
Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Ques: An electric dipole of dipole moment p is lying along uniform electric field E. Calculate the work done in rotating the dipole by 90 degrees.
Ans: The work done in rotating the dipole by 90 degrees when dipole moment is lying along uniform electric field is “pE”.
Explanation: The potential energy of an electric dipole in a uniform electric field is given by an expression: U = -pEcosθ.
- where p is the dipole moment,
- E is the electric field strength,
- θ is the angle between the dipole moment and the electric field.
Initially, the dipole moment is aligned with the electric field, so θ = 0, and the potential energy is:
U1 = -pEcos0 = -pE
When the dipole is rotated by 90 degrees, the angle between the dipole moment and the electric field becomes θ = 90 degrees, and the potential energy becomes:
U2 = -pEcos90 = 0
The change in potential energy is then equal to the work done
Work Done = ΔU = U2 - U1 = 0 - (-pE) = pE
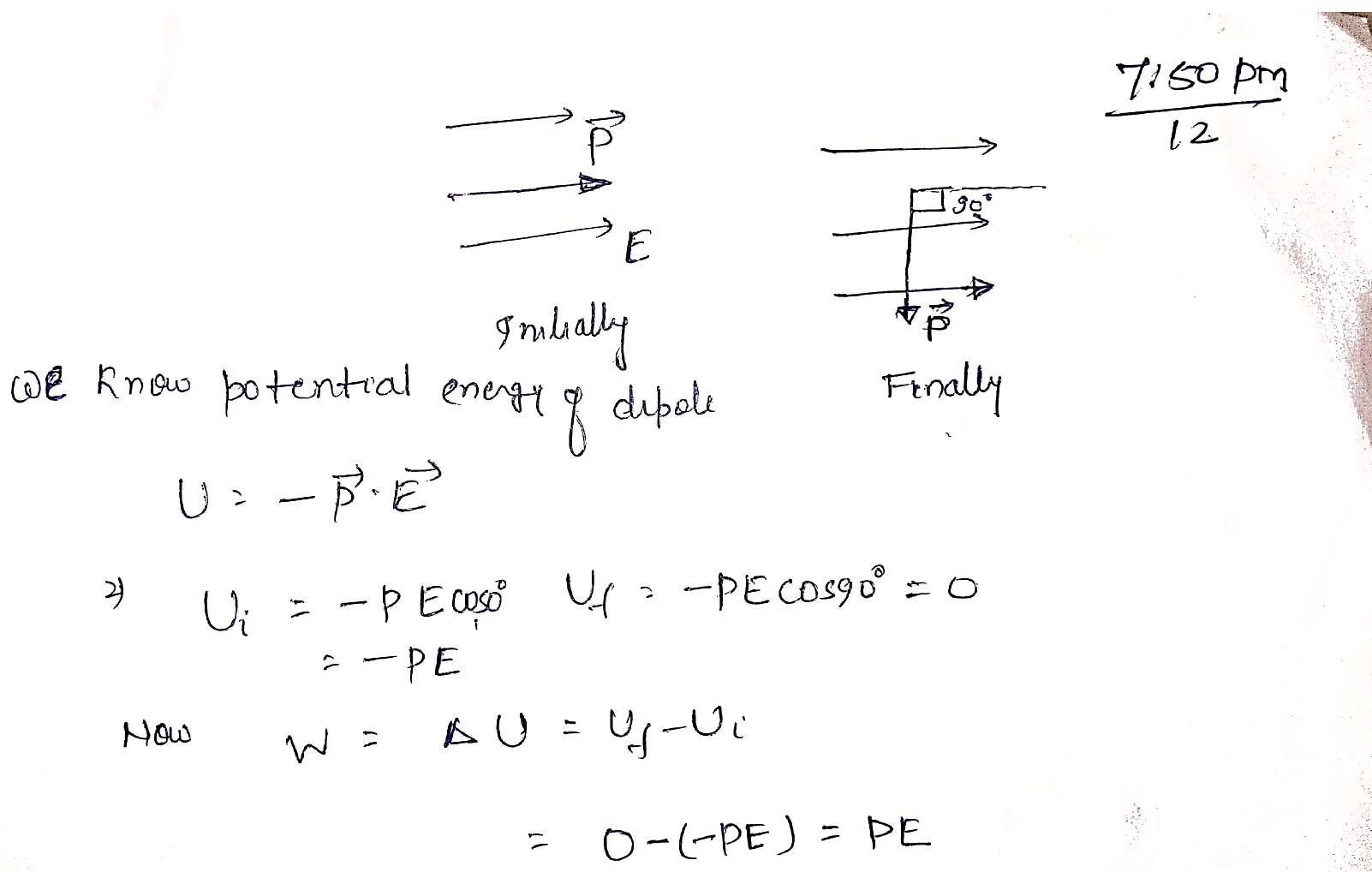
Therefore, the potential energy of the dipole in rotating it by 90 degrees is pE.






Comments