Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells consider a crystal. It is already known that the main characteristic feature of crystalline solids is their regular and repeating pattern of constituent particles. A crystal lattice is obtained when these particles are replaced with representative points. Hence crystal lattice is, basically, a three-dimensional representation of atoms and molecules present in any solid crystal and is represented diagrammatically such that each and every particle is depicted as a point. Possibly, there are 14-dimensional lattices that are known to us. These lattices are named after the French mathematician, Auguste Bravais who first discovered it. This is the reason that they are known as Bravais Lattices.
Read More: State of matter
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms: Lattice, unit cell, solids, Atoms, crystalline or amorphous solids, solid state
Crystal Lattice
Solids are basically of two shapes- one is an amorphous solid that lacks a specific structure or shape. Another is crystalline structure or crystal that possesses a specific organized structure of their particles. The three-dimensional arrangement of constituent particles in crystals is called a crystal lattice.
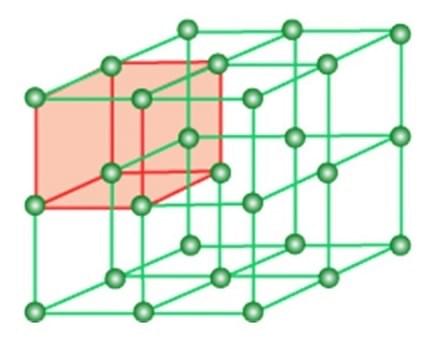
Crystal lattice
Read More: Difference between Cations and Anions
The characteristics of a crystal lattice are:
(a) Each point in a lattice is known as a lattice point or lattice site.
(b) An atom, a molecule (group of atoms) or an ion is represented by each point in a crystal lattice.
(c) Lattice points are joined by straight lines to construct the geometry of the lattice.
The video below explains this:
Packing efficiency Detailed Video Explanation:
Unit Cell
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The smallest portion of a crystal lattice which repeats in different directions to form the entire lattice is known as Unit cell.

Unit cell
The characteristics of a unit cell are:
(i) The dimensions are measured along the three edges, a, b and c. These edges can form different angles, they may be mutually perpendicular or may not.
(ii) The angles held by the edges are α (between b and c) β (between a and c) and γ (between a and b).
Therefore, a unit cell is characterised by six parameters such as a, b, c and α, β, γ.
Read More: Classification of Crystalline Solids
Types of Unit Cell
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Unit cells are generally classified into two categories such as primitive and centred unit cells.

Classification of unit cells
(a) Primitive Unit Cells: In a primitive unit cell constituent particles are present only on the corner positions of a unit cell.
(b) Centred Unit Cells: A centred unit cell contains one or more constituent particles which are present at positions besides the corners.
Read More: Physical and Chemical Classification Of Matter
Centred unit cells are classified into three types:
- Body-Centred Unit Cells: Such a unit cell contains one constituent particle (atom, molecule or ion) at its body-centre as well as its every corners.
- Face-Centred Unit Cells: Such a unit cell contains one constituent particle present at the centre of each face, as well as its corners.
- End-Centred Unit Cells: In such a unit cell, one constituent particle is present at the centre of any two opposite faces, as well as its corners.
There are seven different types of primitive unit cells are found such as:
- Cubic
- Tetragonal
- Orthorhombic
- Hexagonal
- Rhombohedral or Trigonal
- Monoclinic
- Triclinic
Seven Primitive Unit Cells and their Possible Variations are mentioned below:
| System of Crystal | Possible types of unit cell | Length of the edges | Angles obtained by the axis | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cubic | Primitive, Body-centred, Face-centred | a = b = c | α = β = γ = 90° | Zinc blende, NaCl, Cu |
| Tetragonal | Primitive, Body -centred | a = b≠c | α = β = γ = 90° | White tin, SnO2, TiO2 etc. |
| Orthorhombic | Primitive, Body-centred, Face-centred, End-centred | a≠ b≠ c | α = β = γ = 90° | KNO3, Rhombic sulphur |
| Hexagonal | Primitive | a = b≠c | α = β = 90° γ = 120° | Graphite, ZnO,CdS |
| Rhombohedral or Trigonal | Triclinic | a = b = c | α = β = γ≠ 90° | Calcite (CaCO3), HgS |
| Monoclinic | Primitive, End-centred | a≠b≠c | α = γ = 90° β ≠ 90° | Monoclinic sulphur |
| Triclinic | Triclinic | a≠b≠c | α≠β≠γ≠ 90° | K2Cr2O7, CuSO4. 5H2O |
Total 14 possible three dimensional lattices are called Bravais Lattices. The possible variations of the Crystal system are known as Bravais Lattices.
Read More: Conduction of electricity in liquids

Fourteen arrangements of three-dimensional lattices
Total Number of Atoms present in a Unit Cells
Primitive Cubic Unit cell:
Primitive cubic unit cell has atoms only at its corner which are shared between eight adjacent unit cells among which four unit cells in the same layer and four unit cells of the upper (or lower) layer. So, only 1/8th portion of an atom belongs to a particular unit cell. In each of eight corners one atom remains in such position.
Therefore, the total number of atoms in one unit cell is 1/8*8= 1.
Body-Centred Cubic Unit cell (bcc):
In a body-centred cubic unit cell atoms are attached at each of its corners and one atom at its body centre.
(i) For corners: 8 corners × 1/8 per corner atom= 1 atom
(ii) One atom at the body centre: 1 × 1= 1 atom
∴Total number of atoms present per unit cell in bcc = 2 atoms.
Face-Centred Cubic Unit cell (FCC):
(i) For corners: 8 corners atoms × 1/8 atom per unit cell= 1 atom
(ii) 6 face-centred atoms × 1/2 atom per unit cell = 6 × 1/2 = 3 atoms.
∴Total number of atoms per unit cell= 1+3= 4 atoms.
Read More: Three States of Matter
Relation between the length of side of the cube and radius of atoms
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Let, a= length of the cube
r= radius of atoms
For Primitive Cubic Unit cell:
a= 2r
For Face-Centred Cubic Unit cell:
a= 4r/root 2
For Body-Centred Cubic Unit cell:
r= root 3* a/4
-
Calculation of Packing efficiency and void space
Packing efficiency means the percentage of total space filled by the particles in a unit cell. By calculating Packing efficiency we can determine the void space.
| Unit cell | Packing efficiency | void space |
|---|---|---|
| Primitive Cubic Unit cell | 52.4% | 47.6% |
| Face-Centred Cubic Unit cell | 74% | 26% |
| Body-Centred Cubic Unit cell | 68% | 32% |
-
Calculation of the density of unit cell
D= z* M/ a3 * NA
Here, D= density of a lattice, z= atomic number present in a unit cell, a= length of the side of a cube, NA= Avogrado’s Number.
Read More: Physical Nature of Matter
Things to Remember
- Crystal lattice is a symmetrical three-dimensional structural arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules (constituent particles) inside a crystalline solid as points.
- There are seven types of unit cells: Cubic, Tetragonal, Orthorhombic, Monoclinic, Hexagonal, Rhombohedral or Trigonal and Triclinic.
- A unit cell is the smallest portion of a crystal lattice, which when represented in different directions produces the complete crystal lattice.
- Lattice points are joined by straight lines to bring out the geometry of the lattice.
- A unit cell has three edges a, b and c and three angles α, β and γ between the respective edges.
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Change of state | Mendeleev’s Periodic Table | Subatomic Particles of an Atom |
| Periodic Properties of Elements | What are Noble Gases | Thermal conductivity |
Sample Questions
Ques: What do you mean by lattice point in a unit cell? (1 mark)
Ans:- Lattice point means the corner of the unit cell of the crystal contains an atom, ion, or molecule. The cubic unit cell is the simplest repeating unit which has eight lattice points at the corners.
Ques:- What is the reason behind crystal lattice? (1 mark)
Ans:- The electrostatic attraction ions bring them close enough to form a minimum distance of separation. Thus crystal lattice is formed. The arrangement of ions are regular, geometric structure in a crystal lattice.
Ans:- There are seven types of crystal lattice and 14 types of bravais lattice are present.
Ques:- Which type of unit cell has higher packing efficiency and lower packing efficiency? (1 mark)
Ans:- Face centered cubic has higher packing efficiency (74%) and simple cubic crystal has lower packing efficiency (52.4%).
Ques:- What are the types of crystalline solid? (1 mark)
Ans:- Crystalline solids are classified based on the nature of intermolecular forces. The types of crystalline solid are molecular, ionic, metallic and covalent solids.
Ques:- What do you mean by a lattice structure? (1 mark)
Ans:- The lattice structures are ordered topologically, three-dimensional open-celled structures that are composed of one or repeating cells [2,3]. These cells are explained by the connectivity as well as dimensions of their constituent elements that are connected at specific nodes.
Ques:- What are lattice points in crystals? (1 mark)
Ans:- The point in the crystal lattice in a model crystal depicts the placements of structural units like atoms, molecules or ions. Each and every point in the crystal possesses similar surroundings as the actual crystal structural units.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:



Comments