Jasmine Grover Content Strategy Manager
Content Strategy Manager
Glucose, Fructose and Sucrose are some of the important carbohydrates that are required for the human body. Both fructose and glucose are said to be simple sugars. Simple carbohydrates are divided into two types- Disaccharides and Monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are the basic form of carbohydrates and the fundamental source of carbohydrates. They are the most basic form of sugar and are made of one sugar unit. Monosaccharides have different roles within cells. They are the first that are used to store and generate energy. Due to the breakdown of monosaccharides glucose, most of the species produce energy from the bonds. Monosaccharides Examples are Fructose and Glucose.
A molecule that is formed by simple sugars or two monosaccharides is known as a Disaccharide. Disaccharide is also known as double sugar. Disaccharides are formed with the dehydration reaction by removing a water molecule from two monosaccharides. Disaccharides examples are Lactose, Maltose, and Sucrose.
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms: Glucose, Fructose, Simple Carbohydrates, Complex Carbohydrates, Sucrose, Carbohydrates, Sugar, Starch, Lactose, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides
What is Glucose?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Glucose is a monosaccharide. Glucose is found in all of the major carbohydrates like table sugar, starch, etc. The other name of Glucose is grape sugar or blood sugar. Glucose is an aldohexose and a six-membered ring i.e., six-carbon sugar. It is aldohexose because it has aldehyde as a functional group. Glucose is the combined form in nature and also occurs freely. The structure of glucose is a pyranose ring structure.
Glucose is the preferred and primary energy source of the human body. Starch carries glucose. Glucose is found in regular foods like starch, honey, sweet fruits, table sugar, etc. It acts as building blocks for energy sources and cellular structures for the brain and the muscles during physical activity. Glucose is aldohexose because it has aldehyde as a functional group.

Glucose
Uses of Glucose
- Glucose is given to those patients who are extremely ill and unable to eat as it offers calories from carbohydrates.
- Glucose is used in the treatment process of low blood sugar.
- Glucose is used as a precursor for the synthesis of matter.

Benefits of Glucose
Read More:
What is Fructose?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Fructose is a monosaccharide. It is formed in fruits and vegetables. The glycaemic index is less in fructose as compared to glucose. To cellular protein, the binding of fructose is seven times faster than glucose. Fructose is also called D- fructose or fruit sugar. Ketone is the functional group of fructose. It is absorbed mainly in the liver and is not found in starch.
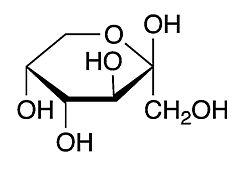
Fructose
Uses of Fructose
- Crystalline fructose is used majorly in the food industry, it is used to improve flavour.
- Fructose is found in flavoured water, low-calorie drinks, energy drinks, etc.
- Fruit sugar is used in smooth, moist cookies, nutrition bars, low-calorie products, etc.
Difference between Glucose and Fructose
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Glucose and Fructose differ from each other in various parameters. The major difference between Glucose and Fructose is given in the below table.
| Glucose | Fructose |
|---|---|
| The structure of Glucose is like pyranose ring-type. | The structure of Fructose is like a furan ring-type. |
| Glucose releases fast energy. | Fructose releases slow energy. |
| Glucose is said to be a six-membered ring. | Fructose is said to be a five-membered ring. |
| It has an aldehyde functional group known as Aldohexose. | It has a ketone functional group known as Ketohexose. |
| Glucose is also called Dextrose, Grape Sugar. | Fructose is also called Levulose, Fruit Sugar. |
| Glucose is formed from the enzymatic hydrolysis of starch and sucrose. | Fructose is produced from corn, sugarcane. |
| The source of Glucose is Table sugar and Starch. | The source of Fructose is Sugar Cane, Vegetables, and Fruits. |
| Glucose produces less fat or it can be said fatless | Fructose produces more fat. It has fatty substances. |
| Glucose is used for the production of Vitamin A, Glycogen, and starch. | Fructose is used to build glycogen and produce ATP. |
| To initiate metabolism, Glucose depends on glucokinase or hexokinase. | To initiate metabolism, Fructose depends on fructokinase. |
| Glucose is the preferred source for the human body. | Fructose is not the preferred source for muscles and the brain. |
| Glucose is less lipogenic. | Fructose is more lipogenic. |

Glucose & Fructose
Things to Remember
- The important carbohydrates that are required for the human body are sucrose, fructose, and glucose.
- Simple carbohydrates are divided into two types- Disaccharides and Monosaccharides.
- Both fructose and glucose are said to be simple sugars.
- Monosaccharides are the basic form of carbohydrates and the fundamental source of carbohydrates.
- Glucose is found in regular foods like starch, honey, sweet fruits, table sugar, etc.
- Disaccharide is also known as double sugar.
- Glucose is a monosaccharide.
- Glucose is an aldohexose and a six-membered ring.
- Glucose is found in all of the major carbohydrates like table sugar, starch, etc.
- Fructose is a monosaccharide. It is formed in fruits and vegetables.
Read More:
Sample Questions
Ques. Explain the preparation of Glucose? (5 Marks)
Ans. The preparation of Glucose is done in two ways:
- From Sucrose: Glucose and Fructose can be obtained in exactly equal amounts by boiling sucrose in an alcoholic solution with dilute HCl and H2SO4.
C12H22O11(Sucrose)+ H2O → C6H12O6 (Glucose)+ C6H12O6 (Fructose)
- From Starch: By the hydrolysis of starch in boiled and dilute H2SO4 at 393 K under pressure, we can obtain Glucose.
(C6H10O4)n (Starch or cellulose) + nH2O + H+ → nC6H12O6 (Glucose)
Ques. Mention some properties of Fructose. (3 Marks)
Ans. The properties of Fructose are:
- Fructose has a melting point of 146°C.
- It has a low melting point.
- Fructose has a density of 1.69 g/cm2 and a molas mass of 180.16 mol/g.
- Refined fructose that is crystallized is powdery and pure.
Ques. What are the uses of Glucose? (3 Marks)
Ans. Some of the uses of Glucose are:
- Glucose is given to those patients who are unable to feed and are extremely ill because it provides calories from carbohydrates.
- Glucose is used for low blood sugar treatment.
- Glucose is used as a predecessor for the synthesis of matter.
Ques. From where does fructose come? (2 Marks)
Ans. Fructose comes from sugar beets, corn, sugar cane. From corn-starch, high-fructose corn syrup is made and consists of more fructose than glucose as compared to regular corn syrup. Fructose has the sweetest taste but it has less impact on blood sugar.
Ques. In what ways glucose provides energy? (3 Marks)
Ans. The process through which Glucose provides energy is as follows:
- Glucose is absorbed directly into all cells and bloodstream.
- Glucose goes through oxidation that outcome the release of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate).
- ATP is high molecule energy that produces energy for the cell. This is the main reason for which we get immediate energy from glucose.
Ques. What are the main characteristics of simple carbohydrates? (3 Marks)
Ans. The main characteristic of simple carbohydrates is simple carbohydrates digest quickly than complex carbohydrates and are made up of a short chain of molecules.
Simple carbohydrates are found in fruits and milk naturally, or can be produced artificially and are added to foods to sweeten, improve the structure and texture, prevent spoilage. Simple carbohydrates produce a spike in blood glucose, and thus they provide the body with a short-lasting source of energy.
Ques. In what way do simple carbohydrates differ from complex carbohydrates? (3 Marks)
Ans. Complex Carbohydrates have a more source of energy and take a long time to digest as compared to simple carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates are found in food like syrups and table sugar, whereas complex carbohydrates are found in food like pasta and bread.
Simple carbohydrates in processed foods or those with added sugar need to be avoided such as candy, sugary drinks, syrups, fruit juice concentrate, baked goods or some cereals, etc. Complex carbohydrates are the better choice in terms of energy.
Ques. In what ways fructose is used? (3 Marks)
Ans. Fructose is used for various purposes. Some of them are:
- Fructose is found in flavoured water like low calories items, energy drinks, etc.
- To improve flavour, Crystalline fructose is used in the food industry.
- Fructose or fruit sugar is used in the manufacture of low-calorie products, nutrition bars, moist cookies, etc.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:



Comments