
Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
A DC motor is a device that converts direct current electrical energy to mechanical energy. In a DC motor, the input electrical energy (direct current) is transformed into mechanical rotation and then further into a rotational force. Direct Current or DC motor is an electric machine that helps the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy. DC motors are used in toys, small tools, electric vehicle propulsion, elevator, and steel rolling mills.
Key Terms: DC Motor, Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule, Magnetic Field, Shunt-wound DC Motor, Compound wound DC motor, Series wound DC motor
What is DC Motor?
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
DC motor refers to any class of rotary electrical motors that converts direct current electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- The most common types of DC Motors are dependent on the forces produced by magnetic fields.
- Simply stated, any electric motor that is operated using direct current or DC is called a DC motor.
- Almost, all types of DC motors have some internal mechanism.
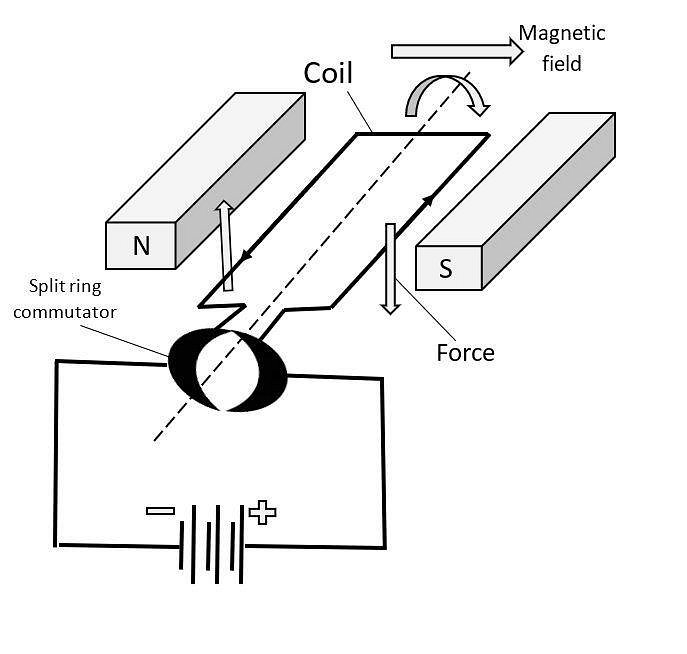
DC Motor Diagram
Frequently Asked Questions on DC MotorQues. What is the objective of a DC motor? (2 marks) Ans. A direct current or DC motor is an electric machine that is known to transform electrical energy into mechanical energy. DC motors are seen to obtain electrical power via direct current, further converting the energy into mechanical rotation. Ques. What will happen with the increase in speed of a DC motor? (1 mark) Ans. The emf increases when the speed of a DC motor increases, causing the current drawn to decrease. |
Download PDF: DC Motor Notes
Parts of a DC Motor
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A DC motor is made up of the following main parts:
Armature or Rotor
The armature of a DC Motor is a cylinder of magnetic laminations insulated from one another.
- The armature or rotor is perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder.
- The armature rotates on its axis and is separated from the field coil by an air gap.
Field Coil or Stator
A field coil of a DC motor is a non-moving part wherein winding is wound to produce a magnetic field. The electromagnet has a cylindrical cavity in between its poles.
Commutator and Brushes
- The commutator is a cylindrical structure in a DC Motor that is made up of copper segments that are stacked together but are insulated from each other due to mica.
- The commutator works to supply electrical current to the armature winding.
- Brushes are basically carbon and graphite structures. These brushes conduct electric current from the external field to the rotating commutator.
- Therefore, the commutator and the brush unit are responsible for transmitting power from the static electrical circuit to the mechanically rotating region known as the rotor.
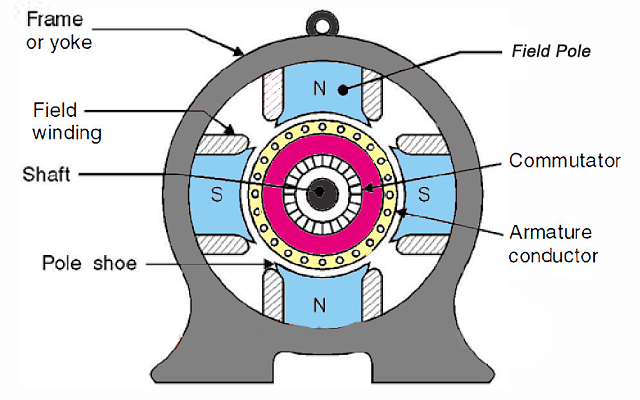
DC Motors Parts
Read More:
Working Principle of DC Motor
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The working principle of DC Motor is Fleming’s Left-hand rule that is when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a torque and has a tendency to move. This is known as Motoring Action.
Working of DC Motor
- When the DC Motor, field coil is energized, a magnetic field is created in the air gap.
- The magnetic field that is created is in the direction of the radii of the armature.
- The magnetic field enters the armature from the side of the North pole of the field coil and exits from the South pole side.
- The conductors located on the other pole get subjected to a force of the same intensity in the opposite direction.
- These two forces create a torque that leads to the motor armature to rotate.
If the direction of current in the wire is reversed, the direction of rotation also reverses. When magnetic field and electric field interact they produce a mechanical force that tends to rotate the Armature.

DC Motor Working
Working principle of DC motorA current-carrying conductor when kept in a magnetic field gains torque and develops a tendency to move. Hence, when electric fields and magnetic fields interact with each other, a mechanical force arises. This is the principle on which the DC motor works. |
Types of DC Motor
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
DC motors range widely in terms of applications, from electric shavers to automobiles. Based on this wide range of applications, they are classified into different types based on the field winding connections to the armature as:

DC Motor Types
Self-Excited DC Motor
The field winding is attached either in series or parallel to the armature winding in self-excited DC motors. The self-excited DC motors can be further classified into:
Shunt-wound DC motor: Here, the field winding is parallel to the armature.

Series wound DC motor: Here, the field winding is connected in series with the armature winding.

Compound wound DC motor: The DC motors that have both shunt and series field winding is called compound wound DC motor. The compound motor is further divided into:
- Cumulative Compound Motor
- Differential Compound Motor

Separately Excited DC Motor
The field coils are energized from an external source of DC supply in a separately excited DC motor.
Also Read: NCERT Solutions for Class 6 to 12 PDFs
Applications of DC Motor
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The applications of various types of DC Motors are given below:
Shunt DC Motors
As the shunt DC motors possess a fairly constant speed and medium starting torque, they are used in the following applications:
- Lathe machines
- Centrifugal and reciprocating pumps
- Blowers and fans
- Drilling and milling machines
- Machine tools
Series DC motors
On account of the high starting torque and variable speed of series DC motors, they are used in the following applications:
- Conveyors
- Hoists, Elevators
- Cranes
- Electric Locomotives
Cumulative Compound DC Motors
Due to the high starting torque of cumulative compound DC motors, they are used in the following applications:
- Shears
- Heavy Planers
- Rolling mills
- Elevators
Construction of DC Motor
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
There is a stator inside DC Motors which are poles with copper-binding also known as Field binding as magnetic fields are attached to it.
- Those permanent magnetic fields are controlled by the on and off switch in DC Motors.
- Then comes the Armature which has binding on it.
- The commutator comes between the two brushes.
- The movement occurs there in DC motors and the pressure comes on the shaft.

Also Read:
| Concepts Related to This Unit | ||
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Revision Notes | Difference between ac and dc motor | Electric generator |
Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Fleming’s Left Hand Rule states that if the index finger, middle finger, and thumb of your left hand are extended mutually perpendicular to each other and if the index finger represents the direction of Magnetic Field, the middle finger indicates the direction of the current, then the thumb represents the direction in which force is experienced by the Shaft of the DC motor.
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- A direct current (DC) motor is a form of electric machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- DC motors take electrical power through the direct current and convert this energy into mechanical rotation.
- The three main types of DC motor that are available are: Shunt, Series, and Compound.
- DC shunt motors can be used for many applications such as plastic or wire extrusions.
- DC motor failure can lead to reduced efficiency and even complete downtime in some of the operations.
Sample Questions
Ques 1. No-load speed of which of the following motor is highest? (2 marks)
(1) Differentially compound motor
(2) Cumulative compound motor
(3) Series Motor
(4) Shunt Motor
Ans: 3. Series Motor
Explanation: At the time of starting, flux is very less in DC series motor. So as we know the inverse relationship between speed and flux i.e. fluxes decrease when speed increase. Therefore we never start the DC series motor at no load.
Ques 2. Which of the following load normally need starting torque more than the rated torque? (3 marks)
(1) Conveyors
(2) Blowers
(3) Centrifugal pump
(4) Air compressor
Ans: 1. Conveyors
Explanation: Starting torque is also called the locked-rotor torque and the motor current at this point is referred to as the ‘locked rotor current. At this stage, the rotor reactance is higher than its resistance, as the rotor frequency is at its highest (equals the supply frequency). Starting torque is the amount of torque required to overcome the inertia of a standstill motor. Conveyors require high starting torque because the material is placed before the starting of the Conveyors belt.
So obviously we require more torque to overcome the load at the starting period. Therefore conveyor required high starting torque and constant speed. Series motor is suitable for conveyor belts operating in a particular region of its torque-speed characteristics. In industries BLDC is used, as BLDC provides PWM speed controlling method which is easier to vary the speed as well as with low maintains.
Ques 3. Which of the following rule is used to determine the direction of rotation of the DC motor? (2 marks)
(1) Columb’s Law
(2) Lenz’s Law
(3) Fleming’s Right-hand Rule
(4) Fleming’s Left-hand Rule
Ans: 4. Fleming’s left-hand rule.
Explanation: When a current-carrying conductor such as a wire attached to a circuit moves placed in a magnetic field, an electric current is induced in the wire due to Faraday’s law of induction. The right hand is held with the thumb, first finger, and second finger mutually perpendicular to each other. The thumb is pointed in the direction of the motion of the conductor relative to the magnetic field i.e. direction of the force. The forefinger is pointed in the direction of the magnetic field. The middle finger represents the direction of the induced or generated current within the conductor.
Ques 4. Which part of the DC motor can sustain maximum temperature rise? (2 marks)
(1) Armature Winding
(2) Field winding
(3) Slip Ring
(4) Commutator
Ans: 4. Commutator
Explanation: The commutator is made up of copper segments. This copper segment is insulated from each other with the help of mica. Mica has a very high dielectric stress of about 1180 kV/cm and the next best is Diamond. It can withstand high temperatures, up to 600 deg C.
Ques 5. The ratio of starting torque to full load torque is least in: (2 marks)
(1) Differential Compound Motor
(2) Shunt motor
(3) Series Motor
(4) Cumulative compound motor
Ans: 1. Differential Compound motor
Explanation: In the differential compound, motor two field windings i.e. shunt and series windings oppose each other. This causes a reduction in flux and consequences a decrease in torque.
Ques 6. The number of the pole in Small Dc Motor Up to 5 H.P is: ( 2marks)
(1) 2 poles
(2) 4 poles
(3) 8 poles
(4) 10 poles
Ans: 1. 2 poles
Explanation: Small H.P motors require only 2 poles because the number of poles is inversely proportional to the speed therefore 2 pole motor runs at high speed than 4 pole motor. Two pole motor has better efficiency. Two pole motor has better rpm and noise performance.
Ques 7. The efficiency of the DC motor at maximum power is: (2 marks)
(1) 90%
(2) 100%
(3) Around 80%
(4) Less than 50%
Ans: 4. Less than 50%
Explanation: Why efficiency of D.C motor is below 50%. The DC motor develops maximum power when the Back EMF is half the applied voltage is Eb = V/2. Practically it is not possible to develop an exact 50% of maximum power because in that case, the current would be much beyond the rated current of the motor. Some of the energy is wasted in the form of heat and other losses. Therefore motor efficiency is below 50%.
Ques 8. In which of the following applications DC series motor is used? (2 marks)
(1) Centrifugal Pump
(2) Motor Operation in DC and AC
(3) Water pump drive
(4) Starter for car
Ans: 4. Starter for car
Explanation: In DC series motor Torque (Ta) increases as the Square of armature current (Ia) Ta ∝ Ia2. So DC motor provides high starting torque which is required to start a car.
Ques 9. In the DC machine, the fractional pitch winding is used: (3 marks)
(1) To reduce the Harmonic in generated EMF
(2) Improve Cooling
(3) Increase EMF
(4) To reduce the copper losses
Ans: 1. To reduce the Harmonic in generated EMF
Explanation: In full pitched coils, as one conductor of a turn in a coil cuts N pole, the other conductor of the same turn cuts S pole resulting in the production of induced emf(E), i.e. phase angle is 180 degree. In short-pitched coils, both conductors of the same turn in a coil don’t cut the respective poles simultaneously. So phase angle is slightly less than 180 degree. As a result, the magnitude of induced emf gets reduced to E × Cos (nα/2)
Where E × Cos (nα/2) is called a pitch factor
For eliminating 3rd harmonic from Generated EMF,
Cos (3α/2) = 0
3α/2 = π/2
α = π/3 = 60°
Ques 10. A three-point starter is suitable for: (2 marks)
(1) Shunt Motor
(2) Series Motor
(3) Shunt & Compound Motor
(4) Shunt, Series, and compound motor
Ans: 3 point starters in DC Shunt and Compound machines serve for the following purposes. It limits the high starting current into the armature by having the resistance high at the time of starting and reducing it during the running conditions. It also protects the motor from overload and under-voltage conditions.
Ques 11. Can a DC motor run over an AC motor? (2 marks)
Ans: Yes, the DC series motor functions on a single-phase AC supply because of the torque, which varies as the product of the armature and field current which is always positive. Thus, a positive average torque causes the motor to rotate.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Also Check:





Comments