
Content Strategy Manager
Dispersion of Light is the phenomenon of splitting of white light into multiple colors on passing through a transparent medium. The pattern in which these color components appear on passing through the prism is called a spectrum. A prism is a solid object made up of glass, which has two triangular bases and three rectangular bases. Its opposite surfaces are equal and parallel to each other. Sir Issac Newton discovered that white light consists of seven different colors. When a narrow beam of sunlight or white light passes through a glass prism, then the light of seven different colors emerges. These consist of several wavelengths.
Refraction of light refers to a change in direction or the bending of a wave passing from one medium to another due to the change in speed of the wave. Refraction of Light shows passing of white light passes through a prism and results in each colour refracting at a very different angle. Violet colour falls on the extreme end of this spectrum while Red at the least. Examples of refraction of light by Prism are the twinkling of stars, Optical illusions, formation of mirages, and Rainbows, etc.
Key Terms: Prism, triangular bases, rectangular bases, Light, Sunlight, wavelengths, spectrum, VIBGYOR
Dispersion of Light by Prism
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The dispersion of white light happens because of angle of refraction, The process of refraction can be defined as the blending of light when it passes from one medium to another medium. The light deviates twice on passing through the glass prism, initially when it enters the prism and second time when it comes out of it. Since all the colors have different wavelengths and are refracted from different frequencies and deviation angles, hence the Violet color blends the most and red the least.
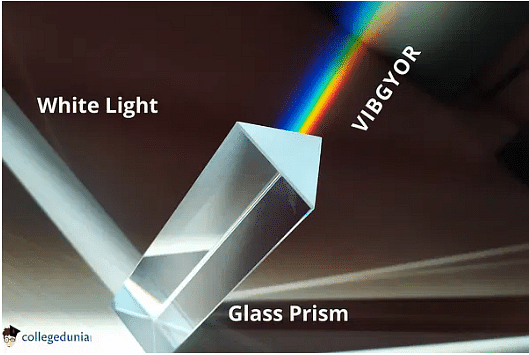
Dispersion of Light by Prism
On the similar lines the concept of rainbow can also be understood. On rainy days with the presence of raindrops in the air and sunlight, we get to experience the rainbow.When the white sunlight enters the raindrops, then the white light is refracted and an arc of seven color components is formed on the surface of the sky. The raindrops here work as a glass prism for the sun’s white light.
The process of dispersion can be understood well through cauchy’s formula. The formula states that there is a phenomenological relationship between refractive index and wavelength of light.So the dispersion is because of the refractive index n depends on the wavelength of light λ.
n= A+ B/ λ2
Where n is the Refractive index, λ is the wavelength and A and B are constants which are determined for a material by putting in the equation to measure refractive indices at the known wavelengths. In other words the Refractive index is inversely proportional to the square of wavelength of light. Smaller the value of wavelength larger is the value of Refractive index. Hence ‘n’ is maximum for violet and least for red, therefore violet has the maximum dispersion whereas red has minimum.
Also Read:
Refraction of Light by Prism
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Light travels from one medium to another, due to which, the speed of its propagation changes. Thus, the light bends or gets refracted. When light passes through a prism, it gets refracted towards base of the triangle. Refraction of Light through prism is illustrated in the diagram below.

Refraction of Light Through Prism
Different colours in the spectrum of light have different wavelengths. Thus, the speed with which these colors bend, varies according to their wavelengths. Violet color bends the most and has the shortest wavelength. Red color bends the least and has the longest wavelength. Therefore, dispersion of white light into its spectrum of colours takes place when refracted through a prism.
Visible Light Spectrum
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Visible light spectrum is a segment of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to human eye. This range of wavelengths is called visible light. Human eye can detect wavelengths from 380 to 700 nanometers. The wavelength of light related to frequency and energy determines the perceived color. The edges of the visible light spectrum blend into the ultraviolet and infrared levels of radiation.

Visible Light Spectrum
Prism Experiment
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
A prism is a polyhedron with a triangular base and three rectangular lateral surfaces. It is used as an optical object to study the behaviour of white light when it is passed through it. The light bends at various angles like an angle of incidence, angle of reflection, angle of refraction, and angle of deviation.
In the Prism Experiment, by tracing the path of the rays of light through a glass prism, following observations can be noted:
- The incident ray bends towards the normal when it enters the prism and while leaving the prism it bends away from the normal.
- With the increase in the angle of incidence, the angle of deviation decreases. After attaining the minimum value, it increases with an increase in the angle of incidence.
Also Read:
Things to Remember
- Prism is a solid object made up of glass, which has two triangular bases and three rectangular bases.
- The phenomenon of splitting of white light into multiple colors on passing through a transparent medium is known as Dispersion of light, and the pattern in which these seven color components appear on passing through the prism is called spectrum.
- The seven emerging colors appear from the process of dispersion through the glass prism in the sequence of VIBGYOR ( from top to bottom ), which is an acronym for Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and red.
- The dispersion of white light happens because of angle of refraction, The process of refraction can be defined as the blending of light when it passes from one medium to another medium.
- The light deviates twice on passing through the glass prism, initially when it enters the prism and second time when it comes out of it.
- Since all the colors have different wavelengths and are refracted from different frequencies and deviation angles, hence the Violet color blends the most and red the least.
Previous Year Questions
- When a light ray enters from oil to glass on oilglass interface… [JIPMER 2019]
- A point object O is placed in front of a glass rod having spherical end of radius of… [BITSAT 2018]
- The size of the image of an object, which is at infinity, as formed by a convex lens… [JEE ADVANCED 2003]
- The frequency of a light ray is… [DUET 2003]
- A bubble in glass slab (μ=1.5) when viewed from one side appears at… [NEET 2000]
- A bulb is located on a wall. Its image is to be obtained on a parallel wall with… [NEET 2002]
- A convex lens is dipped in a liquid whose refractive index is equal to… [NEET 2003]
- A lens forms real and virtual images of an object, when the object is at… [AP EAPCET 2018]
- An observer can see through a pin-hole the top end of a thin rod of height… [JEE ADVANCED 2002]
- A vessel of depth 2d cm is half filled with a liquid of refractive index… [VITEEE 2017]
- A and B are two parallel sided transparent slabs of refractive indices… [WBJEE 2016]
- A convex lens of focal length 10 cm and refractive index… [UPSEE 2019]
- Two beams of red and violet colour are made to pass separately through… [UPSEE 2019]
- An isosceles prism of angle 120∘ has a refractive index 1.44… [JEE ADVANCED 1995]
- A rectangular glass slab ABCD of refractive index… [JEE ADVANCED 2000]
- A diverging beam of light from a point source S having divergence angle… [JEE ADVANCED 2000]
- A hollow double concave lens is made of very thin transparent material… [JEE ADVANCED 2000]
- A ray of light is incident on an equilateral glass prism placed on a… [JEE ADVANCED 2004]
- A slit of width 'a' is illuminated by red light of wavelength… [KCET 2021]
- Which of the statements are correct with reference to single slit diffraction… [KCET 2021]
Sample Questions
Ques. Which color least deviates from the prism? (1 mark)
a)Violet
b)Red
c)Green
d)Yellow
Ans. Option B. Red
Explanation: When white light falls on a glass prism, each colour in it is refracted by a different angle, from which red colour is least deviated and violet most.
Ques. The dispersion by prism depends on (1 mark)
a)Shape of prism
b)Height of prism
c)Angle of prism
d)Material of prism
Ans. The dispersion by prism depends on the material of the prism i.e option D.
Explanation: Angle of dispersion depends on Angle of the prism, the material of the prism and the wavelength of light passing through it.
Ques. The dispersion by prism occurs due to angle of? (1 mark)
a )Reflection
b )Refraction
c )Intersection
d )Incidence
Ans. The dispersion by prism happens due to angle of refraction, which is a process of blending of light when it passes from one medium to another so its option B. Refraction
Ques. What happens when white light passes through hollow prism ? (1 mark)
a )Only dispersion
b )Only deviation
c )Nothing happens
d )Option A and Option B both
Ans. When white light passes through hollow prism nothing happens as in order for dispersion there should be a surface for refraction. If the prism is hollow then light wouldn't get dispersed and there will be no resulting seven color components.
Ques. How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary, if the incident violet light is replaced with red light? (All India 2008) (2 marks)
Ans. We know that λ red > λ violet, therefore µ red < µ violet and hence δ red < δ violet.
When incident violet light is replaced with red light, the angle of minimum deviation of a glass decreases.
Ques. What is 'dispersion of white light'? State its cause. Draw a ray diagram to show the dispersion of white light through a glass prism. (3 marks, All India 2017)
Ans. Definition: The splitting of light into its seven constituent colours due to refraction is called dispersion.
Cause: When entering a medium, like glass, light of different colours bend at different angles with respect to the incident beam. Since white light is a composite of seven different colours, it splits into a spectrum of seven colours when entering a prism, causing dispersion.
Violet (V) bends the most while Red (R) bends the least.

Dispersion of white light by a glass prism
Ques 8. "Rainbow is an example of dispersion of sunlight". Justify this statement by explaining, with the help of a labeled diagram, the formation of a rainbow in the sky. List two essential conditions for observing a rainbow. (2016)
Ans. After a rain-shower, water droplets suspended in the atmosphere act like tiny prisms for the sunlight. They refract and disperse the incident sunlight, then reflect it internally, and finally refract it again when it comes out of the raindrop. We see the colours in a rainbow because of the dispersion of sunlight inside a raindrop.
Two essential conditions for a rainbow to form:
- the sun should at the opposite side of the viewing direction,
- suspended water droplets must be present in the air.
Ques 9. How did Newton show that the white light of the sun contains seven colours using two identical prisms? Draw a ray diagram to show the path of light when two identical glass prisms are arranged together in inverted position with respect to each other and a narrow beam of white light is allowed to fall obliquely on one of the faces of the first prism. (2 marks, Delhi 2016)
Ans. Newton passed white light from the sun through a glass prism, obtaining its spectrum of seven colours. He still needed proof that there weren't any other possible colours.
For this, he placed a second identical prism in an inverted position with respect to the first prism, and observed white light emerging from the other side of the second prism. This showed that sunlight was made of seven colours.
Ques 10. Define the following terms in the context of spherical mirrors:
i) Pole
ii) Center of curvature
iii) Principal Axis
iv) Principal Focus (4 marks)
Ans. i) Pole: The centre of the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror.
ii) Centre of curvature: The reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is part of a sphere. The centre of that sphere is called the centre of curvature.
iii) Principal axis: An imaginary line passing through the pole and the centre of curvature. The principal axis is normal to the mirror at the pole.
iv) Principal focus: The point on the principal axis, at which incident light rays parallel to the principal axis converge or appear to diverge from, is called the principal focus of the lens.
Ques 11. How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary, if the incident violet light is replaced by red light? Give reason. (Delhi 2017)
Ans. The angle of minimum deviation decreases, when violet light is replaced by red light because the refractive index for violet light is more than that for red light.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:





Comments