Namrata Das Exams Prep Master
Exams Prep Master
Centripetal force and centrifugal force are the types of forces that help in the movement of an object in a curved path. Centripetal force is a force that acts on an object in a circular motion and is directed towards the axis of rotation or center of curvature. On the other hand, centrifugal force is a pseudo force that acts along the radius and in a direction that points away from the center point.
NCERT Solutions of: Class 11 Physics Chapter 5 Laws of Motion
| Table of Content |
What is Centripetal Force?
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The centripetal force is referred to as:
| The force which is acting on an object in curvilinear motion and which is discovered to be oriented towards the axis of rotation or centre of curvature. |
The unit of centripetal force is the newton.
In Newton, we can represent centripetal force. But first, let's talk about how the object ended up on the circular path in the first place. Newton's first law states that unless moved on by an external force, an item will continue to move in a straight line. The centripetal force is the external force at work here.

Centripetal Force
It's vital to remember that the centripetal force is only a name for the net force that causes an object to move in a circular direction, not a fundamental force. Centripetal pressures include the tension in the string of a tethered swinging ball and the gravitational force that keeps a satellite in orbit. Multiple independent forces can be used as long as they add up (through vector addition) to provide a net force pointing towards the circular path's center.
Read also:
| Related Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Frictional Force | Impulse Units | Newton’s second law of motion |
| Newton’s third law of motion | Inertia | Banking of Roads |
| Rolling Friction | Types of friction | Sliding Friction |
Calculating Centripetal Force
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The mass multiplied by the square of tangential velocity divided by the radius of the circular path yields centripetal force. By doubling the tangential velocity, the centripetal force can be quadrupled. As a result, the mathematical formula for centripetal force is as follows:
| F = mv2/r |
Here, F is the centripetal force, m is the object's mass, v is the object's speed or velocity, and r is the radius.
Real-Time Examples of Centripetal Force
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
This power can be felt in a variety of scenarios in real life. A few of them are listed below.
- Turning a car (or any vehicle)
- Riding a roller coaster and going through loops
- Using a string to spin a ball
- Planets in the solar system orbit the sun in a heliocentric orbit.

Examples of Centripetal force
Also Read: Impulse units
What is Centrifugal Force?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
In a circular motion, centrifugal force is a false force that acts along the radius and is directed away from the circle's center. When measurements are taken in an inertial frame of reference, the force does not exist. It only comes into play when we go from a ground/inertial reference frame to a rotating reference frame.
The unit of centrifugal force is the newton.
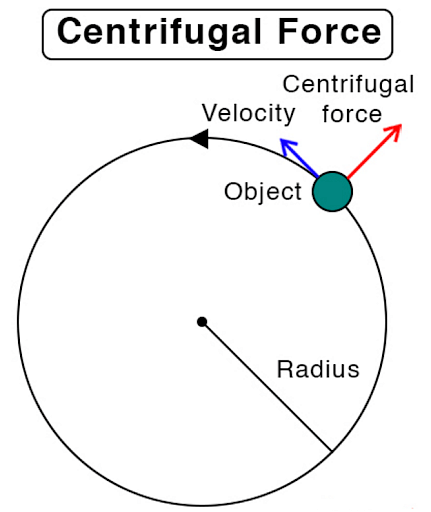
Centrifugal Force
Calculating Centrifugal Force
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
A fictional centrifugal force is described by taking the centripetal force formula (which describes an actual event) and reversing the direction of the force.
| F = – mv2/r |
Here, F is the centripetal force, m is the object's mass, v is the object's speed or velocity, and r is the radius.
Examples of Centrifugal Force
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Passengers in a car perceive an outward push to the right when a car in motion makes a rapid left turn. This is due to passengers being subjected to centrifugal force.
- A bucket of water is rotated in a vertical circle at a specific speed to prevent water from falling. Because the weight of water is balanced by the centrifugal force acting on it, this is the case.
- The earth bulging at the equator and flattering at the pole is caused by centrifugal force.
Also read:Friction Force Formula
Difference between Centripetal Force and Centrifugal Force
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
| Centripetal Force | Centrifugal force |
|---|---|
| The component of force applied on an object in curvilinear motion that is directed toward the axis of rotation or center of curvature is known as centripetal force. | In a circular motion, centrifugal force is a false force that acts along the radius and is directed away from the circle's center. |
| It is observed from an inertial frame of reference. | It is observed from a non-inertial frame of reference. |
| It occurs when a body approaches the center of a circle and contains a certain orientation along the circle's center. | It occurs in a body that has a direction along the circle's center from the center towards the body. |
| The centripetal force is a physical force that prevents an item from flying away. | The centrifugal force is the inertia of motion, not an actual force (moving) |
| When a car travels through a curve on a circular horizontal road, the centripetal force created by friction between the vehicle's tyres and the road surface helps the automobile to negotiate the curve. | Passengers in a car perceive an outward push when the vehicle is in motion and makes a rapid left turn. This is due to passengers being subjected to centrifugal force. |
Also Read:
| Important Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Motion in physics | Tension Force | Derivation of Centripetal Acceleration |
| Aristotle Fallacy | Coefficient of Static Friction | Static Friction |
| Impending Motion | Pseudo force | Kinetic friction |
Things to Remember
- The element of force that acts on a body in a curvilinear motion and is discovered to be oriented towards the center of the curvature is known as centripetal force.
- The centripetal force is always perpendicular to the direction of displacement of the object.
- The mathematical formula for centripetal force is F = mv2/r.
- Centrifugal force is a pseudo force in a circular motion which acts along the radius and is directed away from the centre of the circle.
- The mathematical formula for Centrifugal force is F = – mv2/r.
- Centripetal force and Centrifugal force can be represented in Newton.
- Centripetal force is based on Newton’s second law of motion.
Previous Year Questions
- Suppose the gravitational force varies inversely as the nth power of distance… [JEE Advanced 2015]
- Ten one-rupee coins are put on top of each other on a table. Each coin has a mass m…
- The transverse displacement of a string fixed at both ends is given by y… [AMUEEE 2013]
- A truck is stationary and has a bob suspended by a light string, in a frame attached to the truck… [NEET 2019]
- When a same force of 5 N is applied to two balls A and B separately, they move along the direction of the force with a velocity of 5 ms… [KEAM]
- The one which does not represent a force in any context is… [KEAM]
- The position-time graph of a particle of mass 4kg is shown in the figure… [AMUEEE 2012]
- If a stone of mass 0.05kg is thrown out a window of a train moving at a constant…
- A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle, the motion of the particle takes place in a plane…
- The heart is pumping blood at x kg per unit time, with a constant velocity v. The force required is… [KEAM 2013]
- A bullet of mass 10g moving horizontally with a velocity of 400ms−1 strikes a wooden block of mass 2kg which is… [NEET 2016]
- Three blocks of mass 4kg, 2kg,1kg respectively are in contact on a frictionless table as shown in the figure… [NEET 2015]
- 250 N force is required to raise 75 kg mass from a pulley. If rope is pulled 12 m then the load is lifted to 3m… [NEET 1989]
- An object flying in air with velocity (20^i+25^j−12^k) suddenly breaks in two pieces whose masses are in the ratio 1:5… [NEET 2019]
- A boy of mass 50 kg is standing on a weighing machine placed at the floor of a lift… [AP EAPCET]
Sample Questions
Ques 1. What is the centripetal force given as an example? (2 marks)
Ans. A force operating at an angle to the direction of motion on a moving body, causing it to follow a circular or curved path. A centripetal force is the force of gravity acting on a satellite in orbit; friction between the tyres of an automobile making a turn also acts as a centripetal force on the car.
Ques 2. What causes a centripetal force? (1 mark)
Ans. The centripetal force that causes the Earth's round motion around the Sun – or any satellite's circular motion around any celestial body – is caused by the gravitational attraction between them. The centripetal pressures are always directed toward the circular path's center.
Ques 3. Is centripetal force real force? (2 marks)
Ans. The centripetal force would be real under this definition, whereas centrifugal force would not. The force required to move something in a circle is known as centripetal force. The object will move in a circle if there is a constant magnitude centripetal force that is always perpendicular to the direction of motion.
Ques 4. Where is the centrifugal force used? (1 mark)
Ans. Centrifugal force on examining the rotating coordinate system can be used to rotate equipment such as centrifuges, centrifugal pumps, centrifugal governors, and centrifugal clutches, as well as centrifugal trains, planetary orbits, and banked curves.
Ques 5. What is the source of centrifugal force? (1 mark)
Ans. Rather, the rotation of the reference frame is to blame. Humans do not sense the centrifugal force as a psychological abnormality. Not only humans but everything in a rotating reference frame is affected. Because of centrifugal force, the planet bulges out at the equator.
Ques 6. How does the centripetal force work? (2 marks)
Ans. When the centripetal force is applied to an item moving in a circle at a constant speed, the force is always directed inward since the object's velocity is tangent to the circle. This implies that the force is always oriented perpendicular to the displacement direction of the object.
Ques 7. Give examples of Centripetal force. (1 mark)
Ans. Centripetal force is demonstrated by the rotation of the moon around the earth and the spinning of the top.
Ques 8. Does centripetal force increase with speed? (1 mark)
Ans. Yes. The centripetal force is calculated using the formula mv²/R. This implies that as the particle's speed increases, so does the centripetal force it experiences.
Ques 9. Does centripetal force increase with radius? (1 mark)
Ans. No. The centripetal force is calculated using the formula mv2/R. This implies that as the radius of the particle's rotation increases, the centripetal force it experiences diminishes.
Ques 10. Compare Centrifugal force and centripetal force. (2 marks)
Ans. A non-inertial frame of reference observes centrifugal force, whereas an inertial frame of reference observes centripetal force. Centrifugal force is directed away from the circle's center, while centripetal force is directed toward the axis of rotation or center of curvature.
Ques 11. What is the law of centrifugal force? (2 marks)
Ans. Every action has an equal and opposite response, according to Newton's third law of motion. The action of the centripetal force is countered by the response force of the centrifugal (center-fleeing) force. The magnitude and direction of the two forces are equal.
Ques 12. A ball is traveling with uniform translatory motion. This means that (a) it is at rest; (b) the path can be a straight line or circular and the ball travels with uniform; (c) all parts of the ball have the same velocity (magnitude and direction) and the velocity is constant; (d) the centre of the ball moves with constant velocity and the ball spins about its centre uniformly. (4 marks)
Ans. (c) When a body moves in a way where the linear distance covered by each particle of the body is the same during the motion, then the motion is said to be translatory or translation motion.
Translatory motion can be of two types namely, curvilinear or rectilinear, accordingly as the paths of every constituent particle are similarly curved or straight line paths. Here it is important that the body does not change its orientation. Here we can also define it further in uniform and non-uniform translatory motion.
(b) is uniformly translatory motion.
Ques 13. What is meant by unbalanced forces? (1 mark)
Ans. Unbalanced forces can be defined as the forces of unequal magnitudes and acting in opposite directions on an object simultaneously. The resultant force due to unbalanced forces is non-zero.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here:https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Do Check Out:






Comments