Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Magnetic Flux can be defined as the number of magnetic field lines passing through a surface. Suppose we place an electromagnetic plate beside a magnet, then the number of the magnetic field line from the north to the south pole of the magnet passing through the plate is termed its magnetic flux. Magnetic flux is typically represented using the Greek letter Phi (\(\Phi\)) or Phi suffix B.
Magnetic flux can be expressed as the product of the average magnetic field times the perpendicular area it is penetrating. Since the SI Unit of Magnetic Field is considered Tesla, the SI Unit of Magnetic Flux is termed Tesla m2. Magnetic flux is an extremely useful tool that helps describe the effects of the magnetic force on an object occupying a respective area. The formula of Magnetic Flux is \(\begin{array}{l}\Phi _{B}=B.A=BA\; cos \; \theta\end{array}\).
Read Also: Magnetism and Matter
Key Terms: Magnetic Field, Magnetic Flux Density, Magnet, Flux meter, Current, Guass, Magnetism, Uses of Inductor, Inductor, Magnetic Force, Tesla
What is Magnetic Flux?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Magnetic flux can be expressed as the number of magnetic field lines which are seen to pass via a given closed surface. Magnetic Flux offers the measurement of the total magnetic field which passes via a respective surface area.
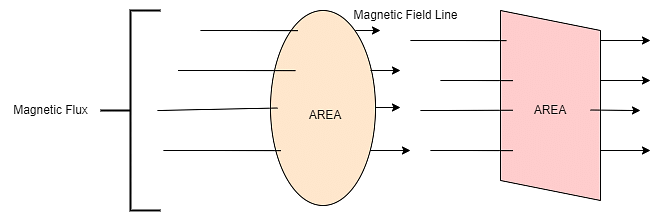
Magnetic Flux
When evaluating the magnetic flux, the component of the magnetic field vector normal to the test area is included. The measurement of magnetic flux is bound to the area as selected. Magnetic flux can be defined as the product of the average magnetic field times the perpendicular area it is penetrating.
The angle where the field lines pass via the surface area is also vital. In case the field lines cross the area at a glancing angle, that is,
- When the angle between the magnetic field vector and the area vector is close to 90ᵒ, then the resulting flux is going to be extremely low.
- When the angle is equivalent to 0ᵒ, the resulting flux is considered maximum.
Mathematically, it can be denoted as:
| \(\phi_{B}\) = B.A = BA cos\(\theta\) |
Where,
- θ = angle between vector A and vector B
If magnetic field is non-uniform and can be found in different parts of the surface and is different in both magnitude and direction, then the total magnetic flux via the given surface can be denoted as the summation of the product of every area element and its corresponding magnetic field. Thus mathematically,
| \(\begin{array}{l}\phi _{B}=B_{1}.dA_{1}+B_{2}.dA_{2}+B_{3}.dA_{3}+… = \sum_{all}^{} B_{i}.dA_{i}\end{array}\) |
Properties of Magnetic Flux
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Some of the properties of Magnetic Flux are included below:
- Magnetic Flux always forms a close loop.
- It is a scalar quantity.
- It always generates from the North pole and ends at the South pole.
- They never intersect with one another.
- It is denoted by \(\phi _B\)
Read More: Inductance formula
Magnetic Flux Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The formula of Magnetic Flux is represented by:
| \(\phi _B\) = B.A |
Assuming the magnetic field is constant, the magnetic flux passing through a plane of area A is represented as:
⇒ \(\phi _B\) = BAcosθ
Here,
- B = Magnetic Field
- A = Area
- θ = Angle at which the magnetic field line passes through the plane.
Unit of Magnetic Flux
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The Magnetic Flux is basically measured with the help of a Flux meter.
- SI unit of Magnetic Flux is Weber (Wb).
- 1 Weber = 1 tesla × 1 m2
- Its fundamental unit is Volt per second.
- CGS unit of Magnetic Flux is Maxwell (Mx).
- 1 Wb = 108 Mx.
Also Read:
Conditions for Maximum and Minimum Magnetic Flux
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
In order to obtain the maximum or minimum magnetic flux, the angle at which the field line passes the surface plays a very important role.

Magnetic Flux Representation
- Here, if the angle between the magnetic field lines and the given surface is 90°, then the magnetic flux produced is very low or zero, i.e.,
For AB, that is θ = 90°, then according to the formula of magnetic flux we get:
⇒ \(\phi _B\)= ABcos90° = 0
- If the angle between the magnetic field lines and the surface is 0°, then the magnetic flux is maximum.
For A || B that is θ = 0°,
⇒ \(\phi _B\)= ABcos0° = AB = Maximum
Read More: Gauss Law for Magnetism
What is Magnetic Flux Density?
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The Magnetic Flux Density can be defined as the measure of the strength of the magnetic field at one particular point.
- It is expressed as the force acting per unit current per unit length.
- It is denoted by B.
- The SI unit is Tesla (T) or Kgs-2 A-1
- The CGS unit of Magnetic Flux Density is Gauss (G) or (Gs). It is a vector quantity.
Magnetic Flux Density Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The formula for the Magnetic Flux Density is represented as:
| B = F/ Il |
Here,
- F = Total force acting on the area
- I = Current flowing through the area
- l = Length of the area
Read More:
Difference between Magnetic Field and Magnetic Flux
[Click Here for previous Year Questions]
Some of the major differences between Magnetic Field and Magnetic Flux are:
| Magnetic Field | Magnetic Flux |
|---|---|
| Magnetic Field is the area around the magnet within which the moving charge particles experience the force of magnetism. | Magnetic Flux is the number of magnetic field lines passing through a surface. It shows the strength of the magnetic field within a specific area. |
| F = qvB | \(\phi _B\)= B.A |
| Its SI unit is Tesla (T) | Its SI unit is Weber (Wb) |
Read More: Magnetic Properties of Material
Previous Year Questions
- If a transformer of an audio amplifier has output impedance 8000 0 and the speaker has input impedance…...[JCECE 2005]
- A conducting loop in the shape of a right angled isosceles triangle of height 10cm10cm is kept such that the 90∘ vertex is…..[JEE Advance 2016]
- A 10m long horizontal wire extends from North East to South West. It is falling with a speed of 5.0ms−1……. [ JEE Main 2019]
- If a current of 2.0A2.0A flows through the smaller loop, then the flux linked with bigger loop is…… [JEE Main 2013]
- A coil of cross-sectional area A having n turns is placed in a uniform magnetic field B….. [JEE Main 21018]
- A copper rod of mass m slides under gravity on two smooth parallel rails, with separation ll and set at an angle of θ with the horizontal….. [JEE Main 2018]
- A copper wire is wound on a wooden frame, whose shape is that of an equilateral…. [JEE Main 2019]
- A metallic rod of length ll is tied to a string of length 2l and made to rotate with angular speed…. [JEE Main 2013]
- A square frame of side 10 cm and a long straight wire carrying current 1 A are in the plane of the paper…. [JEE Main 2014]
- If the rod makes n rotations per second, then the time averaged magnetic moment of the rod is… [JEE Main 2019]
- Figure shows a circular area of radius R where a uniform magnetic field….
- In a coil of resistance 100Ω , a current is induced by changing the magnetic flux through it….. [JEE Main 2017]
- When current in a coil changes from 5A to 2A…. [JEE Main 2015]
- Which radiation in sunlight, causes heating effect?
- X -rays are….
- Arrange the following in decreasing order of wavelength
- Which is having minimum wavelength...[NEET 2002]
- The speed of radio-waves is equal to….. [JIPMER 1998]
- Gamma rays and visible light waves rays are a,ba,b and cc respectively, then…. [UPSEE 2016]
Things to Remember
- Magnetic Flux can be defined as the number of magnetic field lines passing through a surface.
- Magnetic Flux always forms a close loop.
- It always generates from the North pole and ends at the South pole.
- The formula of Magnetic Flux is represented by: \(\phi _B\)= B.A
- The Magnetic Flux is basically measured with the help of a Flux meter.
- SI unit of Magnetic Flux is Weber (Wb).
- The Magnetic Flux Density can be defined as the measure of the strength of the magnetic field at one particular point.
Electromagnetic Induction Handwritten Notes PDF
Read More: Induced electromotive force and current
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the magnetic flux in a closed surface? (1 mark)
Ans. The magnetic flux in a closed surface is always zero.
Ques. What is the SI and CGS unit of the magnetic flux density? (1 mark)
Ans. The SI unit of magnetic flux density is Tesla (T) and CGS unit is Gauss (G).
Ques. What is the primary source of magnetism? (1 mark)
Ans. The primary source of magnetism is the movement of charged particles.
Ques. Why only cosθ is associated with Magnetic Flux and not sinθ? (1 mark)
Ans. Since sinθ does not seem to satisfy the conditions for obtaining the maximum and minimum magnetic flux, only cosθ is used with the formula of magnetic flux.
Ques. What is magnetic flux? (1 mark)
Ans. Magnetic flux is the number of magnetic field lines which pass through a given surface.
Ques. Name the unit of magnetic permeability. (1 mark)
Ans. Tesla is considered the unit of magnetic permeability.
Ques. The area of cross-section of a coil is 10–2 m2. It has 100 turns and is positioned in a magnetic field of strength 1 T. The axis of it makes an angle of 60° with the field. Thus, determine the total flux associated with the field. (2 marks)
Ans. As per the given question,
B = 1 T
A = 10–2 m2
θ = 60°
n = 100
Thus, ΦB = ΦB = nBAcosθ
= 100 × 1 × 10(−2) × cos 60°
= 0.5 Wb
Ques. A rectangular loop with dimensions of 0.50 m and 0.60 m respectively. The values of B are mentioned as 0.02 T and 45°, respectively. Evaluate the magnetic flux at the surface. (2 marks)
Ans. Asper the given questions,
Dimensions of rectangular loop = 0.50 m and 0.60 m respectively,
- B = 0.02T
- θ = 45°
Magnetic flux formula can be represented as:
\(\therefore\) ΦB = BA Cosθ
Thus, Area, A = 0.50 × 0.60
= 0.3 m2
ΦB = 0.02 × 0.3 × Cos 45
= 0.00312 Wb
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:






Comments