
Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Electrical current is defined as the rate at which the electrons flow in a conducting material. Electrical current related multiple choice questions are covered in the article below. These are based on the CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus.
The micro atomic particles of any matter is made of electrons which are either tightly held or loosely bound to the molecular structure of the material. Electrons are negatively charged and their movement gives rise to an electric current. This electron movement gives a substance its ability to conduct electricity. Based on this ability materials are further classified as conductors and insulators.
Electrical current is measured in Coulombs per second. The SI unit is Ampere and is denoted by ‘A’. 1 Ampere is defined as the movement of 1 coulomb of charge in one second.
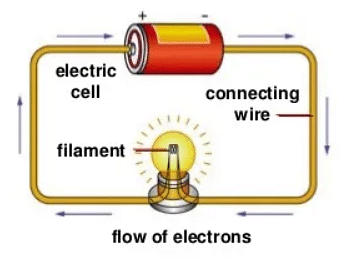
Electric Current Flow in a Circuit
Read More: Current Electricity
Class 12 Electrical Current MCQs
Q.1. One Ampere is defined as:
- 2 Coulomb of charge flowing per second
- 1 Coulomb of charge flowing per second
- No charge flowing condition
- Charge Passing per minute
Click here for the answer
A.1: The correct option is B) 1 Coulomb of charge flowing per second
Explanation: One Ampere is defined as one coulomb of charge flowing per second.
1A= 1Cs-1
Q.2. If 0.6A of current flows through an electrical circuit for 6 minutes, the amount of electric charge flowing through it is___________
- 60 C
- 36 C
- 360 C
- 216 C
Click here for the answer
A.2: The correct option is D. 216 C
Explanation: Electric Current (I)= Charge (Q)/ Time (t)
Here, I= 0.6A
t= 6 min
We have to find Q.
Therefore,
Q= I x t
=0.6 X 6 x 60
= 216 C
Q.3. Calculate the number of electrons passing through the conductor per second if 1mA current flows through the conductor.
- 1.6 x 1016
- 6.25 x 1015
- 6.25 X 1019
- 1.25 x 1012
Click here for the answer
A.3: The correct option is B. 6.25 x 1015
Explanation: I = Q/t
I= 1mA = 1x10-3 A
t= 1 sec
Total charge passing through the conductor = n*e
Thus ne= It
e= It/n
=1 x 10-3 x1/ 1.6 x10-19
= 6.25 x 1015
Q.4. Device which produces electric current is ___________
- Ammeter
- Generator
- Galvanometer
- Motor
Click here for the answer
A.4: The correct option is B. Generator
Explanation: Generators produce electric current by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Read More:
| Important Topics from Class 12 Chapter 3 Current Electricity | ||
|---|---|---|
| Static Electricity | Cells in Series & Parallel | Resistor Applications |
| Wheatstone Bridge | Ohm’s Law | Potentiometer |
| Carbon Resistor | Galvanometer | Resistance |
| Voltage Divider Formula | Network Analysis | Resistance and Length Formula |
| Electrical Circuit | Resistor | Kirchoff’s Laws |
| Internal Resistance | Power and Resistance | Current Density Formula |
Q.5. __________ converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Ammeter
- Galvanometer
- Motor
- Potentiometer
Click here for the answer
A.5: The correct option is C. Motor
Explanation: An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Q.6. Electric current is the flow of __________charges.
- Positive
- Neutral
- Positive and Negative
- Negative
Click here for the answer
A.6: The correct option is D. Negative
Explanation: Electron flow gives rise to electric current. Electrons are negatively charged particles and hence electric current is the flow of negative charges.
Q.7. What is the direction of electric current?
- Equal to 1 Ohm
- Opposite to work done
- Opposite to the direction of conventional current in conductors
- None of the above
Click here for the answer
A.7: The correct option is C. Opposite to the direction of conventional current in conductors
Explanation: Flow of negative charges causes the flow of current. By convention, the flow of charges is from positive to a negative potential. Electrons however are negative charges that flow from the negative to the positive terminal. Hence electric current flows opposite in direction to the conventional current flow.
Read More: NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Current Electricity
Q.8. Electric current is a ____________ quantity.
- Vector
- Scalar
- Both A and B
- None of the above
Click here for the answer
A.8: The correct option is B. Scalar
Explanation: Electric current follows the scalar law of addition. Hence if the angle between the wires is changed, the total current in the wire does not vary.
Q.9. An ammeter measures?
- Electric Current flow
- Electric Potential
- Electric Field
- Direction of electric field
Click here for the answer
A.9: The correct option is A. Electric Current flow
Explanation: The ammeter measures the current flowing through the circuit. This is connected in series in a circuit thus allowing it to measure the current flowing through the circuit.
Q.10. What is the dimensional formula of electric current?
- [M0 L0 T0 A1]
- [M L3 T0]
- [M L T-2]
- [M L2 T-3]
Click here for the answer
A.10: The correct option is A. [M0 L0 T0 A1]
Explanation: The unit of electric current is Amperes. Hence, the mass, length, and time components are zero in the units of an electric current. This gives us the dimensional formula for electric current as [M0 L0 T0 A1].
Q.11. The study of electric charges in motion is _________
- Static electricity
- Charge mobility
- Electronic mobility
- Current electricity
Click here for the answer
A.11: The correct option is D. Current Electricity
Explanation: Motion of electric charges causes the electric current. Thus, the study of this motion is called current electricity.
Q.12. Which conductor facilitates the movement of positive and negative charges?
- Thermosets
- Electrolytic solutions
- Metallic conductors
- Polymers
Click here for the answer
A.12: The correct option is B. Electrolytic solutions
Explanation: Solutions that can conduct electricity are electrolytic solutions. These are ions in which both positive and negative charges move. Polymers and thermosets cannot conduct electricity. In metallic conductors, the electrons are the charge carriers.
Also Check Out:






Comments