Muskan Shafi Education Content Expert
Education Content Expert
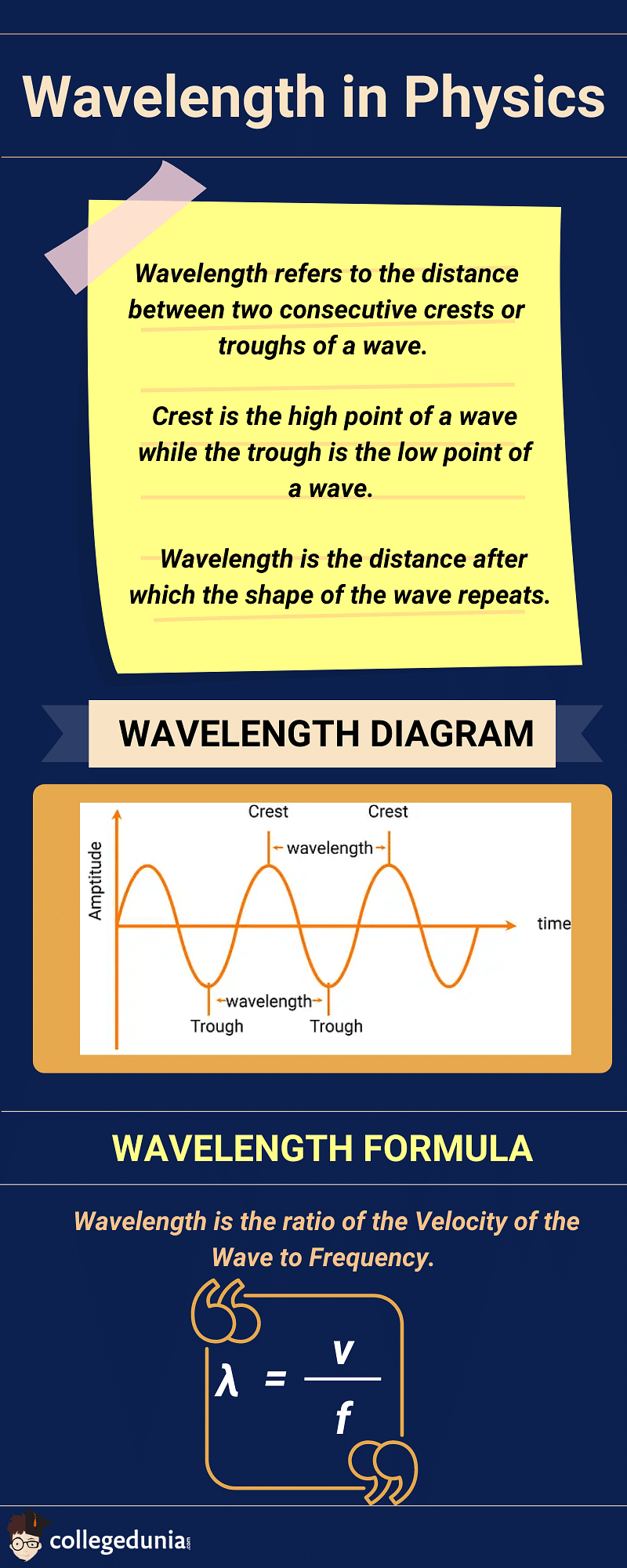
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive points on a wave. The consecutive points refer to two points or particles in the same phase and are referred to as two crests or two troughs.
- Wavelength is expressed as the ratio of Wave Velocity to Frequency.
- Frequency and Wavelength are inversely proportional.
- The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength.
- Wavelength is denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ).
Wavelength Formula is given as
| \(\lambda = {v \over f}\) |
Here, λ refers to the Wavelength, v is the Wave Velocity, and f is the Frequency.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Wavelength, Wave, Frequency, Electromagnetic Waves, Lambda, Wave Velocity, Crests, Troughs, Wien's Displacement Law
What is Wavelength?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Wave refers to a dynamic disturbance that transfers energy from one point to another. In Physics, the two most important types of waves are Mechanical Waves and Electromagnetic Waves.
- Wavelength refers to the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave.
- These two consecutive crests or troughs have to be in the same phase.
- Crest is the high point of a wave while the trough is the low point of a wave.
- In simpler words, Wavelength is the distance after which the shape of the wave repeats.
- It is represented by lambda (\(\lambda\)).
- Wavelength is in an inverse relationship with Frequency.
- The dimensional formula of Wavelength is [m0 l1 t0].
- The SI unit of Wavelength is meter (m).

Wavelength
Wavelength Formula
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Wavelength is the ratio of the Velocity of the Wave to Frequency. Wavelength Formula is as follows:
| \(\lambda = {v \over f}\) |
Where
- \(\lambda\) = Wavelength in m.
- v = Wave Velocity in m/sec.
- f = Frequency in Hz.
Read More:
| Related Concepts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Waves | Impedance of free space | Scintillation Counter |
| Electromagnetic Spectrum | Types of Radiation | Magnetic field lines |
Solved Examples on Wavelength Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Given below are some solved examples of the Wavelength Formula:
Example 1: The speed of sound is around 340 m/s and the frequency of the wave crest is 20.0 cycles per second. Find the wavelength of the sound wave.
Solution: According to the question,
- Frequency (f) = 20.0 cycles per seconds
- Wave velocity (v) = 340 (m/s)
Using the Wavelength Formula,
λ = v/f
λ = 340 / 20
λ = 17 m
So, the wavelength of the sound wave is 17 m.
Example 2: A motorboat creates waves while traveling across the surface of the sea. The waves travel towards the shores of the sea at a velocity of 1.50 m/s. and the distance between the wave crests is given as 2.0 m. What will be the frequency of the wave?
Solution: Given that
Velocity v = 1.50 m/s
Wavelength λ = 2.0 m
Using the Wavelength Formula,
λ = v/f
Rearranging the formula,
f = v/λ
f = 1.50/2.00
f = 0.75 waves/s
Therefore, the frequency of the wave is 0.75 waves per second.
What is Wavelength?
Wien’s Displacement Law
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Wien's Displacement Law was given by the German Physicist Wilhelm Wein. The law states that the black-body radiation curve will peak at different wavelengths for different temperatures. These wavelengths are inversely proportional to the temperature.
| \(\lambda (max)= {b \over T}\) |
Where
- \(\lambda\) (max) = Peak Wavelength
- b = Wein’s Displacement Constant
- T = Absolute Temperature

Wien’s Displacement Law
Energy of Photon Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Energy of a Photon can be determined through the Planck-Einstein Relation. Planck-Einstein Relation states that the energy E of a photon is directly proportional to its frequency.
E ∝ v
E = hv
The frequency (v) can also be denoted as c/\(\lambda\). Therefore,
| E = hc/λ |
Where
- E = Energy of the Photon
- h = Planck’s Constant
- c = Speed of Light
- λ = Wavelength
Also check:
Things to Remember
- Wave is defined as a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another location.
- Wavelength is the distance between the two successive crests or troughs of a wave.
- It is the distance over which the shape of the wave repeats.
- It is denoted by the symbol \(\lambda\) and is measured in meters (m).
- Wavelength is calculated as the ratio of Wave Velocity and Frequency.
- Wavelength Formula is given as \(\lambda\) = v / f.
Previous Year Questions
- The electric field associated with an e.m. wave in vacuum is... [NEET 2012]
- The ratio of contributions made by the electric field… [NEET 2020]
- The velocity of the electromagnetic wave is parallel to… [NEET 2002]
- Wavelength of light of frequency 100 Hz… [NEET 1999]
- What is the cause of ''Greenhouse effect''… [NEET 2002]
- Which of the following statement is false for the properties of… [NEET 2010]
- Which of the following rays is emitted by a human body… [VITEEE 2010]
- A 100Ω resistance and a capacitor of 100Ω reactance are connected in… [NEET 2016]
- The electric field part of an electromagnetic wave in a medium is… [NEET 2009]
- The electric and magnetic fields of an electromagnetic wave are… [NEET 1994]
- In which of the following, the emission of electrons does not take place… [NEET 1990]
- If λv,λx,λm represent the wavelengths of visible light… [NEET 2005]
Sample Questions
Ques. What is a Wave? (2 Marks)
Ans. Wave is a disturbance or variation that travels through a medium and transfers energy from one point to another. Waves may take a number of shapes, from a finite-width pulse to an infinitely long sine wave. It can take the form of elastic deformation, a variation of pressure, electric or magnetic intensity, electric potential, or temperature.
Ques. What is Wavelength? (3 Marks)
Ans. Wavelength refers to the distance between the two successive crests or troughs of a light wave.
- The Greek letter lambda (λ) is used to denote wavelength.
- The distance between either one crest or trough of one wave and the next wave is referred to as wavelength.
- It is measured in meters (m).
Ques. What is the formula for Wavelength? (3 Marks)
Ans. Wavelength is the ratio of Wave Velocity to Frequency, thus, the Wavelength Formula is given as
\(\lambda\) = v / f
Where
- \(\lambda\): Wavelength
- v: Wave Velocity
- f: Frequency
Ques. What are the different types of Waves? (3 marks)
Ans. The different types of Waves are as follows:
- Periodic and Non-Periodic Waves
- Standing and Travelling Waves
- Mechanical and Electromagnetic Wave
- Gravitational Waves
- Longitudinal and Transverse Wave and many more
Ques. Find the wavelength, frequency, and wave velocity if the number of ripples per second is 12 and the distance between a crest and a trough is 15cm. (3 Marks)
Ans. We know that
Frequency = Ripples per second
Therefore, Frequency = 12 Hz
Wavelength = 2 x Distance between Crest and Trough
Therefore, Wavelength = 2 x 0.15 = 0.3 m
Wave Velocity = Wavelength x Frequency
Therefore, Wave Velocity = 0.3 x 12 = 3.6 m/sec
Ques. A tuning fork vibrates with a frequency of 150 Hz and executes 40 vibrations. If the sound travels a distance of 30 m, determine the wavelength of the sound produced. (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that
- Frequency = 150 Hz
- Number of Vibrations = 40
- Distance Travelled by the Sound = 30m
Wavelength = Distance Travelled / Number of Vibrations
Wavelength = 30 / 40
Wavelength = 0.75 m
Thus, the wavelength of the sound produced is 0.75 m.
Ques. A harmonic wave is moving along a rope. where the source generating the waves completes 50 to and fro motions in a time interval of 20 s. Is a trough travels a distance of 3 m in 4s, what will be the wavelength of the wave? (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that
- Time taken for 50 Oscillations = 20 s.
- Time for 1 Oscillation t = 20/50 = 0.4 s
- Frequency of 1 Oscillation f = 1/0.4 = 2.5 Hz
It is given that the wave travels a distance of 3 m in 4 s.
Wave Speed v = Distance/Time = 3 / 4 = 0.75 m/s
Using the Wavelength Formula, we get
λ = v / f
λ = 0.75/2.5
λ = 0.3 m
The wavelength is calculated as 0.3 m.
Ques. What will be the wavelength of the sound wave if the speed of sound is about 300.0 m/s and the frequency of the wave crest is 15.0 cycles per second? (3 Marks)
Ans. It is given that
- Frequency f = 15 cycles per second
- Wave velocity v = 300 meter per second
Using the Wavelength Formula,
λ = v/f
λ = 300/15
λ = 20 m
Therefore, the wavelength of the sound wave is 20.0 m.
Ques. What is a Longitudinal Wave? (3 Marks)
Ans. A longitudinal wave is defined as a type of wave in which the movement of the particles in the medium is in the same dimension as the direction of movement of the wave.
The waves included in longitudinal waves are:
- Sound Waves
- Compression Waves
- P-type Earthquake Waves
Ques. What are Electromagnetic Waves? (1 Mark)
Ans. Electromagnetic waves are a type of wave that does not need any object medium for propagation. They can travel through the vacuum easily. Electromagnetic waves are produced due to various magnetic and electric fields.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:



Comments