Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Auxin and gibberellin are plant hormones that occur naturally and are synthesised artificially. They are also known as plant growth regulators. Like humans and animals, plants have a chemical component that regulates growth and development processes in the plant cell.
Auxin is the primary plant hormone that promotes shoot growth. It primarily encourages cell division and elongation. On the other hand, Gibberellin is a plant hormone that, in addition to cell elongation, has a function in seed germination and flowering. The structure and function of each plant hormone are the essential differences between auxin and gibberellin.
| Table of Content |
Auxins and Gibberellins
Plant growth regulators Auxins and Gibberellins are two chief families of hormones. Hormones that control and manage all aspects of a plant's growth and development are called plant growth regulators. Both of these hormones influence plant growth and regulate developmental processes such as flowering, organogenesis, root initiation, sex expression, etc. Auxins and gibberellins have a variety of physiological reactions.
Also Read:
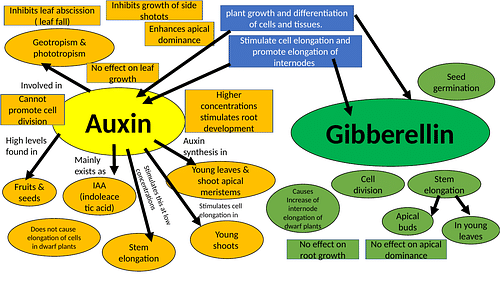
Auxin and Gibberellin
What are Cytokinins?
Cell division and differentiation are induced by cytokinins. Cytokinins boost protein and enzyme activity in tissues and promote RNA production. In-plant cell cultures, the most commonly utilised cytokinins are kinin and benzyl-aminopurine. While cytokinin is primarily responsible for cell division, it also has additional activities, including cell expansion in young leaves, tissue differentiation, flowering, fruiting, and the prevention of leaf ageing. As many as 100 cytokinins have been identified, some of which are produced naturally and others synthesised. Natural cytokinin zeatin is the most active, while manufactured cytokinins are less active.

Cytokinins
What are Regulators for Plant Growth?
Chemical chemicals that affect all elements of plant growth and development are known as plant growth regulators. Plant growth hormones or phytohormones are other names for them. Plant growth regulators include auxin, cytokinin, gibberellins, and abscisic acid, to name a few.
Also Read:

Plant Growth Regulator
Auxins: Definition
Auxins are a series of plant hormones that can be found naturally or synthesised experimentally. They serve a crucial function in plant growth development. The apical meristem of shoots, immature leaves, and seeds are the major producers.

Auxin
Gibberellins: Definition
Gibberellins are a collection of naturally occurring organic growth Hormones that control different developmental processes, including stem elongation, and regulate growth, seed germination, flowering, enzyme induction, and so on. More than 70 gibberellins have been identified.

Gibberellin
Similarities Between Auxin and Gibberellin
- The phytohormones auxin and gibberellin are responsible for the growth of the shoot.
- The effector organ requires only a small amount of these hormones.
- Their synthesis takes place in one region of the body, and then they are transported to the effector organ to elicit physiological, biochemical, or morphological responses.

Auxin and Gibberellin
Difference between Auxin and Gibberellin
| Features | Auxin | Gibberellin |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | It's an unsaturated structure with a side chain that might be single or double. | It's a side-chain-free saturated tetracyclic gibbane structure. |
| Discovered in | Higher plants have this. | It can be found in both higher plants and fungi. |
| Dominance at the apex | This results in apical dominance. | It does not affect apical dominance. |
| Root Development | At normal concentrations, auxin suppresses root development. | Such consequences do not exist. |
| Growth of the Shoots | Encourages the growth of shoot segments. | Encourages the growth of the healthy shoot. |
| Growth of the Leave | Has a negligible impact on leaf growth. | Enhances the growth of the leaves |
| Elongation of the stem | Shoots that are genetically small and do not elongate. | Shoots that are genetically small and often elongate |
| Bolting | It does not affect bolting. | It causes rosette plants to bolt. |
| Growth of Calluses | It is necessary for callus development. | It plays no part in the development of calluses. |
| Dormancy of Seeds and Buds | Auxin does not affect the dormancy of seeds or buds. | Gibberellin is important for seed germination and breaking dormancy in seeds and buds. |
| Formation of Roots | It aids in the formation of roots. | It doesn't encourage roots. |
| Hormonal Reactions | Some plants respond to auxin by being feminised. | Some plants respond to gibberellin by becoming more masculine. |
| Transport | Basipetal transport is demonstrated. | Both acropetal and basipetal transportation is possible. |
| Functions | Axion elongation, cell differentiation, cell division, cellular expansion, isodiametric expansion, and lateral expansion are important processes in plants. | Seed germination, stem elongation, flowering, dormancy, sex expression, enzyme induction, and leaf and fruit withering are important processes. |
Also Read:
Auxin and Cytokinins
The ratio of auxins and cytokinins has a crucial effect in the morphogenesis of culture systems, just as it does in plant tissue culture mediums. Root initiation, callus initiation and embryogenesis occur when the ratio of auxins to cytokinins is high. Conversely, the ratio of auxins to cytokinins is kept low for axillary proliferation and shoot proliferation. GA3 promotes callus development and elongation in dwarf plantlets.

Auxin and Cytokinin
Cell division occurs when multiple living cells from a living plant are extracted and cultivated in a medium containing cytokinin and auxin, resulting in a mass of undifferentiated cells known as a callus. The callus can then differentiate and create both shoot and root, resulting in the development of a new plant. Auxin promotes root production, while cytokinin promotes shoot growth. Thus, superior forms can be perpetuated via this method of vegetative propagation.
Things to Remember
- The plant hormone auxin regulates cell elongation during phototropism and gravitropism.
- Cytokinin is a plant hormone that promotes cell division and regulates a variety of developmental processes in plants.
- Gibberellins regulate shoot elongation, seed dormancy, seed germination, gender expression, fruit and flower maturation, seedless fruit development, and the ageing of leaves and fruit.
- Auxin is a naturally occurring plant hormone that can also be synthesised. For example, indole acetic acid, indole acetaldehyde and indole ethanol are all naturally occurring auxins.
- Synthetic auxins are employed as a herbicide and as growth inhibitors. For example, naphthalene acetic acid, indole butyric acid and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid are all present.
Also Read:
| Kranz Anatomy | Plant Breeding | Transportation in Animals and Plants |
| Difference Between C3 and C4 Plants | Taxonomic Hierarchy of Plants and Animals | Aestivation in Plants |
Sample Questions
Ques: What are Auxin and Gibberelin's physiological functions? (4 marks)
Ans: Auxins
- Dominance at the apex
- Parthenocarpy
- The distinction between xylem and phloem
- The development of roots in stem cuttings
- Controlling weeds
- Abscission control
- Controlling the lodging
Gibberellins
- Parthenocarpy
- Seed dormancy is broken.
- Flowering and bolting
- Elongation of the stem
- Expression of sex
Ques: What are some uses of Gibberellins? (3 marks)
Ans: Gibberellins are fungi that help seeds germinate quickly and are commercially available. Gibberellins are also produced by plants, albeit in far smaller quantities than those produced by fungi. It is beneficial to vineyard owners since it greatly enhances the crop. This is due to the fact that when gibberellin molecules are sprayed on the vines, the quantity of sugar and water in each fruit increases. It also encourages the development of dwarf species, which can be speedily created by using gibberellins. Gibberellins produce male flowers in plants, for example in cucumber, which are utilised to obtain pollen with desired features.
Ques: What are Cytokinins? (3 marks)
Ans: Plant hormones called cytokinins encourage cell division and differentiation in the root and shoot systems of plants. All bacteria, thorny plants and mosses, insects and fungi have been found to have them. Hormones are mostly produced at the root meristem, and there are approximately 200 different natural and synthetic variations. It may induce cell division, but it also maintains the protein level required for mitosis. Mitosis is a process that helps to replace damaged cells daily, which encourages growth. As a result, it promotes cell expansion and proliferation, which impacts leaf senescence and apical dominance.
Quest: Is auxin present in all plants? (2 marks)
Ans: Auxin can be found in all sections of a plant, however, at varying amounts. The most important auxin is indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), which is the most potent native auxin and generates the majority of auxin actions in intact plants.
Ques: What's the difference between gibberellin and auxin hormones when it comes to planting growth? (2 marks)
Ans: Auxin stimulates cell elongation, particularly in shoots, apical dominance and rooting. In contrast, gibberellin promotes cell growth in stems, leaves, and other aerial components by promoting cell elongation and increased internodal length.
Ques: What function does gibberellin play in seed germination? (2 marks)
Ans: Gibberellins operate as a chemical messenger and break the dormancy of seeds, causing them to germinate. Its hormone attaches to a receptor, calcium activates the protein calmodulin, and the complex binds to DNA, producing an enzyme that stimulates embryo growth.
Ques: What are the similarities and differences between auxins and gibberellins? (3 marks)
Ans: Auxin's primary purpose is to aid plant growth. Auxin encourages plant cells to grow longer, and auxin is produced mostly in the apical meristem. Gibberellins are growth hormones that make plants grow taller by stimulating cell elongation.
Ques: Where are auxins produced? (2 marks)
Ans: Auxin is a naturally occurring plant hormone that helps plants grow longer stems. It's made at the tip of the shoot, at the stem apices.
Ques: What distinguishes Auxins from Gibberellins and Cytokinins? (2 marks)
Ans: The main distinction between auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins is that auxins promote stem elongation, whereas gibberellins promote shoot growth and seed germination, and cytokinins promote cell division. They are largely secreted from the roots and then move up the plant to aid growth.





Comments