Namrata Das Exams Prep Master
Exams Prep Master
Any decay in which the atomic nucleus of a certain element emits 42He and converts into an atom of a completely different element is known as alpha decay or -decay. Due to the emission of a helium atom, this decay results in a drop in mass number and atomic number and is denoted by the Greek letter α. Let’s discuss the topic in-depth along with some important questions.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Radioactivity, Alpha Decay, Beta Decay, Gamma Decay, Q value, Gamow theory, Atoms, Helium, Nucleus, Emission
What is Alpha Decay?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The transition of a radioactive nucleus into helium is known as alpha decay. During this transition, the starting element transforms into an entirely another element, changing its mass and atomic number in the process. Alpha decay can occur in any element heavier than lead. Lighter elements, on the other hand, show no signs of radioactive decay.

Alpha decay is a type of radioactive decay in which unstable atomic nuclei emit a helium nucleus (alpha particle) and transition into a more stable element in the process. The alpha particle, which was ejected out, is made up of four nucleons: two neutrons and two protons. The ratio of protons to neutrons in the parent nucleus is reduced by alpha radiation, resulting in a more stable structure. The nucleus of a helium atom is identical to an alpha particle. Ernest Rutherford, who employed alpha particles in his gold foil scattering experiment, conducted the first observations and investigations of alpha decay.
The atomic number of the radioactive sample changes as the alpha particle, which is made up of two protons and a neutron, exits the nucleus. After alpha decay, the element left behind is two atomic numbers and four mass numbers smaller.
For example, Uranium 238 92 decays to form Thorium23490.
23892U → 238-492-2Th + 42He → 23490Th + 42He
Thus, the transformation of a nucleus in an alpha decay can be written as;
AZX → A-4Z-2Y + 42α
Also Read:
Alpha Decay Equation
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Henry Becquerel discovered radioactivity. A Uranium compound was wrapped with black paper and placed in a drawer containing photographic plates. Later examination of the plates revealed that they had been exposed. Thus, the concept of radioactive decay was born as a result of this exposure. Such kinds of radioactivity can be observed.
- Gamma Decay (Photons having high energy are emitted)
- Beta Decay (Emission consists of Electrons)
- Alpha Decay (Emission consists of Helium nucleus)
Consider this alpha decay example to fully comprehend this. Assume that element Z has the mass number a and the atomic number b. This element converts to X during decay. Take a look at the following equation.
abZ → a-4b-2X + 42He
where:
42He is the released alpha particle.
a-4b-2X is the daughter nucleus, the ending nucleus.
abZ is the parent nucleus, the starting nucleus.
As a result, on both sides of this equation, the mass number and the atomic number balance out.
Occurrence of Alpha Decay
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Only the strongest elements experience alpha decay. The element's nucleus must be big enough or unstable enough to undergo spontaneous fission-like modifications. In such elements, it is the most common type of degradation. The alpha particles that are emitted from the nucleus have an energy level of roughly 5 MeV and a speed of around 5% of that of light. It's worth noting that alpha particles have a charge of +2 because they don't have any electrons. Because of its charge and mass, an alpha particle reacts violently with its environment, losing all of its energy practically instantly. A few centimeters of air can halt their forward momentum.
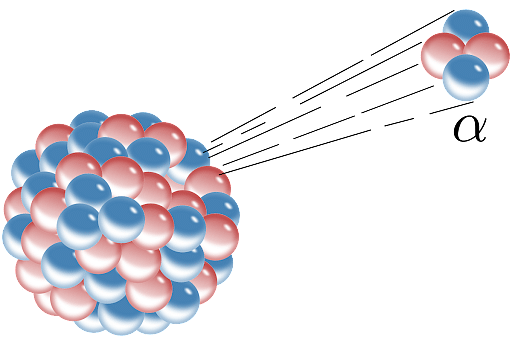
This type of radioactive decay reacts most aggressively with the human body due to its heaviness and charge. They have a strong ionizing power, which allows them to cause havoc on tissue. The victims' bodies develop blisters and burns as a result of an alpha radiation overdose.
Alpha Decay Example
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
One of the popular examples of alpha decay is the decay of uranium 23892U to thorium 23490Th with the emission of a helium nucleus 42He.
23892Ur → 23490Th + 42He
Other examples of alpha decay are:
23793No → 23391Pa + 42He
17578Pt → 17176Os + 42He
14964Gd → 14562Sm + 42He
Q value of Alpha Decay
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The difference between the total of the rest masses of the initial reactants and the sum of the end product masses is known as the Q-value in physics and chemistry. The Q-value is the difference between the final and beginning mass energy of the decaying products, to put it another way.
For alpha decay equations, this Q-value is,
Q = (mX – mY – mHe) c2
This decay's energy Q is split evenly between the modified nucleus and the Helium nucleus.

Gamow Theory of Alpha Decay
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The relationship between the energy of an alpha particle emitted and the decay constant for a radioactive isotope is defined by Gamow Theory or Geiger-Nutall law. It was created in 1911 by John Mitchell Nutall and Hans Geiger, hence the name.

When comparing shorter-lived isotopes to longer-lived isotopes, this rule clearly shows that shorter-lived isotopes emit more energy. Decay, on the other hand, is only one sort of radioactive decay. Beta and gamma decay can also occur in a nucleus.
Application and Importance
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Smoke detectors use radioactive materials that undergo alpha decay. Americium is a common element because it is a primary producer of alpha particles. Alpha particles are released inside the smoke detector. As a result, the air inside the detector becomes ionized. Because smoke in the detector absorbs this alpha radiation, the ionization is altered and the alarm is triggered if smoke is present.
Alpha particles are also utilized in a technique called Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectroscopy (APXS). The elemental composition of rocks and soil is determined using this method. This method was employed by NASA on their trips to Mars, notably the Pathfinder probes, to figure out what elements were present in Martian rocks.
In the medical field, alpha particles are also useful. TAT, or targeted alpha therapy, is a revolutionary cancer treatment that uses alpha decay to attack cancer cells. When lead-212 is ingested, it travels to the tumor location and emits alpha radiation, which kills all of the cells in the area.
Things to Remember
- Alpha decay is a nuclear process in which an unstable nucleus transforms into a different element by ejecting a particle containing two protons and two neutrons.
- Although alpha decay is not very penetrating, ingesting a chemical that undergoes it is dangerous because the released alpha particles can rapidly damage inside tissues despite their low range. Contact with membranes and live cells causes this harm.
- The alpha decay equation is: abZ → a-4b-2X + 42He; where: 42He is the released alpha particle, a-4b-2X is the daughter nucleus, the ending nucleus, abZ is the parent nucleus, the starting nucleus.
- For alpha decay equations, this Q-value is, Q = (mX – mY – mHe) c2
- This decay's energy Q is split evenly between the modified nucleus and the Helium nucleus.
- The relationship between the energy of an alpha particle emitted and the decay constant for a radioactive isotope is defined by Gamow Theory or Geiger-Nutall law.
- Alpha particles are utilized in a technique called Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectroscopy (APXS).
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the atomic mass number of the emitted alpha particle? (1 mark)
Ans: The atomic mass number of the emitted Alpha particle is four.
Ques. What is the penetration depth of an alpha particle? (1 mark)
Ans: The penetration power of Alpha particles is low which is usually few centimeters of air or by the skin.
Ques. What is the polarity of charge of the alpha particle? (1 mark)
Ans: The polarity of the alpha particle is positively charged.
Ques. What is alpha decay? (1 mark)
Ans: The transition of a radioactive nucleus into helium is known as alpha decay. During this transition, the starting element transforms into an entirely another element, changing its mass and atomic number in the process.
Ques. Which elements can undergo alpha decay? (1 mark)
Ans: Alpha decay can occur in any element heavier than lead. Lighter elements, on the other hand, show no signs of radioactive decay.
Ques. What is the use of the Geiger-Nutall Law? (1 mark)
Ans: The Geiger-Nutall law establishes a relationship between a radioactive isotope's decay constant and the energy of the released alpha particle.
Ques. How does alpha decay take place? (2 marks)
Ans: Only the strongest elements experience alpha decay. The element's nucleus must be big enough or unstable enough to undergo spontaneous fission-like modifications. In such elements, it is the most common type of degradation. The alpha particles that are emitted from the nucleus have an energy level of roughly 5 MeV and a speed of around 5% of that of light. It's worth noting that alpha particles have a charge of +2 because they don't have any electrons. Because of its charge and mass, an alpha particle reacts violently with its environment, losing all of its energy practically instantly. A few centimeters of air can halt their forward momentum.
Ques. What do you mean by the Q-value of alpha particle? (2 marks)
Ans: The difference between the total of the rest masses of the initial reactants and the sum of the end product masses is known as the Q-value in physics and chemistry. The Q-value is the difference between the final and beginning mass energy of the decaying products, to put it another way.
For alpha decay equations, this Q-value is,
Q = (mX – mY – mHe) c2
This decay's energy Q is split evenly between the modified nucleus and the Helium nucleus.
Ques. State the applications of alpha decay. (2 marks)
Ans: Smoke detectors use radioactive materials that undergo alpha decay. Americium is a common element because it is a primary producer of alpha particles. Alpha particles are released inside the smoke detector. As a result, the air inside the detector becomes ionized. Because smoke in the detector absorbs this alpha radiation, the ionization is altered and the alarm is triggered if smoke is present.
Alpha particles are also utilized in a technique called Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectroscopy (APXS). The elemental composition of rocks and soil is determined using this method. This method was employed by NASA on their trips to Mars, notably the Pathfinder probes, to figure out what elements were present in Martian rocks.
Ques. Write about the Gamow theory of alpha decay. (2 marks)
Ans: The relationship between the energy of an alpha particle emitted and the decay constant for a radioactive isotope is defined by Gamow Theory or Geiger-Nutall law. It was created in 1911 by John Mitchell Nutall and Hans Geiger, hence the name. When comparing shorter-lived isotopes to longer-lived isotopes, this rule clearly shows that shorter-lived isotopes emit more energy. Decay, on the other hand, is only one sort of radioactive decay. Beta and gamma decay can also occur in a nucleus.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Do Check Out:



Comments