
Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Electric circuit is the path for transmission of electric current. An electric circuit consists of a device that gives energy to the charged particles (battery), devices that use current (lamps), and connecting wires. The performance of electric circuits is basically described through Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s laws. Electric current is the flow or electromotive force through an electrical circuit. The unit used to measure electric current is Ampere. An electric circuit can also be a closed path making it a loop. Electric current flow takes place because of the closed circuit. Every circuit is designed to provide power to one or more loads. For example, in a boombox, power goes to the speakers.
Electric circuits are classified as –
- A direct-current circuit carries a current flowing in one direction only.
- An alternating-current circuit carries a current that pulsates back and forth many times every second. Most household circuits are alternating current circuits.
- A series electrical circuit includes a path along which the current flows through each component.
- A parallel circuit includes different branches so that the current divides and just a part of it flows through any branch.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Electric Circuit, Circuit Formula, Cell, Switch, Light bulb, Connecting Wires, Electric Current, electrons, insulator, electric power, electrical energy, electric cell
Electric Circuit
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
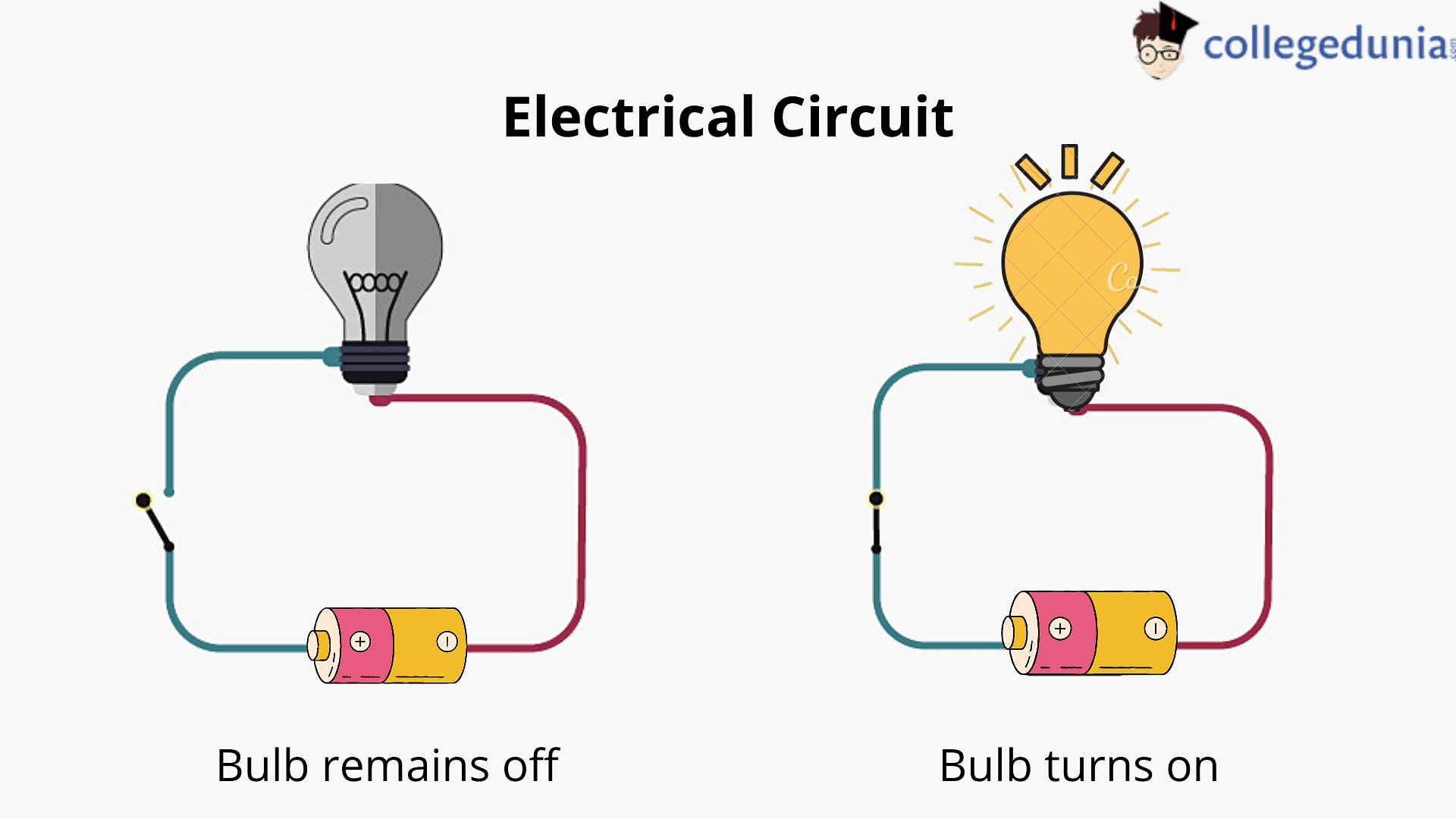
Electric circuit is a closed channel in which an electric charge can pass. A simple electric circuit consists of a supply, a bulb or other load, and the wires that connect them. When the terminals of a bulb are linked to the terminals of an electric current source through connecting wires, a possible difference is created across the bulb's terminals. The bulb shines as a result of the current flowing through the electric circuit.
- Electrical circuits are closed paths or loops that form a network of electrical components through which electrons can flow.
- The path of electrical circuits is made of electrical wires and is powered by a cell or a battery.
- When all components of an electric circuit are connected by wires composed of conductors, the circuit is said to be complete.
- If an insulator is present in the circuit's route, it becomes unfinished.
An electric circuit is a collection of electronic parts that work together to create a closed circuit for current to flow. A source of electrical energy (electric cell), a load that uses electric power, and interconnecting wires make up an electric circuit.
Electric Circuit ExperimentTo conduct an experiment, we need an electric bulb, wire, tape, and a battery.
Electrical Circuit Experiment An electrical circuit is complete only when there is at least a closed loop from the positive end to the negative end. The electrical circuit inside a television is more complicated comparatively and has different components. |
Faulty electrical circuits can cause fire due to electrical failure.
The video below explains this:
Types of Circuits Detailed Video Explanation:
Do Check Out:
Electric Circuit Formula
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The following are the formulas for Electric circuit or currents:
- Electric Current:
\(I = \frac{Q}{t}\)
I = Current, Q = Charge Flowing, t = Time period
- Resistance:
\(R = \rho . \frac{L}{A}\)
R = Resistance, p = Resistivity value of wire, L = Wire Length, A = Cross sectional area
- Voltage:
Δ V = I . R
V = Electric Potential difference
- Power:
\(P = \frac{\Delta E}{t}\)
P = Power, E = Energy gain or loss, T= Time period
- Series Circuit:
Req = R1 + R2 + R3 + ...
R = Resistors, Req = Total Resistance
- Parallel Circuit:
\(\frac{1}{R_{eq}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3} + ...\)
R = Resistors placed parallelly, Req = Total resistance
Electric Circuit Symbols
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Parts of an electric circuit that enable or control the supply of electrical current in a circuit are known as components. All these components act as conductors and also allow current to flow throughout these. Some of these electrical parts are connected to form an electric circuit. Some of the components of an electric circuit are –
- A cell or Battery is the power source.
- A load, also known as a resistor, is a light bulb that lights when the circuit is turned on.
- Conductors are made of copper wires with no insulation. One end is connected to the load and the other connects the power source to the load.
- Switch is a small gap in a circuit that can be used to open or close it.
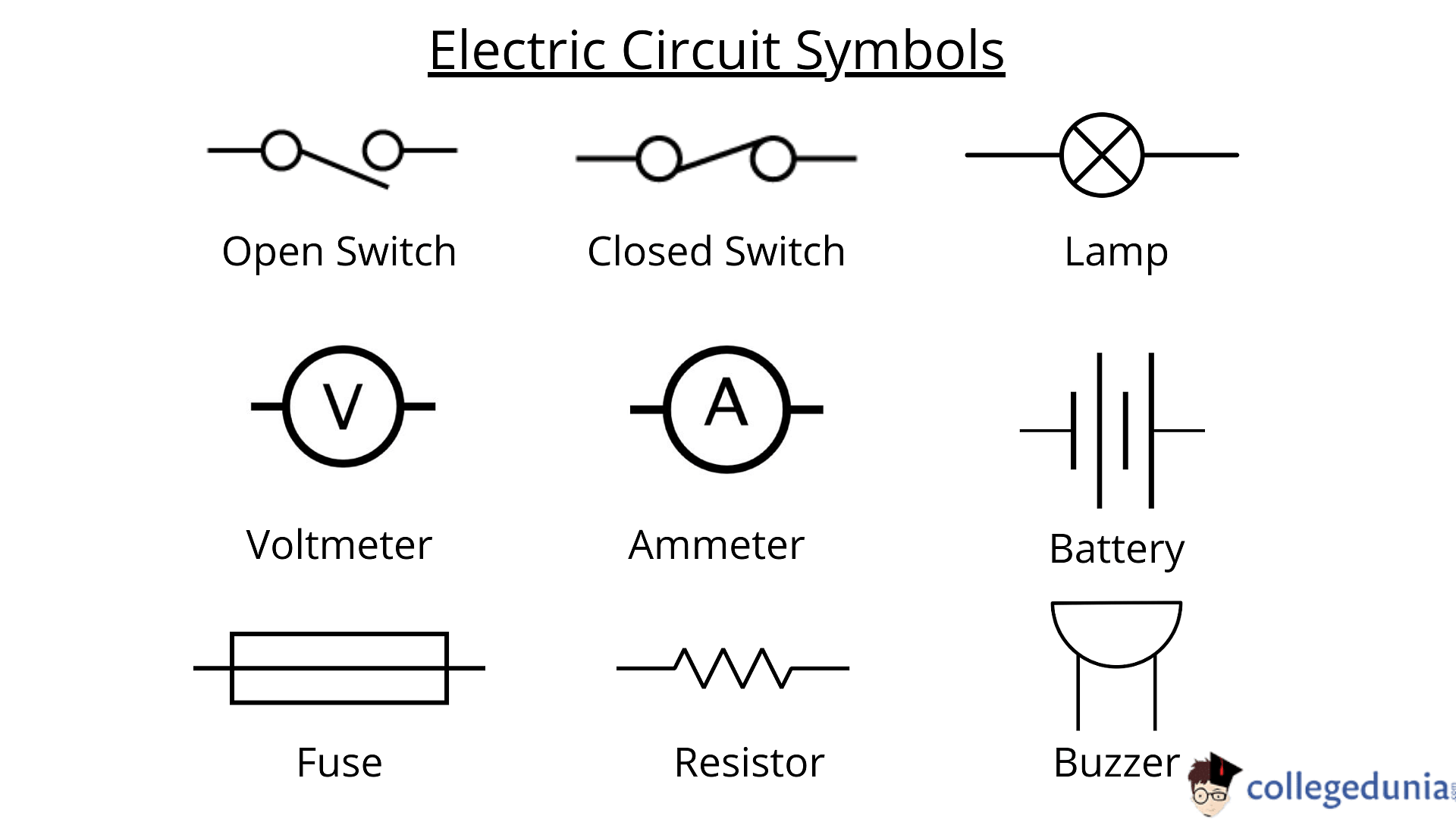
Electric Circuit Symbols
Some important electronic components are discussed below-
Cell
A cell is an electrical circuit's power source. It has two positively and negatively charged terminals.
- The negative terminal is an electron source that, when linked to a circuit, produces energy. Take, for example, a standard torch battery.
- If the load is correctly installed to its terminals, the chemical process in the cell generates the flow in the electric circuit.
- There are two terminals on an electric circuit – positive and negative.
- The longer line represents the positive end of the electric cell, while the shorter line represents the negative end.
Read More: Current Electricity Important Questions
Switch
A switch is an electronic appliance that can disrupt a circuit by diverting electricity from one conductor to the other or to an insulator.
- Open and closed connections are the two types of switch configurations.
- The connections are isolated and the circuit is broken, therefore no current flows in an open circuit.
- The electric circuit will be open if the switch is in the OFF position, and no electricity will flow through it.
- Since the circuit is closed while the switch is in the ON mode, current can flow via the electric circuit.
Light Bulb
A light bulb is a gadget that uses electricity to produce light. By current that passes through a small wire known as the filament, light bulbs convert electricity into light.
- Tungsten is a substance that lights up when electric current flows through it, hence the filament is usually made of it.
- The strong resistance supplied by the substance tungsten is responsible for the emission of light.
- In addition to lighting, light bulbs are employed in electronic equipment such as indicators, traffic signals, and automotive indicator lights, among other things.
Read More: Cells In Series and Parallel
Connecting Wires
Connecting wires are constantly utilized to interconnect different circuit elements in an electric circuit.
- Electrical conductivity is established among two components in an electrical circuit using wires.
- They have a very low resistance to the current passing through them.
- The wires are coated with a variety of colored coatings.
- Color codes are used to identify between neutrality and ground, as well as a live wire, which varies by nation.
- The materials used to make these cables allow electricity to travel through them. For example- Copper and Aluminium.
Also Check Out:
Types of Electric Circuits
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The following are the types of circuits:
- Series Circuit: The elements of a series circuit are linked in series, or one after the other, with no wire branching. Regardless of how many resistors are contacted along the route, the current flowing through all items connected in series is the same.
- Parallel Circuit: A parallel circuit has units that are connected in parallel, which means that one point in the circuit sections, with wires traveling to two different parts, and then the sections rejoin. The voltage over each parallel-connected element is the same.
- Open Circuit: Since the loop is interrupted at some point, no current can flow in an open circuit. The term "closed circuit" refers to a circuit in which the entire loop has been constructed and current can flow. Obviously, the latter is more fascinating to research.
- Short Circuit: A short circuit is something in which the resistive parts have been skipped and there is a large amount of current flowing. Circuit breakers are devices that are set in circuits to "break" (open) the circuit and cease current flow in order to safeguard against damages to the circuit and electronic devices, as well as to prevent fires.
Also read: Carbon Resistor
Things To Remember
- Electric circuits are closed paths, forming a network of electrical components through which current can flow.
- Individual resistor resistances are combined together in a series circuit to obtain the circuit's overall resistance.
- A simple circuit comprises the conductors, power source, switch, and load.
- When electrons interact with other ions and atoms in the wire, some of their power is transformed to heat.
- Despite the fact that separate devices have varying voltages opposite them, the current flowing through the series circuit is the same.
Also read: Potentiometer
Previous Year Questions
- If now we have to change the null point at the 9th wire, what should we do?… [DUET 2007]
- Just after key K is pressed to complete the circuit, the reading will be …. [KEAM 1999]
- When the same resistances are connected in series across the same cell, the power developed is…. [KCET 1998]
- The resistance between any two terminals when connected in a triangle is…. [NEET 1993]
- The equivalent resistivity of the combination when two wires of the same dimensions but resistivities are connected is...[KCET 2003]
- The value of R for which the power delivered in it is maximum is given by... [NEET 1992]
- The internal resistance of the cell is… [KCET 2019]
Sample Questions
Ques. What are the properties of electric circuits? (5 Marks)
Ans. Electric circuits have the following basic properties:
- A circuit is a path that is always closed.
- A circuit must always have at least one energy source that serves as an electron source.
- An unregulated and controlled type of power, as well as resistors, capacitance, and inductors, are among the electric elements.
- Electrons pass from the negative end to the positive electrode in an electric circuit.
- The passage of traditional power is from the positive to the negative terminal.
- The current flow causes a potential decline in the various elements.
Ques. Explain the domestic Electric Circuit. (5 Marks)
Ans. Electricity is generated at power plants and delivered to our houses by power lines. Through the main power source, this electricity enters the electric boards that are installed in our homes. The power in our homes is supplied by the mains via three main cables.
The term "live wire" refers to one of these wires (or positive). The live wire has a red insulation coating, while the neutral wire has a white insulation cover (or negative). In the event of a current leakage, the ground wire, which is wrapped in green insulation, protects us from electric shock. It is linked to the ground and gives a low current route.
Ques. What is an Electric Circuit Simulator? (3 Marks)
Ans. An electric circuit simulator is a piece of software that simulates the activity of electrical devices and systems using mathematical models. It aids in the comprehension of an electric circuit's function by allowing the user to inspect and test the circuit in a software application before producing the final circuit board.
Because the manufacture of electronic circuits, particularly integrated circuits (ICs), is costly and time-consuming, it is better and more cost-effective to evaluate the circuit's behavior and functionality using a circuit simulator before creation.
Ques. What is Electric Circuit Analysis? (3 Marks)
Ans. The practice of assessing and locating all electrical variables in a circuit of diverse electronic parts is known as electric circuit analysis. Kirchhoff's law can handle certain electric circuits that cannot be reduced by series-parallel arrangements. The following are the two primary terminologies employed in this law:
- The place where three or more conductors intersect is known as a junction.
- Any enclosed conducting route in an electric circuit is referred to as a loop.
Ques. What Precautions should be taken while using Electric circuits? (5 Marks)
Ans. The following are some safety precautions to take when using electricity:
- When working, always use shielded tools.
- Do not utilize any equipment that has frayed cables, damaged insulation, or faulty plugs.
- Know your country's wire code.
- When dealing with electricity, stay away from water at all times. Wet hands should never be used to touch or attempt to fix any electrical equipment or circuits. It improves the electrical current's conductivity.
- Avoid using devices with frayed cords, broken insulation, or broken plugs at all costs.
Ques. What is Static Electricity? (2 Marks)
Ans. Charges that aren't flowing are referred to as static electricity. But there's a lot more to it than that! The key to understanding static electricity is that it arises when there is a disparity of charge, and this imbalance primarily creates electrostatic force, which means that because of the roles of charge-carrying atoms, there is the possibility for electrical current that flows (to restructure the charge).
The positive and negative energy (i.e. protons and electrons) in atoms, and by inference most ordinary items, are balanced, making them electrically neutral when viewed as a whole.
Ques. What is Ohm’s Law? (2 Marks)
Ans. The current through a wire is proportionate to the voltage over the conductor, according to Ohm's law. Many substances (including metals) can do this if the temperature (and other physical parameters) stay constant. The proportionality constant, R, is the resistivity, and the unit is the ohm, which has the symbol Omega.
V, equals, I, R is the formula for the relationship.
V=IR
The voltage across the wire is V, and the current that flows through it is I. If follows Ohm's Law, its resistivity must be unaffected by current or voltage.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Also Read:







Comments