Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Genetics and Evolution is part of the final portion for CBSE Class 12 Biology. There are no deleted portions in this unit. Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance is part of Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation.
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms: Chromosomes, genetics, Mendel’s theory, mutations, genes, meiosis
What are Chromosomes?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Chromosomes are microscopic, thread-like structures which are primarily responsible for carrying the genetic information of a person in the form of genes. These chromosomes are made from nucleic acids and proteins and have a thread-like structure. The major theory that recognizes the function of chromosomes as carriers of genetic material is called “The Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance.”
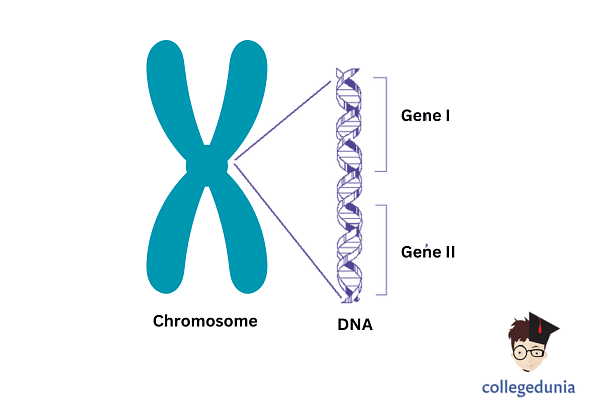
What is the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance?
[Click Here for Previous Years Questions]
The Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance states that individual genes are found at specific locations inside specific chromosomes.
Although it was Mendel who had initially put forth the theory of genes affecting character, he was unable to gain any recognition for it. Then in 1900, three scientists, de Vries, Correns and von Tschermak independently discovered chromosomes existing inside the nucleus, thus proving Mendel’s theory. Advancements in microscopy allowed scientists to minutely observe the process of cell division cementing their findings.
This theory was then firmly established in 1902 and 1903 by Sutton and Boveri. They compared the behaviours of chromosomes to genes and deduced certain parallels, thus justifying Mendel’s Law. Both scientists published independent papers proposing parts of this theory.
This theory is supported by three observations:
- Chromosomes come in matched pairs in any organism. One pair comes from the mother (or female parent) and one pair comes from the father (or the male parent).
- During Meiosis, the matched chromosomes separate, so that each sperm and egg receives only one member.
- During Meiosis, the members of chromosome pairs are separated independently of another.
These are the three main postulates of Mendel’s laws, and therefore, one can conclude that the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance supports Mendel’s Law.
Read More About Difference between Gene and DNA
Linkage and Genetic Recombination
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Once the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance was proven, several scientists carried forward work to determine the reason for variations. The most notable among these is T. H. Morgan who proved sexual reproduction gave rise to chromosomal variations.
T. H. Morgan’s Experiments
T. H. Morgan used Drosophila melanogaster, also known as the common fruit fly, to study chromosomal variations due to sexual reproduction.
Morgan identified that fruit flies inherit their eye colour from their parents. He assumed that male fruit flies have two chromosomes X and Y, making their combination (XY). While the female fruit flies have two X chromosomes, making their combination (XX).
He selected specific combinations of fruit flies and used their offsprings to determine which gene was responsible for the eye colour. For example, a white-eye male flue was crossed with a normal red-eye female flue. He studied their offsprings to determine that the X chromosome was responsible for the eye colour among flies.

Therefore, Morgan proved that if two genes were present on the same chromosome, the next generation had a higher probability of getting a parental gene combination than a non-parental gene combination. This physical association of genes was called ‘linkage’. These helped Morgan identify how the frequency of these linked genes influenced the physical traits of the next generation.
Sturtevant, a student of Morgan, discovered the position of linked genes on chromosomes. He used gene mapping and the frequency of the genetic combination to create a map. This concept is widely used during Human Genome Projects.
Also Read:
| Important Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Incomplete dominance | Pleiotropy | Genotype |
| Linkage and crossing over | Inheritance Definition | Chromosomal Abnormalities |
Factors Affecting Recognition of Mendel’s Theory
[Click Here for Previous Years Questions]
It was Mendel who had first published his ideas on the Theory of Inheritance of Characters, in 1865. However there were several factors due to which they weren’t recognised till the early 1900s.
- Lack of easy wide-spread communication caused his work to remain mostly hidden from society.
- His Theory on Inheritance wasn’t as widely publicized, affecting the number of people it reached.
- Mendel’s concept of genes responsible for controlling character was not accepted by his contemporaries at that time.
- Mendel used mathematical foundations to explain biological phenomena. This was an unprecedented application which was considered unacceptable and rejected by several biologists.
- Although Mendel posited genes as discrete and stable units, he was unable to provide any physical evidence for the existence of said genes.
Read more: Mendelian Inheritance
Observations of Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The key observations of The Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance are as follows:
- During meiosis, homologous chromosomes move as discrete structures. They are independent of other chromosome pairs during the entire process of cell division.
- Chromosomes in each homologous pair are distributed into pre-gametes randomly.
- Each parent synthesizes two gametes which will constitute only half of the chromosomal composition of the next generation.
- The number of chromosomes in male and female gametes (sperm and egg respectively) is the same; and is not influenced by size, shape or morphology. Both parents will contribute equally to the genetic material of the next generation.
- The gametic chromosomes from both parents fuse during fertilization. The process results in the offspring chromosomes, which have the same number as the parents.
Read More: MCQ on Chromosomes
What are mutations?
[Click Here for Previous Years Questions]
A mutation is defined as the permanent change of the structure of a gene. A single variation change in DNA can cause a permanent change in the structure of the gene. This is transmitted to all the subsequent generations of the parent. This permanent change can be as a result of deletion, insertion or rearrangement of the sections of genes i.e a change in the basic sequence of the DNA, A, C, G and T.
Read More: Difference between Gene and DNA
Previous Years Questions
- Which of the following is an example of pleiotropy ?…..[ CUCET 2011]
- Who proposed the chromosomal theory of inheritance ?….[CUCET 2010]
- The children of a father with type 'O' blood and mother with type….[COMEDK UGET 2012]
- Epicanthus skin fold above the eyes and transverse palmer….[COMEDK UGET 2007]
- Distance between the genes and percentage of….[COMEDK UGET 2015]
- Which one of the following is a sex-linked disease….[CUCET 2010]
- The science that deals with the application of principles….[CUCET 2010]
- A 10 years old patient is found to have the following….[COMEDK UGET 2012]
- Which of the following genes shows the heterozygous...[BHU UET 2008]
- Which chromosomal constitution refers to Jacob's syndrome….[BHU UET 2012]
- Which of the following is an example of intergenic gene….
- Which of the following is not considered as a mutagen…
- Haemophilia is an example of….
- In order to lessen the suffering of phenylketonurics...[AMUEEE 2014]
- In Mendel's experiments with garden pea, round seed shape..[JKCET 2015]
- Genotypic and phenotypic ratio in monohybrid cross remains..[JKCET 2011]
Sample Questions
Ques: Where are chromosomes found? (1 mark)
Ans. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of all cells. They are the thread-like coiled material that is seen in the diagram of a cell.
Ques: Who first studied chromosomes? (1 mark)
Ans. Carl Wilhelm von Nageli was the first to study cell divisions and come to the decision that chromosomes existed.
Ques: What does the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance recognize? (1 mark)
Ans. The Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance recognises chromosomes as the carriers of genetic material.
Ques: What are the observations that support the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance? (1 mark)
Ans. Three observations support the theory:
- In all organisms, chromosomes come in matched pairs. One is inherited from the father, and the other is inherited from the mother.
- Homologous pairs separate during meiosis so that every sperm or egg receives one chromosome.
- Each chromosome forms gametes and the sorting of gametes is done independently.
Ques: How does the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance help advance our knowledge of genetics? (1 mark)
Ans. The Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance states that specific genes can be found on specific locations in specific chromosomes. This knowledge can be used to understand and study the behaviour of chromosomes in mitosis and how this affects the physical attributes of the next generation.
Ques: What causes mutations? (1 mark)
Ans. Chromosomal Mutations occur due to errors during meiosis. If the DNA’s base sequence (A, C, G and T) is changed, the DNA-synthesized proteins inside the body also change. This results in permanent mutation.
Ques: Do mutations have a positive effect or a negative effect? (1 mark)
Ans. The positive or negative effect of a mutation can be understood by extensively studying the physical traits of the successive generations. Mutation results in different variations in species and therefore a common conclusion cannot be drawn.
Ques: What are some examples of negative mutations? (1 mark)
Ans. All types of cancer are an example of a mutation-related diseases. These have an adverse effect on successive generations. Another example is Sickle Cell Anaemia which results in the production of different genetic code for haemoglobin. Thereby, the red blood cells take the form of a sickle cell.
Ques: How was gene location on chromosomes discovered? (1 mark)
Ans. Boveri and Sutton discovered the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance which stated that genes are present on specific locations on a chromosome. Further on, Thomas Morgan observed a mutation in the eye colour of fruit flies and based on the inheritance pattern concluded that the gene responsible for mutation of eye colour is located on the X-chromosome.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Do Check Out:




Comments