Jasmine Grover Content Strategy Manager
Content Strategy Manager
Model organisms are non human species, made under specific laboratory settings with certain biological processes. They have been extensively researched, are easily maintainable, and have experimental benefits. A scientist takes the help of model organisms to learn about various other organisms that are difficult to understand. It acts as a major instrument for therapeutic research.
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms: Model organisms, Genetics, Non-human characteristics, Genomes, Worms, Zebrafish, Organisms, Genes
Benefits of using model organisms in genetic research
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Reproduction in vast quantities
- Extremely short generation time which lets many generations to be observed parallel.
- Organisms are made of genomes and genes that are similar to humans
- Used to make a highly detailed genetic map
- Scientists find out about certain traits and diseases from these species as they have an altered DNA which results in a different characteristic.
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cytoplasm and Protoplasm | Fundamental Unit of Life | Animal Cell |
| Animal Cell Diagram | Endoplasmic Reticulum | Protoplasm |
Different types of models
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
| Mammalian models | Non-mammalian models | Plant models |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Types of model organisms
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Some of the notable types of model organisms are:
House mouse(mus musculus)
Mice have a short generation time which helps the scientists to observe different generations of mice at a time. They often reproduce every 3 weeks and have different advantages of being a model organism.

Mice or House Mouse
Worm (Caenorhabditis elegans)
These species have large bodies and a rapid life cycle. It is easy to carry out extensive experiments over many generations as they are self-fertile hermaphrodites. They have similar genes as human beings. They make themselves ideal to study the process of basic molecular biology as they have an ortholog.

Worm
Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
They share 70% of the human genes with humans. They produce 50-300 eggs, are stored in large groups, and are easily bred which is why they are easily maintained. Scientists can experiment on their eggs as the embryos of zebrafish are laid and fertilised externally.

Zebrafish
Yeast (saccharomyces cerevisiae)
Yeast is easy to maintain as they can adjust in any environmental condition and they multiply every 2 hours. They are the simplest eukaryotic organism which is cheap and simple to experiment with. It is considered the best model organism.

Yeast
Fly fruit (drosophila melanogaster)
The fruit fly is an old model organism that is used for research for a very long time. Before it was discovered that DNA is a kind of genetic material, genes were discovered inside the chromosome of a fly fruit.
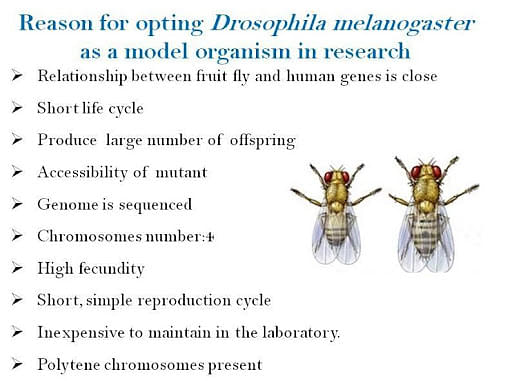
Fly fruit
Things to Remember
- Model organisms can reproduce rapidly in large quantities, are easily manipulative, have a short life span, and develop quickly.
- Scientists can alter the genomes of zebrafish or create transgenic animals by injecting one-celled embryos.
- Yeast was the first eukaryotic genome to be completely sequenced and is very flexible to genetic alteration
- Models organisms help scientists to understand the certain disease and their symptoms as they develop rapidly
- They are an essential instrument for clinical research with their ability to help in identifying the cause of newly formed disease
- Nonhuman model organisms such as drosophila (the fly fruit), plants (rice and Arabidopsis), yeast, bacteria, Caenorhabditis elegans have also been classified.
- There are three types of models- plant model, mammalian model, and non-mammalian model
Read More:
Sample Questions
Ques. What are the different characteristics of model organisms? (2 Marks)
Ans. The characteristics of a model organism are:
- Is identical to other organisms or systems
- The growth and the development of the organism is well detected and understood
- Determines the nutrients that are essential for the growth
- It is comparably easy to maintain and grow in a limited space
- The cycle of birth, reproduction, and death happens in a short period
- Easy to manipulate
- Reproducing many offsprings in a short period
Ques. What are the limitations of imaging model organisms? (2 Marks)
Ans. Imaging model organisms depends on whether they will be used for the study of molecular events or dynamic studies. The complexity of the model organisms that range from a few cells in C Elegans to large complicated animals like the mouse is also taken into consideration.
Ques. What is the thale cress model organism? (2 Marks)
Ans. In plant biology, thale cress or Arabidopsis thaliana is a kind of flowing plant that is used as a model organism. It belongs to the family of mustard (Brassicaceae) which consists of radish and cabbage. It doesn't have any significant agronomic benefit but it is easy to cultivate and has advantages for research because of its small genome size which is 135Mb and consists of a haploid chromosome number of five.
Ques. What are genetically modified organisms (GMOs)? (2 Marks)
Ans. With the help of genetic engineering, genetically modified organisms are organisms whose genetic material is artificially altered in the laboratory. GMOs help in traditional cross breeding methods between the genes of plants, animals, viruses, and bacteria.
Ques. Explain the three kinds of model organisms. (2 Marks)
Ans. The three kinds of model organisms are a genomic model organism, genetic model organism, and experimental model organisms.
The genomic model organism has a short period, characterised genome which is suitable for studying traits, phenomena, and disease. Genetic model organisms are used to increase the production yield. They are drought-tolerant, increase the nutritional value and add to other consumer benefits. Experimental model organisms are
Ques. How does one select a model organism for its research? (2 Marks)
Ans. Model organisms are chosen based on the responsiveness to experimental manipulation. They are based on the characteristics such as methods for genetic manipulation and short life span.
Ques. Describe TAIR. (2 Marks)
Ans. TAIR is an Arabidopsis information resource. It stores the database of genetic data and molecular biology for the model organism, Arabidopsis thaliana. Information regarding the gene structure, complete genome sequence, DNA and seed supplies, gene product information, genetic and physical markers, genome maps, and articles about the Arabidopsis scientific community is available in TAIR.
Ques. What are the methods for creating transgenic animals? (2 Marks)
Ans. The DNA of a transgenic animal is modified by inserting a foreign gene in the genome of the animal. This modification of the genome is done to polish the genetic traits of the targeted animal. The methods to create a transgenic animal are physical transfection, chemical transfection, viral vectors, bactofection, and retrovirus-mediated gene transfer.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:





Comments