
Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Physics MCQs for Class 12 Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields with Answers have been provided in the article. An electric charge has an electric field associated with it, and a moving electric charge produces a magnetic field. Electromagnetic field is a combination of electric and magnetic fields.
Related Links
- Appearing for JEE Main, Download JEE Mains PYQ for all sabjects
- Appearing for NEET, Download NEET PYQ for all subjects
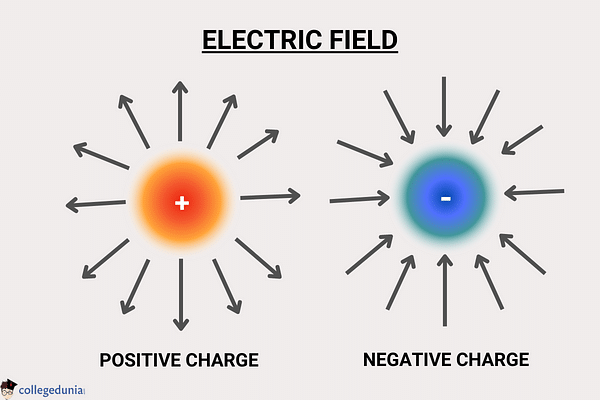
Electric Charges and Fields
Ques 1. An electron is placed in an electric field of intensity 104 Newton per Coulomb. The electric force working on the electron is
- 0.625 x 1013 Newton
- 0.625 x 10-15 Newton
- 1.6 x 1015 Newton
- 1.6 x 10-15 Newton
Click here for the answer
Ans. 1.6 x 10-15 Newton
Explanation- Given that:
E = 104 Newton per Coulomb and q = 1.6 x 10-19 C
F = q E
F = (1.6 x 10-19)x104
F = 1.6 x 10-15 Newton
Ques 2. Force per unit charge is known as ______.
- Electric field
- Current
- Electric flux
- Electric potential
Click here for the answer
Ans. Electric field
Explanation- The space or region around an electric charge in which other charged particles can feel the electrostatic force is described as an electric field by that electric charge. The electric field is indicated by E, and the SI unit for it is N/C. The electric field is defined as the force per unit charge (E = F/q).
Ques 3. Which of the following is false about Electrostatic field lines?
- Field lines start from positive charges and end at negative charges.
- If there is a single positive charge, field lines will end at infinity.
- Two field lines can never cross each other
- Electrostatic field lines form closed loops.
Click here for the answer
Ans. Electrostatic field lines form closed loops
Explanation- The space or region around an electric charge in which other charged particles can feel the electrostatic force is referred to as the electric field by that electric charge. Electric field lines are imaginary lines that are used to illustrate the electric field.
The direction of the electric field at a location on the electric field line is given by the tangent line. Field lines begin with a positive charge and end with a negative charge. They begin and stop at right angles to the charge's surface. There are no loops in electric field lines. Where the number of field lines is greatest, the size of the electric field is greatest.
Ques 4. The magnitude of electric force experienced by a charged particle in an electric field depends on:
- charge of the particle
- the velocity of the particle
- the direction of the electric field
- mass of the particle
Click here for the answer
Ans. Charge of the particle
Explanation- In an electric field, the magnitude of the electric force experienced by a charged particle is given by,
F=Eq°
The magnitude of the electric force experienced by a charged particle in an electric field is dependent on the magnitude of the charge on the particle, as shown by the above equation.
Ques 5. An electric charge enters an electric field region along the direction of the electric field. Which of the following will be the path of the particle's motion?
- Parabola
- Circular
- Straight Line
- None of the above
Click here for the answer
Ans. Straight Line
Explanation- The force experienced by the charged particle is given by:
F = q0E
F and E are vector quantities in this case. Charge, on the other hand, is a scalar quantity. If a charged particle enters an electric field with a positive charge, the force will be in the direction of the field (E). The force will be in the opposite direction of the field if the charge is negative. However, the force will be directed in a straight path. As a result, the charged particle will move in a straight path.
Ques 6. The electric energy density (energy per unit volume) in a region with electric field 'E' is ____________ where ϵo is the permittivity of free space.
- \(\epsilon\)oE / 2
- \(\epsilon\)o2E / 2
- 2E² /\(\epsilon\)o
- \(\epsilon\)oE² / 2
Click here for the answer
Ans. ϵoE² / 2
Explanation- The energy per unit volume, often known as the instantaneous energy density uE, is calculated as follows:
μ= 1/2 ϵo E²
Where E is the electric field's energy density, ϵo is the electric permittivity of space (vacuum) and is the electric field's energy density.
Ques 7. The intensity of the electric field at any point on the surface of a charged conductor is
- zero
- perpendicular to surface
- tangential to surface
- infinite
Click here for the answer
Ans. perpendicular to surface
Explanation- Because there are no parallel components of field lines on the surface of a charged conductor, the electric field at any location on the surface is perpendicular to the surface. Because all of the charges are collected on the conductor's surface, this is the case.
Also Read:
Ques 8. In an electric field E directed downwards a proton of charge e will experience a _________.
- the upward force of magnitude eE
- the downward force of magnitude e/E
- the upward force of magnitude e/E
- the downward force of magnitude eE
Click here for the answer
Ans. Downward force of magnitude eE
Explanation- Given that the proton charge q = e and the electric field E are both equal (downward)
As a result, force F = qE.
F = eE
Because force is always in the direction of the electric field, it will be downward.
Ques 9. A hollow metal ball-carrying an electric charge produces no electric field at points:
- Outside the sphere
- On its surface
- Inside the sphere
- Only at the center
Click here for the answer
Ans. Inside the sphere
Explanation- The electric field within the hollow sphere is zero. They cancel each other out since E is a vector quantity. There is no electric field in the middle. The external field is canceled by the inside field. The electrical charge is always spread evenly throughout the uniformly formed wire.
Ques 10. If the potential at every point on a conductor is the same, then
- Electric field lines of force may begin or end on the same conductor
- No electric field lines of force may begin or end on the same conductor
- The electric field intensity inside the conductor is non-zero
- None of the above
Click here for the answer
Ans. No electric field lines of force may begin or end on the same conductor
Explanation- An equipotential line is a line that connects locations with the same potential. Electric field lines are perpendicular to equipotential lines. The direction of the electric field at each location on the electric field line is represented by the tangent to that point.
Ques 11. The force experienced by a unit positive test charge placed at a point is called
- The magnetic field at that point
- The gravitational field at that point
- The electrical field at that point
- The nuclear field at that point
Click here for the answer
Ans. The electrical field at that point
Explanation- A charged particle's environment in which it exerts an electrostatic force on another item. The force of electrostatic attraction or repulsion is applied to a test charge when it enters the electric field of any charged particle.
Ques 12. The electrostatic force acting per unit positive test charge at a location is a measure of the intensity of:
- Electric potential
- Electric field
- Coulomb force
- Gravity
Click here for the answer
Ans. Electric field
Explanation- The force experienced by a unit charge deposited at any point is specified as the electric field intensity (E). The intensity of an electric field at a particular point is given by:
E=F/q
As a result, the force acting per unit positive test charge at a given place is a measure of the electric field's intensity.
Ques 13. Acceleration of a charged particle of charge 'q' and mass 'm' moving in a uniform electric field of strength ‘E' is
- qE/m
- m/qE
- mqE
- q/mE
Click here for the answer
Ans. qE/m
Explanation- The electric force acting on the charged particle,
F = qE
By Using Newton's second law of motion,
F = ma
qE = ma
a = qE/m
Ques 14. Aspherical conductors of radius 2 cm are uniformly charged with 3 nC. What is the electric field at a distance of 3 cm from the center of the sphere?
- 3x106 V m-1
- 3 V m-1
- 3x104 V m-1
- 3x10-4 V m-1
Click here for the answer
Ans. 3x104 V m-1
Explanation- Given: Q = 3nC = 3 x 10-9 C; d = 3 cm = 0.03 m; K = 9 x 109 (constant)
The electric field at a distance of 3 cm will be:
E= 9 x 109 ×3 x 10-9/0.032
3x104 V/m
Ques 15. The SI unit of the electric field is:
- Cm-2
- Am-1
- Vm-1
- Cm-1
Click here for the answer
Ans. Vm-1
Explanation- The electric field is defined as the force produced by charge or potential multiplied by distance. The volt is the SI unit of electric potential, whereas the meter is the SI unit of distance. Volt/meter, or V m-1, is the unit of potential by distance.
Ques 16. An electron with charge e is at rest in an electric field E. Then the electric force acting on it, is ____?
- Zero
- Ee
- E/e
- 1/Ee
Click here for the answer
Ans. Ee
Explanation- Given: an electron's charge (q) = e and an electric field E
When an electron is put in an electric field E, the force experienced by the electron is
F = eE
As a result, if an electron has a charge of e and is at rest in an electric field E, the electric force acting on it is eE.
Ques 17. The force experienced by a charged particle of -6 C in the external electric field is 60 N towards the north. The electric field intensity will be:
- 10 N/C towards the north
- 10 N/C towards the south
- 6 N/C towards the north
- 6 N/C towards south
Click here for the answer
Ans. 10 N/C towards the south
Explanation-
Given qo = -6C, and F = 60 N towards north
We know that the electric field intensity is given as,
E=F/qo
E=60/6
⇒ E = 10 N/C
The electric field exerts a pull on the negative charge in the opposite direction. As a result, the electric field is directed southward.
Ques 18. A body is positively charged, which implies that
- There is only a positive charge in the body.
- there is positive as well as negative charge in the body but a positive charge is more than a negative charge
- there is equally positive and negative charge in the body but the positive charge lies in the outer regions
- the negative charge is displaced from its position
Click here for the answer
Ans. there is positive as well as negative charge in the body but a positive charge is more than a negative charge
Explanation- When we say a body is charged, we always imply that it has an excess of electrons (negatively charged) or a deficiency of electrons (positively charged) (positively charged).
Ques 19. When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, it
- gives electrons to silk.
- gives protons to silk.
- gains electrons from silk.
- gains protons from silk.
Click here for the answer
Ans. gives electrons to silk.
Explanation- On rubbing a glass rod with silk, excess electrons are transferred from glass to silk. So glass rod becomes positive and silk becomes negative.
Ques 20. In general, metallic ropes are suspended on the carriers taking inflammable materials. The reason is
- to keep the centre of gravity of the carrier nearer to the earth.
- to control the speed of the carrier.
- to keep the body of the carrier in contact with the earth.
- none of the above
Click here for the answer
Ans. to keep the body of the carrier in contact with the earth.
Explanation- For providing a path to the charge induced on the surface of the carriers.
Ques 21. Two similar spheres having +Q and -Q charges are kept at a certain distance. F force acts between the two. If at the middle of two spheres, another similar sphere having +Q charge is kept, then it experiences a force in magnitude and direction as
- 8F towards +Q charge.
- 8F towards -Q charge.
- zero having no direction.
- 4F towards +Q charge.
Click here for the answer
Ans. 8F towards -Q charge.
Explanation- Initially, force between A and C,

When a similar sphere B having charge +Q is kept at the mid-point of line joining A and C, then net force on B is

The direction is shown in the figure.
Ques 22. The quantization of charge indicates that
- Charge, which is a fraction of charge on an electron, is not possible
- A charge cannot be destroyed
- Charge exists on particles
- There exists a minimum permissible charge on a particle
Click here for the answer
Ans. Charge, which is a fraction of the charge on an electron, is not possible
Explanation- The quantization of charge means that when we say something has some charge, we mean by that that how many times the charge of electrons it has. Because the whole charge is associated with an electron.
Previous Year Questions
- Two long current carrying thin wires, both with current II, are held by insulating threads of length L….[JEE Main 2015]
- Let a total charge 2Q be distributed in a sphere of radius RR, with the charge density given by….[JEE Main 2019]
- In finding the electric field using Gauss law the formula...[JEE main 2020]
- For a uniformly charged ring of radius RR, the electric field on its axis has… [JEE Main 2019]
- Charge is distributed within a sphere of radius RR with a volume charge density…. [JEE Main 2019]
- An electric dipole has a fixed dipole moment...[JEE Main 2017]
- A thin disc of radius b=2a has a concentric hole of radius 'a ' in it….. [JEE main 2015]
- A spherically symmetric charge distribution is characterised by a charge density having the...[JEE Main 2014]
- A particle of charge q and mass mm is subjected to an electric field...[JEE Main 20202]
- A long cylindrical shell carries positive surface charge σ in the upper half and negative surface charge…..[JEE Main 2015]
- The value of A such that the electric field in the region between the spheres will be constant, is….[JEE Main 2016]
- Consider a sphere of radius R which carries a uniform charge density ρ…. [JEE Main 2020]
- An electric dipole is formed by two equal and opposite charges qq with separation… [JEE Main 2019]
- Two charges, each equal to q , are kept at x=−a and x=a on the…. [JEE Main 2013]
- A glass rod rubbed with silk is used to change a gold leaf electroscope and the leaves are observed to….[JEE Advance 2011]
- In the given circuit, what will be the equivalent resistance between the points A and B ?…. [JIPMER 2006]
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:






Comments