Anjali Mishra Content Writer-SME
Content Writer-SME
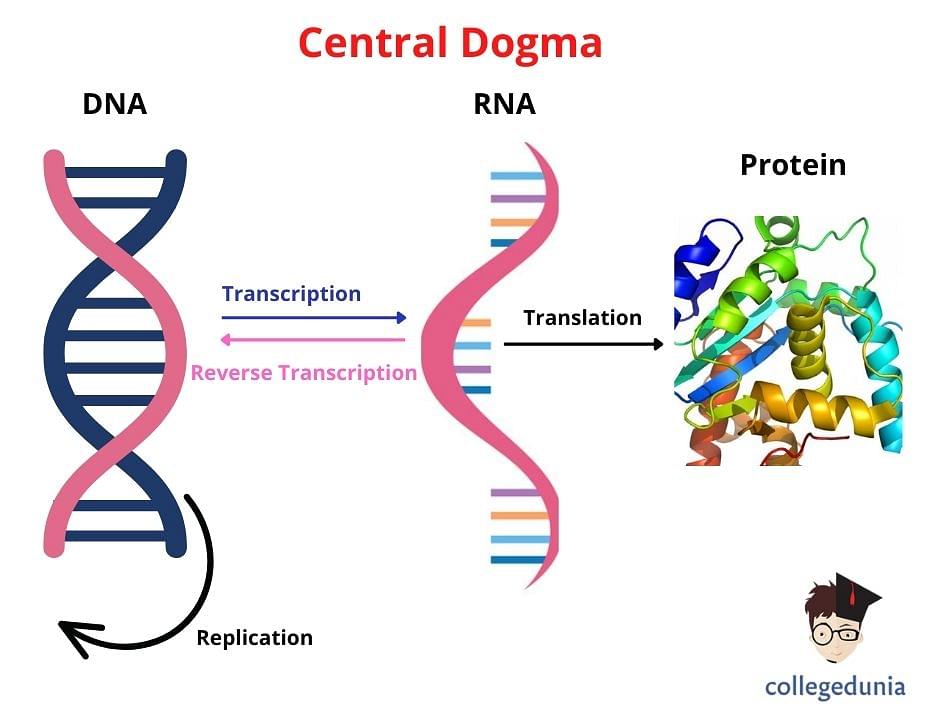
The Central Dogma of molecular biology is a theory proposed by a biologist, Francis Crick in 1958. It is a concept that explains the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA in order to synthesize protein.
- According to Central Dogma of protein synthesis, DNA is an essential component of our human body that plays a significant role in protein synthesis.
- It also explains that RNA acts as a messenger or carrier through which carries the genetic information further through ribosomes.
- Two processes that are involved in the complete synthesis of proteins are: Transcription and Translation.
Central Dogma Definition
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Central Dogma of molecular biology definition can be given as a regulated process that involves the transfer of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein. This theory was first discovered by Francis Crick in the year 1958.
- This process through which DNA instructions are getting converted into functional products is known as gene expression.
Central Dogma of Protein Synthesis
- The process of Central dogma includes a sequential of biopolymers.
- Biopolymers mostly are DNA, RNA and proteins which are sub-divided into three types of transfers – Unknown, General and special transfers.
- Formation of new strand of DNA from the one strand of parent DNA is called semiconservative DNA replication.
Steps of Central Dogma
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
According to Central Dogma of life, replication, transcription, and translation are three important stages of protein synthesis.
Replication
Replication is the first process of protein synthesis in which one original DNA molecule self-repicates to create two identical copies of DNA. The process of DNA replication is further categorized into three steps: Initiation, Elongation, and Termination. This step is regulated by enzyme called DNA polymerase enzyme.
Transcription
In this process, all the genetic information of one single strand of DNA transfers from DNA to RNA. RNA polymerase is an important enzyme for transcription of DNA.
- A DNA strand consists of a structural gene, terminator and promoter.
- During this process, one of the DNA strands acts as a template for synthesis of the complementary RNA.
- The process of transcription is actually the primary step for the gene regulation.
- As the terminator sequence is approached, the newly synthesized RNA strand is released, which undergoes further post-transcriptional changes.

Translation
- During the process of translation, these messages travel from DNA which is present within the cell nucleus to the ribosomes for the formation of specific proteins.
- The energy is specifically provided by the charged tRNA molecules.
- Ribosomes are responsible for the initiation of the process of translation as they contain large and small subunits, with two tRNA molecules in the larger subunits which are placed close so that a form peptide bond forms in between them.
- With the repetition of this process, long chains of polypeptide amino acids are synthesized gradually.
In short, central dogma of life can be stated as a three-step procedure which involves:
DNA to DNA replication (To make new DNA) → DNA to make a new RNA (Transcription) → RNA to the formation of new proteins (Translation)
Genetic Code
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
During the process of replication and transcription, the nucleic acid is copied for the formation of another nucleic acid. The translation process involves the transfer of genetic information to a polymer of amino acids from the polymer of nucleotides. The proposition of genetic code can direct the sequence of the amino acids during protein synthesis.
- According to the scientist, George Gamow, there are 4 bases and 20 amino acids.
- Therefore, the possible permutation combination of 4 x 4 x 4 = 64 codons or amino acids.
- This feature of genetic code is explained according to which, a few amino acids are coded by more than one codon and thus cause them to degenerate.
- Hence, genetic codes degenerate. Each codon is responsible for coding for one specific amino acid.
- These codes are universal irrespective of whatever is the type of the organism.
- The stop codons are triplet, out of 64 codons which are responsible to stop the process of transcription and one of these codons is the initiator codon which is AUG coding for Methionine.
Things to Remember
- Central Dogma is a process that involves the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA, to make a functional product protein.
- Central Dogma takes place in two steps namely Transcription and Translation.
- Transcription is the process that involves the information being transferred from one strand of the DNA to RNA by the enzyme RNA Polymerase.
- Translation is an active process through which the RNA codes for specific proteins and it requires energy.
- Genetic code includes the information of the protein which has been manufactured from RNA.
Previous Years’ Questions (PYQs)
- Central dogma of genetic information is modified by the discovery of…
- Complete the flow chart on central dogma… (NEET 2021)
- Reverse flow of information in central dogma of molecular… (COMEDK UGET 2008)
- Teminism is same as…
- The codons UUU and UUC codes for phenylalanine… (KCET 2016)
- A molecule that can act as a genetic material must fulfill the… (NEET 2016)
- During translation initiation in prokaryotes, a GTP molecule… (NEET 2003)
- In the synthesis of which of the following, the DNA molecule… (KCET 2006)
- Select the correct statement regarding protein synthesis… (KEAM 2012)
Sample Questions
Ques. Who discovered the Central Dogma theory? (1 Mark)
Ans. The theory of Central Dogma was first proposed by the scientist Francis Crick in 1958, who discovered the structure of DNA.
Ques. Describe Central Dogma of Molecular Biology? (3 Marks)
Ans. In simple words, the theory of central dogma states,
“The flow of genetic information which passes from DNA to RNA to further formation of protein. The theory proposes that the DNA contains the required information which is necessary to make all proteins”.
Ques. What is the importance of the theory of Central Dogma? (3 Marks)
Ans. The theory of Central Dogma consists of the formation of protein which is a biological molecule. This process includes both transcription and translation. Hence, it can be said the central dogma holds importance due to the process of synthesis of protein.
Ques. What are the steps of Central Dogma? (3 Marks)
Ans. Central dogma involves two processes- Transcription and Translation. Transcription involves three stages- initiation, elongation and termination. Transcription is separately controlled for each gene in our genome.
Ques. What do you mean by Reverse transcription in Central dogma? (3 Marks)
Ans. Reverse transcription is the transfer of information that takes place from RNA to make a new DNA (the reverse of normal transcription). This occurs generally in the case of retroviruses, like HIV as well as eukaryotes. Through this process, the genetic information from RNA is assembled in a new DNA.
Ques. What is a gene? (3 Marks)
Ans. Gene is known as a molecular entity present in every living body which can replicate, translate as well as transcript and helps in mutation. Gene contains DNA and it is situated in a chromosome linearly.
Genes are responsible for the encoding of regulatory as well as structural RNAs. Various types of encoding protein genes are found both in the plant as well as animal cells which are mainly responsible for their cellular functions.
Ques. What are DNA and RNA? (2 Marks)
Ans. DNA is a molecule that carries all the genetic code present in a living body. Its full form is Deoxyribonucleic acid. The full form of RNA is Ribonucleic acid which is a messenger that helps to convert the code of chemical information of protein products.
Ques. What is a Ribosome? (3 Marks)
Ans. A ribosome is known as a macromolecule which performs the synthesis of proteins in a cell. They are basically the factories of the cell where this information is converted from a code to a functional product.






Comments