Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Acetylsalicylic Acid (ASA) also known as aspirin is a very common medicine and is primarily used to treat inflammation and pain. It is chemically known as Acetylsalicylic Acid (ASA). Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a medication which is mainly used to reduce pain, fever, or inflammation. Aspirin is used to treat certain inflammatory conditions including Kawasaki disease, pericarditis and rheumatic fever.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Acetylsalicylic Acid, Inflammation, Aspirin, Kawasaki disease, Pericarditis, Rheumatic fever, Carboxylic acid, Carbonyl group, aromatic ring, ester
Read More: Specific Heat of Water
How Is Aspirin Formulated and Structured?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Acetylsalicylic acid's chemical formula is C9H8O4. Additionally, the extended formula of the Acetylsalicylic acid is CH3COOC6H4COOH. Furthermore, it has a molecular mass of around 180.159 g mol-1. This molecule forms from an aromatic ring with two functional groups in position –orto: the first is a carboxylic acid substituted by a carbonyl group, and the second is an ester group.
Read More: Solvent Examples
According to its molecular geometry, aspirin is planar. As a result, the carboxylic groups and the phenyl ring are hybridized. According to the commonly used representations for organic molecules, the chemical structure of Aspirin is as follows:
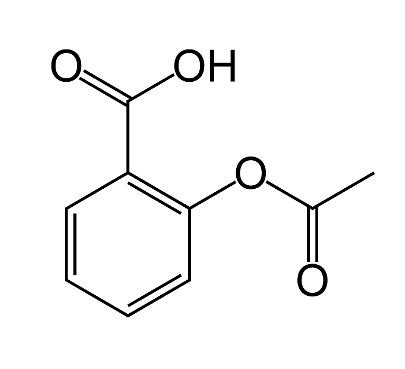
Observation
Acetylsalicylic Acid is also not found in nature, similar to many other compounds. The compound was invented in 1853 and is not found in nature. It was in that year that a French chemist named Charles Frédéric Gerhardt synthesized Aspirin for the first time.
Read More: Number of Moles Formula
Preparation of Acetylsalicylic Acid
By esterifying salicylic acid with acetic anhydride, acetate can easily be synthesized from acetylsalicylic acid. Hence, the ester groups replace the hydroxyl groups present in salicylic acid. Similarly, sulfuric acid can be used as a catalyst.
Physical Properties of Acetylsalicylic Acid
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Acid Acetylsalicylic is normally a crystalline substance that is colourless to white. This substance has an aromatic smell similar to vinegar. The smell of Acetylsalicylic Acid arises from the hydrolysis of salicylic and acetic acid. A bitter taste is associated with Aspirin. Furthermore, the density is 1.40 g mL-1. Acetylsalicylic Acid melts at 135 degrees Celsius. Keeping it at a higher temperature will cause it to decompose. In addition to water, ethyl ether, ethanol, and chloroform, Acetylsalicylic Acid is soluble in chloroform as well.
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Metallic Bonds | Bravais Lattices | Close Packing in One,Two and Three Dimensions |
| Half Life Formula | Activation Energy Formula | Mass Percent Formula |
Chemical Properties of Acetylsalicylic Acid
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The main characteristic of Acetylsalicylic Acid is that it is an anti-inflammatory. Since it inhibits the enzyme cyclooxygenase, it acts as a cyclooxygenase inhibitor. As a result, it suppresses Prostaglandin production (prostaglandins are molecules involved in inflammation).
Uses Of Acetylsalicylic Acid
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The medicine is very popular worldwide and has been available in large amounts for a long time. Aspirin is the name of Acetylsalicylic Acid, which was given by Bayer Laboratory in the year 1897. As soon as its name was given, it was commercialized. Antipyretic and anti-inflammatory properties are the main uses of this medicine.

Acetylsalicylic Acid is given shortly after a heart attack because it decreases the risk of death. It is also used to prevent further heart attacks, ischaemic strokes, and blood clots in people at high risk. The effect of aspirin begins within 30 minutes for pain or fever. Aspirin is considered to be a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and it works similarly to other NSAIDs but it also affects and suppresses the normal functioning of platelets. Among the other uses are rheumatic fever and Kawasaki disease. Additionally, it can also be used as an intermediate in the manufacture of other chemical compounds such as 4-hydroxycoumarin.
Health Hazards of Acetylsalicylic Acid
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A room temperature setting is ideal. Aspirin remains stable at room temperature. It is important, however, to avoid hydrolysis of the medication. When taken for a prolonged period of time, it can lead to ulceration and gastritis. In addition, it cannot be used with aggressive oxidising agents and strong acids and bases.
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tetrahedral and Octahedral voids | Avogadro constant | Point defects |
| Synthetic Polymers | Copolymers | Polytetrafluoroethene (Teflon) |
Things To Remember
- Aspirin is primarily used to treat inflammation and pain.
- Acetylsalicylic acid's chemical formula is C9H8O4. Additionally, the extended formula of the Acetylsalicylic acid is CH3COOC6H4COOH.
- According to its molecular geometry, aspirin is planar.
- Aspirin can also be used as an intermediate in the manufacture of other chemical compounds such as 4-hydroxycoumarin.
- It cannot be used with aggressive oxidising agents and strong acids and bases.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques 1. Acetylsalicylic acid has what purpose? (2 marks)
Ans. The ASA medication is used to treat discomfort, nausea, and swelling of various symptoms such as lower back pain, menstrual pain, headaches, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, joint damage, toothache, shoulder pain and bursitis.
Ques 2. What is the mechanism of action of acetylsalicylic acid? (2 marks)
Ans. Aspirin may reduce stroke and heart attack risks due to its ability to suppress the body's pain receptors. As a result, your arteries are less likely to clot and shrink due to a decrease in platelet clumping and shrinking and a better blood supply to your heart and brain.
Ques 3. In what ways does aspirin benefit us? (2 marks)
Ans. The pain reliever aspirin, or acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is commonly used for treating mild aches and discomforts as well as alleviating fevers. Also, it is a blood thinner that can be used as an anti-inflammatory drug. For long-term use, aspirin can be taken at low doses by those at high risk for blood clots, strokes, and heart disease.
Ques 4. Chemically, what is aspirin called? (2 marks)
Ans. Chemically, aspirin is known as 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid. Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), the chemical component of aspirin, is widely used around the world as an antipyretic and anti-inflammatory agent. Acetylsalicylic acid has a molecular formula of C9H8O4 and an expanded formula of CH3COOC6H4COOH.
Ques 5. Is acetylsalicylic acid soluble in ethanol? (2 marks)
Ans. Aspirin is soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, DMSO, and dimethylformamide, which are to be purged with inert gas. The approx solubility of Aspirin in these solvents is 80, 41 and 30 mg/ml respectively.
Ques 6. How can acetylsalicylic acid help? (2 marks)
Ans. Among its many uses, aspirin is used to treat fever, toothaches, chronic colds, and headaches as well as relieve mild to moderate discomfort. Arthritis, for example, may benefit from this to reduce discomfort and inflammation. In addition to serving as a salicylate, aspirin is also a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
Ques 7. Is aspirin safe for everyone? (2 marks)
Ans. Aspirin is usually safe for people over 16 years of age. Nevertheless, it might not be appropriate for some people. Aspirin should not be given to children younger than 16 unless prescribed by their doctor. Infants who take aspirin are at risk of developing Reye Syndrome.
Ques 8. Aspirin is an anticoagulant, but how does it work? (2 marks)
Ans. Blood clotting is slowed down by anticoagulants like heparin and warfarin (also called Coumadin). In addition to preventing blood clots, antiplatelet medications like aspirin reduce the tendency of blood cells to fold together. If you want to confirm how well the blood clots are, you may need to check your blood daily.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:



Comments