
Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Electrostatics is the study of electromagnetic events that take place when no moving charges are present, i.e. after static equilibrium is achieved. As the electric force is strong, charges quickly achieve their equilibrium positions. Both ranges of the electric field and the electric potential can be calculated using electrostatic mathematical methods using a known arrangement of charges, conductors, and insulators. In contrast, given the right set of conductors with given potentials, it is possible to compute electric fields between the conductors and estimate the charge distribution on the conductors' surface.
- Energy can be stored in a capacitor. The energy that is required to charge this device is stored as the electrostatic energy of the electric field.
- Electric charge or electrostatic charge is the basic property of subatomic particles that causes them to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field.
- Electric charge is denoted by the symbol Q and is measured in Coulomb.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Conductors, Insulators, Electric potential, Electric Charge, Electromagnetic waves, Electric field, Coulomb’s law, Capacitor
What is Electrostatics?
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Electrostatics is a branch of physics dealing with the properties and phenomena of slow-moving or stationary electric charges. Electrostatic phenomena can be understood by Coulomb’s law. According to the laws of electrostatics:
- Like charges repel each other.
- Unlike charges attract each other.
Electrostatics
Positively Charged Particles
The numbers of positive ions in these particles are larger than the negative ions. This means the number of protons is larger than the number of electrons. To neutralize the positively charged particles, electrons from the surroundings come to this particle until the number of protons and number of electrons becomes equal.
Negatively Charged Particles
In the negatively charged particles, the number of electrons is larger than the protons. To neutralize these particles, electrons move to any other particle around or to the ground. This is because the protons cannot move and come to these negatively charged particles.
Neutral Particles
Neutral particles have equal numbers of protons as well as electrons. They have protons, neutrons as well as electrons; however, the number of positive ions is equivalent to the number of negative ions.
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Emf Formula | Wavelength Formula | Maxwell Equation |
| Electroscope | Unit of Electric Flux | Difference Between Earthing and Grounding |
Coulomb’s Law of Electrostatics
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
According to Coulomb's law, 'The electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion involving two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their magnitudes and inversely proportional to the square of their distance.'
The electrostatic force is directed in the direction of the straight line that connects them. The electrostatic force in between two charges is repulsive if their signs are the same; if their signs are different, the force is attractive. When ‘r’ is the distance between two charges (in meters), the force (in Newtons) present in between two point charges q and Q (in Coulomb’s) is given by:
F = \({1 \over 4\pi Eo}\)\( {qQ \over r^2}\)
F = k0\( {qQ \over r^2}\)
- Where, Eo can be defined as the vacuum permittivity or the permittivity of free space.
- Eo ≈ 8.854187817 × 10-12C2N-1m-2
- Eo is equivalent to A2s4kg-1m-3 or C2N-1m-2 or Fm-1 in SI units.
Coulomb’s constant is given by,
k0 = \({1 \over 4\pi Eo}\) ≈ 8.9875×109 Nm2C-2
Here, the charge of a single proton is denoted as e and the charge of the electron as -e –
e = 1.602×10-19 C
Electric Field
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The electric field, E is a unit vector that can be defined anywhere except at the site of point charges and is measured in newtons per coulomb or volts per meter (where it diverges to infinity). It is equal to an electrostatic force F in newtons exerted by Coulomb's Law on a hypothetical short test charge at the location, divided by the amount of the charge q.
\(\overrightarrow{E}\)=\(\overrightarrow{F}\).\(\overrightarrow{Q}\)
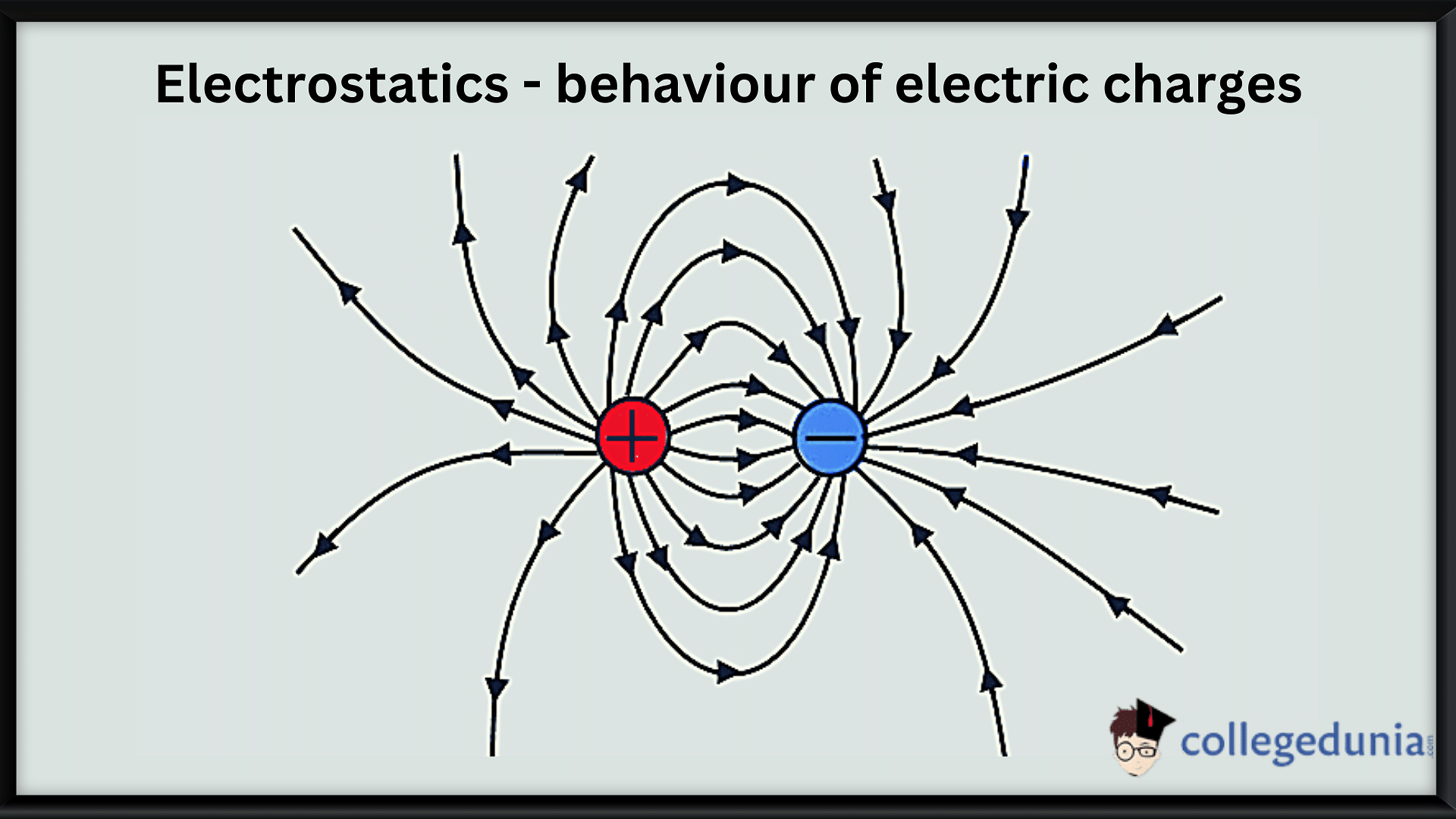
- The electric field can be visualized using electric field lines.
- The field lines start with a positive charge and end with a negative charge.
- The density of these field lines is a measure of the size of the electric field at each given place, and they are parallel to the direction of the field at each point.
Read More: Properties of Electric Charges and Fields
Electrostatics Examples
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Some of the examples of electrostatic phenomena include:
- Operation of laser printer and photocopier.
- The damage of electronic components during manufacturing.
- The attraction of plastic wrap to a person’s hand after it is removed from a package.
- The attraction of paper bits to a charged scale.
- The spontaneous explosion of grain silos.
Things to Remember
- The electromagnetic force is a physical interaction between electrically charged particles.
- Electromagnetic fields are made up of electric fields and magnetic fields.
- Coulomb’s Law of electrostatics states that “The electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion of two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their magnitudes and inversely proportional to the square of their distance”.
- The electrostatic force is directed in the direction of the straight line that connects them.
- The electrostatic force between two charges is repulsive if their signs are the same; if their signs are different, the force is attractive.
- In the presence of an electric field, a surface charge on a conductor will experience a force.
Also check:
Previous Year Questions
- Suppose the charge of a proton and an electron differ slightly.… [NEET 2017]
- When the Gaussian spherical surface is doubled, then then the outward electric flux will be… [NEET 2011]
- The electric field outside a conducting sphere E is... [NEET 2020]
- How to adjust a system of three identical capacitors to get high electrostatic energy with the given battery? [UPSEE 2016]
- A glass rod rubbed with silk is used to change a gold leaf electroscope …. [JEE Advance 2011]
- Two long currents carrying thin wires, both with…. [JEE Main 2015]
- If wires have mass λ per unit length then, the value is…. [JEE Main 2015]
- A glass rod rubbed with silk is used to change a gold leaf electroscope…. [JEE Advance 2011]
- A thin disc of radius b=2a has a concentric hole of….[JEE Main 2015]
- The average velocity and the average speed of the toy car are between 0 to 30 seconds respectively….[NEET 2018]
- The electric flux linked to the surface, in units of volt m is...[NEET 2010]
- maximum torque exerted by the field on the dipole is….[KEAM]
- In finding the electric field using Gauss law the formula….[JEE Main 2020]
- The electric field at a distance x from the axis of rotation is…. [VITEEE 2021]
- If Q is the total charge of this charge distribution, the radius R is...[VITEEE 2011]
Sample Questions
Ques. When two things are rubbed together, a charge of about 50 nC can be generated in each object. Calculate how many electrons must be transferred in order to create this charge. (2 marks)
Ans: We know that,
q=50 nc=50×10-9C
Also, q=ne
∴n=q/e
=50×10-91.6×10-19
=31.25×1010 electrons
Ques. In the human body, the total number of electrons is normally in the order of 1028. Assume you and your friend each lose 1% of this number of electrons for some reason. Compute the electrostatic force between you and your friend if you are separated by 1 meter. Compare this to your current weight. Assume each person's mass is 60 kg and apply the point charge approximation. (3 marks)
Ans: Given that,
n=1028 no.of electrons
r=1m
Loss in electrons=1%
=1026 electrons got lost
Therefore, the charge on each person is given by,
=1026×1.6×10-19
M=60 kg
Fe=\({1 \over 4\pi Eo}\)\( {q1q2 \over r^2}\)
=9×1091026×1.6×10-19×1.6×10-1910261
Fe=23.04×1023N
Hence, Weight, W=mg
=60 x 9.8
=588 N
Ques. 1Å is the distance between two electrons in contact. Find the Coulomb force that exists between them. (2 marks)
Ans: Charge on an electron is given as, q=-1.6×10-19 C
The distance between the two charges, r=1?
The formula for the calculation of electrostatic force between the two electrons is given as
F=\({1 \over 4\pi Eo}\)\( {q1q2 \over r^2}\)
Substituting the above-given values in the expression,
∴F=(9×109Nm2C2)[-1.6×10-19C2/1A02
=2.3×10-8N
Ques. Consider two opposite charges of the same magnitude that are separated by a distance such that the force of F N operates between them. If 60 percent of a charge is shifted from one to another. Calculate how much the force value changes in this situation. (3 marks)
Ans: At first, the electrostatic force between the two charges is defined as,
F=k(\({q^2 \over r^2}\))……..1
When the charge becomes transferred, the electrostatic force is defined as,
F=k\({q1q2 \over r^2}\)……….2
Transferred charge
60% of q= 60/100 x q = 3/5 q
Hence, the charge q1=q-35 q
=2/5 q
Charge q2=q+35q
=8/5q
So, the net force present between these charges is,
F'=k(\({q1q2 \over r^2}\))
=k\({2/5q8/5q \over r^2}\)
=16/25F
Ques. What is the definition of static electricity? (2 marks)
Ans: When certain materials, such as wool on plastic or the soles of shoes on carpet, brush against each other, a static charge is generated. The technique involves pulling electrons off one material's surface and relocating them on the surface of another.
When the surface of the second substance, which is negatively charged with electrons, comes into contact with a positively charged conductor, a static shock ensues.
Ques. What is electrostatic induction, and how does it work? (2 marks)
Ans: Electrostatic induction is a redistribution of charges in an object generated by the electric field of a neighboring charge, as discovered by British scientist John Canton in 1753 and Swedish professor Johan Carl Wilcke in 1762. When a positively charged object is introduced close to an uncharged metal object, the metal's mobile negatively-charged electrons are attracted by the external charge and travel to the side of the metal facing it, resulting in a negative charge on the surface.
Ques. What is the triboelectric effect, and how does it work? (2 marks)
Ans: The triboelectric effect is a sort of contact electrification whereby some materials get electrically charged and then separated when they come into contact with another substance. One of the materials gains a positive charge, while the other gains a negative charge of the same magnitude. Depending on the material, surface roughness, temperature, strain, and other variables, the polarity and strength of the charges created vary.
Ques. What is relative permittivity? (3 marks)
Ans: The dielectric constant (or relative permittivity) is the ratio of a material's electric permeability to that of a vacuum. The dielectric constant of an insulator measures the insulator's ability to store electric energy in an electrical field.
Permittivity is a property of a substance that impacts the Coulomb force between two-point charges. The factor by which the electric field between the charges is reduced relative to the vacuum is known as relative permittivity.
Ques. What is contact electrification? (3 marks)
Ans: Contact electrification is a term that defines a phenomenon in which two or more items come in close proximity to one another and become electrically charged through a variety of causes. When two things are "touched" together, the objects can become charged spontaneously.
One object may generate a net negative charge, while the other produces a positive charge that is equal to and opposite to it. Various physical mechanisms, such as triboelectricity, the Volta effect, varying work functions of metals, and others, can create this phenomenon, which is collectively referred to as contact electrification.
Ques. What is a capacitor? (2 marks)
Ans: A capacitor is an electrical energy storage device that works in an electric field. There are two terminals on this passive electrical component.
Capacitance is the term for a capacitor's effect. While there is some capacitance between two electrical conductors in close proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a device that adds capacitance to the circuit. Originally, the capacitor was called a condenser or a condensator.

Capacitor
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:






Comments