Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Oestrous Cycle, also known as Estrous Cycle, is a cyclical variation in the reproductive phase of non-primate animals. Changes in the ovaries, accessory ducts and hormones secreted by them are all involved. Non-primates only reproduce when the weather is favourable. The Oestrous Cycle is a series of cyclical changes that occur during the breeding process. Seasonal breeders are the name given to these organisms. When a woman becomes pregnant, her Oestrous Cycle comes to an end.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Oestrous Cycle, Estrous Cycle, Reproductive phase, Non-primates, Hormones, Ducts, Reproduce, Menstrual cycle, Ovum, Vaginal canal, Endometrium
Difference Between Oestrus Cycle and Menstrual Cycle
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The key difference between Menstrual and Oestrous Cycles is that Menstrual Flow occurs in primates such as monkeys, apes, and humans, in which an unfertilized ovum along with a ruptured uterine epithelium discharges about 50-100 ml of blood and some mucus through the vaginal orifice and is called menstrual flow, whereas the Oestrous Cycle, in which a female becomes sexually responsive only during a specific season, is referred to as the "hot period" because there is no outflow from the vaginal canal and the endometrium is reabsorbed.
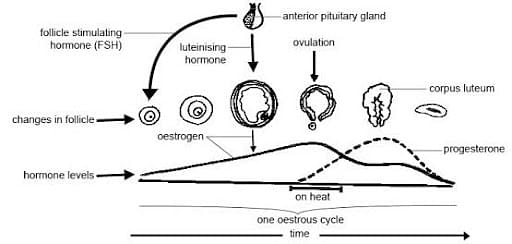
Oestrus Cycle
| Oestrus Cycle | Menstrual Cycle |
|---|---|
| This Cycle is generally observed in Seasonal breeders | The Menstrual Cycle is observed in continuous breeders |
| There is no loss of blood reported in the Oestrus Cycle. | It involves loss of blood |
| This Cycle continues till death | It continues till menopause. |
| Some of the examples are cows and dogs. | Examples: Apes and human |
Also Read: What is Plasma in Blood?
Different Phases of Oestrus Cycle
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
There are around four phases of the Oestrus Cycle they are as follows:

Phases of Oestrus Cycle
Proestrus
One or more ovarian follicles begin to develop. Depending on the species, the number of them varies. Depending on the species, this period might last as little as one day or as long as three weeks. The uterine lining (endometrium) begins to grow under the influence of oestrogen. Vaginal secretions that are bloody may occur in some animals. The old corpus luteum degenerates; the uterus and vagina distend and fill with fluid, become contractile, and produce a sanguine fluid; the vaginal epithelium proliferates, and vaginal cytology reveals a large number of non-cornified nucleated epithelial cells. Proestrus is also known as pro-oestrus, pro-estrum, and pro-oestrum.
Estrus
Estrus, also known as oestrus, is the period when a female is sexually receptive ("in heat"). Ovarian follicles mature under the control of gonadotropic hormones, and oestrogen secretions have the most impact. The female then engages in sexually receptive behaviour, which may be indicated by physiologic changes. Mammalian species, especially monkeys, are frequently seen in estrus. This stage is also known as estrum or oestrum.
The labia of certain animals are reddish. Others may experience spontaneous ovulation. The lordosis reflex, which occurs when an animal spontaneously lifts her hindquarters, is a symptom of estrus, especially in quadrupeds. In livestock, controlled internal medication delivery devices are used to synchronise estrus.
Metestrus or Diestrus
The activity of the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone, characterises this period. The corpus luteum begins to form when the indications of oestrogen stimulation fade. The uterine lining starts to form. The diestrus phase (also known as pseudo-pregnancy) ends with the regression of the corpus luteum in the absence of pregnancy. Instead of shedding, the uterine lining reorganises in preparation for the next cycle. Metoestrus, metestrum, metoestrus, dioestrus, diestrum, and oestrum are some of the other spellings.
Anestrus
The resting phase of the sexual cycle is known as anestrus. This is usually a seasonal occurrence that is influenced by light exposure and the release of melatonin by the pineal gland. Melatonin may suppress long-day breeders' stimulation of reproduction while stimulating short-day breeders' reproduction. Melatonin is hypothesised to work by modulating the gonadotropin-releasing hormone's hypothalamus pulse activity. The time of year, pregnancy, nursing, serious sickness, persistent energy deficiency, and possibly age can all cause anestrus. Due to negative feedback on the hypothalamus/pituitary/gonadal axis, chronic use of anabolic steroids can result in a permanent anestrus. Anoestrus, anestrum, and anoestrum are some of the other spellings.
Some species exhibit postpartum estrus, which is ovulation and corpus luteum production that happens soon after the birth of the young after the pregnancy is over (or termination). The mouse, for example, has a fertile postpartum estrus 14 to 24 hours after giving birth.
Also Read: What is Translation in Biology?
Variability of Oestrus Cycle
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Oestrous Cycle variability varies by species, however, smaller animals have more frequent cycles. Even within species, there is a lot of variation, thus cats can have an Oestrous Cycle that lasts anywhere from 3 to 7 weeks. Because of changes in the environment, domestication can affect Oestrous Cycles. Vaginal smear cytology can be used to determine Oestrous Cycle stages and lengths in most species.
Other prominent mammals' Oestrus frequencies include:
- 18 days for sheep
- 21 days for a goat
- Variable in rabbits
- 13 to 31 days for a donkey (average 23)
- 16 weeks for an elephant
- 9 days Wolf

Variability of Oestrus Cycle
Things to Remember
- It occurs in non-primates such as sheep, rats, cows, deer, dogs and tigers etc.
- It generally consists of a short period of oestrus or heat.
- Blood does not flow in this cycle.
- The 4 phases of the Oestrous Cycle are as follows- Proestrus, Estrus, Metestrus or Diestrus, Anestrus
- Some species, for example- the mouse, go through postpartum estrus.
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Keystone Species | Radicle | Retrovirus |
| Stages of Meiosis | Cloning Vector | Plant Breeding |
Sample Questions
Question- Differentiate between the Menstrual Cycle and Oestrous Cycle? (4 marks)
Answer-
| Oestrus Cycle | Menstrual Cycle |
|---|---|
| This cycle is generally observed in Seasonal breeders | Menstrual Cycle is observed in continuous breeders |
| There is no loss of blood reported in the Oestrus Cycle. | It involves loss of blood |
| This cycle continues till death | It continues till menopause. |
| Some of the examples are cows and dogs. | Examples: Apes and human |
Question- What is the Oestrous Cycle? (2 marks)
Answer- The Oestrous Cycle is a cyclical variation in the reproductive phase of non-primate animals. The Oestrous Cycle is a series of cyclical changes that occur during the breeding process.
Question- What are the 4 phases of the Oestrous Cycle? (2 marks)
Answer- The 4 phases of the Oestrous Cycle are as follows:
- Proestrus
- Estrus
- Metestrus or Diestrus
- Anestrus
Question- What is the heat period in the Oestrus Cycle? (2 marks)
Answer- Estrus, sometimes known as "heat," is a stage in the reproductive cycle when female animals become sexually receptive, signifying that they are ready to reproduce. Estrus is triggered by oestrogen production in the ovary's growing follicles, and ovulation normally happens after the first signs of estrus have been detected.
Question- In which animals do the Oestrus Cycle take place? (3 marks)
Answer- Except for one minor change, all animals go through the same reproductive process. If no fertilisation occurs, some animals shed their endometrium through menstruation, whereas others that are oestrous absorb it. Oestrous animals are what they're called. They are only sexually active during their oestrous phase. It's also known as being "in heat". Humans, on the other hand, have the ability to be sexually active at any moment. However, oestrous animals may produce a bloody discharge around their vagina, which should not be confused with a menstrual period. Cows, dogs, cats, horses, goats, rabbits, rats, and other animals are known to have an Oestrous cycle.
Question- How long does the Oestrus Cycle last in Cows? (1 mark)
Answer- The Oestrus Cycle lasts 21 days in Cows.
Question- What is Postpartum Estrus? (2 marks)
Answer- Postpartum Estrus is ovulation and corpus luteum production that happens soon after the birth of the young after the pregnancy is over (or termination).
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:




Comments