
Content Curator
Polytetrafluoroethylene or Teflon is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene. It is made by free radical polymerisation of many tetrafluoroethylene molecules. Polytetrafluoroethylene or Teflon is a thermoplastic polymer. Its chemical formula is given by (C2F4)n where n represents the number of repetitive monomer units.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Polymer, Synthetic polymers, Alkathene, Ethene, Polyethylene, Monomer, Fluoropolymer, Molecule Monomer, Polymerisation, Tetrafluoroethylene, Polytetrafluoroethylene, Teflon
Also Read: Micelle
What is Polytetrafluoroethylene
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Polytetrafluoroethylene or PTFE is known by the brand name Teflon. It was discovered by Roy J Plunkett in 1938. Mass production of PTFE was undertaken owing to its numerous advantages over other synthetic polymers in the market. A very high melting point, good thermal stability, low friction coefficient were a few of the many advantageous properties that made its use immensely wide. The free radical polymerisation reaction of tetrafluoroethylene can be represented as
n F2C=CF2 → −(F2C−CF2)n−

Teflon
Production and Structure Of Teflon
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Polytetrafluoroethylene is manufactured by free radical polymerisation of tetrafluoroethylene monomers.

For this reaction, a persulfate catalyst is used at high-pressure heating. During the reaction, tetrafluoroethylene decomposes into tetrafluoromethane and carbon. This decomposition can be explosive. So as a precaution special apparatus is used to prevent any side effects of the polymerisation.
Polymerization is conducted in an emulsion of water since PTFE is insoluble in most of the solvents. As a result, a suspension of polymers is formed. Further by the process of agglomeration and drying, we get the end result.
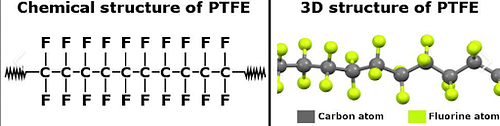
Structure of PTFE
Read More:
Properties Of Teflon
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- PTFE or Teflon is a thermoplastic polymer.
- It is ivory white solid at room temperature.
- The density of Teflon is 2200kg/m3.
- The melting point of Teflon is 600K.
- Teflon has good strength and lubrication at low temperatures (5K). It is thermally stable at low temperatures.
- Teflon is a highly flexible, chemically resistant, non-stick and electrically resistant material.

Flexible Teflon
Also Read: Properties of Matter
Applications Of Teflon
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Teflon or PTFE has a large number of uses owing to its thermal and electrical inertness in variable temperatures.
- In the manufacturing and engineering sector, Teflon is used for making tubes or liners for handling corrosive chemicals. PTFE is also used as a coating for bearings and screws due to its chemical and thermal inertness.
- PTFE coatings provide friction and corrosion-resistant surface for machinery parts thus increasing their work life. A longer lasting machinery means more efficiency and less maintenance cost.
- Teflon is also used in textile finishing as it repels oil and water, reducing the need for dry cleaning.
- Teflon is best known for its non-stick properties due to its high melting point and slippery nature. Non-stick kitchen cookware is made from Teflon.

Non-stick cookware
- Teflon has excellent dielectric properties combined with its high melting point makes it suitable for use in the manufacturing of electrical insulators in connector assemblies and cables. About 50 % of its production is consumed in the insulation of wirings in aerospace and computer applications.

Wiring Insulation
- Due to the low friction coefficient, Teflon is used for plain bearings, gears, slide plates, seals, gaskets, bushings and more.
- In the automotive industry, the blades of windshield wipers are PTFE coated.

Teflon Bearings
- In nail polish PTFE is used because it gives a smooth surface.
- Hairstyling tools like hair straighteners also use PTFE coating due to their high thermal stability.

Hair Straighteners
Advantages Of Using PTFE
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- PTFE or Teflon is thermally stable at high temperatures and its chemical inertness has added value to its wide number of applications in the automobile industry, electrical equipment industry, manufacturing industry, textile industry, etc.
- PTFE is more efficient than other materials like nylon and acetal.

PTFE in Industries
- In the machinery, PTFE adds to the efficiency of the machine parts thus increasing their work-life and reducing maintenance costs.
- In the coating industry, the coating of electrical wires, computer parts and kitchen cookware by PTFE is much more durable than other coating materials.
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Saturated Hydrocarbons | Carbonyl Compounds | Unsaturated Hydrocarbons |
| Alcohols, Ethers and Phenols | Huckel Rule of Aromaticity | Iodoform Test |
| Ester Hydrolysis | Cycloalkanes | Brown Ring Test |
Things To Remember
- PTFE or popularly called Teflon has the chemical formula C2F4
- Teflon is a result of free radical polymerisation of tetrafluoroethylene monomers.
- Teflon is a thermoplastic polymer.
- PTFE is thermally stable at 600K.
- PTFE is chemically inert hence corrosion resistant.
- Teflon has excellent dielectric properties combined with its high melting point makes it suitable for use in the manufacturing of electrical insulators and as coating materials.
- Due to its non-sticking properties, it is widely used in kitchen cookware.
Previous Year Questions
- Buna-N synthetic rubber is obtained by copolymerisation of….[JKCET 2015]
- Which among the following polymers is non - biodegradable?[JKCET 2016]
- Which of the following is an example of thermosetting polymers?….[AMUEEE 2018]
- Which of the following is a monomer of Dacron:...[UPSEE 2017]
- Which of the following is biodegradable polymerof polyamide class ?[GUJCET 2006]
- Bakelite is manufactured by using a mixture of...[COMEDK UGET 2007]
- Which one of the following is a condensation polymer?[WBJEE 2018]
- Nylon 6 is obtained by the condensation of...[AMUEEE 2016]
- Which of the following is a characteristic of Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) ?...[JKCET 2019]
- Choose the correct option(s) from the following...[JEE ADVANCED 2019]
- What is the ratio of butadiene : styrene in SBR ?...[JKCET 2019]
- The reaction for preparing dacron is by the combination of which of the following ?...[JKCET 2018]
- The species which cannot serve as an initiator for the free radical polymerisation, is...[JKCET 2015]
- Nylon is a...[JKCET 2015]
- The monomers used in preparation of dextron are...[MHT CET 2017]
Sample Questions
Ques: What is the monomeric repeating unit of PTFE? What is its melting point and density? (2 marks)
Ans. Tetrafluoroethylene.PTFE or Teflon is made of repetitive units of tetrafluoroethylene.
Melting point- 327o Celsius.
Density- 2200kg/m3.
Ques. Mention the applications of PTFE in the electronic industry. (2 marks)
Ans. PTFE is used to make Teflon coatings in insulators, semiconductor manufacturing, system components, wires and cables. Its thermal stability is one reason for its extensive use in this field.
Ques. Write 3 applications of PTFE. (2 marks)
Ans. (a) PTFE owing to its frictionless, non-stick, chemical inert and thermally stable nature has enormous use in the manufacture of kitchen cookware.
(b) PTFE is also used in the Teflon coating of bearings, screws, and other sliding parts of machines thus reducing friction and increasing the work-life of machines.
(c) In nail polish and hair styling tools Teflon coating is used due to thermal stability.
Ques. Explain the chemical properties of Teflon. (3 marks)
Ans. (a) Thermal stability -It has a melting point of 600K. It maintains high strength, toughness and self-lubrication even at low temperatures of -268o Celsius.
(b) The coefficient of friction of PTFE is 0.05 which is the third-lowest of any known solid material. It means it is very slippery.
(c) It is chemically inert, meaning only very highly reactive alkalis can react with it. Hence it is used for Kitchen cookware. Its chemical and thermal properties make it suitable to be used as a gasket material to handle corrosive chemicals in chemical processing plants.
(d) It is hydrophobic and oleophobic. It shows non-wetting properties.
Ques. What are the advantages of Teflon over Nylon? (2 marks)
Ans. Teflon is preferred over Nylon in the industrial machine manufacturing sector where plain bearings, gears, slide plates, seals, gaskets, bushings, and more applications with sliding action of parts are manufactured. Teflon having a lesser coefficient of friction and lesser chemical reactivity than Nylon is preferred over Nylon.
Both Teflon and Nylon are synthetic polymers and both are thermoplastics. Solid nylon is used in some industries to produce combs and mechanical parts including gears and machine screws. However, Teflon is a hydrophobic material whereas Nylon is hydrophilic.
Ques. What makes PTFE a suitable material for manufacturing electrical equipment? (2 marks)
Ans. Teflon has excellent dielectric properties combined with its high melting point makes it suitable for use in the manufacturing of electrical insulators in connector assemblies and cables. About 50 % of its production is consumed in the insulation of wirings in aerospace and computer applications.
Ques. Explain the process of production of Teflon. Write the chemical equation involved. (3 marks)
Ans. PTFE is manufactured by free radical polymerisation of tetrafluoroethylene monomers.
n F2C=CF2 → −(F2C−CF2)n−
For this reaction persulfate catalyst is used at high-pressure heating. During the reaction, tetrafluoroethylene decomposes into tetrafluoromethane and carbon. This decomposition can be explosive. So as a precaution special apparatus is used to prevent any side effects of the polymerisation. Polymerization is conducted in an emulsion of water since PTFE is insoluble in most of the solvents. As a result, a suspension of polymers is formed. Further by the process of agglomeration and drying, we get the end result.
Ques. What makes PTFE or Teflon suitable for coating kitchenware? List the properties. (2 marks)
Ans. It is chemically inert, meaning only very highly reactive alkalis can react with it. Hence it’s used for Kitchen cookware. Its chemical and thermal properties make it suitable to be used as a gasket material to handle corrosive chemicals in chemical processing plants. It is hydrophobic and oleophobic. It shows non-wetting properties. Thus it is easy to clean. Teflon is the third most slippery substance known to man till now(low friction coefficient).
Ques. What are polymers? (2 marks)
Ans. Polymers are high molecular mass substances (103 — 107u) consisting of a very large number of simple repeating structural units joined together through covalent bonds in a linear fashion. They are also called macromolecules. Ex: polythene, nylon 6,6, bakelite, rubber, etc.
Ques. How are polymers classified on the basis of structure? (5 marks)
Ans. On the basis of structure, polymers are classified into three types. These are linear chain polymers, branched-chain polymers and cross-linked polymers.
- Linear chain polymers: In this case, the monomer units are linked to one another to form long linear chains. These linear chains are placed one above the other and are closely packed in space. The close packing results in high densities, tensile strength and also high melting and boiling points. High-density polyethene is a very common example of this type. Nylon, polyesters and PVC are also linear chain polymers.

- Branched-chain polymers: In this type of polymers, the monomer units are linked to form long chains which also have side chains or branched chains of different Lengths attached to them. As a result of branching, these polymers are not closely packed in space. They have low densities, low tensile strength as well as low melting and boiling points. Some common examples of such polymers are; low-density polyethene, amylopectin, starch, glycogen etc.
- Cross-linked polymers: In these polymers, also called network polymers, the monomer units are linked together to form three dimensional networks as shown in the figure. These are expected to be quite hard, rigid and brittle. Examples of cross-linked polymers are bakelite, glyptal melamine-formaldehyde polymer etc.
Ques. What are natural and synthetic polymers? Give two examples of each. (3 marks)
Ans.
- Natural polymers: The polymers which occur in nature mostly in plants and animals are called natural polymers. A few common examples are starch, cellulose, proteins, rubber nucleic acids, etc. Among them, starch and cellulose are the polymers of glucose molecules. Proteins are formed from amino acids which may be linked in different ways. These have been discussed in detail in unit 15 on biomolecules. Natural rubber is yet another useful polymer which is obtained from the latex of the rubber tree. The monomer units are of the unsaturated hydrocarbon 2-methyl-i, 3-butadiene, also called isoprene.
Examples of natural polymers: Natural rubber, cellulose, nucleic acids, proteins etc.
- Synthetic polymers: The polymers which are prepared in the laboratory are called synthetic polymers. These are also called man-made polymers and have been developed in the present century to meet the ever-increasing demand of modern civilization.
Examples of synthetic polymers: Dacron (or terylene), Bakelite, PVC, Nylon-66, Nylon-6 etc.
Ques. How do you explain the functionality of a monomer? (2 marks)
Ans. The functionality of a monomer implies the number of bonding sites present in it. For example, monomers like propene, styrene, acrylonitrile have the functionality of one which means that they have one bonding site.
Monomers such as ethylene glycol, hexamethylenediamine, adipic acid have the functionality of two which means that they have two bonding sites.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Also check:





Comments