Muskan Shafi Education Content Expert
Education Content Expert
Supercapacitors are electronic devices that are used to hold a huge amount of electric charge. Ultracapacitors or double-layer capacitors are the other names for supercapacitors. They help to store electrical energy utilizing two methods, double-layer capacitance, and pseudocapacitance, in opposition to a traditional dielectric. Double-layer capacitance is electrostatic in origin, while pseudocapacitance is electrochemical, thus, supercapacitors act as a hybrid of conventional capacitors and batteries. A supercapacitor has a capacitance of more than 15 million times more than the self-capacitance of the earth which is approximately 710 F. The maximum charge voltage of a supercapacitor ranges between 2.5 and 2.7 volts.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Supercapacitors, Capacitors, Electric Charge, Ultracapacitors, Capacitance, Batteries, Hybrid Capacitors, Electrodes, Current
Supercapacitors
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Supercapacitors are specially designed capacitors that have a very large capacitance. Supercapacitors basically add up the properties of capacitors and batteries into one device.
- Supercapacitors are also referred to as ultracapacitors or double-layer capacitors.
- Supercapacitors are called an ultracapacitor since they have a higher capacitance value than other regular capacitors.
- They consume less power and are completely safe and easy to operate.
- Supercapacitors use two mechanisms to store electrical energy namely double-layer capacitance and pseudocapacitance.
Supercapacitors
Read More:
| Relevant Concepts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Difference between Capacitor and Battery | Dielectric Properties of Solids | Capacitance Formula |
| Types of Capacitors | Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance | Electrolytic Capacitor |
Types of Supercapacitors
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Supercapacitors are classified into three main types which are
- Electrostatic Double Layer Capacitors
- Pseudo Capacitors
- Hybrid Capacitors
Electrostatic Double Layer Capacitors
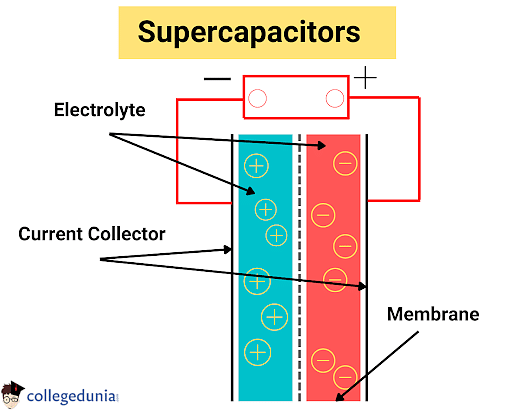
- Electrostatic Double Layer Capacitors comprises two electrodes, a separator, and an electrolyte.
- Electrolyte is a mixture comprising positive and negative ions dissolved in water.
- The two electrodes are separated from each other through a separator.
- The supercapacitors use carbon electrodes with much higher electrostatic double-layer capacitance.
- The separation of charge in electrostatic double-layer capacitors is much less than in a conventional capacitor which ranges from 0.3–0.8 nm.
Pseudo Capacitors
- Pseudo Capacitors are also referred to as electrochemical pseudo-capacitors.
- They make use of metal oxide or conducting polymer electrodes that have a high amount of electrochemical pseudocapacitance.
- They store electrical energy by electron charge transfer between electrode and electrolyte.
- It is done through the oxidation and reduction reaction commonly known as a redox reaction.
Hybrid Capacitors
- Hybrid Capacitors are made by using the techniques of double-layer capacitors and pseudo-capacitors.
- In these capacitors, electrodes with different characteristics are used.
- One electrode has the capacity to display electrostatic capacitance and the other electrode showcases electrochemical capacitance.
- An example of a hybrid capacitor is the lithium-ion capacitor.

Types of Supercapacitors
Read More: Electric Current and Circuit
Characteristics of Supercapacitors
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Here are a few important characteristics of Supercapacitors:
Charge Time
- The charge and discharge times for supercapacitors are equal to those of regular capacitors.
- High charge and discharge currents are achievable owing to the low internal resistance.
- A good example is a mobile phone battery that often takes several hours to fully charge, however, supercapacitors can reach the same charge state in less than two minutes.
Specific Power
- Specific power of a battery or supercapacitor is used to compare various technologies through the maximum power output divided by the total mass of the device.
- The specific power of supercapacitors is 5-10 times greater than that of batteries.
- A typical supercapacitor has a specific power of about 10 kW/kg, while Li-ion batteries have a specific power of 1 to 3 kW/kg.
Cycle Life of Supercapacitors
- Supercapacitors are devices that can be charged and discharged millions of times.
- They have a virtually limitless cycle life in comparison to batteries that only have a cycle life of 500 times or more.
- They are extremely beneficial in applications that frequently need to store and release energy.
Safety of Supercapacitors
- Supercapacitor batteries are considered to be safer in comparison to conventional batteries when mishandled.
- Supercapacitors do not heat up, unlike batteries because of their low internal resistance, whereas batteries explode owing to excessive heating when short-circuited.
Read More: Types of Circuits
Working of Supercapacitors
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The capacitors brings into use of static electricity or electrostatics to store energy.
- Positively and negatively charged ions are present between the two plates of the supercapacitor's electrolyte solution.
- One of the plates develops a positive charge whereas the other plate develops a negative charge when a voltage is placed across the plates.
- The positively charged plate attracts the positively charged ions in the electrolyte solution, whereas the negatively charged metal plate attracts the negatively charged ions towards itself.
- A thin coating of ions is deposited on the inner surface of both plates.
- An electrostatic double layer is formed as a result, which is like connecting two capacitors in series.
- Since the space between their charge layers is relatively small, each of the two resulting capacitors has a high capacitance value.
- A supercapacitor's total capacitance can be calculated by dividing (C1 × C2) by (C1 + C1).
Read More: Current Electricity
Specifications of Supercapacitors
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Here are the specifications of supercapacitors:
- Supercapacitors possess high capacitances of up to 2 kF.
- Supercapacitors store enormous amounts of energy.
- Supercapacitors offer to bridge the gap between conventional capacitors and rechargeable batteries.
- The charging time of a supercapacitor is around 1–10 seconds.
- Supercapacitors store electricity through either electrostatic charge absorption/desorption.
Applications of Supercapacitors
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Supercapacitors are used in a wide range of applications which are:
- Electric cars
- Flywheel in machines
- MP3 players
- Regenerative braking in the automotive industry
- Wind turbines
- Photographic flash
- Static memories (SRAM)
- Industrial electrical motors

Applications of Supercapacitors
Disadvantages of Supercapacitors
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Supercapacitors have a few disadvantages associated with them. The disadvantages of Supercapacitors are as follows:
- Supercapacitors discharge themselves much more frequently which is significantly higher than a battery.
- There are low voltages that exist within individual cells due to which series connections are necessary to attain greater voltages.
- There is a significantly lesser amount of energy stored per unit weight in comparison to an electrochemical battery.
- Supercapacitors deliver a poor energy density compared to batteries. It is equal to between one-fifth and a tenth of the battery's energy.
- They cannot be utilized in circuits with AC or higher frequencies.
Read More:
| Related Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Electrochemistry | Standard Electrode Potential | Difference between Cations and Anions |
| Semiconductor Devices | Electrical Resistance | Unit of Electric Charge |
Difference between Capacitors and Supercapacitors
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The main differences between Capacitors and Supercapacitors are:
| Capacitor | Supercapacitor |
|---|---|
| Capacitors are passive electrical devices with two terminals that retain charge as an electric field between their metal plates. | Supercapacitors are also known as double-layer capacitors, ultracapacitors, or super cap that can hold a huge amount of electric charge. |
| Capacitors consist of two metal plates serving as the anode and cathode of electrodes that are separated by a material known as the dielectric. | In supercapacitors, active carbon is used as the electrode material for electrodes. Supercapacitors use dielectric materials as a separator between the anode and cathode. |
| The current travel through the insulating material when the source voltage is supplied between the two terminals, but the material resists the flow of electrons. | Supercapacitors use either electrostatic double-layer capacitance (EDLC) or a combination of the two known as a hybrid capacitance to store charge. |
| Even though the voltage across the capacitor terminal is equal to the applied voltage, the insulation material continues to stop the flow of electrons. This resistance leads to a shift that has the effect of storing energy as an electrostatically charged field. | They are made up of electrodes with layers of activated carbon. The separator is pressed in between them. An ion-permeable membrane such as graphene acts as the separator and allows for the exchange of electrolyte ions between the electrodes. |
Things to Remember
- Supercapacitors are electronic devices used for storing extremely large amounts of electrical charge.
- Supercapacitors are also referred to as double-layer capacitors or ultracapacitors.
- Double-layer capacitance and pseudocapacitance are the two techniques used by supercapacitors to store energy.
- Supercapacitors act like a combination of regular capacitors and batteries.
- The charge time of supercapacitors is 1–10 seconds.
- Supercapacitors store electricity through either electrostatic charge absorption/desorption.
- Electric vehicles, windmills, flywheel in machines, MP3 players, etc are the various devices in which supercapacitors are used.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is a Supercapacitor? (3 Marks)
Ans. A supercapacitor also called an ultracapacitor, is defined as a high-capacity capacitor with a capacitance value much higher than other capacitors. A supercapacitor has lower voltage limits, that bridge the gap between electrolytic capacitors and rechargeable batteries. They store 10 to 100 times more energy per unit volume or mass than electrolytic capacitors. They can accept and deliver charge much faster than batteries.
Ques. List the characteristics of Supercapacitors. (3 Marks)
Ans. The characteristics of Supercapacitors are as follows:
- Supercapacitors have high capacitance ranging up to 2 kF.
- They store enormous amounts of energy.
- They bridge the gap between conventional capacitors and rechargeable batteries.
- The charge time of supercapacitors is between 1–10 seconds.
- They can store electricity through electrostatic charge absorption/desorption.
Ques. How many types of supercapacitors are there? (3 Marks)
Ans. There are three main types of supercapacitors which are listed below:
- Electrostatic Double Layer Capacitors
- Pseudo Capacitors
- Hybrid Capacitors
Ques. What is the future scope of Supercapacitors? (3 Marks)
Ans. The possible future scope and applications of supercapacitors are in cell phones, laptops, electric cars, and all other devices that currently run on batteries. The most enthralling advantage from a practical perspective is that they have a very fast recharge rate, which would mean that plugging an electric car into a charger for a few minutes would be enough to fully charge the battery.
Ques. What is Graphene? (3 Marks)
Ans. Graphene is one of the most exciting materials that can be used in supercapacitors. It is a substance consisting of pure carbon, arranged in a planar sheet only one atom thick. This substance is extremely porous and acts as an ion sponge. Energy densities achieved using graphene in supercapacitors are comparable to energy densities found in batteries. Graphene is difficult and expensive to produce in industrial quantities, which has literally postponed the use of this technology.
Ques. Are Supercapacitors costly? (3 Marks)
Ans. Yes, Supercapacitors are costly to be used for frequent purposes. Cost is one of the major disadvantages of currently available supercapacitors. The cost per Wh of a supercapacitor is more than 20 times higher than that of Li-ion batteries which makes it less used. However, the costs can be reduced through new technologies and the mass production of supercapacitor batteries.
Ques. Mention one major disadvantage of Supercapacitors. (3 Marks)
Ans. One major disadvantage of Supercapacitors is a relatively low specific energy. The specific energy denotes the measure of the total amount of energy stored in the device divided by its weight. Li-ion batteries that are commonly used in cell phones have a specific energy of 100-200 Wh/kg, while supercapacitors may only store typically 5 Wh/kg. It implies that a supercapacitor that has the same capacity as a regular battery would weigh up to 40 times as much.
Ques. What are the applications of Supercapacitors? (3 Marks)
Ans. The applications of supercapacitors are as follows:
- Electric cars
- Wind turbines
- Photographic flash
- Flywheel in machines
- MP3 players
- Regenerative braking in the automotive industry
- Static memories (SRAM)
- Industrial electrical motors
Ques. State the purpose of a dielectric in a capacitor. (2 Marks)
Ans. A capacitor’s capacity is determined by the area of the plates and their distance from one another. The dielectric serves to enhance the capacitance, C = Q/V, without affecting the size of the plates or their separation. This is what purpose a dielectric holds.
Ques. Mention the difference between a battery and a supercapacitor. (2 Marks)
Ans. Supercapacitors are lighter and have more robust working limitations. They have a longer life expectancy and an unmatched power density. Batteries on the other hand provide a superior energy density and have a higher breakdown voltage.
Check-More:





Comments