
Content Curator
Polythene is the most widely used plastic and is also known as polyethylene or polyethene. The most basic use of polythene is for packaging purposes. They generally contain a linear structure and are said to be additional polymers. Every year over 100 million tonnes of plastic is produced for commercial purposes.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Polythene, Plastic, polyethylene, polyethene, polymers, thermoplastic, Cross-linked polyethylene, monomer, methane, nitrogen, ethane, alkenes
Polythene
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Polythene in most of the cases are thermoplastic that can remould itself on applying heat to it. However, certain kinds of modified polythene plastics exert thermosetting characteristics. Cross-linked polyethylene can be cited as an example of such a kind of plastic and is often called PEX (abbreviated form).

Polythene
Read More: Nylon
Preparation of Polythene
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Polymerization of ethylene (a monomer) under appropriate physical and chemical conditions leads to the formation of polythene. Many molecules of a constituent molecule give it the name poly-ethylene. Polyethylene production occurs with less than 5 parts per million of oxygen, water and other alkenes. However there can be a presence of other compounds during the process of polymerization reaction in the form of contaminants. Some of such contaminants are methane, nitrogen and ethane.
As ethane is considered to be a comparably stable molecule, it needs a proper catalyst during polymerization. The transition of ethene into polythene is exothermic and one of the most common catalysts is titanium(III) chloride.

Reaction of Ethylene in order to form Polyethylene
Two of the most common types of polythene are:
- Low Density Polythene (LDP) :-
- Prepared by polymerization of ethene (C2H4) under high pressure of 1000 to 2000 atm.
- Temperature required is 350K to 570K.
- As ethane is inert hence catalyst like dioxygen or a peroxide initiator is used.
- It is obtained through free radical addition and H-atom abstraction (i.e a hydrogen free radical is abstracted/removed from the substrate).
- LDP has a highly branched structure.
- n CH2=CH2 (gas) → [−CH2−CH2−]n (solid)
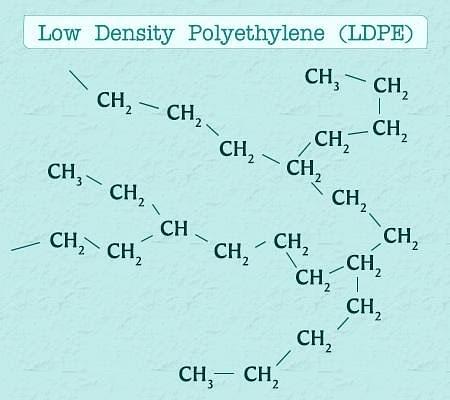
Low Density Polythene
- High Density Polythene:-
- In this case also there is polymerization of ethene but in hydrocarbon solvent and catalyst used is triethylaluminium and titanium tetrachloride (Zieglar-Natta catalyst).
- Temperature required is 333K to 343K.
- Pressure required is 6-7 atm.
- It consists of linear molecules as shown in the image, and has high density due to close packing.
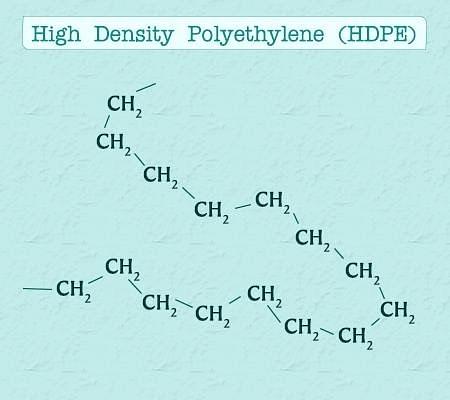
High Density Polythene
Read More: Polymerization
Properties of Polythene
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Physical Properties of Polythene
- The mechanical strength along with rigidity and hardness of polythene is comparatively lower in polythene.
- Synthetic polymers when kept under constant force exert a strong creep.
- They have a waxy texture.
- Melting point of LDP is 105o to 115oC and HDP is 120o to 180oC.
- Density of LDPE is 0.910–0.940 g/cm3 and HDPE is 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm3
- They are considered as a very good insulator of electric current as it has high electrical treeing resistance.
Chemical Properties of Polythene
- Polythene is formed from nonpolar saturated hydrocarbons which have molecules consisting of an extremely high weight.
- SIngle polyethylene macromolecules are not connected through covalent bonds.
- Polythene has a symmetric molecular structure which leads to the crystallization of the molecules and is known as partially crystalline plastic.
- The crystallinity of polymers are directly proportional to its density and chemical stability.
- High resistivity towards acids and alkalis along weak oxidising and reducing agents which includes LDPE, MDPE and HDPE.
- Most of the polyethylenes dissolves in the aromatic hydrocarbons such as xylene or toluene under certain pressure.
Read More: Polypropylene
Uses of Polythene
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Low Density Polyethylene
- It is used in insulation of electricity carrying wire as it is a poor conductor of electricity.
- It is also used in squeeze bottles, toys and flexible pipes due to it’s property of flexibility.
- Most popular use of LDP is plastic bags.
- Used in packing in pharmaceutical industries, films for food packaging, lamination etc.
- Due to lower water absorption it is used in water pipes manufacturing, hoses for the pipes and in fitting industries.
High Density Polyethylene
- HDP is used for manufacturing of buckets, dustbins, bottles, pipes etc. Interestingly polythene has varied usage in our day to day life.
- It is also used in specific packaging areas like crates, trays, bottles for milk and fruit juices, caps for food packaging, jerry cans, drums, industrial bulk containers etc.
- Due to low cost and easy processability it is widely used in consumer goods like garbage containers, toys, ice boxes and housewares.
- Due to it’s high tensile strength HDP is widely used in ropes, fishing and sports nets, nets for agricultural purposes and in decorative fabrics.
Read More: Thermosetting Polymers
Types of Polyethylene
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The various types of polyethylene are:
- High modulus polyethylene or Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE)
- Ultra Low Molecular Weight Polyethylene (ULMWPE)
- High Density Cross-Linked Polyethylene (HDXLPE)
- High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (HMWPE)
- Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE)
- Medium Density Polyethylene (MDPE)
- Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
- Linear Low Density Polyethylene (LLDPE)
- Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE)
Read More: Formaldehyde
Environmental Issues
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Due to the variety of polythene there is a lot of manufacturing of it. If not recycled it leads to the problem of waste management.
- As it is not readily biodegradable it leads to accumulation in landfills and other places causing jam.
- Polythene also produces two greenhouse gases (methane and ethylene) when exposed to radiation.
- Hence these are points of concerns which are answerable and have solutions. Students are encouraged to explore the solutions of the same and find out the steps taken by various governments and NGOs.
Read More: Biopolymers
Things to Remember
- Polythene is a part of CBSE class 12 chemistry syllabus, unit 15, Polymers.
- It carries a total of 8 periods and 4 to 6 marks.
- Chemical formula of polyethylene is (C2H4)n
- Polythene is a polymer of ethene prepared using addition of n ethene.
- Note down the catalyst used for preparation of both the types.
- Properties like flexibility, insulator and inertness makes it useful in container making and wiring.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques 1. After the ban on plastic bags, students of one school decided to make the people aware of the harmful effects of plastic bags on the environment and Yamuna River. To make the awareness more impactful, they organized a rally by joining hands with other schools and distributed paper bags to vegetable vendors, shopkeepers and departmental stores. All students pledged not to use polythene bags in future to save the Yamuna River.
After reading the above passage, answer the following questions (VBT Question)
What values are shown by the students?
What are biodegradable polymers? Give one example.
Is polythene a condensation or an additional polymer? (3 marks)
Ans.
- Values such as vigilant and aware citizens, environment friendly, serviceable and unity are shown by the students in the above case.
- A polymer which can be decomposed by natural processes such as action by bacteria are called Biodegradable polymers.
Example:- PHBV, Nylon-2-Nylon-6
- As an addition process is used for manufacturing of polythene hence it falls under the category of addition polymer.
Ques 2. Name two types of polythene available and explain methods for their preparation ? (5 marks)
Ans. There are two types of polythene viz. Low density polythene (LDP) and High Density polythene (HDP)
- Low density polythene (LDP) :-
- Prepared by polymerization of ethene (C2H4) under high pressure of 1000 to 2000 atm.
- Temperature required is 350K to 570K.
- As ethane is inert hence catalyst like dioxygen or a peroxide initiator is used.
- It is obtained through free radical addition and H-atom abstraction (i.e a hydrogen free radical is abstracted/removed from the substrate).
- LDP has a highly branched structure.
-
n CH2=CH2 (gas) → [−CH2−CH2−]n (solid)
- High density polythene (HDP :-
- In this case also there is polymerization of ethene but in hydrocarbon solvent and catalyst used is triethylaluminium and titanium tetrachloride (Zieglar-Natta catalyst).
- Temperature required is 333K to 343K.
- Pressure required is 6-7 atm.
- It consists of linear molecules as shown in the image, and has high density due to close packing.
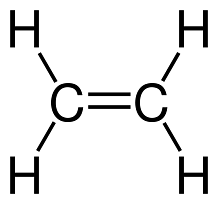
Ques 3. Name the monomer of polythene and draw its structure? (2 marks)
Ans. Ethene is the monomer used for preparation of polythene.
Structure :-
Ques 4. How is polythene manufactured? Write its two uses and properties? (5 marks)
Ans. Polythene is manufactured through addition of monomers of ethene. There are two types of polythene having different methods of their preparation. LDP and HDP are those two types.
Uses of polythene are:
- Polythene is used in the packaging of products.
- Since polythene is considered a good insulator of electric current it is used for making cable jacketing.
Properties of polythene:
- The mechanical strength along with rigidity and hardness of polythene is comparatively lower in polythene.
- Polythene is formed from nonpolar saturated hydrocarbons which have molecules consisting of an extremely high weight.
Ques 5. At a sweet shop in Hyderabad, Rishi bought some sweets. He requested the sales boy to put sweets in a polythene bag. The sales boy refused to do so, instead he kept the sweets in a paper bag.
After reading above passage answer the following questions:
Why did the sales boy refuse to put sweets in a polythene bag ?
As a student of chemistry why would you advocate the usage of paper bags instead of polythene bags? Which value is promoted through the use of a paper bag? (3 marks)
Ans.
- As polythene has its disadvantages like being non biodegradable, it releases harmful gases once oxidized hence showing the quality of aware citizen sales by refusing to put sweets in polythene bags. Again polythene use is banned by authorities/government.
- Paper bags are easily disposable and they do not harm the environment hence I will advocate the usage of paper bags instead of polythene bags. Values such as aware citizens, environment friendly and holistic thinking are promoted through use of paper bags.
- We can arrange activities like poster making, essay writing and webinars to educate students and society so that these values can flourish in society and help society to get rid of menace caused by polythene bags.
Ques 6. What is a cross-linked polythene? (2 marks)
Ans. Cross-linked is a kind of polythene that contains a cross-linked chemical structure. It is basically used for making pipe-work structures, and radiant heating and cooling systems. It can also be used to make household pipework and high voltage cables as it is a good insulator for electricity. Cross-linked polythene is often abbreviated as PEX or XPE.
Ques 7. Difference between HDPE and LDPE. (5 marks)
Ans. The difference between HDPE and LDPE are:
| LDPE (Low Density Polythene) | HDPE (High Density Polythene) |
|---|---|
| Melting point :105oC to 115oC | Melting point: 120-140oC |
| Density of LDPE: 0.910–0.940 g/cm3 | Density of HDPE: 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm3 |
| Made up of branched polymers with loosely held chains | Made up of closely packed linear polymers |
| Tough but flexible | High tensile and stiff |
| Used in making squeeze bottles, silms, sheets, etc. | Used for making dustbins, pipes, laboratory wares. |
Ques 8. Name six types of polythene. (3 marks)
Ans. The six types of polyethylene are:
- High modulus polyethylene or Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE)
- Ultra Low Molecular Weight Polyethylene (ULMWPE)
- High Density Cross-Linked Polyethylene (HDXLPE)
- High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (HMWPE)
- Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE)
Ques 9. State the electrical property of polythene. (1 marks)
Ans. Polythene is considered to be a good insulator of electricity, hence it provides an efficient electrical treeing resistance. However when reduced by adding carbon antistatic and black graphite agents it can easily become electrostatically charged.
Ques 10. State the optical characteristics of polythene. (1 marks)
Ans. HDPE can be said to have the least transparency, LLDPE has a little and LDPE has the most transparency depending on the film density and thermal history it differs from opaque, translucent to transparent. If crystellites are said to be greater than the wavelength of the visible light then transparency also reduces.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:





Comments