Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Omega-3 Fatty Acids, also known as Omega-3 oils, fatty acids, or n−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) with a double bond three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their chemical structure. They are widely distributed in nature and are important constituents of animal lipid metabolism, as well as playing an important role in human diet and physiology. Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid are the three types of omega-3 fatty acids involved in human physiology (DHA). Plants contain ALA, while algae and fish contain DHA and EPA.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Metabolism, Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Eicosapentaenoic Acid, Alpha-Linolenic Acid, Atoms, Fats, Nutrition, Hormones
What are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The human body can synthesise the majority of the fats it requires from other fats or raw materials. This is not true for omega-3 fatty acids (also called omega-3 fats and n-3 fats). Fish, vegetable oils, nuts (especially walnuts), flax seeds, flaxseed oil, and leafy vegetables are high in Omega-3.
They are a component of cell membranes throughout the body and influence the function of cell receptors. They serve as a starting point for the production of hormones that regulate blood clotting, artery wall contraction and relaxation, and inflammation. Because of these benefits, omega-3 fats have been found to help prevent heart disease and stroke, as well as regulate lupus, eczema, and rheumatoid arthritis. They may also play protective roles in cancer and other diseases.

Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Structure 0f Omega 3 Fatty Acids
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Polyunsaturated fatty acids with a C=C double bond in the n-3 position are known as omega-3 fatty acids.
The following omega-3 fatty acids are important in human nutrition: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). The human body cannot produce omega-3 fatty acids from scratch, but it can produce all of the other omega-3 fatty acids required from the omega-3 fatty acid Alpha-linolenic acid. As a result, alpha-linolenic acid is an essential nutrient that must be obtained through food, and the other omega-3 fatty acids that can be synthesised from it within the body or obtained through food are also considered essential nutrients.
The molecular formula of omega 3 fatty acids is C60H92O6.
The structure of omega-3 fatty acids is given below:
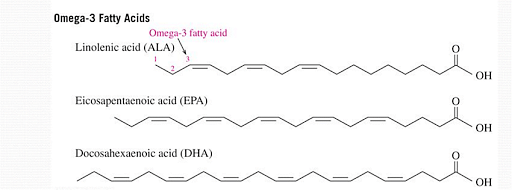
Structure of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
The other names of omega 3 fatty acids are as follows:
| Common Name | Chemical Name | Lipid Name |
|---|---|---|
| α-Linolenic acid (ALA) | all-cis-9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid | 18:3 (n-3) |
| Hexadecatrienoic acid (HTA) | all-cis-7,10,13-hexadecatrienoic acid | 16:3 (n-3) |
| Eicosatrienoic acid (ETE) | all-cis-11,14,17-eicosatrienoic acid | 20:3 (n-3) |
| Stearidonic acid (SDA) | all-cis-6,9,12,15-octadecatetraenoic acid | 18:4 (n-3) |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) | all-cis-5,8,11,14,17-eicosapentaenoic acid | 20:5 (n-3) |
| Eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA) | all-cis-8,11,14,17-eicosatetraenoic acid | 20:4 (n-3) |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) | all-cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic acid | 22:6 (n-3) |
| Docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), Clupanodonic acid | all-cis-7,10,13,16,19-docosapentaenoic acid | 22:5 (n-3) |
| Tetracosahexaenoic acid (Nisinic acid) | all-cis-6,9,12,15,18,21-tetracosahexaenoic acid | 24:6 (n-3) |
| Tetracosapentaenoic acid | all-cis-9,12,15,18,21-tetracosapentaenoic acid | 24:5 (n-3) |
Read More: Nutrient Management
Types of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Polyunsaturated fats are a type of polyunsaturated fat that includes omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are divided into three main categories:
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are known as marine omega-3s since they are usually found in fish.
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is the most common omega-3 fatty acid in most Western diets, and it can be found in vegetable oils and nuts (especially walnuts), flax seeds and flaxseed oil, green vegetables, and some animal fat, particularly from grass-fed animals. The human body uses ALA as its primary energy source, with only minimal conversion to EPA and DHA.
Read More: Difference between Fats and Oils
Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Some foods naturally contain omega-3 fatty acids, and others are enriched. Omega-3 fatty acids can be found in a variety of foods, including those listed below:
- Seafood, including fish (especially cold-water fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring, and sardines)
- Seeds and nuts (such as flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts)
- Plant-based oils (such as flaxseed oil, soybean oil, and canola oil)
- Nutrient-fortified foods (such as certain brands of eggs, yoghurt, juices, milk, soy beverages, and infant formulas)

Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Read More: Difference between Saturated and Unsaturated Fats
Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
According to numerous studies, omega-3 fatty acids are considered to be beneficial to cardiovascular health. The majority of this research focuses on EPA + DHA, although ALA can also benefit your health. Some of the benefits of including omega-3 fatty acids in your diet are as follows:
- Cardiovascular disease risk is reduced.
- Reduced risk of sudden cardiac death due to a heart rhythm abnormality.
- Omega-3 fatty acids help in the prevention of the blood platelets from clumping together, lowering the risk of blood clots.
- Maintaining the smoothness and absence of damage to the artery lining can lead to thick, stiff arteries.
- They also assist in slowing the formation of triglycerides in the liver and lowers triglyceride levels, which are linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
- Inflammation is reduced. Atherosclerosis is thought to be caused by your body's inflammatory reaction (artery hardening). Omega-3 fatty acids reduce the number of molecules released during the inflammatory reaction.
Read More: Coronary Artery Disease
Things to Remember
- Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) containing a double bond three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their chemical structure are Omega-3 fatty acids, also known as Omega-3 oils, 3 fatty acids, or n3 fatty acids.
- The human body can synthesise the majority of the fats it requires from other fats or raw materials. This is not true for omega-3 fatty acids (also called omega-3 fats and n-3 fats).
- Polyunsaturated fatty acids with a C=C double bond in the -3 position are known as omega-3 fatty acids.
- The human body cannot produce omega-3 fatty acids from scratch, but it can produce all of the other omega-3 fatty acids required from the omega-3 fatty acid Alpha-linolenic acid.
- The following omega-3 fatty acids are important in human nutrition: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (DHA).
Sample Questions
Ques. How do omega 3 fatty acids reduce inflammation? (3 Marks)
Ans. Omega-3 fatty acids suppress an enzyme called cyclooxygenase (COX), which produces the prostaglandin hormones that cause inflammation, according to the researchers. The effect is comparable to that of aspirin, which inhibits the COX-2 signalling pathway and hence reduces inflammation and discomfort.
Ques. What are omega 3 fatty acids and where do they come from? (3 Marks)
Ans. The most prevalent omega-3 fatty acid in most Western diets is alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which can be found in vegetable oils and nuts (especially walnuts), flax seeds and flaxseed oil, green vegetables, and some animal fat, particularly from grass-fed animals.
Ques. Why omega 3 fatty acids are good for health? (3 Marks)
Ans. They bind to receptors that control genetic function in cells. Omega-3 fats have been shown to help prevent heart disease and stroke, as well as to assist regulate lupus, eczema, and rheumatoid arthritis, as well as to play protective roles in cancer and other disorders, all of which are likely related to these benefits.
Ques. Can omega 3 fatty acids increase weight? (3 Marks)
Ans. Although omega-3 fatty acids are generally recommended for weight loss, excessive ingestion may have the opposite effect. We all know that fish oil is considerably high in fat and calories, therefore consuming too much of any of these sources might lead to an increase in metabolic weight.
Ques. Does omega 3 fatty acids lower cholesterol? (3 Marks)
Ans. Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to lower blood triglyceride levels considerably. The levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL, or "good") cholesterol improved slightly, but the levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL, or "bad") cholesterol increased.
Ques. What do omega 3 fatty acids? (3 Marks)
Ans. They are found in cell membranes all throughout the body and have an impact on the function of the cell receptors in these membranes. They serve as a source of hormones that regulate blood coagulation, artery wall contraction and relaxation, and inflammation.
Ques. Does omega 3 fatty acids help hair growth? (2 Marks)
Ans. Many people eat fish or take fish oil supplements to encourage hair development and prevent hair loss, which suggests that omega-3 in fish oil offers vital proteins and nutrients to hair follicles and skin.
Ques. Does omega 3 fatty acids lower cholesterol? (3 Marks)
Ans. Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to lower blood triglyceride levels considerably. Although high-density lipoprotein (HDL, or "good") cholesterol levels improved slightly, low-density lipoprotein (LDL, or "bad") cholesterol levels increased significantly.
Also Read:
Also Read:



Comments