
Content Strategy Manager
Polymerization is defined as the process of combining a large number of small molecules in order to form a single macromolecule. Polymer is a large molecule with repeated structural units. A polymer is created when two or more monomers form covalent bonds together. The monomers are the small molecules that act as the building blocks of polymers. On the basis of the kinds of reactions involved, polymerization is classified into two groups- addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. Condensation polymerization refers to the process that involves repeated condensation reactions between two different bi-functional or tri-functional monomers whereas addition polymerization is defined as the process of repeated addition of monomers that create double or triple bonds to form polymers.
| Table of Contents |
Key Takeaways: Polymerization, Polymer, Monomers, Addition Polymerization, Condensation Polymerization, Double Bonds, Chain Polymerization, Alkanes, Unsaturated Compounds, Condensation Polymers, Addition Polymers
Addition Polymerization
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Addition Polymerization is the process when a single molecule or unit forms a polymer by a mutual additive reaction. This process is done without the co-generation of other by-products. Additional polymers can be formed through chain polymerization in which the polymer is formed by sequentially adding different monomer units to an active site of the chain reaction.
Almost all of the polymers are unsaturated compounds such as alkanes and alkenes. The process of addition polymerization takes place through the process of free radical mechanism that is done in three steps- Initiation of free radical, chain propagation, and termination of the chain.
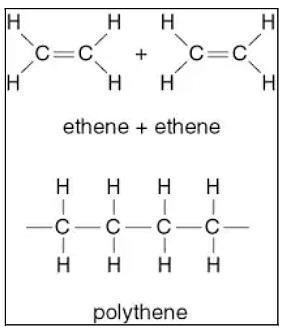
Addition Polymerization
Read More: Addition Reaction of Alkynes
Condensation Polymerization
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Condensation polymerization, the other kind of polymerization apart from addition polymerization, involves repeated condensation reactions between tri-functional or bi-functional monomers. In this, linking monomers results in the formation of condensation polymers. However, this process differs in that it yields a wide range of additional goods. The majority of these products contain water by default.
Condensation processes are used to create these polymers. Small molecules are lost as by-products in this process, which joins the molecules together. Water and methanol are the most often lost molecules in this process. Polycondensation is another process associated with the creation of condensation polymers. Condensation reactions between species of all levels of polymerization are used to create polymers in this technique.
Condensative chain polymerization can also be used for this purpose. Condensative chain polymerization occurs when monomers are added sequentially to an active site in a chain reaction and the polymers are produced. Polyacetals, proteins, and polyamides are only a few examples of the many types of condensation polymers that exist.
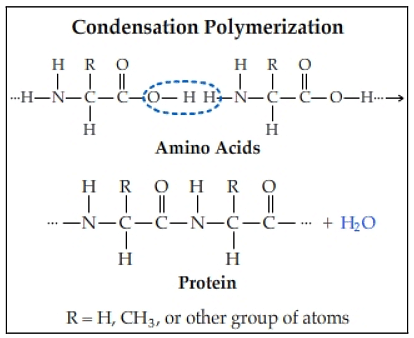
Condensation Polymerization
Read More: Nylons
Difference Between Addition and Condensation Polymerization
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
As we know, Polymerization can be classified into two groups- Addition Polymerization and Condensation Polymerization. The addition polymerization is the process in which monomers are repeatedly added. Polymers can be formed from these monomers, which have double or triple bonds.
When it comes to condensation polymerization, on the other hand, it is a process that involves the condensation of three- or two-functional monomers over and over again.
Here are the key distinctions between these two types of Polymerization:
| Addition Polymerization | Condensation Polymerization |
|---|---|
| Polymers are formed by the addition of monomers. | Condensation of monomers results in the formation of polymers. |
| Monomers must include at least one double or triple bond. | Monomers must have two functional groups that are either identical or dissimilar. |
| The resultant polymers have a molecular weight that is a multiple of the monomer's molecular weight. | The resulting polymer has a molecular weight that is not a multiple of the monomer's molecular weight. |
| Catalysts for polymerization include Lewis acids or bases, radical initiators. | Numerous molecules are used as catalysts for condensation polymerization. |
| There are no by-products produced | Ammonia, water, and hydrochloric acid are created as byproducts. |
| PVC, polyethene, and Teflon are all examples of addition polymerization. | Nylon, bakelite, and silicon are all examples of condensation polymerization. |
In addition polymerization, polymers are generated by merely adding monomers together, whereas condensation polymerization produces tiny molecules like HCl, water, ammonia, and others as by-products.
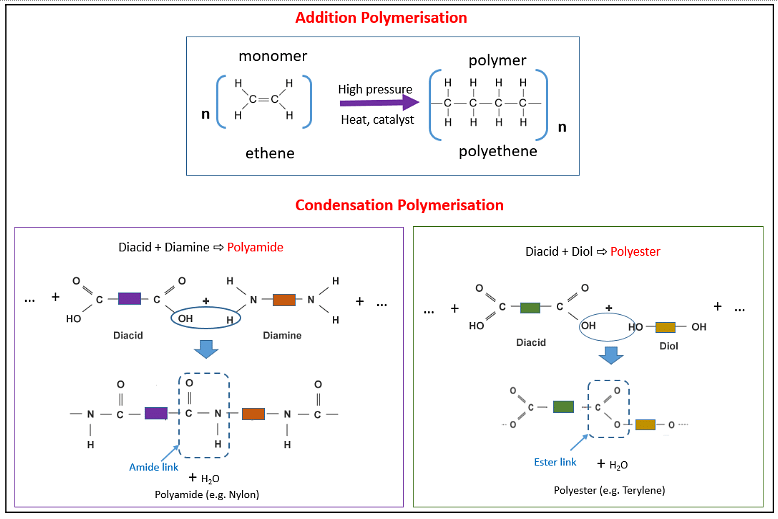
Addition and Condensation Polymerization
Things to Remember
- Polymerization is a chemical process in which a large number of small molecules combine together to form a single macromolecule.
- The degree of polymerization is the most important factor in determining the physical properties of polymer materials.
- Polymers can be polymerized in one of two ways, depending on how they are polymerized. Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization are two types of polymerization.
- In order to create condensation polymers, two different monomeric units must undergo a series of condensation reactions.
- The repeated addition of monomer molecules with triple or double bonds results in the formation of the addition polymers.
- There are no by-products produced in the addition polymerization whereas ammonia, water, and hydrochloric acid are created as byproducts in condensation polymerization.
Sample Questions
Ques. What are Polymers? (3 Marks)
Ans. A polymer can be defined as a macromolecule that is formed by the chemical bonding of larger numbers of molecules being added up together. These repeating units are called monomers and they can vary in a polymer in terms of their number, the order in which they appear and regularity. The relative orientation and the presence of different monomers can vary within the same polymer molecule. The degree of polymerization refers to the number of monomers present in any natural polymer or synthetic polymer.
Ques. Give some examples of addition polymers. (3 Marks)
Ans. Polystyrene, polyethylene, polyacrylates, and methacrylates are examples of addition polymers. Addition polymers are formed by the polymerization of unsaturated monomers that typically contain a CC double bond. Some of the important addition polymers include PE and PVC which are formed by polymerization of ethene (CH2CH2) and vinyl chloride (chloroethene; CH2CHCl), respectively.
Ques. How can you differentiate between addition and condensation polymerisation? (5 Marks)
Ans. Polymerization, as we know, is the process by which a large number of small molecules are joined together to form a larger macromolecule. The building blocks of polymers are monomers, which are small molecules. The two types of polymerization are addition polymerization and condensation polymerization.
The addition polymerization is the process in which monomers are repeatedly added. Polymers can be formed from these monomers, which have double or triple bonds. Condensation polymerization, on the other hand, is a process that involves the condensation of three or two functional monomers over and over again.
Ques. Is a catalyst necessary for condensation polymerization? (3 Marks)
Ans. Esterification of carboxylic acids and alcohols is a well-known esterification process. PETE and Nylon do not require a catalyst because the acid monomers catalyse the process. It is possible to speed up the reaction by using sulfuric acid and other strong acids.
Ques. Give some examples of condensation polymers. (3 Marks)
Ans. Cellulose, starch, and protein polypeptide chains are all examples of natural condensation polymers. Nylon, kevlar, polyester, Bakelite, Melamine, polycarbonates, polyurethanes, and epoxies are some of the synthetic condensation polymers that have been studied.
Ques. Why are condensation polymers stronger than addition polymers? (3 Marks)
Ans. Condensation polymers, in comparison to addition polymers, are more rigid and have a higher tensile strength than addition polymers. Hydrogen bonding enhances the intermolecular forces between the chains of polyamides, making them even stronger. As a result, polyamides are well-known for their high strength.
Ques. Why is addition polymerization also known as vinyl polymerization? (3 Marks)
Ans. Addition polymerization methods include forming polymers by simply linking monomers together without generating any other byproducts. The (CH2=CH-) group, also known as the vinyl group, is found in the majority of monomers involved in chain polymerization.
Read Also:





Comments