Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Atomic Number and Mass number of an atom (A-Z), when added together corresponds to the total number of subatomic particles present in the atom. The atomic number of an atom is given by the total number of protons in its nucleus. Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of all elements. They are the smallest chemically reacting components of an element. Protons, neutrons, and electrons are the subatomic particles of an atom.
What are Atoms?
An atom is the smallest unit of matter. Atoms, whether neutral or ionised, make up every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. They are incredibly small, measuring about 100 picometers in diameter.

Atom and its subatomic particles
Protons, neutrons, and electrons make up an atom. Protons and neutrons are heavier than electrons and are found in the nucleus, the atom's core. Protons and neutrons almost have the same mass. However, in comparison, a proton is 1,835 times heavier than an electron. The number of protons and electrons in an atom is always equal.
Read More:
Atomic Number
The atomic number of an atom is determined by the total number of protons in its nucleus. The letter 'Z' is used to signify it.
Example: The atomic number of iron is 26 because an atom of iron has 26 protons in its nucleus. A given element's atoms all have the same number of protons, and thus the same atomic number.
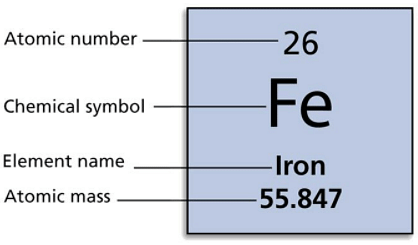
Atomic Number of Fe
The atomic numbers of different elements are different. For example, all carbon atoms have an atomic number of 6, whereas all oxygen atoms have an atomic number of 8.
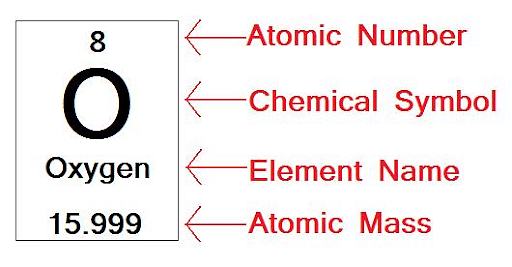
Atomic Number of Oxygen
The atomic number may be shown as a left subscript in the symbol denoting a certain nuclear or atomic species. For example, 8O can be written for an atom or nucleus of iron.
Read More: Energy Level Diagram
Isotopes
Isotopes are elements with the same atomic number and periodic table position but varying mass numbers. These isotopes have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes have nearly identical chemical properties, their atomic weights and physical attributes differ.

Isotopes of Hydrogen
Example: ¹H (protium), ²H (deuterium), and ³H (hydrogen) are the three naturally occurring isotopes of hydrogen (tritium).
Importance of Atomic Number
- It aids in the identification of a certain atom's element.
- The order of the elements in the periodic table is determined by their atomic number.
- It aids in the discovery of any element's qualities. The valence electron, on the other hand, determines an element's chemical bonding behaviour.
Read More:
Mass Number
The total number of protons and neutrons (known collectively as nucleons) in the nucleus of an atom is known as the mass number or atomic mass number or nucleon number. It is expressed in atomic mass units. The letter 'A' is used to signify it.

Mass Number
The mass number is different for the isotopes of the same element. As a result, the number of neutrons (N) in a given nucleus is determined by the difference between the mass number and the atomic number
Z: N = A Z = N = A Z = N = A Z = N = A Z = N
The most prevalent isotope of carbon, for example, is 66C. There are six protons and six neutrons in it.

Isotopes of Carbon
The atomic mass is calculated by averaging the mass numbers of its naturally occurring isotopes. A decimal is frequently included in the resultant number. Because chlorine is made up of multiple isotopes, some with an atomic mass of 35 amu and others with an atomic mass of 37 amu, the atomic mass of chlorine (Cl) is 35.45 amu.
Properties of Mass Number
- This number is determined by the total number of protons and neutrons in a certain element.
- The total number of protons in all atoms of an element remains the same.
- In most cases, atomic mass and mass numbers are two distinct words that can differ somewhat. In the vast majority of circumstances, they are not the same. However, because the weight of an electron is so little, we can assume that an atom's atomic mass is about equal to its mass number.
- Isobars are a type of element that exists in nature. These are atoms with the same mass number but different atomic numbers from different elements.
- The mass number of elements can be changed as a result of alpha decay, which eliminates two protons and two neutrons from a radioactive nucleus.
Read More: Orbitals
Differences Between Atomic Number and Mass Number
The key differences between atomic number and mass number are given below.
| Atomic Number | Mass Number |
|---|---|
| The number of electrons in an atom is known as its atomic number. It's the same as how many protons are in a neutral atom. | The total number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus is known as the mass number, often known as the atomic mass number or nucleon number. |
| It is denoted by the symbol z | It is represented by A. |
Things to Remember
- The total number of protons in an atom's nucleus determines its atomic number. The letter 'Z' is used to signify it.
- The atomic number determines the order of the elements. The elements are listed in order of their ascending atomic numbers.
- The number of protons in an atom of an element can be used to calculate an atomic number.
- The total number of protons and neutrons (known collectively as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus is known as the mass number, also known as the atomic mass number or nucleon number. It is roughly equivalent to the atomic mass of an atom given in atomic mass units. The letter 'A' is used to signify it.
- The mass number of elements can be changed as a result of alpha decay, which eliminates two protons and two neutrons from a radioactive nucleus.
Read More:
Sample Questions
Ques. Who was the first to discover the atomic number? Why is Z used to represent the atomic number? [2 marks]
Ans. The atomic number determines the number of protons (positive charges) in an atom's nucleus. Henry Gwyn-Jefferies Moseley was the first to coin the word.
The atomic number Z stands for "Zahl," which means "German number." Before 1915, the sign Z denoted an element's position in the periodic table.
Ques. How do you calculate atomic mass from the atomic number and neutron count? [2 marks]
Ans. One can calculate the atomic mass of a single atom of an element by adding the mass of protons and neutrons. The mass number of an element is determined by the sum of its protons and neutrons: mass amount = protons + neutrons.
Ques. Write the complete symbol for the atom (X) with the given atomic number (Z) and atomic mass (A) [3 marks]
(i) Z = 17,A = 35
(ii) Z = 92, A = 233
(in) Z = 4, A = 9.
Ans.
Ques. Symbols 7935 Br and 79Br can be written whereas symbols 35 79 Br and 35Br are not accepted. Answer in brief. [3 marks]
Ans. In the symbol BA X of an element :
A denotes the atomic number of the element
B denotes the mass number of the element.
The atomic number of the element can be identified from its symbol because no two elements can have the atomic number. However, the mass numbers have to be mentioned in order to identify the elements. Thus,
Symbols s 7935 Br and 79Br are accepted because the atomic number of Br will remain 35 even if not mentioned. Symbol 35 79 Br is not accepted because the atomic number of Br cannot be 79 (more than the mass number = 35). Similarly, the symbol 35Br cannot be accepted because the mass number has to be mentioned. This is needed to differentiate the isotopes of an element.
Read More: Clemmensen Reduction Reaction
Ques. An element with mass number 81 contains 31.7% more neutrons as compared to protons. Assign the symbol to the element. [3 marks]
Ans. An element can be identified by its atomic number only. Let us find the atomic number.
Let the number of protons = x
Number of neutrons = x + [ x×31.7 / 100 ] = (x × 0.317x)
Now, Mass no. of element = no. of protons =no. neutrons
81 = x + x + 0-317 x = 2.317 x or x = 81 / 2.317 = 35
∴ No. of protons = 35, No. of neutrons = 81 – 35 =46
Atomic number of element (Z) = No. of protons = 35
The element with atomic number (Z) 35 is bromine 8135 Br
Ques. An ion with mass number 37 possesses one unit of negative charge. If the ion contains 11 -1% more neutrons than the electrons, find the symbol of the ion. [3 marks]
Ans. Let the no. of electron in the ion = x
∴ the no. of protons = x – 1 (as the ion has one unit negative charge)
and the no. of neutrons = x + x×11.1 / 100 = 1.111 x
Mass no. or mass of the ion = No. of protons + No. of neutrons
(x – 1 + 1.111 x)
Given mass of the ion = 37
∴ x- 1 + 1.111 x = 37 or 2.111 x = 37 + 1 = 38
x = 38 / 2.111 = 18
No. of electrons = 18 ; No. of protons = 18 – 1 = 17
Atomic no. of the ion = 17 ; Atom corresponding to ion = Cl
Symbol of the ion = 3717Cl
Read More: Tollen’s Test
Ques. An ion with mass number 56 contains 3 units of positive charge and 30.4% more neutrons than electrons. Assign a symbol to the ion. [4 marks]
Ans. Let the no. of electrons in the ion = x
∴ the no. of the protons = x + 3 (as the ion has three units positive charge)
and the no. of neutrons = x + x×31.7 / 100
= xc + 0.304 x
Now, mass no. of ion = No. of protons + No. of neutrons
= (x + 3) + (x + 0.304x)
∴ 56 = (x + 3) + (x + 0.304x) or 2.304x = 56 – 3 = 53
x = 53 / 2.304
= 23
Atomic no. of the ion (or element) = 23 + 3 = 26
The element with atomic number 26 is iron (Fe) and the corresponding ion is Fe3+.
Read More: Williamson Ether Synthesis
Ques. Define atomic number, mass number and neutron. How are the three related to each other? [5 marks]
Ans. Atomic Number (Z): The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons present inside the nucleus of its atoms.
Since, an isolated atom has no net charge on it, in neutral atoms, the total number of electrons is equal to its atomic number.
Atomic number (Z) = Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom = Number of electrons in the neutral atoms
Mass Number (A): The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom is called its mass number. Mass number is denoted by A. Thus, for an atom, Mass number (A) = Number of protons (p) + Number of neutrons (n)
A = p + n
Neutron: It is neutral particle. It is present in the nucleus of an atom. Expect hydrogen (which contains only one electron and one proton but no neutron), the atoms of all other elements including isotopes of hydrogen contain all the three fundamental particles called neutron, proton and electron.
The relation between mass number, Atomic no. and no. of neutrons is given by the equation:
A = Z + n
Where A = Mass number
Z = Atomic number n = number of neutrons in the nucleus.
Ques. The nucleus of an atom has 6 protons and 8 neutrons. What are its atomic number and mass number? What is this element1? [2 marks]
Ans. At. No. = 6;
Mass No. = 6 + 8 = 14
Element is Carbon.
Ques. What is the atomic number of an element whose mass number is 23 and contains 12 neutrons in its nucleus? What is the symbol of an element? [2 marks]
Ans. Atomic number = No. of protons in the nucleus
= Mass no. – No. of neutrons
= 23 – 12 = 11
The element is sodium and its symbol is Na.
Read More:



Comments