Sahaj Anand Content Writer | Journalism Graduate
Content Writer | Journalism Graduate | Updated On - Dec 30, 2025
Reproduction is the process of formation of new organisms from the parent organism. It occurs in both plants and animals. There are two types of reproduction: asexual and sexual.
- In asexual reproduction, new organisms are produced from a single parent. Animals that reproduce asexually are bacteria, fungi, archaea, etc.
- In sexual reproduction, new organisms are produced from a male and a female parent. Plants, mammals, and reptiles are animals that reproduce asexually.
In this article, we will dive deep into what is reproduction, types of reproduction, plant and animal reproduction.
What is Reproduction?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A biological process whereby an organism reproduces to give rise to an offspring is called reproduction. This process enables and ensures the continuity of species, generation after generation, and is the main feature of life on Earth.
- Reproduction takes place in both unicellular and multicellular organisms like amoeba, bacteria, yeats, algae, paramoecium, humans, etc.
- This process occurs by the division of cells. Cell division in asexual reproduction is called mitosis whereas in sexual reproduction it is called meiosis.
Types of Reproduction
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Reproduction is the basis of life which is usually categorised into two types:
- Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction is a type of reproduction the production of offspring by a single parent. The offspring produced are identical to the parent as no fusion of gametes takes place.
- In this type of reproduction, multiplication, and growth occur rapidly in a short time period.
- Cell division occurs by mitosis by which the cell divides into two daughter cells
- Asexual reproduction is commonly observed in the plant kingdom and some single-celled organisms.
- Examples of asexual reproduction include Amoeba, paramecium, fungi, plants, etc.
![Asexual Reproduction]()
Figure: Asexual Reproduction in Amoeba
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a process of the development of new organisms in which both parents are involved. It involves the fusion of male and female gametes. In this process, genetic variation can be observed.
- This is a complex type of reproduction where multiplication and growth occur very slowly.
- Cell division occurs by meiosis. It is a process where four haploid cells are produced from one diploid cell (parent cell).
- Sexual reproduction is commonly observed in multicellular organisms.
- Examples of sexual reproduction is human reproduction and flowering plant reproduction.
![Sexual Reproduction]()
Figure: Sexual Reproduction in Humans
Reproduction in Plants
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Reproduction in plants takes place asexually and sexually. In this section, we will discuss these types in detail.
Asexual Reproduction in Plants
Plant reproduce by asexual reproduction and is commonly observed in lower plants and is further divided into four types:
- Budding
- Vegetative Propagation
- Sporogenesis
- Fragmentation
Budding
Budding is a type of asexual reproduction, where a new individual grows from a small outgrowth (bud) of the parents’ body. The bud remains attached to the parent body but later detaches and develops into a mature organism.
- Examples of budding include potato, dahlia, etc.
- When a potato is left undisturbed for a long time, the formation of bud takes place, also called the ‘eyes of the potato’.
Vegetative Propagation
It is a process of asexual reproduction, where plants reproduce via different parts of the plants like the stems, roots, or buds. These parts are called the vegetative parts of the plant. The following are the common ways of vegetative propagation.
- Sub-aerial stems called stolon and runners take part in vegetative propagation.
- Modified roots or tubers give rise to new plants. Examples of roots include Dahlia, tapioca, sweet potato, etc.
- Buds present on the leaves of certain plants detach and form new organisms. Examples: Begonia and Bryophylum
Sporogenesis
Spore formation or sporogenesis is a process of reproduction that occurs by spores. Examples of organisms that produce spores are most fungi.
- In most flowering plants, both male and female gametes reproduce by this process.
- Other examples include mosses and ferns which grow in favorable conditions to give rise to new individual organisms.
Fragmentation
In fragmentation, the parent organism divides itself into many fragments giving rise to new organisms. Fragments of the plant is mediated by the winds for the formation of new plants. Example- Mosses and liverworts.

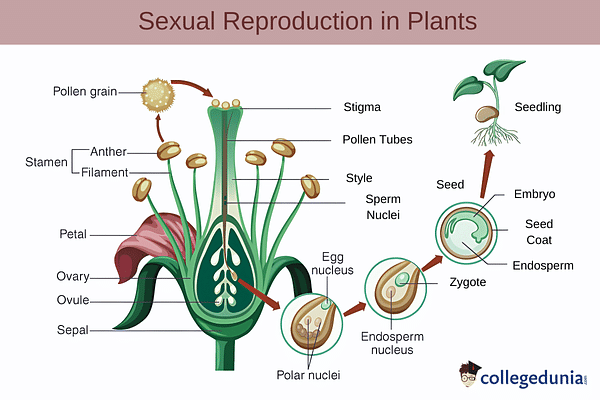
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Sexual Reproduction in plants involves the fusion of two gametes; a male gamete and a female gamete. This type of reproduction usually occurs in flowering plants where the male gamete is the anther and the female gamete is the egg cell. Sexual reproduction takes place via pollination followed by fertilization.
- Pollination: It is defined as the transfer of pollen grains from the male gamete to the female gamete of a flower.
- Fertilization: After pollination, the process of fertilization occurs where both male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote.
![Sexual Reproduction]()
Reproduction in Animals
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Just like plants, animals also reproduce asexually as well as sexually. In this section, we will discuss these types in detail.
Asexual Reproduction in Animals
Asexual reproduction in animals does not involve the formation of gametes. It takes place by four means namely:
- Binary fission
- Budding
- Fragmentation
- Parthenogenesis
Binary Fission
Binary fission or fission is an asexual mode of reproduction where a single cell divides into two individual cells. These cells carry the same genetic information as their parent cell.
- Examples of binary fission include Amoeba, paramecium, etc.
- The new organisms produced by binary fission are identical to their parent (or parent cell).
Budding
The process of budding is similar to the plants where an organism develops from a bud or an outgrowth.
- Examples of budding include hydra, corals, etc.
- In hydra, a bud develops on the body of the parent organism and detaches when the organism is formed.
Fragmentation
This type of reproduction is generally seen in sponges, cnidarians, echinoderms, annelids, and planaria. Here, the body of the organism breaks into fragments from which new organisms are formed.
ParthenogenesisParthenogenesis is a process in which the development of an organism takes place without the egg being fertilized.
- This mode of reproduction occurs in both vertebrates and invertebrates.
- Examples of parthenogenesis include wasps, bees, ants, reptiles, amphibians, etc.
Sexual Reproduction in Animals
Sexual reproduction in animals takes place via two processes: fertilization and embryo development. When male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote (embryo) this process is termed fertilization. Fertilization is further divided into two types: internal and external.
- In internal fertilization, gamete fusion takes place inside the organism's body. Example- Mammals.
- In external fertilization, gamete fusion takes place outside the organism's body. Example- fish.
Things to Remember
- Reproduction is a process that introduces genetic variation in the offspring and plays an important role in the evolution of species.
- Gametes are the reproductive cells of an organism.
- Females reproduce through gametes called ova, while male gametes are called sperms.
- The fusion of sperm (male) and egg cells (female) gives rise to a fertilized egg or zygote.
- Sexual reproduction in flowering plants takes place by transfer of pollen grains called pollination.
Sample Questions
Ques. Why asexual reproduction of fungi advantageous over the sexual reproduction of fungi? (2 marks)
Ans. Asexual reproduction is advantageous over sexual reproduction due to the following reasons:
- It requires only one parent for reproduction.
- Such a type of reproduction is more efficient.
- Asexual reproduction is faster than sexual reproduction.
Ques. What are the three levels of reproduction? Explain. (2 marks)
Ans. The three-levels of reproduction are discussed below:
- Replication: In replication, two identical copies of DNA are produced from a single DNA.
- Molecular reproduction: The traits which the organisms inherit are stored as generic information in the DNA.
- Cell reproduction: The process of reproduction takes place by cell division. In sexual reproduction, one cell divides into four daughter cells.
Ques. Differentiate between sporulation and fragmentation. (2 marks)
Ans. Sporulation and fragmentation are the types of asexual reproduction. The table below shows the difference between the two:
| Sporulation | Fragmentation |
|---|---|
| Spores are formed that carry genetic material of the parent | The parent cell divides into fragments from which forms a new organism |
| Spores survive in adverse conditions | Need suitable environmental conditions to survive |
| Wide dispersion | Localized dispersion |
Ques. What is the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction? (3 marks)
Ans. The table below shows the difference between the two:
| Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
|---|---|
| Only one parent takes part in the formation of offspring. | Both parents take part in the formation of offspring. |
| No fertilization of egg takes place. | Fertilization of egg takes place. |
| No gamete formation | Formation of gamete is involved. |
| Identical offsprings. | Non-identical offsprings. |
Ques. What do you mean by fertilization? Mention its types. (2 marks)
Ans. When male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote this process is called fertilization. It is also called syngamy. There are two types of fertilization: external and internal.
- External fertilization: The fertilization that takes place outside the female body, i.e. in the external medium, is called external fertilization. E.g., most aquatic organisms and amphibians.
- Internal fertilization: The fertilization that takes place inside the female body is called internal fertilization. Eg: Terrestrial organisms belonging to fungi, animals, and plants.
Ques. Write a note on reproduction in flowering plants. (5 marks)
Ans. In flowering plants, reproduction is sexual. It involves both male and female flowers.
- The female reproductive organs of plants are called gynoecium. It is made up of ovaries and a stigma style.
- The male reproductive organs of plants are called androecium. It is made up of anther and stamens.
- Pollen grains are carried out with the help of pollination to the stigma of the flower.
- After reaching the stigma, it is transferred to the ovaries, where the process of fertilization takes place.
- In the final process, ovaries become fruits, and ovules become fruits bearing seeds.
Ques. Differentiate between mitosis and meiosis. (2 marks)
Ans. Mitosis and meiosis are the types of cell division. The table below shows the difference between the two:
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|
| Produces two daughter cells. | Produces four daughter cells. |
| Occurs in asexual reproduction. | Occurs in sexual reproduction. |
| Helps in reproduction and cell repair. | Helps in gamete formation. |
Ques. What are the different phases of sexual reproduction? (3 marks)
Ans. The different phases of sexual reproduction are as follows:
- Juvenile Phase: The growth phase of an individual organism, after its birth and before it reaches its reproductive maturity is called the juvenile phase. It is also known as the vegetative phase in plants.
- Reproductive Phase: It is the phase when an individual organism reproduces sexually.
- Senescent Phase: It is the period when an organism grows old and loses the ability to reproduce.
Ques. Where does reproduction take place in plants? (1 mark)
Ans. Reproduction in plants takes place in the reproductive part which is the flower.
- The flower contains the male reproductive part called the stamen and the female reproductive part is the pistil.
Ques. Reproduction without seeds is called ________. (1 mark)
Ans. Reproduction without seed is called vegetative propagation.






Comments