Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
The maximum displacement of the waves is referred to as amplitude. In addition, you will learn about amplitude, amplitude formula, formula derivation, and a solved example in this topic. Furthermore, you will be able to comprehend amplitude after completing the topic.
The peak-to-peak amplitudes of electric oscillations can be measured using metres or by watching the waveform on an oscilloscope if proper equipment is used.
| Table of Content |
What is Amplitude?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The amplitude of a wave is defined as the measure of the height of the wave. In other words, it is the distance between crest or trough and the mean position of the wave.
Also Read: Difference Between Longitudinal And Transverse Wave
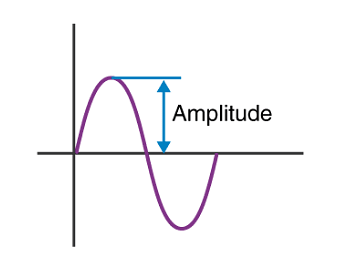
Amplitude
Also Read:
| Topics Related to Amplitude Formula | ||
|---|---|---|
| Wave Optics | Radio Waves | Unit of Vibration |
| Unit of Wavelength | Electromagnetic Waves | Frequency and Wavelength |
Amplitude Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The highest displacement of the waves is referred to as amplitude. The amplitude formula helps in the calculation of the sine and cosine functions. A is the symbol for amplitude. The sine (or cosine) function can be written as:
= A sin (ωt + θ) or = A cos (ωt + θ)
OR
Position = amplitude × sine function (angular frequency × time + phase difference)
Here,
- x = displacement of wave (meter)
- A = amplitude
- ω = angular frequency (rad/s)
- t = time period
- θ = phase angle
The amplitude formula can alternatively be written as the average of the sine or cosine function's highest and lowest values. The absolute value of the amplitude is always used (Amplitude = (max + min) / 2)
Types of Amplitude
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Types of Amplitude are as follows-
-
Peak Amplitude:
Peak amplitude is frequently employed in audio system measurements, telecommunications, and other applications where the measurement is a signal that swings above and below a reference value but is not sinusoidal.
The greatest absolute value of the signal if the reference is zero; if the reference is a mean value (DC component), the peak amplitude is the maximum absolute value of the deviation from that reference.
Peak Amplitude
-
Semi Amplitude:
The term "semi-amplitude" refers to half of the peak-to-peak amplitude. The word amplitude or peak amplitude is used to refer to semi-amplitude in the bulk of scientific literature. It is the most often used metric of orbital wobble in astronomy, and measuring tiny radial velocity semi-amplitudes of neighbouring stars is critical in the hunt for exoplanets (see Doppler spectroscopy).

Semi Amplitude
-
Ambiguous Amplitude:
In general, only symmetric periodic waves, such as a sine wave, a square wave, or a triangle wave, have a straightforward and unambiguous usage of peak amplitude. The peak amplitude of an asymmetric wave (for example, periodic pulses in one direction) becomes confusing. This is due to the fact that the value varies depending on whether the maximum positive signal is measured relative to the mean, the maximum negative signal is measured relative to the mean, or the maximum positive signal is measured relative to the maximum negative signal (the peak-to-peak amplitude) and divided by two (the semi-amplitude).

Ambiguous Amplitude
-
Peak to Peak Amplitude:
Peak-to-peak amplitude (abbreviated p–p) is the difference in amplitude between the peak (highest amplitude value) and the trough (lowest amplitude value, which can be negative). Peak-to-peak amplitudes of electric oscillations can be measured using metres or by watching the waveform on an oscilloscope with suitable equipment. Peak-to-peak is a simple measurement on an oscilloscope, with the waveform's peaks clearly identifiable and measured against the graticule.

Peak to Peak Amplitude
-
Root Mean Square Amplitude:
The root mean square (RMS) amplitude is commonly used in electrical engineering: the RMS is defined as the square root of the mean over time of the square of the graph's vertical distance from the rest state; i.e. the RMS of the AC waveform (with no DC component).
The RMS amplitude is commonly employed for complex waveforms, particularly non-repeating signals like noise, because it is both unambiguous and has physical importance. The average power conveyed by an acoustic, electromagnetic, or electrical wave, for example, is proportional to the square of the RMS amplitude (and not, in general, to the square of the peak amplitude)
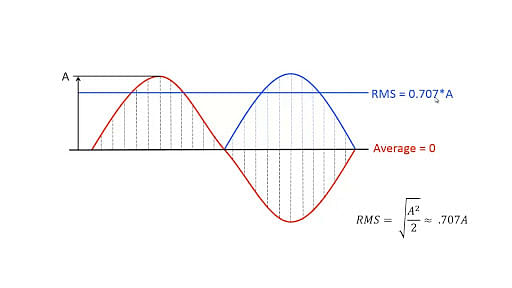
Root Mean Square Amplitude
Also Read:
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Amplitude is a measure of the strength or intensity of a wave that is calculated by looking at a graph of a wave and measuring the height of the wave from its resting position.
- The amount of energy carried by a wave is proportional to its amplitude. A large amount of energy is carried by a high amplitude wave, while a small amount of energy is carried by a low amplitude wave.
- A wave's or vibration's amplitude, also known as its peak amplitude, is a measure of its departure from its centre value.
- Amplitudes are always positive numbers (e.g., 3.5, 1, 120) and never negative (for example: -3.5, -1, -120). Because distance may only be higher than or equal to zero, amplitudes are positive; negative distance cannot exist.
- Peak-to-peak amplitude is the distance from the top of one peak to the bottom of another.
Also Read: NCERT Solutions for Class 6 to 12 PDFs
Sample Questions
Ques: What is an illustration of amplitude? (1 Marks)
Ans: The length and width of waves, such as sound waves, as they travel or vibrate are referred to as amplitude. The amplitude of a radio wave is measured by how much it travels back and forth.
Ques: What is data amplitude? (1 Marks)
Ans: Amplitude is a tool for evaluating data on user behaviour. It is used by product, marketing, and growth teams to derive insights about user behaviour from data for decision making. User statistics in real time, including retention, funnels, revenue analysis, and customizable user segmentation.
Ques: Is it true that amplitude decreases with distance? (1 Marks)
Ans: Because the wavelength of a sound wave grows with distance from its source, its amplitude drops. The amplitude of a sound wave diminishes as one moves away from its source because the wave's energy is dispersed over a wider and bigger region.
Ques: What effect does amplitude have on light? (2 Marks)
Ans: The amplitude of a wave indicates the intensity or brightness of the light in comparison to other light waves of the same wavelength. Waves 1 and 2 share the same wavelength but have distinct amplitudes. Light's wavelength is an essential characteristic since it influences the nature of the light.
Ques: What is the connection between scattered light intensity and amplitude? (2 Marks)
Ans: The intensity of dispersed light is discovered to be inversely related to the fourth power of light wavelength. This relationship holds true when the size of the air molecules is significantly less than the wavelength of the incoming light.
Ques: What role does amplitude play in sound? (2 Marks)
Ans:The volume of a sound is determined by its amplitude; sound waves with larger amplitudes are louder. The sound wave generated by a theatrical performer presenting their lines to the audience, for example, has a larger amplitude than the sound wave produced by an audience member whispering to a friend.
Ques: What is an amplitude modulation? (2 Marks)
Ans: Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation method used in electronic communication, most often for radio wave transmission of messages. The amplitude (signal strength) of the carrier wave is changed in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal, in amplitude modulation.
Ques: What is the relationship between amplitude and energy? (2 Marks)
Ans: The greater the amplitude, the greater the energy. The quantity of energy carried by them is proportional to their frequency and amplitude. The greater the frequency, the greater the energy, and the greater the amplitude, the greater the energy.
Ques: What is the difference between amplitude and volume? (2 Marks)
Ans: The loudness or volume of a sound wave is determined by its amplitude. A greater amplitude indicates a louder sound, whereas a lesser amplitude indicates a softer sound. Thus, the volume we hear is determined by both the amplitude of a sound wave and whether its frequency falls within a range to which the ear is more or less sensitive.
Ques: What exactly is the difference between amplitude and frequency? (2 Marks)
Ans:The height of a wave is measured from the highest point on the wave (peak or crest) to the lowest point on the wave (trough). Frequency is the number of waves that pass through a particular place in a given time period, and it is commonly represented in hertz (Hz), or cycles per second.



Comments