Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Artificial hybridization is defined as a process of usage of selective pollen grains for conducting the process of pollination and fertilization. The process of pollination is the process of reproduction in plants. In pollination, plants undergo the process of transferring pollen grains from the anther to stigma. Cross-pollination and self-pollination are the two kinds of pollination. To achieve successful pollination, the pollen and the stigma selected should be similar to each other. The 'similarity' may be in the origin, type, location, etc. In the case when the pollen grains and stigma are not similar, there is a much higher rate that the pollination may not be successful, which means that the pollination will not take place. In commercial crop production, artificial hybridization is used for the production of various kinds of species of plants that have characteristics of both the plants which have been pollinated. In this article, we will learn more about artificial hybridization in plants and the steps involved in it.
| Table of Contents |
Key Takeaway: Artificial Hybridization, Pollination, Fertilization, Plants, Reproduction, Commercial Crop, Pollen Grains, Stigma, Crop production
What is Artificial Hybridisation?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Artificial hybridization is a process of usage of selective pollen grains for conducting the process of pollination and fertilization. It involves crossing various genera and species to achieve a desirable character. This desirable character comprises the characteristics of both the genera and species. It is generally used in commercial crop production.
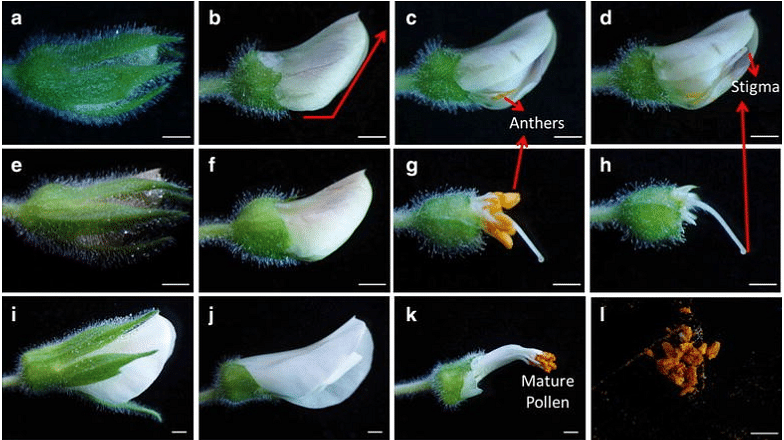
Artificial Hybridization in Plants
Also Read: Polyembryony
What is Pollination?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
In pollination, plants undergo the process of transferring pollen grains from anther to stigma. It can also be described as an act where the pollen grains are transferred from the male anther to the female stigma. Pollination can be divided into two broad categories:
- Cross-Pollination: In the case of Cross-Pollination, the pollen grains from the male anther are being transferred to not the same flower's female stigma. It is being transferred to another flower of the same species.

Cross pollination of pea plants
- Self-Pollination: In the case of Self-Pollination, the pollen grains from the male anther are being transferred to the female stigma of the same flower.
It is important to remember that the seeds are produced only in the case of self-pollination.
Also Read: Gemmule formation
Steps Involved in Artificial Hybridisation
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
For achieving artificial hybridization, the two steps involved are:
-
Emasculation
Another name for artificial hybridization is the process of selective breeding. To achieve this, the anthers must release pollen grains. So, the anthers before releasing pollen grains must be thrown away. This process which involves the removal of anthers employing forceps is termed Emasculation.
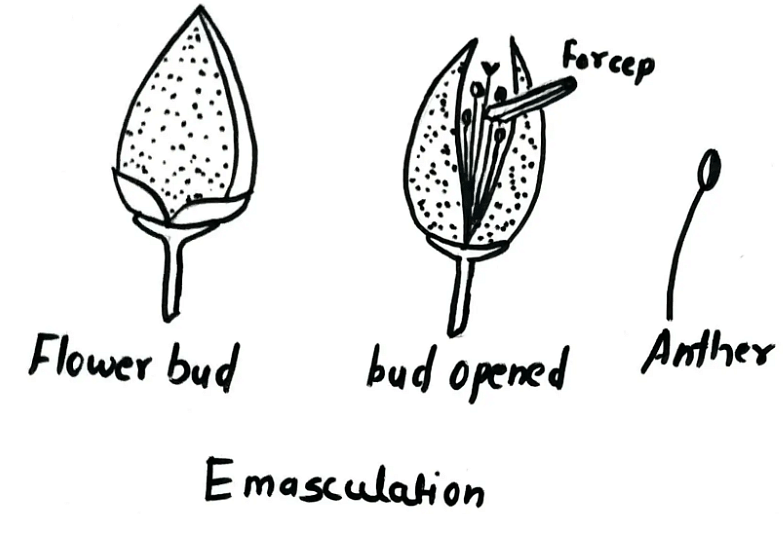
Emasculation
The step of removal of anthers is not termed to be necessary in the case of unisexual flowers.
-
Bagging
The process in which the emasculated flower is protected from being infected or contaminated. It is protected from being contaminated by unsuitable pollen grains; these undesirable pollen grains may be harmful as they may become a barrier in the process. It is covered with a bag; being covered, it still accomplishes receptivity.
The bagging process is done before the flower is open in unisexual flowers. A female flower is protected from contamination by bagging and emasculation. Once the flower attains stigma receptivity, the desired pollen is brushed on the stigma. This is resealed for further growth.
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Apomixis | Double fertilization | Budding |
| Fragmentation | Parthenocarpy | Artificial Pollination |
Things to Remember
- Artificial hybridization is defined to be a process of usage of selective pollen grains for conducting the process of pollination and fertilization.
- To achieve successful pollination, the pollen and the stigma selected should be similar to each other.
- It is important to remember that the seeds are produced only in the case of self-pollination
- Another name for artificial hybridization is the process of selective breeding.
- The process which involves the removal of anthers employing forceps is termed Emasculation.
- In pollination, plants undergo the process of transferring pollen grains from the anther to stigma.
- Pollination can be divided into two broad categories: Cross-Pollination and Self-Pollination.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is Artificial Hybridization? (3 marks)
Ans. Artificial hybridization is a process wherein selective pollen grains are used for the purpose of conducting the process of fertilization and pollination. It mainly involves crossing various species and genera to achieve a desirable character. It is generally used in the production of commercial crops. Here, artificial hybridization is used for the production of various species of plants that have characteristics of both the plants which have been pollinated.
Ques. What are the steps involved in Artificial Hybridisation? (2 marks)
Ans. For achieving artificial hybridization, these two steps are involved:
- Emasculation
- Bagging
Ques. What are Pollination and its types? (5 marks)
Ans. In pollination, plants undergo the process of transferring pollen grains from anther to stigma. It can also be described as an act where the pollen grains are transferred from the male anther to the female stigma. Pollination can be divided into two broad categories:
- Cross-Pollination
- Self-Pollination
In the case of Cross-Pollination, the pollen grains from the male anther are being transferred to not the same flower's female stigma. It is being transferred to another flower of the same species.
In the case of Self-Pollination, the pollen grains from the male anther are being transferred to the female stigma of the same flower. It is important to remember that the seeds are produced only in the case of self-pollination.
Ques. How can we achieve successful pollination? (2 marks)
Ans. To achieve successful pollination, the pollen and the stigma selected should be similar to each other. The 'similarity' may be in the origination, type, location, etc. In the case when the pollen grains and stigma are not similar, there is a much higher rate that the pollination may not be successful, which means that the pollination will not take place.
Ques. What is Emasculation? (2 marks)
Ans. Another name for artificial hybridization is the process of selective breeding. To achieve this, the anthers must release pollen grains. So, the anthers before releasing pollen grains must be thrown away. This process which involves the removal of anthers employing forceps is termed Emasculation. The step of removal of anthers is not termed to be necessary in the case of unisexual flowers.
Ques. What is Bagging? (2 marks)
Ans. The process in which the emasculated flower is protected from being infected or contaminated. It is protected from being contaminated by unsuitable pollen grains; these undesirable pollen grains may be harmful as they may become a barrier in the process. It is covered with a bag; being covered, it still accomplishes receptivity. The bagging process is done before the flower is open in unisexual flowers. A female flower is protected from contamination by bagging and emasculation. Once the flower attains stigma receptivity, the desired pollen is brushed on the stigma. This is resealed for further growth.
Ques. What is the 'similarity' term used to refer to in the process of pollution? (3 marks)
Ans. The 'similarity' may be in the origination, type, location, etc. In the case when the pollen grains and stigma are not similar, there is a much higher rate that the pollination may not be successful, which means that the pollination will not take place. Unsuccessful pollination is not considered in any of the circumstances, especially in the case of commercial crop production. Here, in commercial crop production, artificial hybridization is used for the production of various kinds of species of plants that have characteristics of both the plants which have been pollinated.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:




Comments