Arpita Srivastava Content Writer
Content Writer
Carbohydrates are macronutrients and one of the three primary sources of nutrition for our bodies. Carbohydrates are named for the chemical elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen that they contain. Carbohydrates, which include carbohydrates, fibres, and starches, are important nutrients. They can be found in grains, vegetables, fruits, and dairy products such as milk and cheese.
| Table of Content |
What are Carbohydrates?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The cells, muscles, and tissues in our body use this sugar as a source of energy. The excess energy or sugar is retained in our muscles and liver in case we need it again. The word "carbohydrate" comes from the French term "hydrate de Carbone," which means "carbon hydrate." Cn(H2O)n is the general formula for this class of organic compounds. They are the basic food groups that are important for living a healthy lifestyle. Carbohydrate-rich foods are converted to glucose or blood sugar by the digestive system during the digestion phase.
Classification of Carbohydrates
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Carbohydrates are divided into two categories: simple and complex, based on their chemical structure and degree of polymerization.
Simple Carbohydrates
One or two sugar molecules make up simple carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates cause blood sugar levels to rise because molecules are easily digested and converted. Milk products, alcohol, vegetables, processed sugars, candies, and other foods contain a lot of them. These carbohydrates are referred to as "empty calories" because they lack fibre, vitamins, and minerals.
In the presence of sunlight, plants synthesise glucose (C6H12O6) from raw materials such as carbon dioxide and water. Photosynthesis is a mechanism that transforms solar energy into chemical energy. Consumers eat plants and collect the energy contained in the bonds of the compounds that plants create.
1. Monosaccharides
A carbohydrate monomer, also known as a monosaccharide, is glucose. Mannose, galactose, fructose, and other monosaccharides are examples.
Monosaccharides are further divided into groups based on the number of carbon atoms:
- Trioses (C3H6O3): These molecules have three carbon atoms each. For Eg: Glyceraldehyde
- Tetroses (C4H6O4) are monosaccharides with four carbon atoms per molecule. For Eg: Erythrose
In the same manner, we have :
- Pentoses,
- Hexoses, and
- Heptoses, as well.
2. Disaccharides
A disaccharide is formed when two monosaccharides combine. Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose, and other carbohydrates with two monomers are examples.
3. Oligosaccharides
Oligosaccharides are carbohydrate molecules produced by the condensation of 2-9 monomers. Trioses, pentoses, and hexoses are all oligosaccharides by this convention.
Complex Carbohydrates
Starchy foods contain two or more sugar molecules and are thus referred to as complex carbohydrates. In comparison to simple carbohydrates, molecules in Complex Carbohydrates are digested and converted slowly. They are found in large quantities in potatoes, corn, cereals, lentils, peanuts, beans, whole-grain bread, peas, etc.
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates made up of several monomers polymerized together. Polysaccharides contain starch, glycogen, cellulose, and other carbohydrates that have a lot of branching and are homopolymers (made up of just glucose units).
- Amylose and amylopectin are the two elements of starch. Amylopectin is a branched-chain that starts with amylose and ends with amylopectin.
- Animal starch is a type of glycogen. It has a similar structure to starch, but with more branching.
- The key structural part of the plant cell wall is cellulose, which is a structural carbohydrate. It's a tensile-strengthening fibrous polysaccharide. Unlike starch and glycogen, cellulose polymerizes into a linear polymer.
Primary functions of Carbohydrates
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Following are some of the functions of carbohydrates:
- Carbohydrates' primary role is to provide energy and food to the body and nervous system.
- Carbohydrates including sugars, starch, and fibre, are abundant in grains, fruits, and dairy products.
- They are considered as one of the essential components of food.
- They are known by other names such as starch, simple sugars, and complex carbohydrates.
- It so plays a role in fat metabolism and helps to keep you out of ketosis.
- Proteins being the main source of energy, carbohydrates helps in breaking them down.
- Amylase is an enzyme that aids in the breakdown of starch into glucose, which is then converted into energy for metabolism.
Different Sources of Carbohydrates
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Many fruits contain simple sugars in the form of fructose.
- All dairy products contain galactose.
- Lactose can be present in large quantities in milk and other dairy products.
- Maltose can be found in a variety of foods, including cereal, beer, potatoes, processed cheese, and pasta.
- Sucrose is derived from sugar and honey, both of which contain small quantities of Vitamins and minerals.
Milk, fruits, and vegetables all contain basic sugars that contain minerals and vitamins. Many refined and other processed foods, such as white flour, white rice, and sugar, are labelled "enriched" because they lack essential nutrients. Using vitamins, carbohydrates, and all other organic nutrients in their natural forms is very beneficial.
Carbohydrate Foods
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Sugar consumption leads to an abnormal rise in calories, which eventually leads to obesity, and low calories, in turn, leads to malnutrition. As a result, in order to live a healthier life, a well-balanced diet must be preserved. That is why dietitians emphasise the importance of a well-balanced diet.
Let's examine the distinctions between good and bad carbohydrates.
| Good Carbohydrates | Bad Carbohydrates |
|---|---|
| High in Nutrients | Low in nutrients |
| Moderate in calories | High in calories |
| Low in saturated fats and sodium | High in saturated fats and sodium |
| Low in cholesterol and trans-fat | High in cholesterol and trans-fat |
| They're complex carbohydrates. Legumes, tomatoes, whole grains, fruits, and beans are some examples. | Foods classified as poor carbs are typically devoid of nutritional value. White flour, potatoes, pastries, sodas, and processed foods are some examples. |
Examples of Carbohydrates
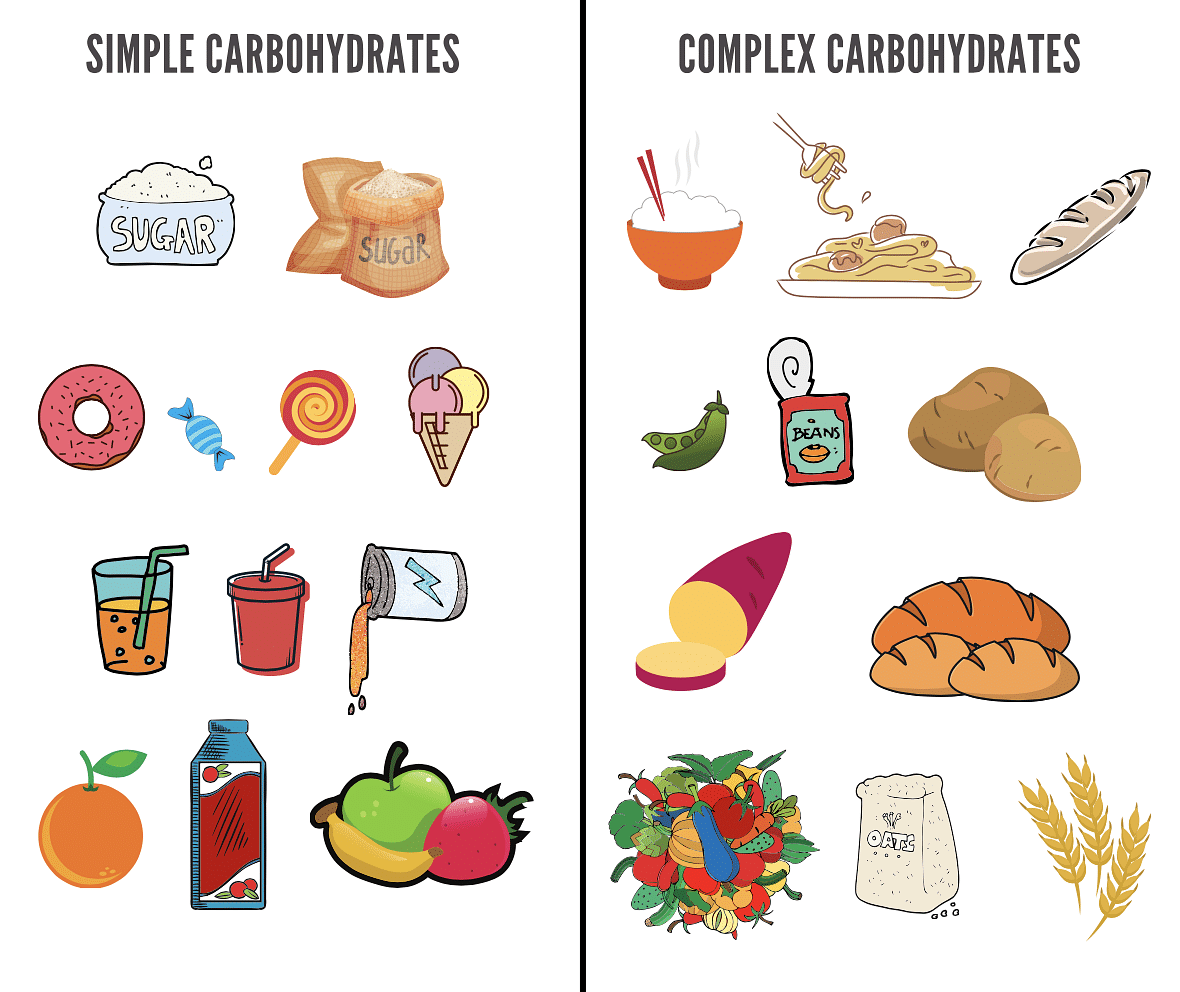
Examples of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates can be found in the following examples:
Sample Questions
Ques. What exactly is a carbohydrate? What are the different types of carbohydrates? (3 marks)
Ans. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms make up carbohydrate biomolecules. They are a significant energy source. Fruits and vegetables contain sugars, starch, and fibres.
Carbohydrates are divided into the following categories:
- Simple carbohydrates
- Complex carbohydrates
Ques. What role do carbohydrates play in our bodies? (2 marks)
Ans. Carbohydrates give the body energy. It breaks down into glucose and reaches our blood. Glucose is used by body cells to generate ATP.
Ques. Name a few carbohydrate sources. What do you mean by simple carbohydrates? Give specific examples. (3 marks)
Ans. Carbohydrates can be found in a number of foods, including bread, milk, potatoes, cookies, corn, and so on.
Simple carbohydrates are those that the body breaks down easily and converts into energy. Simple carbohydrates are primarily found in fruits, milk, and dairy products.
Ques. How are carbohydrates broken down by our digestive system? (2 marks)
Ans. Salivary amylase activity kicks off carbohydrate digestion in the mouth. They are not completely digested in the stomach, but rather in the intestine.
Ques What distinguishes complex carbohydrates from simple carbohydrates? (2 marks)
Ans. The sugar molecules in complex carbohydrates are strung together in long, complex chains. Carbohydrates can be found in a variety of foods such as peas, beans, vegetables, and grains.
Ques. What are the three different styles of simple carbs? (3 marks)
Ans. Simple carbohydrates are divided into three categories:
- Monosaccharides
- Disaccharides
- Polysaccharides
Ques. Name some examples of bad carbohydrates that are harmful to one's health. (4 marks)
Ans. Carbohydrates that are bad for you include:
- Bread made of white flour
- Sugary beverages
- Pastries
- Chocolates and candies
Ques. What are monosaccharides? (All India 2010)
Ans. These are the simplest carbohydrates which cannot be hydrolysed to smaller molecules. Their general formula is (CH2O)n where n = 3 – 7
Example: glucose, fructose etc.



Comments