected to this pressure and the bulk modulus of copper is 1.38 x 1011 Pa? (3 Marks)
Ans. It is given that the pressure in the testing center is 255 MPa.
Using the Bulk Modulus Formula,
K = V(∆P) / ∆V
(ΔV / V) = 255 × 106 / 1.38 × 1011 × 100
Thus, the change in volume of the copper piece in percentage is 0.184%.
Ques. Calculate the bulk modulus of a liquid compressed in a cylinder from 0.0125 m3 volume at 80 N/cm2 pressure to 0.0124 m3 volume at 150 N/cm2 pressure. (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that
- ΔP = 150 – 80 = 70 N/cm2
- ΔV = 0.0124 – 0.0125 = -0.0001 m3
- V = 0.0125 m3
Using the Bulk Modulus Formula,
K = ΔP × V / ΔV
K = 70 × 0.0125 / 0.0001
K = 8750 N/cm2
Thus, the bulk modulus of the liquid is 8750 N/cm2.
Ques. The pressure of a liquid increased from 70 N/cm2 to 130 N/cm2 and the amount of liquid in the container shrunk by 0.15%. Calculate the bulk modulus. (3 Marks)
Ans. It is given that,
- ΔV = V × 0.15 /100 = 15V × 10-4 m3
- Volume of liquid = V m3
- ΔP = 130 – 70 = 60 N/cm2
- Volumetric Strain = 15 × 10-4
Using the Bulk Modulus Formula,
K = ΔP × V / ΔV
K = 60 / 15 × 10-4
K = 4 × 104 N/cm2
Ques. How to calculate Bulk Modulus? (2 Marks)
Ans. Bulk modulus is associated with a volume strain when a volume is compressed. The bulk modulus formula is calculated using the given formula,
\(K = {\Delta \ P\over \Delta \ V/V}\)
Here, K is the Bulk Modulus, ΔP is the change in the Pressure or Force Applied Per Unit Area, v is the initial volume of the Material, and ΔV is the change in the Volume of the Material due to the compression.
Ques. The change in pressure is 80 N/Cm2, and the object’s actual volume is 0.128 m3, Calculate the volume change is the bulk modulus is 7390 N/cm2. (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that,
- ΔP = 80 N/cm2
- K = 7390 N/cm2
- V = 0.128 m3
Using the Bulk Modulus Formula,
K = ΔP × V / ΔV
ΔV = ΔP × V / K
ΔV = 80 × 0.128 / 7390
ΔV = 10.24 / 7390
ΔV = 0.0013 m3
Ques. The change in pressure is 78 N/cm2, and the volume change is 0.128 m3. Calculate the object’s actual volume if the bulk modulus is 7390 N/cm2. (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that,
- ΔP = 78 N/cm2
- K = 6390 N/cm2
- ΔV = 0.1 m3
Using the Bulk Modulus Formula,
K = ΔP × V / ΔV
V = K × ΔV / ΔP
V = 6390 × 0.1 / 78
V = 8.192 m3
Check-Out:






Comments