Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Serine is an amino acid that was first isolated from Sericin and was obtained from the hydrolysis of common proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid, which means it is synthesized inside the human body using various chemical reactions. In mammals, it is synthesized from glucose. Serine and its various derivatives are also important compounds in biological membranes. Serine is also an important component in the field of medicine, used for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease and schizophrenia.
Read more: Isotopes and Isobars
Key Terms: Serine, Amino Acid, Hydrolysis, Proteins, Glucose, Schizophrenia, Proteins, Carbon, Carboxyl Group
Amino Acids
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Amino acids (short for α-amino carboxylic acid) are molecules that combine to form proteins. They consist of three parts attached to a carbon atom called the alpha carbon atom.
- A basic amino group (—NH2)
- An acidic carboxyl group (—COOH)
- an organic R group (or side chain)
Each molecule of an amino acid contains a central carbon atom. Attached to the carbon atom are the amino group and carboxyl group. The remaining two bonds of the carbon atom are connected to a hydrogen atom and the R group. The basic structure of an amino acid is:
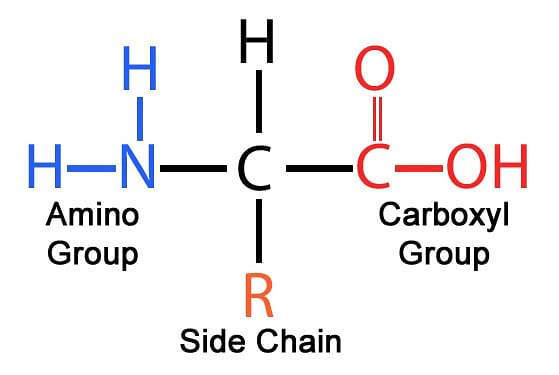
Structure of Amino Acids
Usually, amino acids have L(levorotatory) and D(dextro-rotatory) isomers based on if the crystalline form rotates polarized light to the left or right. Naturally occurring proteins contain L forms of amino acids.
Amino acids can be divided into essential, non-essential, and conditional amino acids:
- Essential amino acids are the ones that cannot be synthesized by the human body.
- Non-essential amino acids can be produced or synthesized by the human body.
- Conditional amino acids are usually non-essential but become essential during the time of sickness or stress.
Serine is a non-essential amino acid.
Structure of Serine
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The chemical formula of Serine is HO-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH or HO2C-CH(NH2)-CH2-OH, or more commonly, C3H7NO3.

Structure of Serine
Occurrence of Serine
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Serine was first obtained from natural silk protein Sericin by Emil Cramer in 1865. It got its name from the Latin name of silk, Sericum. In 1902 its structure was established.
Serine can be found in a large number of edible sources. Food sources with high Serine content include edamame, eggs, lamb, pork, liver, salmon, seaweed, sardines, tofu, etc.
Read More:
| Related Topics | |
|---|---|
| Interhalogen compounds | Atoms and Molecules |
Uses of Serine
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
In humans, the L-isomer of Serine is involved in protein synthesis and normal functioning of the human body. It is an important factor in cell growth and development and is needed for the proper metabolism of fat and fatty acids. It is also crucial for the synthesis of phosphatidylserine, a component of the membrane of brain cells
- As Serine is a non-essential amino acid, it does not have to be taken with a diet but is synthesized within the human body using chemical reactions.
- Serine also gives rise to an amino acid glycine which is hence characterized as a non-essential amino acid.
- D-Serine is a subject of great study and debate in the medical field. Studies and clinical trials show that it can be used in the treatment of schizophrenia(alone or in combination with antipsychotics). It may also be used as an antidepressant and has shown effectiveness in reducing cognitive dysfunction in seniors.
Things to Remember
- Amino acids are molecules that combine to form proteins. They consist of three parts attached to a carbon atom also known as an alpha carbon atom - a basic amino group (—NH2), an acidic carboxyl group (—COOH), and an organic R group (or side chain). The R group is unique for each amino acid.
- Amino acids have L and D isomers. The classification is based on whether the crystalline form rotates polarized light to the left or the right.
- There are essential, non-essential, and conditional amino acids. Essential amino acids are not synthesized or processed inside the human body. Non-essential amino acids are synthesized or processed within the human body through chemical reactions. Conditional amino acids are usually non-essential but become essential during the time of sickness or stress.
- Serine is a non-essential amino acid, obtained by hydrolysis of common proteins. It was first isolated from silk protein Sericin in 1865.
- Serine adheres to the basic structure of amino acids. Its R chain is HO-CH2 and its chemical formula is written as C3H7NO3. It has L and D isomers.
- Serine can be found in a large number of edible sources like edamame, eggs, lamb, pork, liver, salmon, seaweed, sardines, tofu, etc.
- In the human body, the L-isomer of Serine is important for protein synthesis and normal functioning. It is an important factor in cell growth and development and is needed for the proper metabolism of fat and fatty acids. It is also involved in the synthesis of phosphatidylserine, a component of the membrane of brain cells.
- The D-isomer of Serine is studied in the medical field. It is said to be effective in the treatment of schizophrenia and depression.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is Serine? When was it first isolated and its structure defined? (2 Marks)
Ans. Serine is a non-essential amino acid that can be obtained from common proteins by the method of hydrolysis. It was first isolated from Sericin, a silk protein, by Emil Cramer in 1865. Its structure was defined in 1902.
Ques. Explain the structure of Serine. (1 Mark)
Ans. The basic structure of Serine is like that of any other amino acid. Each molecule of Serine contains a central carbon atom called the alpha carbon atom. Attached to the carbon atom are the amino group and carboxyl group. The remaining two bonds of the carbon atom are connected to a hydrogen atom and an organic R group. The R group of Serine is HO-CH2
Ques. How does the Serine synthesize? (1 Mark)
Ans. Serine can also be synthesized in the human body under the regular physiological circumstances by making it a non-essential amino acid.
Ques. What happens if the Serine is mixed with alanine and glycine? (1 Mark)
Ans. They can produce peptide bonds and can have secondary and tertiary structures.
Ques. Which one of the following is a disaccharide:- starch, maltose, fructose, glucose? (1 Mark)
Ans. Maltose
Ques. What is the difference between acidic amino acid and basic amino acid? (1 Mark)
Ans. Acidic amino acid contains 2 carboxylic acids groups and 1 amino group. Basic amino acids contain 2 amino acids and one —COOH group.
Ques. Write the name of the linkage joining two nucleotides. (1 Mark)
Ans. Phosphodiester linkage.
Ques. What are the functions of Serine? (2 Marks)
Ans. Important functions of Serine are as follows:
- Serine plays an essential role in the synthesis of several biological vital compounds, namely cysteine, glycine, purines, phosphides, pyrimidines, proteins, and many more.
- It also plays a vital role in metabolism. Serine protease, which is found in the digestive system, breaks down the proteins that help an enzyme catalyze in its chemical reaction.
Check-Out:



Comments