Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
The major difference between Monocytes and Lymphocytes is that Monocytes are large phagocytic white blood cells with a simple oval nucleus and lymphocytes are small white blood cells with a single round nucleus. Blood cells consist of fluid straw-coloured plasma with red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets floating in it. They protect our body from various infections. White Blood Cells (WBCs) are the nucleated blood cells. They are further differentiated into granulocytes and agranulocytes. Blood is the only fluid connective tissue in the human body. In this article, we will explore the differences between monocytes and lymphocytes.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms:
White Blood Cells, Monocytes, lymphocytes,, agranulocytes, monocytosis, lymphocytosis, immunity, innate immunity, adaptive immunity, acquired immunity and leukaemia
White Blood Cells
The chief defence system of our body comprises several types of white blood cells (WBCs). WBCs are scientifically called leukocytes because they are colourless or white in colour. Leucocytes defend the body system against different kinds of infections. The invading infectious agents have antigens on their body surface. Leukocytes produce special proteins called antibodies that protect the body from these antigens.
Based on the presence or absence of granules in the cytoplasm, WBCs are classified into granular white blood cells and agranular white blood cells. There are five types of WBCs- Monocytes, Lymphocytes, Eosinophil, Basophil and Neutrophil.
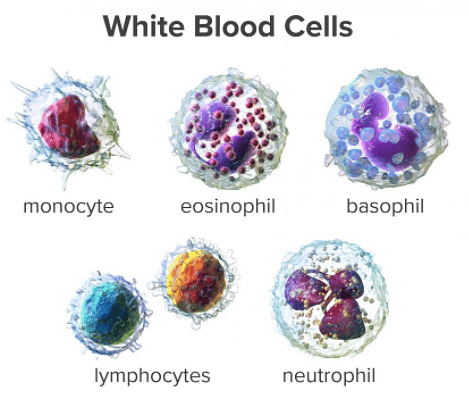
Monocytes
Monocytes are the largest white blood cells. They are amoeboid cells with a large and kidney-shaped nucleus. The size of a monocyte is three times the size of a typical red blood cell. They kill pathogens through phagocytosis.

Monocyte
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are spherical cells with a round shaped nucleus. They produce specific responses to different pathogens through the production of special proteins called antigens. The lifespan of Lymphocytes is significantly longer than the other types of white blood cells.
Lymphocyte
Difference Between Monocytes and Lymphocytes
A brief account of the differences between monocytes and lymphocytes are given in the following table:
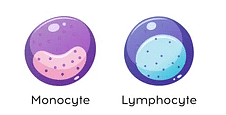
Diagrams of Monocytes and Lymphocytes
| Basis of Comparison | Monocytes | Lymphocytes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 200-600 monocytes in 1 microlitre of blood. | 1000-4800 lymphocytes in 1 microlitre of blood. In children 3000-9500 in 1 microlitre blood. | ||
| Percentage count | 2-10% of total circulating white blood cells | 20-30% of total circulating white blood cells | ||
| Decrease in count | A decrease in the count of monocytes indicates a serious condition like cancer. | Decreased levels of cells indicate a sign of infection. | ||
| Size | 12-20 millimicrons in diameter. | Smaller ones are 7-10 millimicrons and larger ones are 10-12 millimicrons in diameter. | ||
| Shape | Oval or amoeboid (ever-changing shape) with pseudopodia. | Definite spherical shape. | ||
| Lifespan | 24 hours (generally fixed life span) | A few weeks, a few months, or a few years (Variable lifespan) | ||
| Cell cytoplasm | Blue-grey coloured | Sky-blue coloured | ||
| Transparency of cytoplasm | Cloudy and opaque | Clear and transparent | ||
| Presence of granules | Visible granules are absent. | Granules are absent in the cytoplasm. | ||
| Vacuoles | The appearance of vacuoles is rare. | Vacuoles are commonly seen. | ||
| Nucleus | Soft, spongy and oval, bean or kidney-shaped nucleus. | Dense, oval and stretched nucleus. | ||
| Nuclear staining | Stains with pale-bluish violet stain. | Stains with deep purplish-blue stain. | ||
| Functions | Phagocytosis, antigen presentation and cytokinin production | Antibody production, destruction of cancer cells and viruses. | ||
| Type of Immunity | Innate immunity | Adaptive or acquired immunity | ||
| Immunity reaction | Monocytes act immediately, or within a few hours of infection or injury in response to the antigens in the blood. | Lymphocytes need specific antigens to show an immune response. | ||
| Mode of attack on foreign bodies | They kill antigens. | They neutralize antigens. | ||
| Subtypes | Dendritic cells and macrophages | T-cells (T-lymphocytes), B-cells (B-lymphocytes), and natural killer cells. | ||
| Excess count | Monocytosis is the excessive production of monocytes. | Lymphocytosis is the excessive production of lymphocytes. | ||
Things to Remember
- Monocytes and lymphocytes are agranulocytes found in the blood of mammals.
- Some fine azurophilic (lilac-blue) granules in the cytoplasm with bean-shaped nucleus are monocytes, whereas a spherical nucleus without granules are lymphocytes.
- Monocytes hardly live for a day, whereas lymphocytes live for a week, a month or a year.
- Monocytes are blue-gray in colour, whereas lymphocytes are deep purplish-blue in colour.
- Monocytes behave like amoeba due to the development of pseudopodia.
- Monocytes show innate immunity, whereas lymphocytes show adaptive or acquired immunity.
- Monocytes are also called phagocytes because they eat infectious agents.
- Macrophages and dendritic cells are two types of monocytes.
- B-cells, T-cells and natural killer cells are types of lymphocytes.
- Monocytes are also called macrophages when they invade other body tissues.
- Monocytosis is the excessive production of monocytes, whereas lymphocytosis is the excessive production of lymphocytes.
| Also Read | ||
|---|---|---|
Important Questions
Ques: What are the different types of lymphocytes and what are their significance? (3 Marks)
Ans: Lymphocytes are of three types. They are T-cells (T-lymphocytes), B-cells (B-lymphocytes), and natural killer cells.
B cells produce antibodies against antigens. T-cells destroy cancer cells and viruses. Natural killer cells detect and destroy cancer cells.
B-cells and T-cells are classified as memory cells and regulatory cells. Here ‘B’ indicates bone marrow and ‘T’ indicates thymus.
Ques: What are monocytes? What is the difference between monocytosis and monocytopenia? (3 Marks)
Ans: Monocytes: Monocytes are a kind of white blood cell without granules in their cytoplasm. They are amoeboid structures with a kidney-shaped nucleus. They destroy pathogens through a process called phagocytosis.
Monocytosis: Monocytosis is the presence of high levels of monocytes in the blood. It indicates the presence of some chronic infection, cancer, or an auto-immune disorder.
Monocytopenia: Monocytopenia is an abnormal fall in the count of monocytes. It indicates blood cancer called leukaemia.
Ques: What is meant by immunity? What is the difference between innate immunity and acquired immunity? (3 Marks)
Ans: Immunity: It is a complex biological process. It is a property of the body system to recognise, tolerate, or reject foreign bodies invading into the body. It is of two kinds – innate immunity and acquired immunity.
Innate immunity: It is the kind of immunity that develops with the birth of an organism. Monocytes show innate immunity.
Acquired immunity: It is also called adaptive immunity. It is developed by an organism after being exposed to a certain infection, Lymphocytes show acquired immunity.
Ques: What are monocytes? Why is it bad to know about a sudden fall in the count of monocytes? (5 Marks)
Ans: The human body consists of fluid connective tissue called blood. Blood consists of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets in plasma. White blood cells may be granular or agranular. The agranular white blood cells are monocytes and lymphocytes.
Monocytes are a type of white blood cells. They are agranular due to the absence of conspicuous granules in the cytoplasm. They protect the body against different kinds of infections. Sudden fall in the count of monocytes has clinical significance.
Sudden fall in the count of monocytes may occur due to damage to bone marrow, the chief site of production of monocytes. It may be due to some kind of cancer in the body tissues or due to the destruction of bone marrow cells due to chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Ques: Why are monocytes and lymphocytes called agranulocytes? How are they useful to control infections? (5 Marks)
Ans: The blood of mammals consists of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. WBCs form the chief defence mechanism. They are of two types based on the presence or absence of granules in the cytoplasm. White Blood Cells are either agranulocytes or granulocytes. Agranulocytes do not have granules in the cytoplasm. There are two types of agranulocytes- monocytes and lymphocytes.
Monocytes act upon pathogens within a short period of infections. They kill infectious agents in different ways through phagocytosis, antigen presentation and cytokinin production. Phagocytosis means engulfing microorganisms through cell eating.
Antigens are the indicator proteins present on the surface of bacteria or viruses. Likewise, monocytes present the occurrence of infections in the body. On the other side, lymphocytes produce special proteins called antibodies to counteract the effect of antigens. They also destroy cancer cells and viruses entering the blood.
| Also Read | |
|---|---|
Ques: What is the difference between leukocytes and lymphocytes? Explain the answer briefly. (5 Marks)
Ans: Our body consists of fluid connective tissue called blood. Blood consists of blood cells or corpuscles. They are of three types, namely erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes (white blood cells), and thrombocytes (blood platelets).
All white blood cells are called leukocytes because they are white (leucos=white). These leukocytes are classified as granulocytes and agranulocytes. Granulocytes are eosinophils, basophils and neutrophils. Agranulocytes are monocytes and lymphocytes. So, lymphocytes are a kind of leucocyte.
Lymphocytes are so-called because they are mainly present in the lymphatic system of the body of mammals.
All lymphocytes are leukocytes, but all leukocytes are not lymphocytes.
Ques: Why is blood test important? What is the chief difference between monocytes and lymphocytes? What does it mean if the monocytes and lymphocytes are high in blood? (5 Marks)
Ans: Doctors suggest patients to undergo different kinds of blood tests to diagnose a particular kind of disease. Under the microscope, the lab technician observes and counts the number of different kinds of blood cells. After studying the blood report, the doctor can diagnose a particular kind of disease.
Both monocytes and lymphocytes are agranular leukocytes. Monocytes have a kidney-shaped nucleus, whereas lymphocytes have a spherical nucleus. Moreover, monocytes are responsible for the destruction of disease-causing organisms by phagocytosis, whereas lymphocytes just trigger a specific immune response against a particular pathogen.
High levels of monocytes in the blood indicate that the body is suffering from some chronic infection, cancer, or any other auto-immune disorder. The high levels of lymphocytes in the body are called lymphocytic leukocytosis. This indicates some viral infection.
Ques: What are Kupffer cells? What is their significance (5 Marks)
Ans: The liver is the largest gland in the human body. It consists of different kinds of cells called hepatocytes. Kupffer cells are phagocytic macrophages. They are modified monocytes of the blood system. They form the lining of the sinusoids of the liver. They engulf and break down red blood cells in the liver. Kupffer cells are monocyte derived macrophages.
They perform scavenger and phagocytic functions to remove protein complexes, small waste particles, aged blood cells, and destroyed cell debris from the hepatic portal blood system. They are the first innate immune cells that protect the liver from bacterial infections.





Comments