Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Central force exists when the force between two bodies is directed along the line linking the two bodies' centres of mass. Because most of the fundamental forces we know about are of this type, including gravitational, electrostatic, and some nuclear forces, researching central force motion is critical in physics.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Central force, Force, Motion, gravitational force, electrostatic force, nuclear force, fundamental force, Planets, comets, stars, satellites
What is a Central Force?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The force that works along the line connecting the centres of two interacting bodies is known as the central force. A central force is always directed away from a fixed location and towards the centre. The central force is described in classical mechanics as the force applied on an object that focuses along the line connecting the object and the origin. The central force's size is solely determined by the distance between the object and the centre.
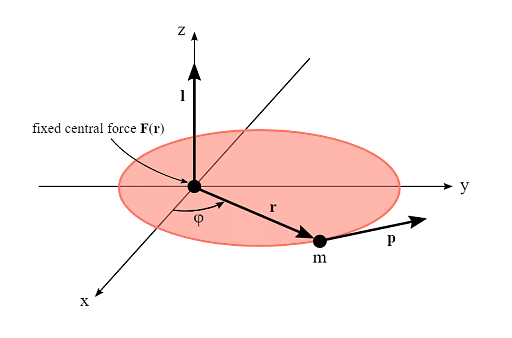
Central Force
Furthermore, one of the few problems in classical mechanics that can be entirely solved is the motion of a system consisting of only two bodies interacting via a central force (once you add a third body it becomes, in general, unsolvable).
Planets and comets orbiting a star, satellites orbiting a planet, binary stars, and classical scattering of atoms or subatomic particles are examples of such systems. Quantum mechanics is required for a complete explanation of atoms and subatomic particles, yet even here, a classical study of core forces can provide a lot of information.
Also Read: Magnetic field and magnetic force
Equation of Central force
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The central force's mathematical equation is:
\(F = F(r) \hat{r}\)
Where,
F → Conservative central force.
r → Vector magnitude and |r| is the distance to the centre of force
![]() = r/r → Unit vector in the direction of r.
= r/r → Unit vector in the direction of r.
We created a central force that satisfies two criteria. We can now generate the new equations using these descriptions of the characteristics:

Equation of Central force
- A central force is solely dependent on the distance between the two bodies.
f21 = -f12 = f(r2-r1)r/r
b. It indicates the direction of the line that connects the two bodies.
F21 = -f12 = f(r2-r1) = f(r)
Central force is a conservative force which is expressed as follows:
F(r)=\(-\frac{du}{dr}\)
Where,
F(r) → Magnitude of a central force
U(r) → Time-independent potential energy
For a particle under central force to be in a uniform circular motion should have centripetal force as follows:
F(r)= \(\frac{mv^2}{r}\)
Where,
r → Initial radius
v → Speed that satisfies the equation of centripetal force
Read More:
Motions in Central force
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Bounded motion: The distance between two bodies or objects has a similar value in this motion and never exceeds the established values. The motion of the planets around the sun is an example of this type of movement.

Motions in Central force
Unbounded motion: The distance between the two bodies or objects is infinity in the initial and final stages of this motion. The dispersion of alpha particles in the Rutherford experiment is an example of this type of movement.
Also Read: Cyclotron
Examples of Central forces
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Many natural events define the central force in physics such as planets orbiting the sun, Natural satellites that revolve around the earth, In terms of movement against each other two charged particles, Gravitational Force and Projectile Motion, Electrostatic, Magneto static Forces and Simple Harmonic Motion.

Examples of Central forces
Also Read:
Things to Remember
- An object's angular momentum should be conserved if it is solely subjected to the central force.
- The magnitude of the central force is determined solely by the object's distance from the centre.
- When estimating the motion of the planets in the Solar System, the solution to the central-force issue frequently provides a decent first approximation of the true velocity.
- The magnitude of a central force can always be written as the derivative of a time-independent potential energy function if the central force is a conservative force.
- If the initial radius r and speed v satisfy the centripetal force equation, any central force can create uniform circular motion.
- The gravitational connection exemplifies classical activity, whereas the Coulomb interaction exemplifies quantum behaviour.
Sample Questions
Ques. Why does a planet in an elliptical orbit around the sun not have a constant angular momentum? (2 marks)
Ans. The sun is at one of the foci in an elliptical orbit, therefore the distance between the planets and the sun changes as the planet spins. As a result, the planets' linear speed, kinetic energy, and potential energy do not remain constant.
Ques. Explain central forces with respect to gravitational force. (2 marks)
Ans. Universal constant of gravitation G is numerically equal to the force of attraction between two particles of unit mass each separated by unit distance.
Important Characteristics of Gravitational Force
(i) Gravitational force between two bodies is a central force i.e., it acts along the line joining the centres of the two interacting bodies.
(ii) Gravitational force between two bodies is independent of the nature of the intervening medium.
Ques. Give one example each of central force and non-central force. (3 marks)
Ans. Examples of central force:
(i) Gravitational force due to point mass.
(ii) Electrostatic force on the point charge.
Examples of non-central force:
(i) Nuclear force which depends upon the spin of particles.
(ii) Magnetic systems acting between two current carrying loops
Ques. How is the gravitational force between two point masses affected when they are dipped in water keeping the separation between them the same? (2 marks)
Ans. Gravitational force acting between two point masses ml and m2 is given by the relation,
F = G m1m2/ r2
It does not depend upon the medium separating the two point masses. Therefore, gravitational force acting between two point masses will remain unaffected when they are dipped in water keeping the separation between them the same. Only their apparent weights change, there is no effect on masses.
Ques. Is it true that all central forces are conservative? (2 marks)
Ans. No, not all central force fields are spherically symmetric or conservative. However, when the centre force is spherically symmetrical, it is discovered to be conservative.
Ques. Is it possible for a body to have inertia but no weight? (3 marks)
Ans. The weight of a body is the force with which it is attracted towards the centre of earth. When a body is stationary with respect to the earth, its weight equals gravity. This weight of the body is known as its static or true weight.
Inertia is a property of mass. Hence, a body can have inertia (i.e., mass) but no weight. Everybody always has inertia but its weight (mg) can be zero, when it is taken at the centre of the earth or during free fall under gravity or a body placed at a very large distance from earth. Basically the weight of a body can be zero when acceleration due to gravity is zero, that condition is called weightlessness.

Satellite
For example, When a satellite revolves in its orbit around the earth:
Weightlessness poses many serious problems to the astronauts. It becomes quite difficult for them to control their movements. Everything in the satellite has to be kept tied down. They can be displaced due to their inertia. Creation of artificial gravity is the answer to this problem.
Ques. Do natural satellites move around the earth due to central force? (1 mark)
Ans. Yes, natural satellites move around the earth due to central force.
Ques. An astronaut inside a small spaceship orbiting around the earth cannot detect gravity. If the space station orbiting around the earth has a large size, can he hope to detect gravity? (2 marks)
Ans. The value of acceleration due to gravity, supposed to be constant inside a small spaceship orbiting around the earth, and hence astronauts feel weightlessness. If the size of the space station orbiting around the earth is very large, then the astronaut inside the spaceship will experience variation in acceleration due to gravity.
Ques. Is the centripetal force the same as central force? (2 marks)
Ans. No, The central force acts on two bodies from centre to centre, whereas the centripetal force acts on a body in a circular motion towards the centre.
Ques. Define Bounded and Unbounded motion. (2 marks)
Ans. Bounded motion: The distance between two bodies or objects has a similar value in this motion and never exceeds the established values. The motion of the planets around the sun is an example of this type of movement.
Unbounded motion: The distance between the two bodies or objects is infinity in the initial and final stages of this motion. The dispersion of alpha particles in the Rutherford experiment is an example of this type of movement.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Do Check Out:





Comments