
Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Hydraulic machines are machines or tools that operate using fluid power. A great amount of electricity is transferred through hoses and little tubes in these machines.
- The fluid is passed throughout the machine to motors and hydraulic cylinders where it is pressurized before being sent to end effectors via control valves and tubes.
- The hydraulic system is similar to pneumatic systems as it is also based on Pascal's law which asserts that any pressure applied to a fluid inside a closed system would be transmitted equally everywhere in all directions.
- Instead of a compressible gas, a hydraulic system uses an incompressible liquid as its fluid.
- Hydraulic systems are typically used to lift very heavy weights which are very difficult to lift.
- Hydraulic machines are based on the principle of pressure.
Read More: Mechanical Properties of Fluids
| Table of Content |
What are Hydraulic Machines?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Hydraulic Machines are types of machinery which use fluid power for their functioning.
- In these types of machines, a very large amount of power is transferred via small tubes and hoses.
- Herein, fluid is further transmitted all throughout the machine to motors and hydraulic cylinders.
- There, it gets pressurized and is then transferred to the end effectors via control valves and tubes.
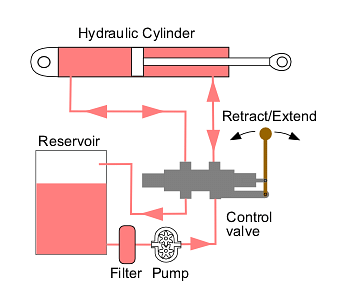
Hydraulic Machines
Pascal’s Law
As per Pascal’s law for the transmission of fluids:
- When an external pressure has been applied on any particular part of a fluid in a vessel, it is transmitted equally in all directions.
- The hydraulic system is like pneumatic systems that are based on Pascal's law.
- Pascal’s law further states that any pressure that has been applied to a fluid inside a closed system is going to transmit the pressure equally everywhere and in all directions.
- A hydraulic system is known to use an incompressible liquid as its fluid, instead of a compressible gas.
Pascal Law Formula
The formula of Pascal's law is:
| F = PA |
Where,
- F = Force applied
- P = Pressure which is transmitted
- A = Cross-sectional area
Read More:
| Concept Related Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Specific Heat Capacity of Water | Viscosity | Surface Energy |
| Value of R in ATM | Derivation of Continuity Equation | Terminal Velocity Formula |
Applications of Hydraulic Machines
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Some of the Hydraulic Machine applications are:
Hydraulic Brakes
Breakers, also known as hydraulic brakes, are braking mechanism arrangements in which appropriate brake fluid is utilized to transfer pressure from the control mechanism to the brake mechanism. Automobile hydraulic brakes function on the same principle.
- When we apply a small amount of effort to the pedal with our foot, the master piston moves inside the master cylinder and the pressure created is communicated through the brake oil which acts on a larger piston.
- A strong force is applied to the piston which is pushed down, expanding the brake shoes against the brake lining.
- We can observe that a fair force on the pedal results in a huge retarding force on the wheels in this way.
- The hydraulic brake system has the advantage that the pressure applied by pressing a pedal is distributed evenly among all cylinders which are normally coupled to the four wheels resulting in equal braking effort on all four wheels.
Hydraulic Lift
A Hydraulic Lift refers to an elevator powered by fluid pressure generated by a suitable fluid. It is commonly used in service shops and garages to raise automobiles.
- A hydraulic lift consists of two pistons that are separated by a liquid-filled gap.
- A piston with a tiny cross-section A1 is employed to exert a force, of say F1, on the liquid immediately.
- The pressure, given by P = F/A, is passed via liquid to the larger cylinder which is then connected to a larger piston with an area A2, resulting in an upward force given by P x A2.
| F2 = P x A2 = \(\frac{F}{A_1}\) x A2 |
- Thus, we can state that the piston can hold a large force such as the weight of a car or truck that is parked on the platform.
- The platform can be moved up or down by altering the force at the A1 area.
- As a result, we can say that the applied force has been increased by a factor of A2/A1, where A2/A1 is the overall mechanical advantage of the device.
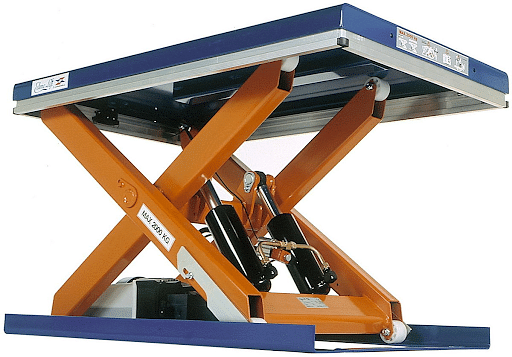
Hydraulic Lift
Hydraulic Jacks
Hydraulic jacks are more powerful than other tools as they can lift more weight. Hydraulic jacks are divided into two categories: Floor Jacks and Bottle Jacks.
- For storing and transporting hydraulic fluid, a hydraulic jack consists of a cylinder and pumping system.
- A hand-driven or mechanically powered pump is used to apply pressure to the fluid in the pumping system.
- The one-way valve directs the fluid toward the jack cylinder and prevents it from returning. Pascal's principle is used to guide the process.
Read More: Bulk Modulus

Hydraulic Jacks
Hydraulic Shock Absorbers
This is a stress absorption and dampening device.
- The components of a shock absorber are a cylinder filled with hydraulic oil and a piston.
- The piston will rise and fall in response to the string's compression and expansion.
Read More: Conservation of energy
Uses of Hydraulic Machines
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Today, hydraulics is used in practically every industry to move machines and equipment to fulfil various tasks. The uses of hydraulic machines are:
- Some examples are the usage of cranes in construction, tractors in agriculture, forklifts in manufacturing, and braking in transportation.
- Hydraulic machines use hydraulic fluid pressure to power movement or to provide a basic source of energy.
- Dump trucks, aluminium or plastic extruders, cranes, jackhammers, and hose crimpers are all examples of hydraulic machines.
- Metal stamping, injection moulding, and hose crimping are other activities performed by hydraulic machinery.
- The spinning motors, such as the Ferris wheel, are a great source of enjoyment in amusement parks. They use hydraulics technology to power rides and subsequently offer a motion to them.
- The concept of Hydraulics is used in almost every vehicle on the road. Brake fluid is an essential component of a vehicle's braking system. The act of pressing one's foot on the brake pedal causes a rod and piston within the master cylinder to move, achieving the desired effect which is slowing or halting the car.
- Lifting a big motor vehicle for repair and maintenance would be quite difficult without a hydraulic system. The system helps lift any heavy load to the appropriate height by using hydraulic fluid.
Read More:
Things to Remember
- Hydraulic Machines are a kind of machine which use fluid power to help its functioning.
- Pascal’s law claims that pressure applied to a fluid inside a closed system is going to transmit the pressure equally everywhere and in all directions.
- Some of the applications of Hydraulic systems are Hydraulic Jacks, Hydraulic Lift, Hydraulic Brakes, and Hydraulic Shock Absorbers.
- Hydraulic systems are utilized to lift very heavy weights which are very difficult to lift.
- A hydraulic machine is based on the principle of pressure.
Previous Year Questions
- A boy's catapult is made of rubber cord which is… [JEE Main 2019]
- A soap bubble, having radius of 1mm, is blown from a detergent solution… [NEET 2019]
- A liquid is filled upto a height of 20cm20cm in a cylindrical vessel… [KEAM]
- The force acting on a window of area 50cm×50cm of a submarine… [KEAM]
- A small spherical ball falling through a viscous medium of negligible density… [KEAM]
- A spherical ball of diameter 1cm and density… [KEAM]
- A man grows into a giant such that his linear dimensions… [JEE Main 2017]
- If the ratio of diameters, lengths and Young's modulus of steel… [NEET 2013]
- Ice pieces are floating in a beaker A containing water and also… [KEAM]
- Two wires are made of the same material and have the same volume…. [NEET 2018]
Sample Questions
Ques: How do hydraulic machines work? (1 mark)
Ans: A hydraulic machine is based on Pascal's law. Pascal’s law asserts that when pressure is applied directly to a confined fluid, it expands. Then a pressure change takes place throughout the fluid. A piston functions as a pump within the hydraulic press imparting a modest amount of mechanical force to a small region of the sample.
Ques: Define Hydraulic Brakes. (1 mark)
Ans. Hydraulic brakes, also called Breakers, are braking mechanism arrangements where appropriate brake fluid is used in order to transfer pressure from the control mechanism to the brake mechanism.
Ques: What are some of the hydraulic systems' drawbacks? (1 mark)
Ans. Hydraulic systems have a number of drawbacks, one of which is that they might leak, and the fluids present inside them are frequently corrosive to paint and seals. Another disadvantage, when compared to machines that use gears and shafts, is that any power transmission results in some losses owing to fluid flow resistance through the piping process.
Ques: Explain the benefits of hydraulic systems. (1 mark)
Ans. One of the benefits of a hydraulic system is the ease and precision with which it may be regulated. Hence they are capable of generating vast amounts of power. Hydraulic systems, therefore, have fewer moving components than mechanical and electrical systems in general.
Ques: What characterizes a hydraulic machine? (2 marks)
Ans. Hydraulic systems have the ability to apply force or torque multiplication without the use of mechanical gears or levers, regardless of the distance between the input and output by changing the effective areas in the two connected cylinders or changing the effective displacement (cc/rev) between a motor and pump. Hydraulic ratios are typically used with a torque ratio or a mechanical force for optimum machine designs, such as track drives and excavator boom motions.
Ques: What is Pascal’s law? Show its diagrammatic representation. (2 marks)
Ans. Pascal’s law states that any pressure applied to a fluid inside a closed system will transmit the pressure equally everywhere and in all directions.

Pascal’s Law
Ques: Determine the pressure difference which comes when a woman is seen to go 10m deep inside the water. (Take the density of water = 1000Kg/m3.) (3 marks)
Ans. The difference between the pressures can be expressed by:
P1 – P2 = dgh
As per the given question:
- d = 1000,
- g = 10,
- And, h = 10
P1 – P2 = dgh
⇒ P1 – P2 = (1000)(10)(10)
⇒ P1 – P2 = 105 Kg/m2
Ques: The area of A is said to be 60 cm2 while the area of B is 4,200 cm2, thus find the external input force of F. (3 marks)
Ans. Force of F can be evaluated by using the equation of Pascal’s principle:
F1 / A1 = F2 / A2
⇒ F1 / 60 cm2 = 3500 N / 4200 cm2
⇒ F1 / 60 = 35 N / 42
⇒ F1 = (60)(35) / 42
⇒ F1 = 2100 / 42
⇒ F1 = 50 Newton
Ques: What are some Hydraulic Machine applications in everyday life? (3 marks)
Ans.The application of hydraulics in everyday life:
- Hydraulics are extensively used to move machinery and equipment. Some examples include cranes on construction sites and production warehouses.
- Hydraulic machines use hydraulic fluid pressure to power movement.
- The Hydraulic machine applications can easily be found in dump trucks, aluminium extruders, and cranes with jackhammers or hose crimpers.
Ques: Give a short note on “Hydraulic Lift”. (5 marks)
Ans. Hydraulic Lift can be defined as a type of device which helps to lift things by applying force to a liquid inside a cylinder, driving the piston higher.
- The piston is driven higher by incompressible oil injected into the cylinder.
- The piston then comes down due to the forces of gravity when the valve opens to discharge oil.
- The hydraulic lift has been based on the principle of Pascal’s Law to help produce force or motion.
- Pascal’s Law claims that a change of pressure on an incompressible liquid in a confined area is evenly distributed in every direction.
- A hydraulic system works when the force which is applied is at one point to an incompressible liquid, transmitting the force to a second point.
- The procedure involves two pistons connected through an oil-filled pipe.
Also check:







Comments