
Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
When an electric dipole of dipole moment vector p is placed in a uniform electric field vector E, it experiences a torque given by the formula:
| τ = p × E |
where τ is the torque vector, p is the dipole moment vector, and E is the electric field vector.
The magnitude of the torque is given by:
| |τ| = p E sin θ |
where θ is the angle between the dipole moment vector and the electric field vector.
The maximum torque occurs when the dipole moment vector is perpendicular to the electric field vector, i.e., when θ = 90 degrees. In this case, sin θ = 1, and the magnitude of the torque is:
| |τ|max = p E |
Therefore, the maximum torque experienced by the dipole is equal to the product of the dipole moment and the electric field strength.
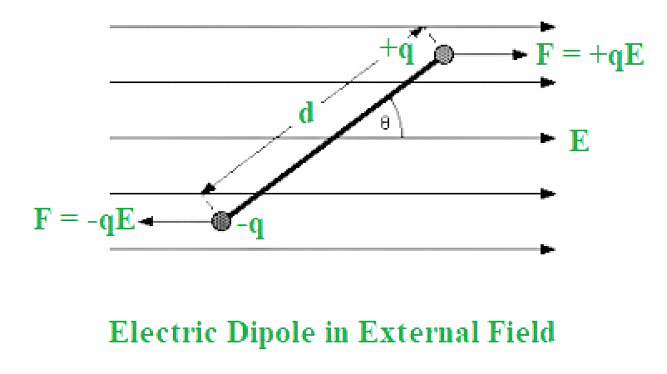
Electric Dipole in External Field
Also check:






Comments